Received 17 November 2015; accepted 14 December 2015; published 17 December 2015


1. Introduction
Highway flexible pavements constitute more than 90% of the national pavements of most of the countries. It is produced from hot mix asphalt (which is a mixture of well graded aggregate combined with a bituminous binder to provide a stable structure for passing vehicles), and continually faces different failure problems. These problems may be sourced from hot mix asphalt or from underlying layers either base, subbase or subgrade failures. Hot mix asphalt concrete would have a long life even under heavy traffic, severe conditions like moisture; high and low temperature, when designed and laid properly.
It is believed that moisture or water is one of the greatest factors which will have an inverse effect on the performance of hot mix asphalt. It manifests itself as a reduction in overall strength and it will increase rutting potential, decrease fatigue life and accelerate stripping potential of the mixture.
Working on solving these problems related to flexible pavement up to now at macro and micro level did not provide satisfaction to engineers and road administers and also did not give the idea of solving the problems from the root, so the need of solving problems at nano levels became necessary. Since bitumen itself has a great influence on the characteristics of mixture and because bitumen in most refineries is produced in the secondary process, or it can be said it is by-product. It will not lead the bitumen to compete with fuel and other products, and from here it obtains better performing asphalt in petroleum refining process. When the product does not meet the pavement structure requirements, modification has been used as one of the best and most attractive alternatives for improving asphalt and asphalt concrete properties.
Nanotechnology is the creation of new materials, devices, and systems at the molecular level associated with atomic and molecular interactions strongly influencing macroscopic material properties [1] . In recent years, nanotechnology has gradually been incorporated into the field of modified asphalt [2] . In the last decade or so, nanotechnology emerged as the potential solution to greatly enhance the performance and durability of construction materials. Nanomaterials are defined as materials with at least one dimension that falls in the length scale of 1 - 100 nm. Due to the small size and high surface area, the property of nanomaterials is very different from normal size materials [3] . To demonstrate many of the prospective applications, researchers have conducted a series of positive and effective efforts dealing with the preparation of modified asphalt to demonstrate the mechanism of modification and the resultant improvement in performance [2] . Some researches showed that fatigue cracking, rutting and moisture resistance of asphalt binders and mixtures are improved with the addition of nanomaterials [3] . Ghafarpoor [4] carried out comparative rheological tests on bitumen and mechanical tests on asphalt mixtures containing unmodified and nanoclay modified bitumen. The results have shown that nanoclay could improve properties of bitumen such as stiffness and aging resistance and decrease phase angle in compared to unmodified asphalt and asphalt mixtures properties such as stability, resilient modulus, and indirect tensile strength.
Moghadas et al. [5] performed a test to investigate the performance characteristic of asphalt mixture by using zycosoil as an anti-strip agent with limestone and granite aggregate. It was seen that the fatigue life increased because of formation of a hydrophobic nanolayer on aggregate, and aggregate coverage with zycosoil increased the amount of filler and decreased the void content in asphalt mixture. It is also observed that the zycosoil modified aggregate surface caused a better compaction of asphalt mixture [6] . Rohith [7] investigated the stability and Marshall Property of hot mix asphalt specimens produced at 155˚C, 130˚C and 115˚C and compared with warm mix asphalt specimens containing zycotherm nanomaterial produced at 130˚C and 115˚C. It was concluded that the stability and Marshall Property were improved with the addition of 0.1% of zycotherm nanomaterial. Another study conducted by Yao et al. [8] on asphalt and asphalt mixtures by using nanosilica at 4% and 6% by weight of bitumen estimated the characteristics of nanomodified asphalt binder and mixture. Different tests (such as Rotational Viscosity RV, Dynamic Shear Rheometer DSR, Bending Beam Rheometer BBR, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy FTIR, Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM, Asphalt Pavement Analyzer APA, Dynamic Modulus DM and flow number FN) were performed to analyze the change in chemical bonding and rheological properties of modified asphalt binder and also the performance characteristic of asphalt mixture after modification. It was shown that the anti-aging property, rutting and fatigue cracking performance of nanosilica modified asphalt binders are enhanced and the addition of nanosilica in the control asphalt mixture significantly improves the dynamic modulus, flow number and rutting resistance of asphalt mixtures. The nanotechnology, with the usage of asphalt and asphalt mixture properties, has the following benefits [9] :
Ø Improve the storage stability in polymer modified asphalt;
Ø Increase the resistance to UV aging;
Ø Reduce the moisture susceptibility under water, snow and deicers;
Ø Improve the properties of asphalt mixtures at low temperature;
Ø Improve the durability of asphalt pavements;
Ø Save energy and cost;
Ø Decrease maintenance requirements.
