Ougenioxylon chinjiensis sp. nov., a New Fossil Species of the Family Leguminosae from Chinji Formation Salt Range, Punjab Pakistan ()
1. Introduction
The presence of fossilized plant remaining in the Tertiary deposits of Pakistan has been known since 1879, when Balanford [1] reported them while working on the geology of Sindh region. However no effort was made to investigate and identify these plant fossils from this region. Prof. K. M. Khan established Paleobotany research lab at Institute of Plant Sciences (formerly Department of Botany) and along with his co-workers reported a number of petrified woods from different fossiliferous localities of Sindh province (Khan & Rahmatullah, 1968 [2] ; Khan et al., 1971 [3] ; Khan & Rahmatullah, 1972 [4] ; Khan & Rajput, 1976 [5] ; Rehmatullah et al., 1984 [6] ; Rajput & Khan, 1982 [7] ; Rajput & Khan, 1984 [8] ; Saeed et al., 1984 [9] ; Rajput et al., 1985 [10] ; Ahmed et al., 1989 [11] ; Ahmed et al., 1991 [12] [13] ; Ahmed et al., 1993 [14] ; Bhutto et al., 1993 [15] ; Ahmed et al., 2007 [16] [17] ; Shar et al., 2007 [18] ). No attempt was made to explore the other provinces of Pakistan.
The present work deals with the first systematic study of a petrified wood from Punjab province, Pakistan. The petrified wood sample was collected from the fossiliferous locality of Chinji National Reservoir district Khushab, which is 50 km away from Khushab City and 175 km in northwest of Faisalabad in the heart of Salt range. Fossil woods are buried on the slopes of sedimentary rocks. Some of these fossils are in complete log of 4 - 6 m long. The present work deals with the anatomical description and the affinities of a fossil wood.
2. Material and Methods
The specimen No. TR. 20, Plate 1(a) . The material (TR. 20 silicified wood was collected by the first author from Chinji National Reserve, district Khushab, Punjab Pakistan. The wood was a small piece of mature secondary xylem fossil about 9 cm in length and 4 cm in diameter. The colour of fossilized wood was brown the anatomical sections, of required direction were prepared by the conventional Rock cutting and grinding thin sections technique [19] . Most of the preliminary investigations were made with the Lietz Ortholux II light microscope and Lietz Steriozoome microscope. Photographs were taken with Ortholux II Microscope at the Paleobotany lab, Institute of Plant Science, University of Sindh, Jamshoro, Pakistan.

