Assessment of Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices of Food Handlers in Attieke Production Units in Relation to Food Hygiene and Safety in Côte d’Ivoire in 2012 ()
1. Introduction
Attieke is the major fermented plant food of Côte d’Ivoire. It is a steamed granular cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) meal, couscous-like product, with slightly sour taste and whitish colour (Figure 1) [1] . It is consumed two to three times a day with meat, fish or vegetables. The processing of cassava into attieke needs several hard steps. Roots are peeled, cut into pieces and then washed three times with fresh water. Before milling, 5% - 10% (w/w) of inoculum, 10% (v/w) water and about 0.1% (v/w) of palm oil are added and the pieces are ground into a fine paste and left to ferment for about 12 to 15 h at ambient temperature (30˚C - 37˚C). After fermentation, the dough is continuously pressed and then sieved and granulated. The grains obtained are sun-dried for few min to half an hour [2] . After drying, fibres and dirt are removed by sprinkling and grains are steamed for about 20 - 25 min. The attieke obtained is packaged into plastic bags, sealed airtight and sold on local markets or transported in cars at ambient temperature (30˚C - 37˚C) in other localities.
Recent data on attieke consumption do not exist, but reference [3] estimated the consumption of attieke between 28,000 and 34,000 tons per year, the equivalent of 40,000 - 50,000 tons of fresh cassava; in which 100 tons was daily produced only for Abidjan. The firm of attieke production keeps alive many thousands families in Côte d’Ivoire and even in West African region. It generates around 20 billion CFA franc (about 30 million euros) per year [4] .
However attieke is still produced following traditional methods. Very few attention is granted to production environment, staff’s hygiene, production material, and inputs (water, traditional inoculum) used in the process. Most of attieke are processed by small scale producers, thus making quality control difficult. In other respects, the product is usually subject to various handling, storage and marketing conditions, some of which may introduce microorganisms. Indeed, foodborne diseases account for a considerable degree of morbidity and mortality and can have various origins such as chemical and parasitic; however, microbiological sources stand out for posing a great risk to public health because of the severity of the clinical symptoms and the large number of foods and microorganisms that can be involved [5] . Moreover, improper handling is responsible for most cases of foodborne disease, including the inappropriate use of temperature during food preparation and conservation, cross contamination, poor personal hygiene and inadequate equipment [6] . When food handlers do not practice proper personal hygiene or correct food preparation, they may become vehicles for microorganisms, through their hands, cuts or sores, mouth, skin and hair, among others [7] .
Reference [8] showed that attieke was most of the time susceptible to contamination by bacteria and moulds. Knowing that the food product constitutes a major part of daily diet of many Côte d’Ivoire homes and most part of West Africa, information on this study will help to develop appropriate understanding of its spoilage and will also help to ensure its microbiological safety and the sanitary safety of consumer. The aims of this study were to investigate the food safety knowledge and practices of food handlers and to assess the sanitary conditions of attieke production units in the South of Côte d’Ivoire.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Population
The study was conducted during 4 months from September to December 2012 in seven (7) departments (Abidjan, Dabou, Jacqueville, Grand-lahou, Divo, Sikensi and Adzopé) in the South of Côte d’Ivoire (Figure 2), where attieke was abundantly produced. In every department four (4) localities were inspected except the department of Abidjan where seven (7) localities were inspected. Thus, a total of 775 attieke production units were visited in 31 localities at a rate of 25 production units per locality.
2.2. Data Collection
A cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate the food safety knowledge and practice of food handlers and assess the sanitary conditions of attieke production units. The survey was conducted using the method required by international standards to meet health inspections of food units. A questionnaire was developed to assess conditions of hygiene in which attieke is produced. The questionnaire was established according to the method required by international standards to achieve sanitary inspections of food units [9] . The questionnaire was subjected to a preliminary validation on 15 production units to assess its clarity, the suitability of wording, and the average time needed for its completion. Based on this pilot study, necessary modifications were identified and
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 1. Attieke samples (a) in a plate and (b) packaged in plastic bags for retail sale.
