Price and Quantity Competition in a Mixed Duopoly with Emission Tax ()
1. Introduction
In many countries, state-owned enterprises in the energy and manufacturing sectors employed few environmental technologies and thus damaged the environment. This is also observed when environmental policies are imposed on such public as well as private firms. The markets of these public firms affect their production and emissions, and consequently affect the environmental policies of the governments. There are some recent studies on the environmental policies in such markets1. However, the previous literature generally assumes the case of the quantity competition. This paper examines the difference between price and quantity competition in a mixed duopoly with emission tax; in a mixed duopoly, one public firm competes with one private firm in the market2.
This paper compares the optimal emission tax rates in a mixed duopoly. A number of studies have focused on optimal emission taxes under imperfect competition3. Taxing emissions in order to reduce social damage worsens the distortion caused by imperfect competition. Barnett [10] , the early contribution to this issue, shows that the optimal emission tax falls short of the marginal social damage cost because the weaker emission tax corrects the distortion in market power caused by imperfect competition.
Previous studies on environmental policies in a mixed oligopoly have focused on their role under privatization. In the case of a single domestic market, Kato [3] considers tradable emission permits, while Bàrcena-Ruiz and Garzòn [1] consider emission tax. Naito and Ogawa [4] compare emission tax with the command-and-control regulation. On the other hand, Ohori [5] investigates the effect of privatization under emission taxes in an international market. While the studies discussed above provide interesting results, they do not consider price-setting oligopolies.
In this paper, four potential combinations are considered: 1) both the firms choose prices, 2) both the firms choose quantities, 3) the public firm chooses price and the private firm chooses quantity, and 4) the public firm chooses quantity and the private firm chooses price. We find that social welfare is the highest under Bertrand competition. Then, the emission tax rate should be sufficiently lower than the marginal social damage cost.
2. The Model
Consider a domestic market in which one public firm (Firm 0) and one private firm (Firm 1) compete. Firms 0 and 1 are assumed to produce differentiated substitutable goods for which the inverse demand functions are given as , where
, where  and
and  denote firm i’s price and quantity, respectively and the parameter
denote firm i’s price and quantity, respectively and the parameter  indicates the degree of substitutability. For simplicity, one unit of a product causes one unit of emission, which damages the local environment. The firm cannot reduce emission except by reducing output. Total emissions are given by
indicates the degree of substitutability. For simplicity, one unit of a product causes one unit of emission, which damages the local environment. The firm cannot reduce emission except by reducing output. Total emissions are given by  and the social damage is given by
and the social damage is given by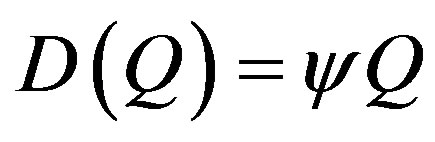 , where
, where  denotes the constant marginal damage cost.
denotes the constant marginal damage cost.
We assume that both firms have identical technologies and linear production costs; the latter is denoted by , where
, where  is the constant marginal cost. Firm i’s profit is denoted by
is the constant marginal cost. Firm i’s profit is denoted by , where
, where  denotes the environmental tax rate. We assume that the solutions are interior
denotes the environmental tax rate. We assume that the solutions are interior  and
and . Following Beladi and Chao [2] and Ohori [6] , firm
. Following Beladi and Chao [2] and Ohori [6] , firm ’s objective function is defined as the sum of the consumer surplus and the producer surplus (i.e., profits of both the firms) and is given by
’s objective function is defined as the sum of the consumer surplus and the producer surplus (i.e., profits of both the firms) and is given by , where
, where  denotes consumer surplus. On the other hand, firm 1 aims to maximize its own profit.
denotes consumer surplus. On the other hand, firm 1 aims to maximize its own profit.
The government sets the emission tax rate such that social welfare  is maximized.
is maximized.
 , (1)
, (1)
where  denotes the tax revenue.
denotes the tax revenue.
