Complete Semigroups of Binary Relations Defined by Semilattices of the Class ∑1(X,10) ()
1. Introduction
Let X be an arbitrary nonempty set, D be an X-semilattice of unions, i.e. such a nonempty set of subsets of the set X that is closed with respect to the set-theoretic operations of unification of elements from D, f be an arbitrary mapping of the set X in the set D. To each such a mapping f we put into correspondence a binary relation 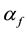 on the set X that satisfies the condition
on the set X that satisfies the condition
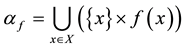
The set of all such 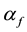
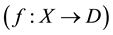 is denoted by
is denoted by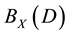 . It is easy to prove that
. It is easy to prove that 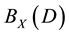 is a semigroup with respect to the operation of multiplication of binary relations, which is called a complete semigroup of binary relations defined by an X-semilattice of unions D.
is a semigroup with respect to the operation of multiplication of binary relations, which is called a complete semigroup of binary relations defined by an X-semilattice of unions D.
Recall that we denote by 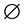 an empty binary relation or empty subset of the set X. The condition
an empty binary relation or empty subset of the set X. The condition 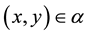 will be written in the form xαy. Further let
will be written in the form xαy. Further let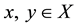 ,
, 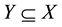 ,
, 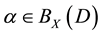 ,
, 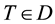 ,
, 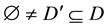 ,
, 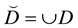 and
and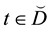 . Then by symbols we denoted the following sets:
. Then by symbols we denoted the following sets:
![]()
By symbol ![]() is denoted an exact lower bound of the set D' in the semilattice D.
is denoted an exact lower bound of the set D' in the semilattice D.
Definition 1. We say that the complete X-semilattice of unions D is an XI-semilattice of unions if it satisfies the following two conditions:
a) ![]() for any
for any![]() ;
;
b) ![]() for any nonempty element Z of the semilattice D.
for any nonempty element Z of the semilattice D.
Definition 2. We say that a nonempty element T is a nonlimiting element of the set D' if ![]() and a nonempty element T is a limiting element of the set D' if
and a nonempty element T is a limiting element of the set D' if![]() .
.
Definition 3. Let![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() . A representation of a binary relation
. A representation of a binary relation
![]() of the form
of the form ![]() is called quasinormal.
is called quasinormal.
Note that, if ![]() is a quasinormal representation of the binary relation
is a quasinormal representation of the binary relation![]() , then the following conditions are true:
, then the following conditions are true:
1)![]() ;
;
2) ![]() for
for ![]() and
and![]() .
.
Let ![]() denote the class of all complete X-semilattices of unions where every element is isomorphic to a fixed semilattice D.
denote the class of all complete X-semilattices of unions where every element is isomorphic to a fixed semilattice D.
The following Theorems are well know (see [1] and [3] ).
Theorem 4. Let X be a finite set; δ and q be respectively the number of basic sources and the number of all automorphisms of the semilattice D. If ![]() and
and![]() , then
, then
![]()
where ![]() (see Theorem 11.5.1 [1] ).
(see Theorem 11.5.1 [1] ).
Theorem 5. Let D be a complete X-semilattice of unions. The semigroup ![]() possesses right unit iff D is an XI-semilattice of unions (see Theorem 6.1.3 [1] ).
possesses right unit iff D is an XI-semilattice of unions (see Theorem 6.1.3 [1] ).
Theorem 6. Let X be a finite set and ![]() be the set of all those elements T of the semilattice
be the set of all those elements T of the semilattice
![]() which are nonlimiting elements of the set
which are nonlimiting elements of the set![]() . A binary relation
. A binary relation ![]() having a quasinormal
having a quasinormal
representation ![]() is an idempotent element of this semigroup iff
is an idempotent element of this semigroup iff
a) ![]() is complete XI-semilattice of unions;
is complete XI-semilattice of unions;
b) ![]() for any
for any![]() ;
;
c) ![]() for any nonlimiting element of the set
for any nonlimiting element of the set ![]() (see Theorem 6.3.9 [1] ).
