1. Introduction
8-hydroxyquinoline (HL, Figure 1), known also as oxine, is a bidentate chelating agent. It forms three species: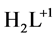 ,
, 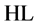 and
and 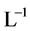 [1] . The anionic ligands,
[1] . The anionic ligands, 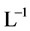 , form the precipitates MeL2 with some divalent metal ions
, form the precipitates MeL2 with some divalent metal ions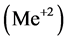 , or MeL3 with some trivalent metal ions
, or MeL3 with some trivalent metal ions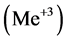 . The related precipitates are known as 8-oxyquinoli- nates (oxyquinolinates), or briefly as oxinates.
. The related precipitates are known as 8-oxyquinoli- nates (oxyquinolinates), or briefly as oxinates.
The oxine and its complexes, functioning as a transcription inhibitor [2] , exhibit antiseptic, disinfectant, and pesticide properties [3] [4] . Its 1% solution in alcohol is used in liquid bandages [5] , to prevent infections (for external use only). The oxine derivatives were of interest as anti-cancer drugs [6] [7] .
Oxidative damage is frequently found in many diseases such as aging, atherosclerosis, cancer, diabetes [8] and neurodegenerative diseases [9] . Free radicals are continuously produced in cells through a wide range of biological processes [10] . For example, the changing oxidation stage of Cu, which is a cofactor of superoxide
dismutases (SOD), results in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [11] . Therefore, antioxidant defenses, such as those afforded by tocopherol, ascorbic acid, SOD enzyme, and catalases, are necessary in the maintenance of homeostasis [12] . In this context, the oxine derivatives have been reported as potent antioxidants [13] - [16] , which arise from their chelating ability. It is widely known that mixed ligand metal complexes can commonly occur in biological fluids from various bioactive ligands with metal ions [17] . Ability to chelate and lipophilicity have been regarded as essential to the action of oxine. The most widely held hypothesis on the mechanism of action of oxine holds that oxine is only active when it can form saturated chelates with metals in the medium which enters the cell and dissociate. Oxine possesses potent coordinating ability and good metal recognition properties [18] . Chelation of oxine with metals in the medium was found not to be a requirement for oxine fungitoxicity [19] . Potentiation of the action of oxine by metals is explained by the formation of more fungitoxic and soluble metal oxinates and antagonism by the formation of less soluble or less active metal oxinates.
In conclusion, metal ions play a very important role in biological processes, and metal homeostasis is required for the maintenance of metal balance [20] [21] . Many diseases arise from the loss of homeostasis including metal overload and deficiency, which are caused by abnormal metal metabolism or metal absorption. Of all the hydroxyquinoline derivatives, oxine is the most interesting one to be explored, owing to its multifunctional properties, such as diverse bioactivities and therapeutic potentials [22] .
It is also worth noting that aluminum oxinate, AlL3, is a common component of organic light-emitting diodes (OLED’s) [23] . Variations in the substituents on the quinoline rings affect its luminescence properties [24] . Oxine is also widely used for analytical and separation purposes [25] - [27] .
In this context, we are interested in the manner of calculation of (1) the solubility s [mol/L] and (2) pH of the solution obtained after introducing pure oxinate MeL2 into pure water. The calculations will be made with use of Excel spreadsheets applied to an algorithm based on some balances and full physicochemical knowledge on the systems in question, involved in the related equilibrium constants.
2. Equilibrium Constants
The precipitates of oxinates are characterized by the solubility product  values. For the oxinate of MeL2 type we have:
values. For the oxinate of MeL2 type we have:
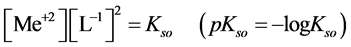 (1)
(1)
The soluble complex species 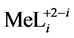 are characterized by stability constants
are characterized by stability constants :
:
 (2)
(2)
The stability constants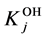 of the related hydroxo-complexes are defined as follows:
of the related hydroxo-complexes are defined as follows:
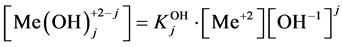 (3)
(3)
The ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() values are collected in Table 1 for selected Me-ions. Dissociation constants
values are collected in Table 1 for selected Me-ions. Dissociation constants ![]() of oxine [1] are formulated as follows:
of oxine [1] are formulated as follows:
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
and ionic product of water:
![]() (6)
(6)
![]()
Table 1. Selected equilibrium constants [28] - [31] for some Me+2 ions.