The aim of the study is to investigate the effects of zycotherm nanomaterial in two different modification methods with two types of aggregate (limestone and basalt) after asphalt concrete (asphalt mixtures) produced with them. The effectiveness of using zycotherm nanomaterial on:
² Volumetric properties of hot mix asphalt such as Marshal stability, flow, air void, void in mineral aggregate and voids filled with asphalt in a mixture;
² Resistance of compacted asphalt mixture to moisture induced damage;
² Mixing zycotherm with bitumen binder to investigate (DSR) dynamic shear rheometer test parameter and (BBR) bending beam rheometer test parameter to estimate rutting and fatigue life;
² Stripping value of aggregate when aggregate mixed with zycotherm treated bitumen.
2. Material Preparation
2.1. Aggregate Preparation
Two types of aggregate (basalt and limestone) are used in this study for asphalt mixture production to investigate the zycotherm nanomaterial effect on their behaviour and to compare them with respect to their usage with this material. The aggregates were brought from two different sources in Turkey and their physical properties of both basalt and limestone are given in Table 1.
The aggregate grading used for both aggregate types is shown in Table 2.
![]()
Table 1. Basalt and limestone test results.
![]()
Table 2. Aggregate gradation used for both aggregate types.
2.2. Bitumen Binder
Bitumen used for this study was taken from Tupras-Izmit refinery. One grade of bitumen is used for investigation purposes and it was 50/70 penetration grade bitumen. The physical properties such as penetration, softening point, specific gravity and other properties are given below in Table 3.
2.3. Zycotherm Additive
Zycotherm silane is an additive used for modifying hot mix asphalt concrete and offers a wide spectrum of benefits, due to the unique properties of Alkyl Siloxane Nano layer produced [10] .
The typical specification of zycotherm is listed herein under:
Active ingredient: organosilane compound
Solid content: 65% ± 2%
Appearance: clear pale yellow liquid
Flash point: >80˚C
Solubility in water: soluble
2.4. Design Procedure
The modification of bitumen and bituminous mixture is done by the following steps:
1+ Zycotherm is added directly to bitumen by weight of bitumen at three 3 different percentages (0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) while the bitumen is heated at 135C.
2+ Zycotherm is diluted in water at (1:400) range and the aggregate is marinated with this dilution by weight of aggregate at three 3 different percentages (1%, 3% and 5%). Then the aggregate is left to dry after this marinating and it is heated at 160˚C - 170˚C for HMA sample production.
After modification, the samples were prepared for testing with both modification systems.
2.5. Experimental Work
A series of tests were conducted on bitumen samples that contain zycotherm with 3 different percentages to determine the performance characteristics of hot mix asphalt produced with both aggregate types with both systems of modifications.
Bitumen tests were (penetration, softening point and Superpave binder tests as RTFOT, PAV, DSR and BBR tests). HMA tests were (Marshall Test, indirect tensile strength test and retained stability test). The determination of the stripping value of aggregate was also conducted.
Penetration and softening point are two tests as per AASHTO T49, ASTM D5 for penetration and AASHTO T53, ASTM D36 for softening point test. These were conducted with 3 percentages of zycotherm addition (0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5% with control samples) to determine the modification influence on penetration and also on the softening character of bitumen.
Super pave binder tests were established to address the contribution of asphalt binder to rutting, low temperature cracking and fatigue cracking (AASHTO M320). Modified samples were prepared with zycotherm at 3 different percentages (0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) and tested with super pave binder tests such as RTFOT, PAVT, DSRT, and BBRT as follows:
![]()
Table 3. Physical properties of original bitumen used.
