Quantification of the distribution of blood flow pressure with postures ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Hemodynamic parameters, especially the blood pressure, vary with postures. Sudden postural change will bring out the large fluctuation of the blood pressure, which may lead to hypotension, syncope, even falls [1]. These symptoms are the manifestations of orthostatic intolerance (OI). OI does harm not only to the astronauts in the aerospace field [2], also to the patients in the clinical medicine [3].
In recent years many researches have focused on the blood pressure variation with the postural change. There are two main types of methods. One is test method [4-7], and the other is modeling and simulation one [2,8-10]. Olufsen et al. [2] performed the study of blood pressure and blood flow variation during the postural change from sitting to standing by presenting a mathematical model. This model utilized 11 compartments to predict the dynamic changes of the arterial blood pressure and some other haemodynamic parameters. It included two types of control mechanisms: autonomic regulation and autoregulation. The effects of gravity on venous blood pooling during the postural change was described by a physiologybased submodel, one dimensional model. Heusden et al. [9] developed a baroreflex model combined with a lumped-parameter model of the circulation. Gravity was introduced into the model as the formulation of the hydrostatic column. During the first 5 s after head-up tilt (HUT) and tilt back, the direct effect of gravity on the pulmonary circulation influenced the blood pressure (BP) response, and the response to HUT was mainly determined by the response of the venous system. JYA Foo [10] introduced a mathematical model using only a few empirical parameters and the measured lower limb vascular path length. The aim was to monitor blood pressure with different postures by estimating the pulse transit time, which was inversely correlated to the BP change. The reliability of the model was assessed by measuring the value of the pulse transit time at the sitting and supine positions at discrete intervals from 23 healthy children.
The previous studies did not quantitatively analyze the DBFP in so many different postures because gravity, as a scalar, was introduced into these studies.
The present study was focused on the simulation of the pressure contour, extreme pressure and its position to quantify the DBFP in the inner carotid artery with single definite posture. Gravity was taken into consideration as a vector. It is worthy to study this issue so as to assist the researchers in postural/hemodynamical model simplification and in identifying the effective range to defense for astronauts or patients clinically.
2. METHODS
The postural model for the single vessel has been developed in a previous paper [11]. As a body force in this model, gravity was first introduced as a term to reflect the postural change. Therefore, it could realistically reflect the effect of gravity.
Equation of continuity
 (1)
(1)
Equation of motion for fluid
 (2)
(2)
where  represents the inertial force,
represents the inertial force, 
represents the surface force,  represents the body force, which was identified as the key term to reflect the postural change,
represents the body force, which was identified as the key term to reflect the postural change,  is the blood density,
is the blood density,  is the body force per unit mass of blood,
is the body force per unit mass of blood,  is the second order stress tensor of the blood pressure,
is the second order stress tensor of the blood pressure, 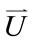 is the blood velocity, and A is the cross-sectional area of the vessel.
is the blood velocity, and A is the cross-sectional area of the vessel.
In the large systemic artery such as the inner carotid artery, the blood flow can be assumed to be homogeneous, incompressible, viscous and Newtonian fluid [12,13]. The vascular wall is assumed to be rigid [14,15]. The dimension of the vessel [16] and the property of the blood [13,17] are listed in Table 1, where L is the length of the vessel, D1 and D2 are the inlet and outlet diameters of the vessel, respectively, ρ is the blood density, and μ is the blood viscosity. The boundary conditions used in this postural model were as follows. The inlet and outlet pressures were set to constants, respectively, and the pressure difference was 199.98 Pa (1.5 mmHg). The rigid wall condition was given.
A commercial finite element software package ADINA (ADINA R & D, Inc., Watertown, MA, USA) was used as the tool for simulation in this study. The software has been used by many researchers such as Tang et al. [18,19] and Kaazempur-Mofrad et al. [20] for various biological systems in the last several years. 3D fluid element was meshed. Mesh analysis was performed until the relative error between solutions from two consecutive meshes was less than 1%. Numerical computational model-FE model is shown in Figure 1.
In this study, thirteen different postures were considered. The schematic diagram of the different postures is shown in Figure 2. The 0˚ posture corresponded to supine one, 90˚ to upright, –90˚ to upside-down, the postures between –90˚ and 0˚ were denoted as the negative tilting ones, and the postures between 0˚ and 90˚, as the positive tilting ones. More postures were included in this study than before. Therefore, more comprehensive hemo-

Table 1. Geometric and material parameters of the single vessel.

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of different postures of a single vessel.
dynamic responses could be obtained in different postures.
3. RESULTS
The contour charts of the blood flow pressure in different postures in the inner carotid artery are shown in Figure 3 with G ≠ 0. The DBFP varied with the posture and gravity. As G ≠ 0, at upright (90˚) and upside-down (–90˚) postures, the DBFP took on 2D axisymmetrical one, and
3D asymmetrical distribution at any other posture (0˚, ±15˚, ±30˚, ±45˚, ±60˚, ±75˚). From –90˚ to 0˚, the asymmetrical degree of the DBFP increased step by step, and gradually decreased from 0˚ to +90˚. As G = 0, the 2D axisymmetrical distribution existed at all single definite postures. This indicates that modeling a single vessel as a 2D model is reasonable in space.
The extreme values of the blood flow pressure in different postures are shown in Figure 4. Both the maximum pressure (Pmax, corresponding to SBP) and the minimum pressure (Pmin, to DBP) increased with increasing postures from –90˚ to +90˚ as G ≠ 0. The increase rate of Pmax was significantly different from that of Pmin. To Pmax, the increase rate from –90˚ to 0˚ was smaller than that from 0˚ to 90˚. To Pmin, vice versa. Comparing the increase rate between Pmax and Pmin, the one of Pmin was larger than that of Pmax from –90˚ to 0˚. From 0˚ to 90˚, however, vice versa. With G = 0, Pmax and Pmin kept invariant although the posture varied.
Figure 5 shows that the position obviously differs between Pmax and Pmin with postures as G ≠ 0. At the negative tilting postures, Pmin moved from the 2/3 length