New Single Input Multiple Output Type Current Mode Biquad Filter Using OTAs ()
Received 28 February 2016; accepted 18 April 2016; published 21 April 2016

1. Introduction
OTA-C structures are suitable for realizing electronically-tunable continuous-time filters in a variety of technologies such as bipolar, CMOS and Bi-CMOS and therefore, widely used for designing voltage mode (VM) as well as current-mode (CM) filters. Although a number of CM OTA-C biquads are reported in earlier literature [1] - [22] , those of [1] - [6] are of multiple-input-multiple-output type or multiple-input-single-output type [7] - [9] . Thus, only the circuits of [10] - [22] realize single-input-multiple-output (SIMO) type CM biquad filters, with which this paper is concerned. SIMO type biquad using five active devices and two grounded capacitors (GCs) is given in [15] [18] [20] , that by using four active devices and two GCs is given in [12] - [14] [16] [17] [22] . In [10] , SIMO type biquad is made by using three active devices, one grounded and one floating capacitors presented whereas in [19] [21] SIMO type biquad made by using three active devices, two GCs and one additional passive element. In [25] SIMO type biquad presented using two active devices and two grounded capacitors, in this circuit input current is not at low impedance terminal. In the next section proposing a new SIMO type CM mode biquad using three active devices and two GCs with following desirables features: 1) realizibility of all the five standard filter functions namely, low pass (LP), band pass (BP), high pass (HP), band reject (BR) and all pass (AP); 2) realizibility of all the five functions without requiring any design constraint/matching conditions; 3) availability of explicit current outputs at high-output-impedance nodes and the input at low input impedance node; 4) independent tunability of ω0 and bandwidth (BW) with the gain is unity (v) employment of both grounded capacitors; and 5) use of a small number of active building blocks.
2. Proposed Circuit
The Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) is the widely used and most significance active building block. This happens to be an attractive active device because it offers electronic tunability of filter parameters. So the circuit diagram of the Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) is Figure 2(a). The characteristic equations of the OTA are given as (1)-(2) and its MOS implementation is shown in Figure 2(b) as shown in [24] .
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
The proposed new circuit configuration is shown in Figure 1.
A straight forward analysis reveals the following transfer functions for the configuration of Figure 1
LPF: (3)
(3)
BPF: (4)
(4)
BRF: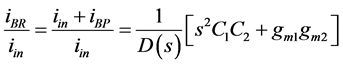 (5)
(5)
HPF: (6)
(6)
APF: (7)
(7)
where, .
.
The various parameters of the realized filters are given by:
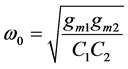 ,
,  and
and  (8)
(8)
Note that from Equation (8) it is clear that the bandwidth can be fixed by gm1 and then center frequency can be controlled by gm2.
Sensitivity analysis for this confirmation shows that
 ,
, (9)
(9)
which all are no more than 0.5.
3. Simulation Results
The workability of the proposed new circuits has been verified by SPICE simulations using CMOS OTAs is shown in Figure 2 (as shown in [24] ) and CMOS current followers is shown in Figure 3 (as shown in [23] ). Whereas aspect ratios for various MOSFETs employed in the differential-input-dual-output (DIDO)-type OTAs is shown in Table 1, the supply voltages used were VDD = 1.0 V, VSS = 1.0 V, and the aspect ratio for the CMOS current follower is shown in Table 2, and the supply voltages used were VDD = 1.0 V, VSS = 1.0 V, VBIAS1 = −0.47 V, VBIAS2 = −0.71 V, whereas 0.18 µm CMOS technology parameters obtained from TSMC were used.
![]() (a)
(a)![]() (b)
(b)
Figure 2. (a) Symbolic notation of MO-OTA; (b) CMOS realization of the MO-OTA [24] .
![]()
Figure 3. An exemplary CMOS implementation of the dual output current follower (DOCF) [23] .
![]()
Table 2. Aspect Ratios of dual output current follower (DOCF).
To achieve the SIMO-type filters with f0 = 1 MHz and quality factor of Q0 = 0.73, the capacitors values were selected C1 = C2 = 9 pF and the trans-conductance (gm) parameters were gm1 = 80.6 µA/V and gm2 = 39.2 µA/V. All the five filter responses are shown in Figure 4. Continuous line in Figure 4(a) shows the simulated outputs whereas dashed line represents the ideal or theoretical output of the derived filter configuration. For AP response, the magnitude as well as phase response is shown in Figure 4(b). One can see in Figure 4(a) the simulated and ideal responses are in good agreement to each other.
To test the input dynamic range of the proposed filters, the simulation of the BPF as an example has been done for a sinusoidal input signal of f0 = 1 MHz. Figure 5 shows that the input dynamic range of the filter extends up to amplitude of 5 µA. The dependence of the output harmonics distortion on the input signal amplitude is illustrated in Figure 6.
For input signal amplitude lower than 8µA the total harmonic distortion (THD) has been found to be of less than 4.0%. The obtained results show that the circuit operates properly even at signal amplitudes of about 8 µA. Figure 7 shows the simulation results for variation of Q0 while keeping f0 fixed (1 MHz) with C1 = C2 = 9 pF (see Table 3). Figure 8 shows the simulation results for variation f0 of while keeping Q0 =1 with C1 = C2 = 9 pF (see Table 3).
![]()
![]() (b)
(b)
Figure 4. PSPICE Simulation results: (a) Gain response of LPF, BPF, HPF and Notch; (b) Gain and Phase response of APF.
![]()
Figure 5. Time domain response of the band-pass filter of the proposed circuit for 1 MHz sinusoidal input current of 5 µA.
![]()
Figure 6. Dependence of output current total harmonic distortion on input current amplitude of the band-pass filter of proposed configuration.
![]()
Figure 7. Simulation results for control of Q0 while keeping f0 fixed (1 MHz) for band pass filter.
![]()
Figure 8. Simulation results for control of f0 while keeping Q0 (=1) fixed for band pass filter.
![]()
Table 3. The gm1 and gm2 values for controlling of Q0 and for controlling f0.
4. Conclusion
This paper introduces a new universal filter which employs one current follower, two OTAs and only two grounded capacitors. This circuit has been verified theoretically and simulated using Orcad PSPICE software. The circuit consists of the following features: 1) all the five standard filtering responses are available without putting any additional active or passive component/device; 2) the current mode circuit offers electronic tunability for the frequency as well as for the bandwidth; 3) the input is applied at low impedance port and the output is taken from high impedance port, and makes this circuit a better proposition for utilizing this circuit for making the higher order filter; 4) all the used capacitors are grounded in nature, which is an important parameter for integrated circuit realization; 5) all the current outputs are explicitly available; 6) this SIMO type universal filter offers unity gain. All the simulated results are in agreement with the theoretical results.