Analytical Third Order Solution for Coupling Effects of Earth Oblateness and Direct Solar Radiation Pressure on the Motion of Artificial Satellites ()
1. Introduction
Analytical theories of celestial mechanics are usually more tractable when tackled within the domain of Hamiltonian mechanics, and fortunately most non-Hamiltonian systems of differential equations can be Hamiltonized by a simple technique [1] [2] . As for as canonical perturbation methods are concerned, the basic demand is a canonical transformation such that the new Hamiltonian has fewer degrees of freedom, which results in integrals of motion equal in number to the number of ingrate coordinated, and thus successive transformations reduce the system to quadratures. If the Hamiltonian is a periodic function of time, a further requirement would be the averaging of the Hamiltonian to eliminate the time.
If the Hamiltonian admits a Taylor series expansion in powers of a small parameter 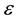 at
at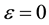 , a generator of the transformation can obtain a series of
, a generator of the transformation can obtain a series of 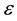 up to any desired power.
up to any desired power.
Many works deal with the effects of solar radiation pressure, Musen (1960) [3] derived first order expansion for the rate of change in the osculating elements using the method of variation of vector elements. Kosai (1961) and Brouwer (1962) [4] [5] used Lagrange’s planetary equations to find the first order solutions with the integration performed between the times of exit from, and entry into, the shadow. The resonance effects produced by the commensurabilities between the different mean motions provided good field for detailed theoretical studies (e.g. Musen, 1960 [3] ; Brouwer, 1962 [5] and Hori, 1966 [6] ). De Moraes (1981) [7] developed semi-ana- lytical theory including the joint effects of direct solar radiation pressure and atmospheric drag for satellites of perigee heights between 500 and 900 Kms. The difficulties arising from solar radiation pressure are analyzed in three very useful and interesting expositions given by Kampos (1968) and Sehnal (1970 and 1975) [8] - [10] . An interesting application is to use solar radiation pressure as means of spacecraft propulsion (solar sailing). The idea is described and its dynamics is studied by Mc Innes and Brouwn (1990) [11] .
It has been repeatedly stated by many authors (e.g. Kampos, 1968; Ferraz-Mello, 1972 and Anselono et al., 1983) [8] [12] [13] that there are no secular or long periodic changes of the semimajor axis and no second order terms (or even, by some author, no secular terms whatever the order). But Geyling and Westerman (1971), Lala (1972) and Sehnal (1975) [10] [14] [15] drew attention to secular terms which appear at higher orders. McMahon, Jay W., (2011) [16] modeled the solar radiation pressure acceleration as a Fourier series which depends on the Sun’s location in a body-fixed frame; a new set of Fourier coefficients are derived for every latitude of the Sun in this frame, and the series is expanded in terms of the longitude of the Sun. Lücking et al. (2012) [17] further explores a passive strategy based on the joint effects of solar radiation pressure and the Earth’s oblateness acting on a high area-to-mass-ratio object. In 2001, Cook found that the most significant effect relating to solar radiation pressure is the changing cross-sectional area of the satellite projected to the Sun [18] .
The present work is concerned with the effects of solar radiation pressure at higher orders to emphasize the effects of the couplings between them and with those resulting from the oblate gravity field of the Earth. The canonical equations of motion are formed in terms of the Delaunay elements augmented with the pair 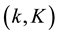 where
where 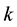 is the mean longitude of the sun. The equations include the radiation pressure force and the geopotential up to
is the mean longitude of the sun. The equations include the radiation pressure force and the geopotential up to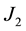 . Two canonical transformations are made to eliminate the short and long period terms in succession respectively. The Hamiltonians and generator are assumed to be expandable as
. Two canonical transformations are made to eliminate the short and long period terms in succession respectively. The Hamiltonians and generator are assumed to be expandable as
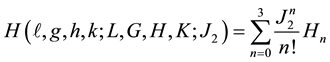
As expected secular terms arise at order 3 from the brackets 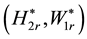 and
and 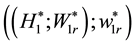 where the suffix
where the suffix 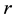 refers to terms arising from solar radiation pressure.
refers to terms arising from solar radiation pressure.