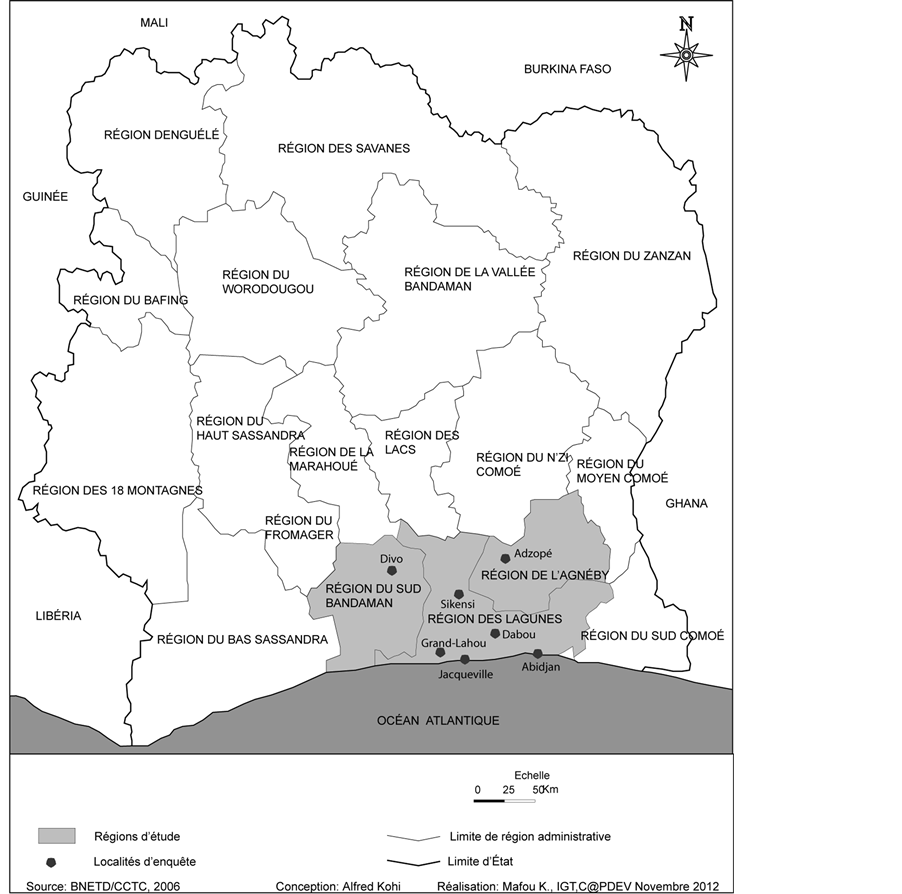
Figure 2. Selected localities for hygiene assessment in attieke production units in various cities of the south of Côte d’Ivoire.
resolved, whereas its results were not included in the final survey. The final questionnaire consisted of six (6) parts: general aspects of the production site hygiene, sanitary equipements, the staff, materials of cooking and service of attieke, quality and mode of water supply, the packaging and storage of attieke on the production sites. All items were multiple-choice questions or statements with 2 - 6 possible answer choices including true/false and yes/no statements.
Five sanitarians were recruited for data collection and supervision. Data collectors and supervisor were oriented about the purpose of the study, the components of the questionnaire and data quality management. Data collectors interviewed the food handlers and observed the food handlers while they were performing their chores to see their food handling practices and collected information on food preparation and handling in the facilities and the sanitary condition of the facilities.
2.3. Microbiological Analysis of Food Handler Hands
Data collection for microbiological analysis of the hands of food handlers was performed using a swab, previously moistened in sterile peptoned buffered water and applied to the entire surface of the hands and between the fingers [10] . Three collections were conducted for 5 selected production units in 3 cities on different days to better represent the data, for a total of 90 samples. Enumeration of coliforms was carried out using plates of Violet Red Bile Lactose agar (VRBL, Merck 10660, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The cultures were incubated for 48 h at 30˚C for total coliforms and 44˚C for faecal coliforms. S. aureus was isolated and enumerated according to the method described by [11] . The research of Salmonella was achieved according to the procedure described in the global Salmonella surveillance and laboratory support project of the World Health Organization [12] .
The parameter recommended by [13] was used, where a satisfactory result is the absence of fecal coliforms and Salmonella on the hands of food handlers.