(see Theorem 6.3.9 [1] ).
Theorem 7. Let D, ![]() ,
, ![]() and I denote respectively the complete X-semilattice of unions, the set of all XI-subsemilatices of the semilattice D, the set of all right units of the semigroup
and I denote respectively the complete X-semilattice of unions, the set of all XI-subsemilatices of the semilattice D, the set of all right units of the semigroup ![]() and the set of all idempotents of the semigroup
and the set of all idempotents of the semigroup![]() . Then for the sets
. Then for the sets ![]() and I the following statements are true:
and I the following statements are true:
1) if ![]() and
and ![]() then
then
a) ![]() for any elements
for any elements ![]() and
and ![]() of the set
of the set ![]() that satisfy the condition
that satisfy the condition![]() ;
;
b) ![]()
c) the equality ![]() is fulfilled for the finite set X.
is fulfilled for the finite set X.
2) if![]() , then
, then
a) ![]() for any elements
for any elements ![]() and
and ![]() of the set
of the set ![]() that satisfy the condition
that satisfy the condition![]() ;
;
b) ![]()
c) the equality ![]() is fulfilled for the finite set X (see Theorem 6.2.3 [1] ).
is fulfilled for the finite set X (see Theorem 6.2.3 [1] ).
Corollary 1. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be some sets, where
be some sets, where ![]() and
and![]() . Then the number
. Then the number ![]() of all possible mappings of the set Y into any such subset
of all possible mappings of the set Y into any such subset ![]() of the set
of the set ![]() that
that ![]() can be calculated by the formula
can be calculated by the formula ![]() (see Corollary 1.18.1 [1] ).
(see Corollary 1.18.1 [1] ).
2. Idempotent Elements of the Semigroups ![]() Defined by Semilattices of the Class
Defined by Semilattices of the Class ![]()
Let X and ![]() be respectively an arbitrary nonempty set and a class X-semilattices of unions, where each element is isomorphic to some X-semilattice of unions
be respectively an arbitrary nonempty set and a class X-semilattices of unions, where each element is isomorphic to some X-semilattice of unions ![]() that satisfies the conditions:
that satisfies the conditions:
![]() (1)
(1)
An X-semilattice that satisfies conditions (1) is shown in Figure 1.
Let ![]() be a family of sets, where P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9
be a family of sets, where P0, P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8, P9
are pairwise disjoint subsets of the set X and ![]() be a map-
be a map-
ping of the semilattice D onto the family sets![]() . Then for the formal equalities of the semilattice D we have a form:
. Then for the formal equalities of the semilattice D we have a form:
![]() (2)
(2)
Here the elements P1, P2, P3, P4, P5, P6, P7, P8 are basis sources, the elements P0, P6, P9 are sources of completeness of the semilattice D. Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() (see [2] ).
(see [2] ).
Lemma 1. Let![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then
. If X is a finite set, then
![]() .
.
Proof. In this case we have: m = 10, δ = 7. Notice that an X-semilattice given in Figure 1 has eight automorphims. By Theorem 1.1 it follows that
![]() ,
,
where ![]() and that
and that
![]() .
.
Example 8. Let ![]() Then:
Then:
![]() .
.