On the basis of (4) and (5) we get:
![]() (7)
(7)
![]() (8)
(8)
3. Formulation of the Basic Functions
If pure MeL2 is introduced into pure water, then the following relationships (concentration and charge balances) are valid:
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10)
(10)
![]() (11)
(11)
where ![]() concentration [mol/L] of the precipitate MeL2,
concentration [mol/L] of the precipitate MeL2, ![]() , and
, and
![]() (12)
(12)
is the solubility of MeL2. Assuming ![]() and applying the relationships (1) - (8), from (9) - (11) after cancellation of similar terms we obtain, by turns,
and applying the relationships (1) - (8), from (9) - (11) after cancellation of similar terms we obtain, by turns,
![]() (13)
(13)
![]() (14)
(14)
where![]() . From (14) we have the equation of the type:
. From (14) we have the equation of the type:
![]() (15)
(15)
where![]() , and:
, and:
![]() (16)
(16)
![]() (17)
(17)
The Equation (15) is named as depressed cubic equation [32] , when perceived in context with the general cubic equation![]() . In contrast to the usual equation of the 3rd degree, where the coefficients
. In contrast to the usual equation of the 3rd degree, where the coefficients ![]() and
and ![]() are specific numbers?in our case the coefficients
are specific numbers?in our case the coefficients ![]() and
and ![]() in Equation (15) are functions of another variable?here: pH. The coefficients are real numbers, and
in Equation (15) are functions of another variable?here: pH. The coefficients are real numbers, and![]() ,
, ![]() , at any pH value.
, at any pH value.
In general, Equation (15) can have real and complex roots for![]() . To distinguish between them, we calculate the sign of the discriminant (see Appendix):
. To distinguish between them, we calculate the sign of the discriminant (see Appendix):
![]() (18)
(18)
where
![]() (19)
(19)
If![]() , one root is real, and two ones are complex conjugates. The real root is as follows (see Appendix):
, one root is real, and two ones are complex conjugates. The real root is as follows (see Appendix):
![]() (20)
(20)
If Δ = 0, all roots are real and at least two are equal. If![]() , we define:
, we define:
![]() (21)
(21)
where![]() . Then the real positive
. Then the real positive ![]() solution of Equation (15) has the form:
solution of Equation (15) has the form:
![]() (22)
(22)
and from Equation (1) we have![]() .
.
The sign of Δ (Equation (18)) can vary with change of the pH value; it also depends on the values of physicochemical constants involved in it. Three possible cases are exemplified by physicochemical systems considered in this paper, namely:
1) ![]() within the pH-range in the vicinity of a pH0 value;
within the pH-range in the vicinity of a pH0 value;
2) ![]() within the vicinity of the pH0 value;
within the vicinity of the pH0 value;
3) ![]() changes its sign in the vicinity of the pH0 value.
changes its sign in the vicinity of the pH0 value.
The pH0 value results from the following calculation procedure. The ![]() values (Equation (20) or Equation (22)) obtained at different pH are inserted into the transformed charge balance (11):
values (Equation (20) or Equation (22)) obtained at different pH are inserted into the transformed charge balance (11):
![]() (23)
(23)
Zeroing the function (23), gives ![]() at pH = pH0. For this pH0 value, considered as pH of the solution obtained after introducing the precipitate MeL2 into pure water, one can calculate concentrations of different species, e.g., the species involved in expression for solubility
at pH = pH0. For this pH0 value, considered as pH of the solution obtained after introducing the precipitate MeL2 into pure water, one can calculate concentrations of different species, e.g., the species involved in expression for solubility![]() , Equation (12).
, Equation (12).
4. Solubility of Oxinates in Aqueous Media
In the calculations, the pH interval 6.0 - 8.5 was taken as the basis for calculation of pH0 value for the systems presented in Table 1. In this interval, the sign for ![]() was taken first for considerations. For
was taken first for considerations. For![]() ,
, ![]() was calculated from Equation (20), whereas for
was calculated from Equation (20), whereas for![]() , the formula (22) was applied. The pH = pH0 values were calculated with accuracy < 0.01 pH units, see Figure 2. At the pH = pH0 values, concentrations of individual species and then solubilities
, the formula (22) was applied. The pH = pH0 values were calculated with accuracy < 0.01 pH units, see Figure 2. At the pH = pH0 values, concentrations of individual species and then solubilities ![]() (Equation (12)) were calculated, see Table 2.
(Equation (12)) were calculated, see Table 2.
Note that in all instances, where MeL2 is the equilibrium solid phase, we have:
![]() (24)
(24)
i.e., it is a constant component in Equation (12), independent on pH values. For comparison, when applying the formula [31] :
![]() (25)
(25)
![]()
Figure 2. Fragments of the z vs. pH relationships (Equation (10)) for indicated precipitates MeL2 in the vicinity of![]() .