2.4. Data Analysis
The data were analyzed using Epi Info 2004 statistical software (Division of Public Health Surveillance and Informatics Epidemiology Program Office, MS K74, Atlanta, Georgia 30341-3717). Descriptive statistics, such as frequency distribution, mean and percentages were employed for the analysis.
3. Results
A total of 775 attieke production units were involved in this survey. Seventy one (71%) were located on public domains particularly non tarred ways, markets, gutters, sidewalk and border of lagoons, with a majority (39%) on non tarred ways, and only 29% was located in private domains (Figure 3). Fifty six (56) percent were built with cement material while 32% was built with wood and 11.2% with a combination of both materials.
All sites are maintained badly with an invasion wastewaters (96% of sites), wild deposits (68% of sites), sickening odor and of harmful on all sites, flies, cockroaches, mice and house pets (Table 1). No production unit possessed a plan of detection and struggle against harmfuls. Among all the attieke production units visited, 109 (14%) used piped drinking water, among which only nine (9) had their personal piped water system and the others were supplied from resellers. The other sources of water supplies on production units which did not have access to potable water were wells, lagoon and rivers.
Only 5% of the production units had toilets and 3% latrines with very few of these latrines clean and attractive. Seventy (70) production units (9%) used septic tank as a mean of final deposal for liquid waste that are generated during the preparation, while 41% used gutters and the others the countryside (50%) (Table 2).
It has been determined that the majority of food handlers in attieke production units did not applied good hygiene practices and did not go through health inspection. They all had their hands in direct contact with food product, without washed them. Table 3 shows the self-reported practices of food handler’s attitudes during attieke production in the period of the study.
Microbiological analyses of the handlers’ hands showed contamination in a large number of samples (Table 4). The highest level of contamination was found in Abidjan, the economic capital. Various species such as S. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter agglomerans, Citrobacter youngae, Klebsiella oxytoca and Citrobacter freundi were identified with high loads, as illustrated in Table 5.

Figure 3. Location of attieke production units visited in this study (September-December 2012).

Table 1. Status of Hygiene around attieke production units in the south of Côte d’Ivoire (September-December 2012).

Table 2. Status of water and sanitation in attieke production in the south of Côte d’Ivoire (September-December 2012).

Table 3. Status of hygiene practices by food handlers in attieke production units in the south of Côte d’Ivoire (SeptemberDecember 2012).

Table 4. Mean microbial loads on the hands of food handlers in attieke production units in three cities in the South of Côte d’Ivoire.
Abs: Absence.

Table 5. Types of bacteria isolated from the hands of food handlers in attieke production units in three cities in the South of Côte d’Ivoire.
4. Discussion
The current study on the assessment of hygienic and sanitation conditions on attieke production units in the South of Côte d’Ivoire revealed the unsatisfactory status of operational level, capacity, hygienic and sanitary condition and future direction. The principal findings which were identified include good coverage of safe water (defined as the availability of tap water) and latrine availability (defined as at least presence of a single latrine), inadequate supervision and inspection by the municipalities and the local health sector, inappropiate solid and liquid waste disposal, absence of food handler’s health check-up, absence of hygienic education to owners and food handlers. This study revealed that the majority of attieke production units were badly located, opencast and they did not have a conventional waste water disposal system. This could be explained by the fact that most of producers live in small concessions where space is limited and such concessions do not allow them to correctly carry out their activity. The consequence of this is that intermediates and final products resulting from attieke processing are exposed to air pollution (dust, exhaust fumes). Similar observations were made by [14] [15] in their survey on the presence on heavy metal on Egyptian fruits and vegetables. The absence of conventional waste water disposal system creates points of backwaters that host breeding sites, entailing thus a temporary or permanent unhealthy. Reference [16] reported that foods prepared in unsanitary conditions are susceptible to contamination and could cause diseases such as diarrhea. Moreover domestic animals (dogs and cats) are known as carriers of pathogens such as E. coli and Salmonella. Therefore, they must be kept away from the production zone [17] [18] .
In accordance with some authors [19] -[21] , an establishment shall not be located anywhere where it is clear that there is a threat to food safety or suitability. In particular, establishments shall normally be located away from:
• Environmentally polluted areas and industrial activities which pose a serious threat to contamination of food.
