Effect of Soil Physico-Chemical Properties and Plant Type on Bacterial Diversity in Semi-Arid Parts in Central Sudan. Part I: Omdurman North Region ()

Subject Areas: Microbiology
1. Introduction
Microorganisms play essential roles in organic matter decomposition, nutrient cycling, and plant productivity. Soil microbes mainly bacteria and fungi are concerned with all the biochemical processes which occur in soils and they play a vital role in maintaining soil productivity. It has been generally hypothesized that reduction in soil microbial diversity will result in reduction in the functional capability of soil [1] .
Soil physico-chemical characteristics influence the composition of the soil microbial community, their activity and the level of microbial mass [2] . It is important to determine optimum diversities of soil microbial populations of vegetation systems for their suitable management. In order to maximize the beneficial effects of microbial activity, there is a need for greater understanding of factors influencing microbial communities and their activities. A number of secondary metabolite compounds, representing a variety of chemical structure isolated from the various microorganisms, may provide interesting leads for further industrial considerations.
The objectives of this study were: 1) to obtain a better understanding of the correlations between microbial population and physic-chemical properties of different soil types in the study area; 2) to study how plant type and soil type affect the microbial diversity and abundance; 3) to explain the differences between the tested habitats.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description and Soil Sampling
Soils were collected from two different sub-regions (Karary and Khor Omer sub-regions (21˚50'19.34"N 89˚26'33.84"E) in the Khartoum State, in arid/semi-arid parts in Central Sudan. Soil samples were collected from 0 - 5 cm and 5 - 15 cm depths and kept in plastic bag. After collection, soil samples were brought to the laboratory and separated into two sub samples; one for bacteriological analysis that was kept in a refrigerator and the other one for the analysis of soil physico-chemical properties. Soil sampling was done in December, 2011.
2.2. Bacteriological Analysis
Nutrient agar medium was used for the enumeration of bacteria present in soil samples [3] . The pH was adjusted before addition of agar and sterilization. Serial dilution plate technique was used for the isolation of microorganism. One gram soil sample was diluted (1:100) with 100 ml distilled water in a sterile conical flask and shaken well. One ml of this suspension was transferred to 9 ml of sterile water for tenfold (1:10) dilution and by following serial dilution further diluted up to 105 times. Plating in duplicate plates was made for each diluted sample. One ml of each of the diluted sample was taken in a sterilized petri dish by pipette. Then, molten agar medium was poured and mixed thoroughly by rotating the petri dish, first in one direction and then in the opposite direction. After setting the medium, the plates were inverted and incubated at 37˚C for 48 h in an incubatorthen, the plates having well discrete colonies were selected for counting. The selected plates were placed on a colony counter (Digital colony counter, DC-8OSK1000086, Kayagaki, Japan) to count the number of colonies.
2.3. Tests
Motility test was determined according to Cruickshank et al., 1975 [4] . Catalase test Oxidation-Fermentation test (O/F), Oxidase test, Sugar fermentation test, Voges-Proskauer test, Nitrate reduction test, Indole production test, Urease test, Citrate utilization were determined according to Barrow and Feltham 1993 [5] . Casein hydrolysis was determined by method described by Williams and Cross, 1971 [6] . Starch hydrolysis was performed according to Collins et al., 1995 [7] . Total a viable count of bacteria was determined [8] .
2.4. Isolation of Streptomyces
Isolation of Streptomyces was performed by the soil dilution plate technique [9] . In this technique; 1 g of each soil sample was taken in 9 ml of sterilized distilled water in pre-sterilized test tube. Serial aqueous dilutions (10−2 - 10−7) were prepared by transferring 1 ml of the soil suspension into 9 ml of sterilized distilled water in sterilized test tubes. Different aqueous dilutions (10−4 - 10−6) of the soil suspensions were applied separately into sterilized Petri-dishes and 20 ml of Starch-Casein Agar salt medium, SCKNO3, was added, mixed thoroughly and the plates were incubated at 28˚C for 7 - 14 days. SCKNO3 medium was prepared by dissolving 10 g soluble starch, 2 g dipotassium hydrogen ortho-phosphate, 2 g potassium nitrate, 2 g sodium chloride, 4 g casein, 0.05 g hydrated magnesium sulphate, 0.1 g calcium carbonate; 0.01 g hydrated ferric sulphate, 15 g agar in one liter of distilled water. The medium was sterilized by autoclaving at 121˚C for 15 minutes. Colonies characteristic of Streptomycetaceae (rough, chalky, powdery and with earth odour) that appeared on the incubated plates were selected, repeatedly sub-cultured for purification and stored at 4˚C onto slants of SCKNO3 medium until further examinations.