Lemma 2. Let![]() . Then the following sets are all proper subsemilattices of the semilattice
. Then the following sets are all proper subsemilattices of the semilattice![]() :
:
1) ![]()
(see diagram 1 of the Figure 2);
2) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 2 of the Figure 2);
3) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 3 of the Figure 2);
4) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 4 of the Figure 2);
5) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 5 of the Figure 2);
6) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 6 of the Figure 2);
7) ![]()
(see diagram 7 of the Figure 2);
8) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 8 of the Figure 2);
9) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 9 of the Figure 2);
10) ![]()
(see diagram 10 of the Figure 3);
11) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 11 of the Figure 2);
12) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 12 of the Figure 2);
13) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 13 of the Figure 2);
14) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 14 of the Figure 2);
15) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 15 of the Figure 2);
16) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 16 of the Figure 2);
17) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 17 of the Figure 2);
18) ![]()
(see diagram 18 of the Figure 2);
19) ![]()
(see diagram 19 of the Figure 2);
20) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 20 of the Figure 2);
21) ![]()
(see diagram 21 of the Figure 2);
22) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 22 of the Figure 2);
23) ![]()
(see diagram 23 of the Figure 2);
24) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 24 of the Figure 2);
25) ![]()
(see diagram 25 of the Figure 2);
26) ![]()
(see diagram 26 of the Figure 2);
27) ![]()
(see diagram 27 of the Figure 2);
28) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 28 of the Figure 2);
29) ![]()
(see diagram 29 of the Figure 2);
30) ![]()
(see diagram 30 of the Figure 2);
31) ![]()
(see diagram 31 of the Figure 2);
32) ![]()
(see diagram 32 of the Figure 2);
33) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 33 of the Figure 2);
34) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 34 of the Figure 2);
35) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 35 of the Figure 2);
36) ![]()
(see diagram 36 of the Figure 2);
37) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 37 of the Figure 2);
38) ![]()
(see diagram 38 of the Figure 2);
39) ![]()
(see diagram 39 of the Figure 2);
40) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 40 of the Figure 2);
41) ![]()
(see diagram 41 of the Figure 2);
42) ![]()
(see diagram 42 of the Figure 2);
43) ![]()
(see diagram 43 of the Figure 2);
44) ![]()
(see diagram 44 of the Figure 2);
45) ![]()
(see diagram 45 of the Figure 2);
46) ![]()
(see diagram 46 of the Figure 2);
47) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 47 of the Figure 2);
48) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 48 of the Figure 2);
![]()
Figure 2. Diagram of all subsemilattices of D.
49) ![]()
(see diagram 49 of the Figure 2);
50) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 50 of the Figure 2);
51) ![]()
(see diagram 51 of the Figure 2);
52) ![]()
(see diagram 52 of the Figure 2);
Diagrams of subsemilattices of the semilattice D.
Lemma 3. Let![]() . Then the following sets are all XI-subsemi-lattices of the given semilattice D:
. Then the following sets are all XI-subsemi-lattices of the given semilattice D:
1) ![]()
(see diagram 1 of the Figure 2);
2) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 2 of the Figure 2);
3) ![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 3 of the Figure 2);
4) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 4 of the Figure 2);
5) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 5 of the Figure 2);
6) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 6 of the Figure 2);
7) ![]()
(see diagram 7 of the Figure 2);
8) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 8 of the Figure 2);
Proof. It is well know (see [1] ), that the semilattices 1 to 8, which are given by lemma 2 are always XI-semi- lattices. The semilattices 9 and 10 which are given by Lemma 2
![]()
(see diagram 9 of the Figure 2);
![]()
(see diagram 10 of the Figure 2);
are XI-semilattices iff the intersection of minimal elements of the given semilattices is empty set. From the formal equalities (1) of the given semilattice D we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
From the equalities given above it follows that the semilattices 9 and 10 are not XI-semilattices. ![]()
The semilattices 11
![]()
(see diagram 1-8 of the Figure 3);
are not XI-semilattice since we have the following inequalities
![]()
The semilattices 12 to 52 are never XI-semilattices. We prove that the semilattice, diagram 52 of the Figure 2, is not an XI-semilattice (see Figure 4). Indeed, let ![]() and
and
![]()
be a family of sets, where ![]() are pairwise disjoint subsets of the set X. Let
are pairwise disjoint subsets of the set X. Let
![]()
be a mapping of the semilattice Q onto the family of sets![]() . Then for the formal equalities of the semilattice Q we have a form:
. Then for the formal equalities of the semilattice Q we have a form:
![]()
Figure 3. Diagram of all subsemilattices which are isomorphic to 11 in Figure 2.
![]()
Figure 4. Diagram of subsemilattice 52 in Figure 2.