The game is constructed using a two-stage decision-making process. In the first stage, the government sets the emission tax rate such that social welfare  is maximized. In the second stage, the two firms simultaneously choose either price or quantity. The game is solved using backward induction.
is maximized. In the second stage, the two firms simultaneously choose either price or quantity. The game is solved using backward induction.
3. Four Potential Situations
In this section, we discuss four potential situations 1) both the firms choose prices (p-p game), 2) both the firms choose quantities (q-q game), 3) Firm 0 chooses price and Firm 1 chooses quantity (p-q game), and 4) Firm 0 chooses quantity while Firm 1 chooses price (q-p game).
p-p game
We consider the first situation wherein both the firms simultaneously set their respective price levels. Consumer surplus is given by
 .
.
The public firm 0 maximizes the sum of producer surplus and consumer surplus  while the private Firm 1 maximizes its own profit
while the private Firm 1 maximizes its own profit . Based on the first-order conditions and arranging, the respective reaction functions are given by
. Based on the first-order conditions and arranging, the respective reaction functions are given by
 ,
,
 .
.
From these reaction functions, we obtain the equilibrium prices:
 ,
,
 .
.
By substituting the above equilibrium prices into Equation (1) and using , we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
, we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
 . (2)
. (2)
Since the second term on the right-hand side of the above equation is negative based on the above assumptions, Equation (2) implies that the optimal environmental tax rate is lower than the marginal social damage cost (thus the Pigouvian tax rate).
Using Equation (2), we obtain the following results:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
q-q game
We consider the second situation wherein both the firms simultaneously choose quantities. Consumer surplus is given by
 .
.
Considering the firms’ maximization problems, the respective reaction functions are given by
 ,
,
 .
.
From these reaction functions, we obtain the equilibrium quantities:
 ,
,
 which implies that Firm 0’s output is higher than that of Firm 1 in equilibrium; that is,
which implies that Firm 0’s output is higher than that of Firm 1 in equilibrium; that is, .
.
By substituting the above equilibrium quantities into Equation (1) and using , we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
, we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
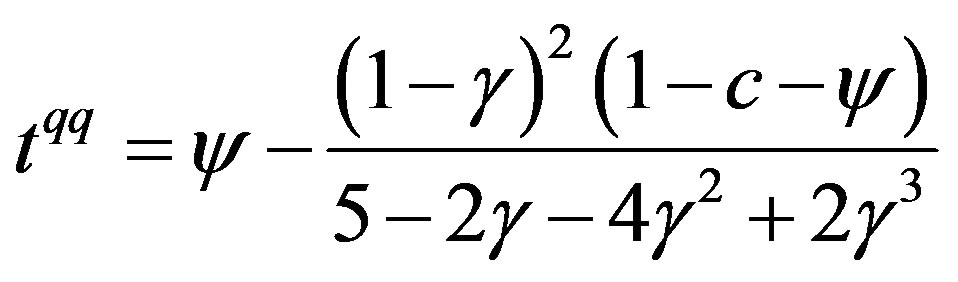 . (3)
. (3)
Since the second term on the right-hand side of the above equation is negative, Equation (3) implies that the optimal environmental tax rate falls short of the marginal social damage cost.
Using Equation (3), we obtain the following equilibrium values:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
p-q game
We now consider the third situation wherein Firm 0 and Firm 1 simultaneously determine the price and quantity, respectively. Consumer surplus is given by
 .
.
On calculating the first-order conditions for both firms’ maximization problems, the reaction functions are given by
 ,
,

From these reaction functions, we obtain the equilibrium price for Firm 0 and equilibrium quantity for Firm 1:
 ,
,
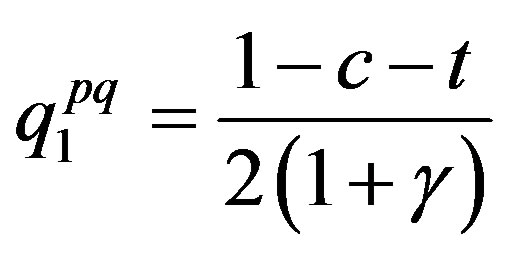 .
