1. Introduction
White light-emitting diodes (LEDs), as “the fourth-generation lighting source”, have a series of advantages, such as a low operating voltage, low energy consumption, high luminescence efficiency, longer lifetime, and environmental friendliness [1] [2] [3] . These advantages make them superior to incandescent, fluorescent, and HID (High-intensity discharge) lamps and provide a very broad range of prospective applications. Currently, most commercially available white LEDs are based on the phosphor-converted (PC) emission method, in which a blue-light GaN (gallium nitride) LED chip is used to excite the yellow phosphor YAG:Ce ((Y1-aGda)3(Al1-bGab)5O12:Ce3+) [4] [5] [6] . In this type of emission, blue light from the chip part is revealed from a gap in the phosphors, with other parts exciting the yellow phosphors to obtain a broadband emission yellow light, which mix together to form white light. Although various white-light color temperatures can be obtained by regulating the intensity ratio, the color-rendering index Ra (CRI) is generally very poor, being in the 60 - 70 range [7] . It is been found through experiment that the lack of red spectral components is the principal reason for the low CRI. Hence, as may be expected, a small amount of red phosphor with YAG:Ce is used as light conversion material to move the CRI into the acceptable range (Ra > 80).
Currently, commercially used red phosphors are still limited to Eu2+ ion activated alkaline earth binary sulfides and Eu3+-doped Y2O2S. Unfortunately, their chemical stabilities and phosphor lifetimes are not desirable and seriously affect the efficiency and LED lifetime. Recently, Eu3+ as rare earth ion doped molybdate and tungstate red phosphors have been extensively investigated owing to their long longevity, low cost, and excellent chemical stability. Furthermore, [MoO4]2− and [WO4]2− can exhibit relatively strong absorbed energy to the doping centers [8] [9] . Most of these materials have been prepared by using the traditional solid-state method. However, usually high temperature, a lengthy heating process, and subsequent grinding are required. The grinding process damages the phosphor surfaces, resulting in the loss of emission intensity [10] . The sol-gel method has some advantages over the traditional solid-state method, including easy stoichiometric control, good homogeneity, low calcination temperature, and shorter heating time, and the prepared samples show a small size and narrow particle size distribution. However, to the best of our knowledge, there are very limited studies on the effect of process parameters on the luminescent properties of phosphors, such as complex reagents and pH value.
Herein, we have first prepared (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors by using the sol-gel method and demonstrated how the parameters of complex reagents and pH value affect the phosphor luminescent properties. We have also investigated the effect of Eu3+-doped concentration on the luminescence intensity.
2. Experiment
Red phosphor samples ((SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3) were prepared by using the sol-gel method. All the chemicals of Eu2O3 (99.99%), SrCO3 (analytical reagent), NaHCO3 (analytical reagent), HNO3 (1:1) (analytical reagent), and (NH4)6Mo7O24∙ 4H2O (analytical reagent) were used as the starting materials without any further purification. According to the chemical formulas above, stoichiometric amounts of the raw material ammonium molybdate (NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O were first dissolved in a suitable volume of deionized water. Then, stoichiometric amounts of Eu2O3, SrCO3, and NaHCO3 were dissolved in dilute HNO3 (1:1) under vigorous stirring to obtain the nitrate solutions of metal ions. Then, a suitable molar ratio of citric acid (analytical reagent) was added to the solution as a chelating agent for the metal ions. The pH value of the final solution was adjusted by addition of a suitable amount of NH3H2O (analytical reagent). Subsequently, the ammonium molybdate solution above was added to the solution and stirred for a few minutes. The obtained solution was then heated in a 80˚C water bath for 5 h, resulting in the formation of an opalescent sol. The prepared sols were further dried at 150˚C in an oven for 24 h to obtain a brown dried gel. Finally, the dried gel was annealed at 700˚C for 4 h in air atmosphere to form the white powders.