.
obtained on the basis of simplified assumptions:![]() ,
, ![]() , we obtain
, we obtain ![]() (see Table 3); note that
(see Table 3); note that![]() , see Equation (12). Thus, the uselessness of formula (25) for calculation of the solubility
, see Equation (12). Thus, the uselessness of formula (25) for calculation of the solubility ![]() of MeL2 is demonstrated. All known species involved with this system and the related equilibrium constants (1) - (6) are included in the balances (9) - (11). It is an example of the two-phase system where minimal solubility of a precipitate is limited by the concentration of soluble species of the same formula (here: MeL2 and MeL2).
of MeL2 is demonstrated. All known species involved with this system and the related equilibrium constants (1) - (6) are included in the balances (9) - (11). It is an example of the two-phase system where minimal solubility of a precipitate is limited by the concentration of soluble species of the same formula (here: MeL2 and MeL2).
5. Solubility of Oxinates in Liquid-Liquid Extraction Systems
Let us consider a two-phase liquid-liquid extraction system, composed of two practically immiscible solvents, e.g. H2O + CHCl3. The CHCl3 is not soluble in water (mutual solubility is less than 0.01%) [33] ; then the presence of the organic phase does not affect the values of equilibrium constants in aqueous phases; the balances involve the division of neutral (uncharged) organic components, ![]() and
and![]() , between the two phases. Interfacial distribution of these components is ruled by the partition constants:
, between the two phases. Interfacial distribution of these components is ruled by the partition constants: ![]() and
and![]() , expressed by the formulas:
, expressed by the formulas:
![]() (26)
(26)
where subscript ![]() denotes organic phase, and notation with lack of subscript (in parentheses) refers to aqueous phase.
denotes organic phase, and notation with lack of subscript (in parentheses) refers to aqueous phase.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() denote volumes [mL] of organic and aqueous phases, and
denote volumes [mL] of organic and aqueous phases, and![]() . The numbers of milimoles of
. The numbers of milimoles of ![]() and
and ![]() are as follows:
are as follows:
![]() (27)
(27)
![]() (28)
(28)
![]()
Table 3. Comparison of s (Equation (12)) and ![]() (Equation (25)) values.
(Equation (25)) values.
At![]() , from (27) and (28), after cancellations, we obtain by turns,
, from (27) and (28), after cancellations, we obtain by turns,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Then we get the equation![]() , where
, where![]() , and:
, and:
![]() (29)
(29)
![]() (30)
(30)
6. Final Comments
For resolution of cubic equations, the Excel spreadsheets were used; the coefficients of these equations were the functions of pH; resolution of the related equation was the primary step for zeroing the transformed charge balance,![]() . Two options applicable for resolution of these equations were distinguished. Other examples with cubic equations involved were presented in [34] - [36] . For more complex systems, e.g. ones involved with struvite, MgNH4PO4 [37] , or dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2 [38] , the iterative computer programs are required [39] .
. Two options applicable for resolution of these equations were distinguished. Other examples with cubic equations involved were presented in [34] - [36] . For more complex systems, e.g. ones involved with struvite, MgNH4PO4 [37] , or dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2 [38] , the iterative computer programs are required [39] .
Appendix
Derivation of Equation (15) at ![]() (Equation (18)).
(Equation (18)).
Setting
![]() (A1)
(A1)
in Equation (15), after further rearrangements we get
![]() (A2)
(A2)
At![]() , i.e.,
, i.e.,
![]() (A3)
(A3)
from (A2) and (A3) we have ![]() and then
and then
![]() (A4)
(A4)
Setting
![]() (A5)
(A5)
in (A3) we have
![]() (A6)
(A6)
![]() (A7)
(A7)
where
![]() (A8)
(A8)
As we see (Equation (A7)), the formulae for ![]() and
and ![]() are identical. Note that
are identical. Note that
![]() (A9)
(A9)
Then, on the basis of Equations (A7) and (A9),
![]()
i.e., ![]() and
and ![]() are interchangeable in Equation (A1). Then from Equation (A1) we have Equation (20). Note that
are interchangeable in Equation (A1). Then from Equation (A1) we have Equation (20). Note that ![]() and
and![]() , at any pH-value, see Equation (19) and comments for Equations (16) and (17).
, at any pH-value, see Equation (19) and comments for Equations (16) and (17).
NOTES
*Corresponding author.