.
By substituting the above equilibrium price for Firm 0 and equilibrium quantity for Firm 1 into Equation (1) and using , we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
, we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
 . (4)
. (4)
Since the second term on the right-hand side of the above equation is negative, Equation (4) implies that the optimal environmental tax rate is less than the marginal social damage cost. Using Equation (4), we obtain the following results:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
q-p game
We consider the fourth situation wherein Firm 0 and Firm 1 simultaneously determine the quantity and price, respectively. Consumer surplus is given by
 .
.
Considering the firms’ maximization problems, the reaction functions are given by
 ,
,
 .
.
From these reaction functions, we obtain the equilibrium quantity for Firm 0 and the equilibrium price for Firm 1:


By substituting the above equilibrium quantity for Firm 0 and the equilibrium price for Firm 1 into Equation (1) and using , we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
, we obtain the equilibrium environmental tax as
 . (5)
. (5)
Since the second term on the right-hand side of the above equation is negative, Equation (5) implies that the optimal environmental tax rate falls short of the marginal social damage cost.
Using Equation (5), we obtain the following results:
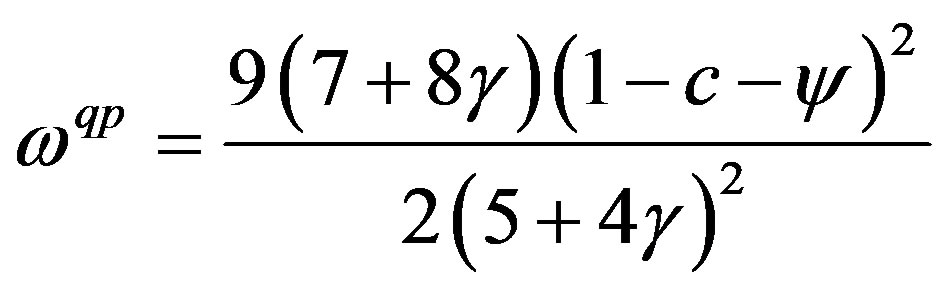 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
4. Comparisons
Based on the results presented in the previous section, we compare the four situations. We first derive the relationship among the equilibrium emission taxes in these four situations:
 , (6)
, (6)
 . (7)
. (7)
From Equations (6) and (7), we can obtain the following propositions.
Proposition 1.
The optimal emission tax is lower than the marginal social damage cost for any of the situations in a mixed duopoly regardless of the degree of substitutability of goods.
The above result is in line with the results obtained previously that indicate that the emission tax should be set lower than marginal damage cost whether the firms choose price or quantity. Equations (6) and (7) also indicate as follows. If the substitutability of goods is low, the equilibrium emission tax is the highest when the public firm chooses price and the private firm chooses quantity. On the other hand, if the substitutability of goods is high, the equilibrium emission tax is the highest when both firms choose quantities.
Next, we compare the equilibrium social welfare values:
 . (8)
. (8)
We summarize this result as follows.
Proposition 2.
Social welfare is the highest when both the public firm and the private firm simultaneously choose prices.
The results imply that the emission tax should be set sufficiently low. Although a sufficiently low emission tax leads to environmental damage, Bertrand competition can increase social welfare.
5. Conclusion
This paper compares price and quantity competition in a mixed duopoly with emission tax. We find that social welfare is the highest when both public and private firms choose prices since the emission tax is then sufficiently lower than the marginal social damage. Although a sufficiently low emission tax deteriorates the environment, Bertrand competition can increase social welfare.
NOTES
2Recent papers that have examined the endogenous choice between price and quantity strategies in a mixed oligopoly include Matsumura and Ogawa [7] and Nakamura [8].
3Most of the researchers of environmental economics have long recognized that the optimal emission tax is equal to the marginal social damage cost (a Pigouvian tax) when firms are perfectly competitive, because their marginal abatement cost equals the marginal damage cost. However, this is not necessarily true for firms in imperfect competition. Refer Requate [9] for a survey.