2. Equation of Motion
In terms of the Delaunay variables 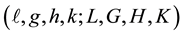 the equations of motion of an artificial satellite about an oblate Earth and perturbed by direct solar radiation
the equations of motion of an artificial satellite about an oblate Earth and perturbed by direct solar radiation
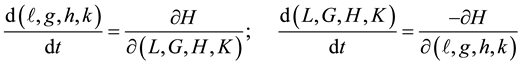 (1)
(1)
With the Hamiltonian [6] [19]
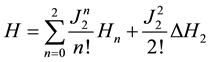 (2)
(2)
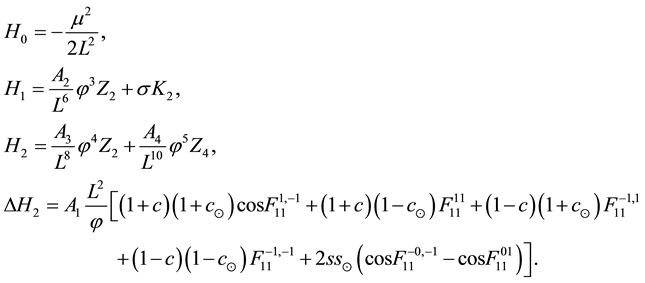 (3)
(3)
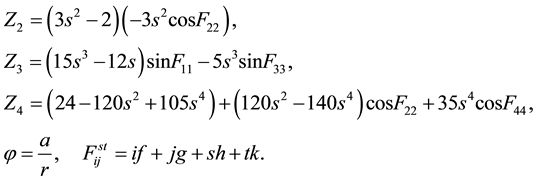 (4)
(4)
And
![]()
![]() is the solar constant,
is the solar constant, ![]() is the speed of light,
is the speed of light, ![]() is the mean distance Earth-Sun.
is the mean distance Earth-Sun.
![]() (5)
(5)
![]()
![]() being is the mean motion of the sun,
being is the mean motion of the sun, ![]() is a constant,
is a constant, ![]() is the obliquity of the ecliptic and
is the obliquity of the ecliptic and ![]() is the equatorial radius of the Earth.
is the equatorial radius of the Earth.
When deriving the above equations the Sun is assumed moving in a circular orbit so that its mean longitude is![]() , and the direction and distance of the satellite from the Sun are considered similar to those of the Earth. Clearly
, and the direction and distance of the satellite from the Sun are considered similar to those of the Earth. Clearly ![]() represents the contribution of solar radiation pressure.
represents the contribution of solar radiation pressure.
3. Short-Period Perturbations
Since ![]() depends only on
depends only on![]() , the angle
, the angle ![]() will be a fast variable while the other angles are slow variables. Therefore, we shall perform two transformations to eliminate, in succession, the short and long period terms. Adopting the transformation techniques developed by Deprit (1969) and Kamel (1969) [1] [20] , the identities for the short period transformation will be:
will be a fast variable while the other angles are slow variables. Therefore, we shall perform two transformations to eliminate, in succession, the short and long period terms. Adopting the transformation techniques developed by Deprit (1969) and Kamel (1969) [1] [20] , the identities for the short period transformation will be:
![]() (6.1)
(6.1)
![]() (6.2)
(6.2)
![]() (6.3)
(6.3)
![]() (6.4)
(6.4)
where ![]() is the Lie derivative generated by
is the Lie derivative generated by ![]() and the Hamiltonian and generating function at order n are obtained from (6.2) by choosing
and the Hamiltonian and generating function at order n are obtained from (6.2) by choosing
![]() (6.5)
(6.5)
Then
![]() (6.6)
(6.6)
The elements of the transformation are obtained from
![]() (7.1)
(7.1)
![]() (7.2)
(7.2)
![]() (7.3)
(7.3)
![]() (7.4)
(7.4)
![]() (8.1)
(8.1)
![]() , n ≥ 1 (8.2)
, n ≥ 1 (8.2)
![]() , n ≥ 1 (8.3)
, n ≥ 1 (8.3)
![]() , n ≥ 1
, n ≥ 1
![]() (8.4)
(8.4)
Performing the operations described in Equations (6) with the secular and periodic terms retained up to the third and second order respectively, we arrive, after some lengthy manipulations, at the following results. All variables are understood to be single primed but the primes will be dropped out for the sake of simplicity of writing.