2.5.1. Marshall Test
It is conducted to determine the optimum bitumen content for both aggregate types and also to determine the strength and flow parameter change with the addition of zycotherm with both of the addition system. Optimum bitumen content is determined with preparing 3 sets of HMA samples prepared at 3.5%, 4%, 4.5%, 5% and 5.5% bitumen content and compacting samples with 75 blow with standard hammer. The optimum content is determined at 4% air void. For limestone, the optimum content is found to be 4.67% and for basalt is 5.03%.
2.5.2. Indirect Tensile Strength Test
It is used for determining the structural properties of a bituminous mixture. It is also aimed to evaluate the moisture susceptibility of bituminous mixtures, and this can be shown with the reduction in the loss of indirect tensile strength after conditioning samples in water at 60˚C.
Indirect tensile strength is calculated with this formula [11] :
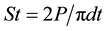 (1)
(1)
whereas St: is the indirect tensile strength, P: is the maximum applied load, d: is the specimen diameter, t: is the specimen height.
The test is performed by preparing the marshal samples of 100 mm diameter and 63.5 mm height, at optimum bitumen content and compacting each side of the specimen with (50 blows for limestone and 60 blows for basalt) to get an air void content of 7% ± 1%.
2.5.3. Retained Stability Index
It is performed by preparing the standard marshal samples (of 100 mm diameter and 63.5 mm height) at optimum bitumen content by applying 75 blows on each side for both limestone and basalt aggregates. Two specimens are selected as a control and tested without moisture conditioning and the two more are selected to be conditioned by keeping them in water bath maintained at 60˚C for 24 hours. The marshal stability and flow of compacted specimens is determined after conditioning them with standard marshal testing machine. The retained stability is expressed as the stability after conditioning samples in water maintained at 60˚C for 24 hours divided by the stability under standard conditions multiplied by 100 according to [11] and [12] .
2.5.4. Stripping Value of Aggregate
IS:6241-1971 states that the stripping value of aggregate is the ratio of uncovered area observed visually to the total area of aggregates, it is expressed as percent.
Control sample and samples with 0.1% zycotherm were added to bitumen prepared with both type of aggregates (limestone and basalt). It is observed that the addition of zycotherm greatly influence the stripping resistance of both aggregate types in comparison to control samples.
3. Result and Discussion
In this paper, rolling thin film oven test, dynamic shear rheometer, bending beam rheometer, pressure aging vessel, penetration test and boiling test were performed on original samples of bitumen binders (samples without zycotherm) and samples contain (0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) zycotherm. The results for penetration and softening points are presented in this section.
3.1. Penetration Test Results
0% = 61.0 mm
0.1% = 55.2 mm
0.3% = 54.35 mm
0.5% = 53.2 mm
3.2. Softening Point Test Results
0% = 47.8˚C
0.1% = 48˚C
0.3% = 51.6˚C
0.5% = 52.3˚C
As it can be seen from the above results of penetration and softening point that there is no great change between the original and modified binder with zycotherm at different percentages. All the values meet the requirements specified by (kgm-ankara-2012).
For the results of other tests DSR and BBR, it is observed that G*/sinδ, G* sinδ, stiffness and m-value are increased for all zycotherm modified bitumen binders and at 0.5% zycotherm addition all these values give the highest values as shown below in Table 4 and Table 5.
It is obvious from the above results that the performance grading is not affected significantly with the addition of zycotherm at different percentages While the increase in analogous G*/sinδ means an increase in resistance to rutting or permanent deformation. An increase in G* sinδ value gives an indication of the improvement from resistance to fatigue cracking (as stated by Superpave asphalt specification). Since an improvement in stiffness and m-value exists, this improvement at 0.5% is the highest so it can be said that the low temperature cracking also will be controlled.
3.3. Indirect Tensile Strength Test Results
As the first trial, the control samples were prepared for both aggregate types and tested. These samples contained 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5% by weight of bitumen and 1%, 3% and 5% by weight of aggregate.
![]()
Table 4. Detail of (RTFOT, DSR, PAV and BBR) of original asphalt binder.
![]()
Table 5. Detail of (RTFOT, DSR, PAV and BBR) of original asphalt binder +0.3% zycotherm.