• Areas subject to flooding unless sufficient safeguards are provided.
• Areas prone to infestations of pests.
• Areas from which waste, either solid or liquid, cannot be removed effectively.
In most production units, water was purchased from resellers and often stored and handled under unsanitary conditions, favourable to microbial contamination. According to reference [22] , the majority of sources of food contamination come from water. Inspection of some water storage barrels showed the presence in the inner walls of greenish foam characteristics of presence of biofilm. This situation, combined with the virtual absence of sanitation and conventional sink increase the risk of spread of germs within populations on the production zones. Therefore, an adequate supply of potable water with appropriate facilities for its storage, distribution and temperature control, should be available wherever it may come in contact with food or is used as an ingredient [19] [23] [24] . Reference [25] describes potable or “drinking” water as the water delivered to the consumer that can be safely used for drinking, cooking and washing.
This study has also allowed establishing a significant breach between food hygiene and safety and the translation of a wide range of knowledge of food handlers to actual practices. This is primarily attributed to financial considerations being more of a priority than food safety [26] , as most food handlers and their families are totally reliant for their financial support on attieke production as remarked by [27] [28] on their studies on Microbiological quality and safety of ready-to-eat street vended foods in Johannesburg. It is therefore quite restrictive for them to put food safety considerations before their economic needs. The assessment of food handlers in attieke production units revealed deficiencies in knowledge, attitudes and practices in the areas of washing hands, food handling, food borne diseases, mode of transmission and prevention. These deficiencies could be ascribed to a total lack of training (none received any formal food hygiene training), or negative attitudes influenced by the desire to survive as noted by [29] by studying the relationship between knowledge, attitude and practices of care givers and food hygiene in Day Care Centers.
Although all people working in attieke production units knew that it was essential for them to be clean, most did not understand that they could be a source of contamination and contaminated hands can be a source of diarrheal pathogens. This explains the observation that most food handlers (90%), although there are opportunities, never washed their hands, 52% wore jewelry during the production process and some of them continued to handle foods despite they had skin lesions. These jewelry and skin lesions may contribute to microbial and chemical contamination of food according to [30] -[32] .
Microbiological analyses of the handlers’ hands show that they were all contaminated by S. aureus and coliforms with various species such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter agglomerans, Citrobacter youngae, Klebsiella oxytoca and Citrobacter freundi. This result showed an association with the absence of exclusive sinks and means for hand washing. Thus, we underscore the importance of correct hand hygiene, as shown by [33] , where they assessed the efficacy of correct hand hygiene and found a reduction in microorganisms from 72.7% to 32%. A number of studies conducted with food handlers have demonstrated that their hygienic-sanitary profile is often unacceptable in terms of health status, personal hygiene practices and habits, raising the risk of hand contamination as well as cross contamination in the handled food. A study carried out in four state schools in Brazil found total coliforms on the food handlers’ hands in three of these and fecal coliforms in two of the institutions [34] , demonstrating that food handlers engage in improper personal hygiene techniques. Reference [35] evaluated the hands of handlers at the university restaurant of the Federal University of Santa Maria of Brazil and found that 27% of the samples showed the presence of S. aureus and fecal coliforms. Reference [36] also found E. coli, S. aureus and Salmonella on the hands of food handlers in Africa; in addition to unsuitable food handling practices as our results has showed it.
It has been demonstrated that food handlers are an important vehicle for microorganisms and that improper handling practices may cause food contamination and consequently foodborne disease, which poses a potential risk to public health. However, the inappropriate practices observed in the present study are due to a number of factors, such as the lack of instruction and awareness about the importance of good food production practices, poor working conditions, among which are the absence of uniforms and individual protective equipment, of exclusive hand wash sinks, as well as the lack of antiseptic liquid soap for correct hygienization, among others.
5. Conclusion
It may be concluded from this study that the hygiene conditions and practices of food handlers in attieke production units in the South of Côte d’Ivoire are inadequate. Therefore, a reformulation of government policies is needed to meet the problems encountered, such as periodical training, the physical restructuring of food units, improved working conditions and constant supervision by qualified professionals, to ensure the quality of attieke in addition to protecting and promoting consumer health.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the International Foundation for Science (IFS) under Grant E/4955-1.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.