The crystal phase of the samples were determined by using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD; X’Pert Pro with a Cu Ka value of 1.5406 Å) in the range of 10˚ ≤ 2θ ≤ 60˚. The morphologies of the samples were measured by a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM; Philips XL30FEG). The room-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra and photoluminescence excitation (PLE) spectra were recorded by using a well-intensity-corrected spectrofluorophotometer (Hitachi F-4600) with identical instrumental parameters.
3. Results and discussion
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns of the series of (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 (x = 0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 1.2, 1.4, and 1.8) samples. The molar ratio of total chelating metal cations and citric acid was 1:1, and the pH value of the solution is adjusted to 4 in the reaction process. When the x value rises from 0.8 to 1.8, only the (112), (004), (200), (204, (220), (116), (312), and (224) diffraction peaks of SrMoO4 appear (JCPDS card no. 08-0482). When the x value decreases from 0.6 to 0, apart from the SrMoO4 phase, only the Na2MoO4 phase (JCPDS card no. 34-0076) appears, which indicates that the Eu3+ and low Na+ dopant do not cause any significant change in the host crystal structure. When x < 0.6, namely, the content of Na+ dopant increases from 1.4 to 2, some new weak diffraction peaks appear in the 2θ range from 10˚ to 28˚, as shown in Figure 2. These peaks can be indexed by Na2MoO4 (JCPDS card no. 34-0076), which indicates that the introduction of high Na+ dopant can cause the appearance of the Na2MoO4 phases.
From Figure 1, it can be seen that the introduction of Eu3+ and Na+ does not cause any obvious change of crystal structure [11] . However, with an increase in the doped Eu3+ concentration, the XRD peaks are red-shifted. This shift may be attributed to some of the smaller Eu3+ ions (ionic radius = 0.095 nm) getting into the SrMoO4 lattice and replacing some of the larger Sr2+ ions (ionic radius = 0.113 nm), resulting in contraction of the lattice and a tiny change of the lattice constant. In addition, the introduction of Eu and Na can alter the intensities of the SrMoO4 diffraction peaks. When the x value decreases from 1.8 to 0.6, there is the decreasing intensity of the SrMoO4 (112) diffraction peak. In fact, the decrease in the x value should cause an increase of Sr content, which leads to the rise of SrMoO4 content. However, we observe a decreasing intensity of the
![]()
Figure 1. XRD patterns of (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors obtained after calcinations at 700˚C for 4 h.
![]()
Figure 2. XRD patterns of (SrNa)1.8Eu0.2(MoO4)3 phosphor.
SrMoO4 (112) diffraction peak. Considerating that the decrease in the x value also causes an increase in Na content, we can conclude that the number of introduced Na dopants could lead to the decreasing intensity of the SrMoO4 (112) diffraction peak as the lattice gets destroyed. When x < 0.6, the intensity of diffraction peaks at 2θ = 28˚ begins to rise. It has been reported that the diffraction peaks of 2θ = 28˚ should come from the NaMoO4 phase [12] . Given that diffraction peaks of NaMoO4 appear with x < 0.6,we conclude that the increasing intensity of diffraction peaks at 2θ = 28˚ should be related to the formation of the NaMoO4 phase owing to the significant introduction of Na.
We further applied field emission scanning electron microscopy to measure the morphologies of the (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 sample, as shown in Figure 3. It can be proved approximately that the (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 crystal particle size is almost 300 nm. From the graph, we notice that many columns or prismlike crystals are well dispersed within the phosphors, which indicates that the particles are mainly single crystals rather than a common conglomeration of many microcrystallites. The narrow size distribution of these grains is very uniform, which can be seen as a direct consequence of the use of the sol-gel process.