(a) (b)
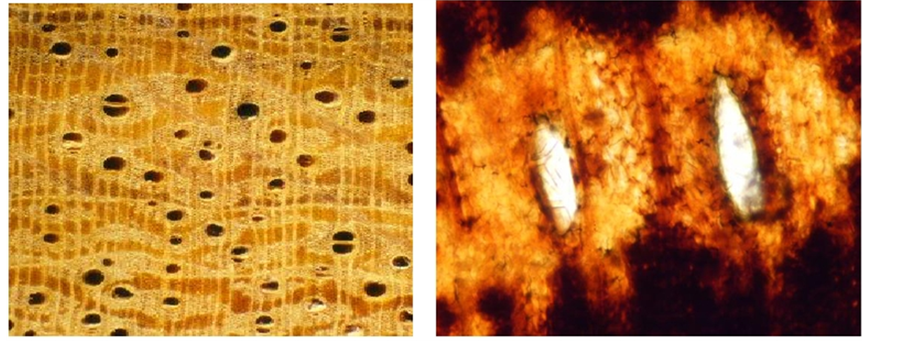
(c) (d)
Plate 1. Ougenioxylon chinjiensis sp. nov. (a) Tangenial longitudinal section showing distribution of xylem rays and end wall of vessels, ×100; (b) Tangenial longitudinal section showing arrangement of xylem rays, ×40; (c) Radial longitudinal section showing the nature of xylem rays, ×160; (d) Radial longitudinal section showing the pits on the wall of vessels, ×600.
3. Diagnosis
3.1. Ougenioxylon chinjiensis
Wood diffuse porous. Growth rings distinct. Vessel small to medium sized, mostly solitary as well as in radial multiples of 2 cells, t.d. 40 - 130 µm, 3 - 7 per sq. mm, r.d. 60 - 297 µm vessel members storied, short with truncated or tailed ends perforation simple intervessel pit pairs small perforation simple; intervassel pit small to medium sized, simple, alternate, circular and crowded. Tylosis absent. Parenchyma paratracheal and apotracheal parenchyma paratracheal parenchyma copious, vasicentric to aliform few aliform-confluent, apotracheal parenchyma diffuse as scattered cells and terminal, xylem rays 1 - 3 mostly Biseriate, 12 - 18 per mm, 10 - 25 cells high; ray tissue homogeneous ray homocellular cells, consisting of procumbent cells. Fibres mostly libriform small, polygonal, septate, thick walled, 5 - 10 µm in diameter.
3.2. Holotype
Thati Rest House, Chinji National Park, district Khushab, Punjab, Pakistan.
Basir Ahmed Arain, TR20, 1993 (Paleobotany museum, Institute of Plant Science, University of Sindh, Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan).
Horizon: Chinji Formation.
Age: Late Miocene.
3.3. Morphological Description
Fossil wood consist of a single piece of silicified wood which is ca. 22 cm long and 8 cm broad. The colour of fossilized wood is dark brown ( Plate 1(a) ).
3.4. Anatomical Description
3.4.1. Cross Section
Plates 1(b)-(d)
Wood diffuse porous. Growth rings distinct, delimited by 1 - 2 cells thick lines of terminal parenchyma. Vessels small to medium sized, oval in shape, unevenly distributed in ground mass, solitary as well as in radial multiples of 2, 3 - 7 per sq. mm. Radial diameter ranges from 60 - 297 µm tangential diameter ranges from 40 - 130 µm tyloses absent wood parenchyma paratracheal and apotracheal, paratracheal abundant, mostly vesicentric to aliform occasionally aliform to confluent. Appotracheal diffuse as solitary or arranged in uniseriate thick lines, delimating growth rings. The shape of parenchyma cells round to oval, diameter ranges from 10 - 25 µm. Fiber cells are polygonal in shape, thick walled, diameter ranges from 5 - 13 µm. Xylem rays are mostly thin running on either side of the vessels
3.4.2. Tangential Longitudinal Section
Plate 2(a) , Plate 2(b)
Vessels composed of elongated cells, their length ranges from 140 - 260 µm with truncate to tailed ends. Vessels are irregularly distributed. Solitary vessels oval in shape those in radial multiples flattened at the places of contact. Xylem rays are numerous, mostly biseriate, homogenous consisting of procumbent cells, 10 - 25 cells high, diameter ranges from 15 - 30 µm 10 - 18 rays per mm. Intervessel pits are simple, alternate, circular to oval and some are elliptical in shape and crowded.
3.4.3. Radial Longitudinal Section
Plate 3(a) , Plate 3(b)
Vessels segments elongated, length of vessels member ranges from 140 - 260 µm, and breadth ranges from 110 - 360 µm. End wall transverse, perforation simple, pits cells rounded alternate. The wood fibers are septate.
3.5. Comparison with Modern Wood
There is a close resemblance in almost all anatomical attributes of the discussed fossil wood with the wood structure of modern genus Ougenia Benth, belonging to the family Leguminosae. After the examination of
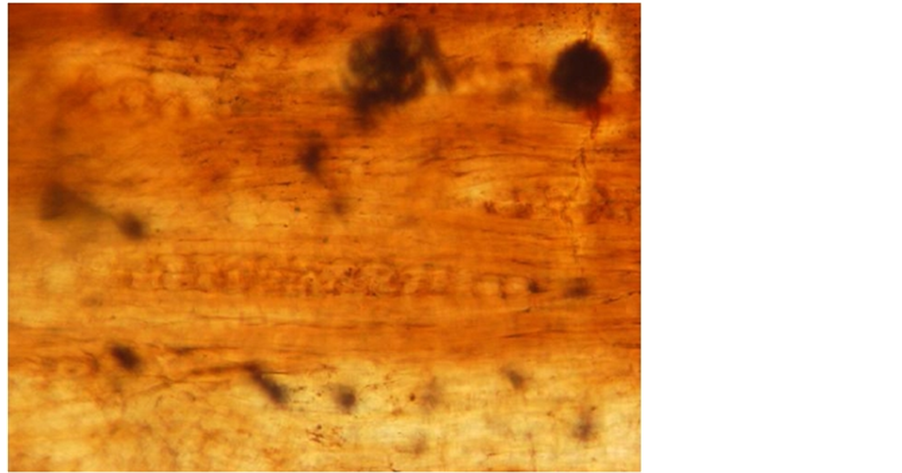
(a)