![]() (3)
(3)
Here the elements ![]() are basis sources, the elements
are basis sources, the elements![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are sources of completeness of the semilattice D. Therefore
are sources of completeness of the semilattice D. Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() (see [2] ). Then of the formal equalities we have:
(see [2] ). Then of the formal equalities we have:
![]()
![]()
We have, that ![]() and
and ![]() for any
for any![]() . But elements T7, T6, T5, T4, T3, T2, T1, T0 are not union of some elements of the set
. But elements T7, T6, T5, T4, T3, T2, T1, T0 are not union of some elements of the set![]() . Therefore from the Definition 1 it follows that Q is not an XI-semilattice of unions. Statements 12 to 51 can be proved analogously.
. Therefore from the Definition 1 it follows that Q is not an XI-semilattice of unions. Statements 12 to 51 can be proved analogously.
We denoted the following semitattices by symbols:
a)![]() , where
, where ![]() (see diagram 1 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 1 of the Figure 5);
b)![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() (see diagram 2 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 2 of the Figure 5);
c)![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() (see diagram 3 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 3 of the Figure 5);
d)![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() (see diagram 4 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 4 of the Figure 5);
e) ![]() where
where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , (see dia- gram 5 of the Figure 5);
, (see dia- gram 5 of the Figure 5);
f)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (see diagram 6 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 6 of the Figure 5);
g)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (see diagram 7 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 7 of the Figure 5);
![]()
Figure 5. Diagram of all XI-subsemilattices of D.
h)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() (see diagram 8 of the Figure 5);
(see diagram 8 of the Figure 5);
Note that the semilattices in Figure 5 are all XI-semilattices (see [1] and Lemma 1.2.3).
Definition 9. Let us assume that by the symbol ![]() denote a set of all XI-subsemilatices of X-semila- tices of unions D that every element of this set contains an empty set if
denote a set of all XI-subsemilatices of X-semila- tices of unions D that every element of this set contains an empty set if ![]() or denotes a set of all XI-sub- semilatices of D.
or denotes a set of all XI-sub- semilatices of D.
Further, let ![]() and
and![]() . It is assumed that
. It is assumed that ![]() iff there exists some complete isomorphism
iff there exists some complete isomorphism ![]() between the semilatices
between the semilatices ![]() and
and![]() . One can easily verify that the binary relation
. One can easily verify that the binary relation ![]() is an equivalence relation on the set
is an equivalence relation on the set![]() .
.
By the symbol ![]() denote the
denote the ![]() -equivalence class of the set
-equivalence class of the set![]() , where every element is iso- morphic to the X-semilattice
, where every element is iso- morphic to the X-semilattice![]()
![]() .
.
Let D' be an XI-subsemilattice of the semilattice D. By ![]() we denoted the set of all right units of the semigroup
we denoted the set of all right units of the semigroup![]() , and
, and
![]()
where![]() .
.
Lemma 4. If X is a finite set, then the following equalities hold
a) ![]()
b) ![]()
c) ![]()
d) ![]()
e) ![]()
f) ![]()
g) ![]()
h) ![]()
Proof. This lemma immediately follows from Theorem 13.1.2, 13.3.2, and 13.7.2 of the [1] . ![]()
Theorem 10. Let ![]() and
and![]() . Binary relation
. Binary relation ![]() is an idempotent relation of the semmigroup
is an idempotent relation of the semmigroup ![]() iff binary relation
iff binary relation ![]() satisfies only one conditions of the following conditions:
satisfies only one conditions of the following conditions:
a)![]() , where
, where![]() ;
;
b)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and satisfies the conditions:
, and satisfies the conditions: ![]() T,
T,![]() ;
;
c)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and sa-
, and sa-
tisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
d)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() , and satisfies the conditions:
, and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
e)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
f)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
g)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
h)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the condi- tions:
and satisfies the condi- tions:![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
Proof. By Lemma 3 we know that 1 to 8 are an XI-semilattices. We prove only statement g. Indeed, if
![]() ,
,
where![]() , then it is easy to see, that the set
, then it is easy to see, that the set ![]() is a generating set of the semilattice
is a generating set of the semilattice![]() . Then the following equalities hold
. Then the following equalities hold
![]()
By statement a of the Theorem 6.2.1 (see [1] ) we have:
![]() .