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10.1)
(10.1)
![]() (10.2)
(10.2)
At the subsequent orders (order 2 and 3) we will be concerned only with terms arising from the radiation pressure and those due to the coupling between oblateness and radiation pressure effects. We thus separate ![]() as
as
![]() (11)
(11)
where the suffixes ![]() and
and ![]() refer to gravity and radiation pressure, respectively. At the second order we have
refer to gravity and radiation pressure, respectively. At the second order we have
![]() (12.1)
(12.1)
![]() (12.2)
(12.2)
where:
![]() (13.1)
(13.1)
![]() (13.2)
(13.2)
Regarding (6.3) we find that the manipulations at order 3 require evaluating
![]() (14)
(14)
where:
![]()
Evaluating these brackets and performing the averaging process in Equation (6.5) we obtain, after lengthy calculations
![]()
(15.1)
![]() (15.2)
(15.2)
![]() (15.3)
(15.3)
![]() (15.4)
(15.4)
So that
![]()
(16)
where the ![]() are functions of , the subscripts
are functions of , the subscripts ![]() and
and ![]() mean partial derivatives with respect to each, and
mean partial derivatives with respect to each, and
![]() (17.1)
(17.1)
![]() (17.2)
(17.2)
For the elements of the transformations, substituting Equations (10.2) and (12.2) into Equation (8) yields
![]()
![]() (18.1)
(18.1)
![]()
![]()
![]() (18.2)
(18.2)
![]() .
.
![]() (18.3)
(18.3)
![]() (19.1)
(19.1)
![]() (19.2)
(19.2)
![]() (19.3)
(19.3)
![]() (19.4)
(19.4)
where:
![]()
where we note that![]() consists only of terms arising from the oblateness effects and therefore need be taken into consideration.
consists only of terms arising from the oblateness effects and therefore need be taken into consideration.
Substitution of Equations (18) and (19) into (7) yields the transformation and inverse.
4. Perturbations of Long Period
After the short-period terms have been eliminated the problem is now reduced to the system of canonical equations with Hamitonian ![]() .
.
We now proceed to eliminate the long-period terms, i.e. those periodic in .
The transformation follows the procedure outlined in Equations (6)-(8) but with the averages and integrations, performed over . The basic identities are now
![]() (20.1)
(20.1)
![]() (20.2)
(20.2)
Performing the processes outlined in Equations (16.1),…, (16.6) and (20) to find ![]() and
and ![]() assuming no resonant conditions the following results follow (all variables are double primed)
assuming no resonant conditions the following results follow (all variables are double primed)
4.1. Zero, First and Second Orders
Remembering that at orders 2 and 3, we are concerned only with the terms including radiation pressure effects we have
![]() (21)
(21)
![]() (22)
(22)
![]() (23)
(23)
![]() (24)
(24)
where:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
And
![]()
4.2. Third Order
From (20.2)
![]() (25.1)
(25.1)
![]() (25.2)
(25.2)
where:
![]() (26)
(26)
So, we can write
![]() ;
;![]() ; (27)
; (27)
By following the above scheme, the expressions for ![]() and
and ![]() can be deduce after a lengthily manipulation.
can be deduce after a lengthily manipulation.