(b)
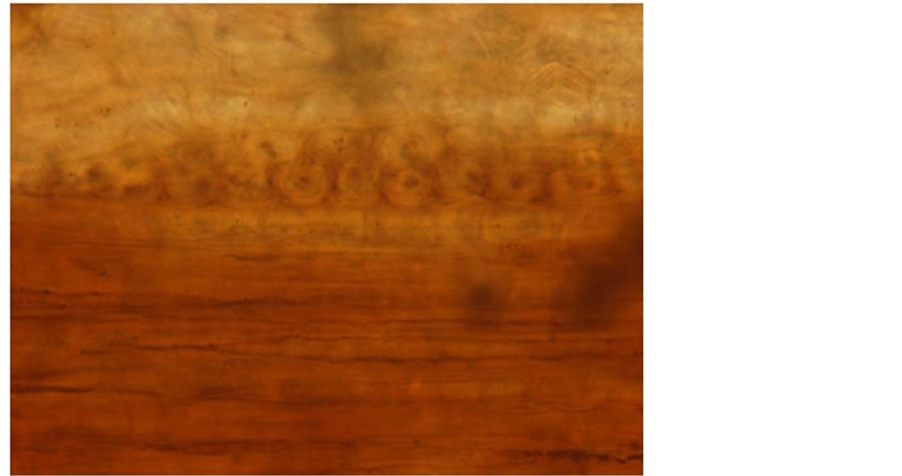

(c)
Plate 2. Ougenioxylon chinjiensis sp. nov. (a) Tangenial longitudinal section show- ing distribution of xylem rays and end wall of vessels, ×100; (b) Tangenial longitudinal section showing arrangement of xylem rays, ×40.

(a)

(b)
Plate 3. Ougenioxylon chinjiensis sp. nov. (a) Radial longitudinal section showing the nature of xylem rays and pits on the wall of vessels, × 100; (b) Radial longitudinal section showing the pits on the wall of vessels of the living Ougenia (Inside wood).
anatomical structure on published description and phtorographs of the modern wood of Ougenia Benth, indicates closest resemblance with wood anatomical structure of Ougenia dalbergioides Benth [20] [21] .
In both, the fossil wood and the modern wood Ougenia dalbergioides the growth rings are marked by terminal parenchyma, the vessels are small to large mostly solitary, often short redial of 2 - 4. The parenchyma mostly vasicentric to aliform occasionally aliform to confluent. The xylem rays are storied, 1 - 4 (mostly 2 - 3) seriate and composed of procumbent cells only and the fibers are semi libriform to libriform and septate.
Due to close resemblance of the fossil wood with the wood structure of the modern genus Ougenia Benth. It has been assigned to the genus Ougenioxylon.
The genus Ougenia Benth comprises of with 2 species, distributed in India and Pakistan, represented locally by only 1 species.
3.6. Comparision with Fossil Woods
Hitherto only one species of Ougenia dalbergioides is reported from Tertiary deposits of Assam. The detailed comparison of this reported species with fossil wood under investigation is given in Table 1.
As the fossil wood described in the contribution shows differences from other described species of Ougenioxylon, therefore it is considered as new species and it is named Ougenioxylon chinjieinsis sp. nov. (Table 2).
![]()
Table 1. Comparison of fossils related to Ougenioxylon.
![]()
Table 2. Graphical and stratigraphical break-up of fossils related to the genus Ougenia Benth.
The specific epithet refers to Chinji Formation to which fossil wood belongs.
4. Conclusion
The anatomical character of the fossil wood indicates that it has diffuse porous wood and the growth rings are absent or indicated by terminal parenchyma. These characters indicate the existence of tropical type of climate of that time.