2.5. Analysis of Soil Physico-Chemical Properties
The pH of the soil was measured in a soil water suspension (1:2, soil:water). The electrical conductivity (EC) analysis was measured in the saturated extract. Na+ and K+ were determined photometrically. The exchangeable cations (Ca++ and Mg++) were determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS, Perkin-Elmer, 047-1705. Saturated percentage (SP) were also determined [10] . Organic carbon content of the soil was determined byWakely and Black method (cited by Moghimi et al., [11] ). Total nitrogen (%) was determined by Kjeldahl method following extraction from 2 g soil with conc. H2SO4. The particle size analysis was carried out by the Pipette method (cited by Moghimi et al., 2013 [11] ).
Once the percentage of sand, silt, and clay is measured, the soil may be assigned a textural class using the table of textural soil types (cited by Subrahmanyam and Sambamurty [12] ).
2.6. Bacterial Diversity Measures
1) Shannon-Weiner Biodiversity Index:
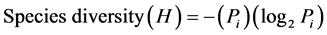
where: P = the proportion of all individuals in the sample which belongs the species i.
2) Simpson Index: 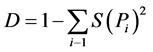
where: D is the index number; S = the total number of species; P = the proportion of all individuals in the sample which belongs to species i (cited by Subrahmanyam and Sambamurty [12] ).
3. Results and Discussion
Eight organisms were isolated from collected soil samples; Actinomyces spp., Streptomyces spp., Bacilluslentus, Bacillus badius, Bacillus pantothenticus, Bacillus mycoides, Bacillus alvei and Bacillus sphericus. Actinomycesspp. have highest frequency in the two studied sub-regions and next are Streptomyces spp.
Microbial diversity indices can function as bio-indicator to show community stability and describing the ecological dynamic of community (and analysis of soil microbial diversity is important to evaluate the importance of perturbations in soil systems). It can also provide an early indication of changes in soil long before it can be measured by changes in organic matter [13] [14] .
The diversity of soil microorganisms of the study habitat is presented in Table 1. The Shannon-Weiner
![]()
Table 1. Diversity of microorganisms in the study area.
diversity Index value for Khor Omer sub-region (1.71261). The Simpson Index value for Khor Omer sub-region was (2.5).
An increasing interest has emerged with respect to the importance of microbial diversity in soil habitats. The extent of the diversity of microorganisms in soil is seen to be critical to the maintenance of soil health and quality, as a wide range of microorganisms is involved in important soil functions. The two main diverse of soil microbial community structure i.e. plant type and soil type.
The composition of the soil microbial community can be altered by plant species, plant diversity, vegetation type, soil type, seasonal variability in water, temperature and availability of organic substances [15] .
The results concerning soil physical and chemical characteristics (pH, EC, SP, soluble cations: Na, K, Ca, Mg and anion P, organic carbon, total nitrogen and soil texture in twodifferent studied sub-regions are presented in Table 2. The correlation effects between the soil parameters on bacterial count were studied Table 3. The diversity of soil microorganisms of the study habitat is presented in Table 3.
The soil of Karary sub-region is predominantly loam. The pH of soil samples ranged from 7.40 to 7.70. The EC values varied from 0.70 - 2.57 mmohs/cm. The total nitrogen was in range 0.035 - 0.065. Organic carbon range between 0.46% and 0.64%. C:N ratio range between 7:1 and 14:1. The SP ranged from 23.4% - 38.9%. Sodium contents ranges between 1.268 and 3.721 Meq/L. As for K it varies between 0.142 and 0.379 Meq/L. Calcium contents was found to vary between 4.0 - 19 Meq/L. Magnesium contents was found to vary between 2.0 and 10.0 Meq/L. P contents ranged between 3.2888 and 3.636 ppm (Table 2). Total bacterial count was positively correlated with EC (r = 0.3868), clay (r = 0.1412), sand (r = 0.5891) and K (r = 0.0265) and negatively correlated with pH, silt, SP, Na, P, Ca, Mg, N and OC (Table 3).
The soil of Khor Omer sub-region is predominantly loam. The pH of soil samples ranged from 7.21 to 7.85. The EC values varied from 0.50 - 0.90 mmohs/cm. The total nitrogen was in range 0.028 - 0.168. Organic carbon range between 0.16% and 0.68%. C:N ratio range between 3:1 and 23:1. The SP ranged from 23.9% - 37.7%. Sodium contents ranges between 2.047 and 31.4 Meq/L. As for K it varies between 0.109 and 0.247 Meq/L. Calcium contents was found to vary between 4.0 - 27 Meq/L. Magnesium contents was found to vary between 3.0 and 20 Meq/L. P contents ranged between 3.288 and 3.3636 ppm (Table 2). Total bacterial count was positively correlated with EC (r = 0.3973), clay (r = 0.1966), silt (r = 0.2116), Ca (r = 0.6733), Mg (r = 0.586) and OC (r = 0.2368) and negatively correlated with pH, sand, SP, Na, K, P and N (Table 3).