The emission spectra of the samples were measured by a using fluorescence spectrophotometer under 275-, 395-, and 465-nm excitation under the same experimental conditions. The intensities of the emission peaks have some differences, although their locations and shapes are similar. The dotted line in Figure 4 shows the emission spectra of (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphors: It consists of four main peaks at 593, 616, 655, and 701 nm. The emission centered at ~593 nm corresponds to the 5D0 → 7F1 transition of Eu3+ ions, and the strongest emission centered at ~616 nm originates from the 5D0 → 7F2 transition of Eu3+ ions. Two weaker emissions centered at ~653 and ~702 nm have been attributed to the transition of 5D0 → 7F3 and 5D0 → 7F4 of Eu3+ ions, respectively [13] [14] [15] . The excitation spectra of the samples were measured by using the same fluorescence spectrophotometer under 616-nm emission. As shown by the solid line of Figure 4, the excitation spectrum contains a broad peak and several spikes. The broad peak located between 200 and 300 nm should come from the overlap of charge transfer bands of O2− → Eu3+ and O2− → Mo6+. Narrowband excitation peaks above 350 nm are caused by the intrinsic f-f transition of Eu3+ ions. Figure 4 also shows the strongest excitation peaks at 395 and 465 nm, which suggests that the
![]()
Figure 3. SEM image of nanometer (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphor.
(SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors can be excited very well by 395-nm near-ultra- violet light and 465-nm blue light. Those two peaks at 395 and 465 nm should be related to the 7F0 → 5L6 transition and 465-nm 7F0 → 5D2 transition, respectively [16] [17] .
In (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors, Eu3+-doped rare earth ions act as luminescent centers in general. Therefore the concentration of Eu3+ ions plays a crucial role in the phosphor luminescent properties. Figure 5 shows the relationship between the intensity of the emission peak at 616 nm and the Eu3+-doped rare earth concentration for x ranging from 0.2 to 1.8. To indicate the influence of excitation wavelength on the intensity of the emission peak, in the experiment we adopted the three excitation peaks mentioned above: 275, 395, and 465 nm.
![]()
Figure 4. Excitation and emission spectra for (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphors.
![]()
Figure 5. The relationship between luminescence intensity and Eu3+-doped concentration of phosphors.
From this graph, it can be seen that there are two maximum luminescence intensities at x = 0.6 and x = 1.4. This may result from SrMoO4 having a scheelite structure and belonging to a tetragonal system, in which the unit cell parameters are a = 0.5394 nm and c = 1.202 nm, respectively. In this structure, Mo6+ in the O2− coordination tetrahedron center forms a 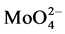 anion complex. There are four adjacent Sr2+ ions around each Mo6+ ion and eight adjacent O2− ions around each Sr2+ ion, forming a distorted cube. When a Na+-doped ion and a Eu3+-doped ion get into the SrMoO4 structure, the Eu3+ ion and the Na+ ion replace the Sr2+ ions in the crystal. When x < 0.6, with increasing Eu3+-doped concentration, the number of luminescence centers in the samples increases, which leads to the increasing phosphor luminescence intensity. When 0.6 < x < 1, owing to Eu3+ ions taking on the same deformation ability and trend, interionic mutual exclusion effects that weaken the degree of their deformation can be generated because of their interactions. Accordingly, some of the Eu3+ ions will lose their luminous power because some outer electrons cannot transition at this condition. The results lead to a reduction of phosphor luminescence intensity. When 1 < x < 1.4, with the further increase of Eu3+ ions, two or more Eu3+ ions may coexist in the same cell. Therefore, the transition power of the outer electrons of Eu3+ ions will be further enhanced, with the crystal field symmetry in the cell increasing. As a result, the phosphor luminescence intensity increases again. When x > 1.4, the too low concentration of Sr2+ and Na+ ions will weaken the ability of the substrate to absorb external energy. Accordingly, the transition power of the outer electrons of Eu3+ ions declines and, therefore, the phosphor luminescence intensity decreases again [18] . From this figure, it can be seen that the emission peak (x = 1.4) of λex = 275nm is broad, the reason maybe that for (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors, the broad excitation peak was located between 200nm and 300nm, and come into being from the charge transfer band overlap of O2− → Eu3+ and O2− → Mo6+, but narrowband excitation peak more than 350nm is caused by intrinsic f-f transition of Eu3+, so the Eu3+ ion concentration has a great influence on the λex = 395 nm and λex = 465 nm.