.
Further, one can see, that the equalities are true:
![]()
We have the elements Z6, T, T' are nonlimiting elements of the sets![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() respectively.
respectively.
By statement b of the Theorem 6.2.1 [1] it follows, that the conditions![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() hold. Therefore, the statement g is proved. Rest of statements can be proved analogously.
hold. Therefore, the statement g is proved. Rest of statements can be proved analogously.
Lemma 5. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calculated by the formula
may be calculated by the formula![]() .
.
Lemma 6. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calculated by formula
may be calculated by formula
![]()
Lemma 7. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calculated by formula
may be calculated by formula
![]()
Lemma 8. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calculated by formula
may be calculated by formula
![]()
Lemma 9. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calculated by formula
may be calculated by formula
![]()
Lemma 10. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 11. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 12. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Figure 6 shows all XI-subsemilattices with six elements.
![]()
Figure 6. Diagram of all subsemilattices which are isomorphic.
Theorem 11. Let![]() ,
,![]() . If X is a finite set and
. If X is a finite set and ![]() is a set of all idempotent elements of the semigroup
is a set of all idempotent elements of the semigroup![]() . Then
. Then![]() .
.
Example 12. Let![]() ,
,
![]()
Then![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() .
.
![]()
We have![]() . Where
. Where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
3. Results
Lemma 13. Let ![]() and
and![]() . Then the following sets exhaust all subsemilattices of the semilattice
. Then the following sets exhaust all subsemilattices of the semilattice ![]() which contains the empty set:
which contains the empty set:
1) ![]()
(see diagram 1 of the Figure 2);
2) ![]()
(see diagram 2 of the Figure 2);
3) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 3 of the Figure 2);
4) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 4 of the Figure 2);
5) ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(see diagram 5 of the Figure 2);
6) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 6 of the Figure 2);
7) ![]()
(see diagram 7 of the Figure 2);
8) ![]()
![]()
(see diagram 8 of the Figure 2);
Theorem 13. Let![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . Binary relation
. Binary relation ![]() is an idempotent relation of the semmigroup
is an idempotent relation of the semmigroup ![]() iff binary relation
iff binary relation ![]() satisfies only one conditions of the following conditions:
satisfies only one conditions of the following conditions:
a)![]() ;
;
b)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and satisfies the conditions:
, and satisfies the conditions:![]() ;
;
c)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and satisfies the
, and satisfies the
conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
d)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() , and satisfies the conditions:
, and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ;
;
e)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
f)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
g)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
h)![]() , where
, where![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and satisfies the conditions:
and satisfies the conditions:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
Lemma 14. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then
. If X is a finite set, then![]() .
.
Lemma 15. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 16. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 17. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 18. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 19. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 20. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Lemma 21. Let ![]() and
and![]() . If X is a finite set, then the number
. If X is a finite set, then the number ![]() may be calcu- lated by formula
may be calcu- lated by formula
![]()
Theorem 14. Let![]() ,
,![]() . If X is a finite set and
. If X is a finite set and ![]() is a set of all idempotent elements of
is a set of all idempotent elements of
the semigroup![]() , then
, then![]() .
.
Example 15. Let![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
Then![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() .
.
![]()
We have![]() . Where
. Where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() .
.
It was seen in ([4] , Theorem 2) that if ![]() and
and ![]() are regular elements of
are regular elements of ![]() then
then ![]() is an XI-subsemilattice of D. Therefore
is an XI-subsemilattice of D. Therefore ![]() is regular elements of
is regular elements of![]() . That is the set of all regular elements of
. That is the set of all regular elements of ![]() is a subsemigroup of
is a subsemigroup of![]() .
.