The results showed that the sandy clay loam, sandy loam, and loam showed the highest bacterial populations (Table 2 and Table 4). Previous studies showed that soil types influence the structure of microbial community, especially bacterial population among soils of different textures [16] [17] . Possible explanation for the higher number of bacteria in soil with caly contents was documented by Carney and Matson 2005 [18] , who mentioned that fine textured soils support more microbial biomass than coarse textured soils. The distribution of microorganisms in various soil textures might be related to soil moisture and nutrient contents as explained by Heritage et al., 2003 [19] , who stated that sandy soils could not retain water very well and drain very quickly. In contrast, clay loam preserves water and hold nutrients for longer period.
From the studied region (the two sub-regions) collected soils, four different textural soil classes (clay loam, sandy clay loam, loam, sandy loam) were detected (Table 2). Data of soil pH values showed some differences among different soil textures. In Khor Omer sub-region, the lowest value (pH = 7.21) was recorded in clay loam and the highest one (pH = 7.85) in loam (Table 2). The highest value of soil organic carbon contents were recorded in the texture soils loam whereas the lowest contents were in clay loam and sandy clay loam. These differences were documented previously by Silver et al., [20] who found that soil texture plays a key role in below ground C storage in soil ecosystems and strongly influences nutrient availability and retention, particularly in fine textural soils. Matus et al., [21] , observed that soil organic carbon tends to be associated with the fine fraction of soils and it was significantly three times in clay-rich soils than coarse soils. Fine texture soil shows more stable aggregates, which in turn may act as a media of greater amount of organic carbon and total nitrogen contents [22] .
The higher bacterial counts observed in Acacia tortilis ssp. spirocarpa rhizosphere in the soil of Karary sub-region and in Panicum turgidum rhizospherein the soil of Khor Omer sub-region. This could be to better availability of nutrients and environmental conditions, which favored their growth.
Bacterial count tend to decrease with increase in soil depth. Decrease in the bacterial counts with increasing soil depth could be related to the organic carbon content of the soil as nutrients are declining with the increase in soil depth. The higher bacterial counts at the surface layer might be due to the presence of litters, twigs, herbs
![]()
Table 2.Some soil physico-chemical properties of different samples from Omdurman North region.
![]()
Table 3. Correlation coefficients of the physico-chemical properties with the viable bacterial count (cfu・g−1 soil) in Karary and Khor Omer sub-regions.
![]()
![]()
Table 4. Total bacterial count of different soil samples from omdurman north region.
and tree canopy which render a moist environment in the soil and favor high microbial activity and hence high microbial populations [23] .
The huge diversity characterizing the Bacillus species at the taxonomic level, is also noticeable for their metabolic features. Development of microbial bioactive compounds technology it depends basically of four steps: isolation and selection of strains with higher activity, fermentation process optimization, application of an appropriate method to cell separation and development of formulations. These bacteria are able to produce a wide range of secondary metabolites with very different natures and structures and displaying broad spectra of activities. The metabolites including antibiotics, pigments, toxins, growth promoters (animals and plants) pheromones, enzyme inhibitors and other bioactive compounds [24] . In general, these metabolites serve as: 1) competitive weapons used against other bacteria, fungi, plants insects; 2) metal transporting agents; 3) symbiosis effectors between microbes and plants, insects; 4) sexual hormones; and 5) as differentiation factors [25] .
Secondary metabolite compounds expands the potential industrial importance of the genus Bacillus [26] . Bacteria from the genus Bacillus are among the entomopathogenic microorganisms most commonly used as biocontrol agents. Among them Bacillus sphaericusis used in vector contol programs of endemic diseases such as dengue, malaria and filariasis. Because they are spore-former bacteria and produce toxins highly specific to target insects are better suited to industrial production and field application. The study of mosquitocidal bacteria from wild resources may provide interesting leads for further industrial considerations.
4. Conclusion
There is a need for greater understanding of physical, chemical, biochemical and biological factors influencing abundance and diversity on microbial habitats. Our results show that field data interpretation of soils properties is difficult, particularly when several factors exerting an influence on microbial communities are involved.
NOTES

*Corresponding author.