4.3. There Order
4.3.1. Expressions for ![]() and
and ![]()
From (16), (26) and (27)
![]() (28.1)
(28.1)
Then
![]() (28.2)
(28.2)
Where:
![]()
![]()
Clearly, Equation (28.2) holds as long as
![]()
4.3.2. Expressions for ![]() and Writing
and Writing
![]() (29)
(29)
Equation (26) can be decomposed such that
![]() (30)
(30)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Regarding ![]() and
and![]() , Equations (25) and (27) yield
, Equations (25) and (27) yield
![]() (31)
(31)
![]() (32)
(32)
![]() (33)
(33)
where
![]()
![]()
![]()
And the primes on the summation signs en Equation (33) indicate that the terms ![]() is excluded. Clearly (33) holds as long as
is excluded. Clearly (33) holds as long as
![]()
For ![]() and
and ![]() we have
we have
![]() (34)
(34)
![]() (35)
(35)
where
And
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Equation (35) holds true as long as
![]()
Finally, for ![]() and
and![]() , we have
, we have
![]() (36)
(36)
![]() (37)
(37)
where:
And
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Again, Equation (37) holds true as long as the above conditions hold. Collecting we find that
![]() (38)
(38)
![]() (39)
(39)
4.3.3. Expressions for ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() (40)
(40)
![]() (41)
(41)
where
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
And
![]()
For ![]() and
and ![]() we have
we have
![]() (42)
(42)
![]() (43)
(43)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Finally, for ![]() and
and ![]() we have
we have
![]() (44)
(44)
![]() (45)
(45)
where:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
4.3.4. Expressions for ![]() and
and ![]()
As ![]() Equation (23) and Equation (26) reduce to
Equation (23) and Equation (26) reduce to
![]()
So that
![]()
where:
![]()
The elements of transformation are easily obtained using Equations (7), (8) with ![]() replaced by
replaced by![]() , the unprimed elements replaced by single primed elements, and with the single primed elements replaced by double primed ones.
, the unprimed elements replaced by single primed elements, and with the single primed elements replaced by double primed ones.
5. Effects of the Earth’s Shadow
In the proceeding developments, effects of entry into, or exit from, the Earth’s shadow are not taken into considerations.
To account for the shadow effects, we note that:
1) The integration processes to find the generators are not (directly) affected since they are more quadrates without integration limits.
2) What is affected and, indirectly, affects derivation of the generator is averaging process over the mean anomaly, performed to obtain the transformed Hamiltonian. To account for the shadow, let the time of exit from the shadow be ![]() where the mean anomaly is
where the mean anomaly is ![]() and let those corresponding to entrance into the shadow be
and let those corresponding to entrance into the shadow be ![]() and
and ![]() Then the averages are to be replaced by definite integrals between these 2 limits.
Then the averages are to be replaced by definite integrals between these 2 limits.
6. Secular Perturbations and Computation of Position and Velocity
After performing the long period transformation, the equation of motions are now reduced to
where ![]() are arbitrary constants
are arbitrary constants
where the constants are be determined from the initial conditions.
Let ![]() be the values of the elements at a given initial epoch
be the values of the elements at a given initial epoch![]() , then can be determined as follows:
, then can be determined as follows:
1) From the elements of the inverse transformations we compute
2) Having determined ![]() and
and ![]() at time
at time![]() , we can compute the position and velocity by any known method.
, we can compute the position and velocity by any known method.
7. Conclusion
Equation (32) reveals that, contrary to previous concept e.g. Kampos (1968) [8] , the direct solar radiation pressure produces secular effects at order 3 as long as the satellite is apart from the earth’s shadow. This emphasizes the importance of taking the effects of the solar radiation pressure into account in high order artificial satellite theories, particularly for those with high area-to-mass ratio flying at high altitudes.
Again, Equation (41) is valid away from the resonant conditions, i.e. as long as![]() ,
, ![]() , while (40) provides another secular part of
, while (40) provides another secular part of ![]() to be add to
to be add to![]() .
.
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to the anonymous referee for helpful comments.