anion complex. There are four adjacent Sr2+ ions around each Mo6+ ion and eight adjacent O2− ions around each Sr2+ ion, forming a distorted cube. When a Na+-doped ion and a Eu3+-doped ion get into the SrMoO4 structure, the Eu3+ ion and the Na+ ion replace the Sr2+ ions in the crystal. When x < 0.6, with increasing Eu3+-doped concentration, the number of luminescence centers in the samples increases, which leads to the increasing phosphor luminescence intensity. When 0.6 < x < 1, owing to Eu3+ ions taking on the same deformation ability and trend, interionic mutual exclusion effects that weaken the degree of their deformation can be generated because of their interactions. Accordingly, some of the Eu3+ ions will lose their luminous power because some outer electrons cannot transition at this condition. The results lead to a reduction of phosphor luminescence intensity. When 1 < x < 1.4, with the further increase of Eu3+ ions, two or more Eu3+ ions may coexist in the same cell. Therefore, the transition power of the outer electrons of Eu3+ ions will be further enhanced, with the crystal field symmetry in the cell increasing. As a result, the phosphor luminescence intensity increases again. When x > 1.4, the too low concentration of Sr2+ and Na+ ions will weaken the ability of the substrate to absorb external energy. Accordingly, the transition power of the outer electrons of Eu3+ ions declines and, therefore, the phosphor luminescence intensity decreases again [18] . From this figure, it can be seen that the emission peak (x = 1.4) of λex = 275nm is broad, the reason maybe that for (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors, the broad excitation peak was located between 200nm and 300nm, and come into being from the charge transfer band overlap of O2− → Eu3+ and O2− → Mo6+, but narrowband excitation peak more than 350nm is caused by intrinsic f-f transition of Eu3+, so the Eu3+ ion concentration has a great influence on the λex = 395 nm and λex = 465 nm.
Citric acid acts as a complexant for a number of metal cations in the sol-gel process [19] . Therefore it plays a vital role in how metal cations enter into the matrix compounds. When the total amount of citric acid is too low, the metal cations cannot enter into the crystal lattice very well. However, if the amount of citric acid is too high, more citric acid will decompose during the annealing pro- cess, and the rapid expansion of the volume will result in partial sintering in the sample. The luminescent properties of the samples will be reduced because of the subsequent decline in surface activity under this condition. Figure 6 shows the relationship between luminescence intensity of 7 mmol (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphor and the amount of citric acid used in this experiment. From this figure, we can see that the highest luminescent efficiency appears for citric acid dosage of almost 24 mmol at 275-, 395-, and 465-nm wavelength excitation, respectively. That is, when the molar ratio of citric acid to metal cations is 1:1, metal cations can enter into the matrix structure of samples very well to form a good crystal. The phosphor luminescent efficiency reaches its highest value under this condition.
The solution pH value has a significant influence on the formation of sol-gel states and crystal compounds. Figure 7 shows the relationship between luminescence intensity of 7 mmol (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphor and the solution pH value in the reaction process. From this figure, we can see that the luminous efficiency of (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphor reaches its maximum when the solution pH is almost 4. That is, the citric acid has its best complexation efficiency under this acidic condition. When the pH value is too large, the solution easily forms a metal hydroxide milk-white precipitate. The milk-white precipitate decomposes under high-temperature annealing to form a metal oxide complex, leading to reduced phosphor luminescence efficiency.
![]()
Figure 6. The relationship between luminescence intensity and the amount of citric acid.
![]()
Figure 7. The relationship between luminescence intensity and the solution pH value.
4. Conclusion
(SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors were successfully prepared by using the sol-gel process. The results of XRD show that (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors have a SrMoO4 structure. The luminescent properties of (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors depend on the Eu3+ concentration, (C6H8O7)∙H2O concentration, and solution pH value. (SrNa)0.6Eu1.4(MoO4)3 phosphor and (SrNa)1.4Eu0.6(MoO4)3 phosphor show superior luminescent properties to other (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors under the same reaction conditions. The (SrNa)2-xEux(MoO4)3 phosphors show the hig- hest emission intensity under experiment conditions at which the solution pH value is almost 4 and the mole amount of citric acid equals the total number of moles of metal cations.