It could be seen from the results that there is an agreement over the increase in tensile strength ratio (TSR) after modification of mixtures produced with both aggregate types and with both modification systems (either directly applying to aggregate or adding to bitumen). In addition, it could be observed that the behaviour of different aggregates is different with both systems.
Tensile strength ratio (TSR) for mixtures made with limestone aggregate with the addition of (0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, 1%, 3% and 5%) zycotherm and zycotherm dilution is (84.32%, 79.29%, 86.46%, 70.65%, 84.41% and 83.27%) respectively.
The (TSR) for mixtures made with basalt aggregate with the addition of (0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, 1%, 3% and 5%) zycotherm and zycotherm dilution is (99.52%, 100.85%, 91.26%, 87.48%, 90.43% and 88.9%) respectively.
3.4. Retained Stability Index
In order to determine the marshal properties and retained stability index property of samples produced with zycotherm and zycotherm dilution, four samples from each zycotherm percentage with control samples for both types of aggregates were prepared. Since zycotherm is chemically changed the surface properties of aggregate, for which it will change chemically the water loving aggregate surface (hydrophilic property) to a water repellent (hydrophobic property). Thus,, from checking the ratio of conditioned stability to unconditioned stability (retained stability index) of the samples, it can be inferred that for all samples that contain zycotherm with both addition system for both limestone and basalt in comparison to control samples is increased.
It is seen that the Limestone retained stability index for control samples was (65.62%), with the addition of 0.1% zycotherm it is increased to 77.84%. Then, further increase of zycotherm to 0.3% it would be increased to 81.48%, and further increase to 0.5% the retained stability is increased to 95.38%. That means with the addition of 0.5% zycotherm, the retained stability (which is a measure of moisture resistance of the mixture), is increased approximately 35%. However, when the modification system is changed and the limestone aggregate is marinated with zycotherm dilution, the retained stability increase changes as for 1% zycotherm dilution and becomes 83.61% and for 3% further increase it becomes 96.31% However, further increasing up to 5%, the retained stability decreased to 90.79%. As shown in Figure 1. From the results, it is noticed that for limestone aggregate an agreement over the increase in retained stability index exists with both modification systems. That means the moisture resistance of asphalt mixtures produced with limestone aggregate modified with zycotherm with both systems is increased.
For samples made with basalt aggregate, the retained stability index for control samples was (67.57%), with the addition of 0.1% zycotherm it is increased to 70.67%., Further increase of zycotherm to 0.3%, it would increase the retained stability index to 89.72%, and further increase to 0.5%, the retained stability is decreased to 82.07%.
However, when the modification system is changed and the basalt aggregate is marinated with zycotherm dilution, the retained stability increase changes as for 1% zycotherm dilution it would become 97.41% and for 3% further increase, it becomes 99.75%. However, further increasing up to 5%, the retained stability decreases to 89.93%. It is noticed from the results that for basalt aggregate an agreement over the increase in retained stability index exists with both modification systems. That means the moisture resistance of asphalt mixtures produced with basalt aggregate modified with zycotherm with both systems is increased.
4. Conclusions
This study was conducted to determine the optimum amount and potential applicability of zycotherm in asphalt and asphalt concrete mixtures with two different systems: directly applying to bitumen, diluting and applying to aggregate in order to address the solution of potential failure problems in flexible pavements. The study is carried out by conducting experimental tests on bitumen and bituminous mixtures. From the test results, it is found that the zycotherm effect on different types of aggregate and with different modification systems is different: Limestone modified with zycotherm is added to bitumen at (0%, 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) by weight of bitumen and TSR and RSI are determined. For both tests at 0.5% zycotherm addition, the highest improvement is obtained. TSR is increased from 71.73% to 86.46% and RSI is increased from 65.62% to 95.38. However, when the modification system is changed and the Limestone is modified with zycotherm dilution, which is applied to aggregate at (0%, 1%, 3% and 5%) by weight of aggregate, TSR and RSI are also determined. It is observed that 3% zycotherm addition gave the highest value. TSR is increased from 71.73% to 84.41% and RSI is increased from 65.62% to 96.31%. When the basalt aggregate is modified with zycotherm and added to bitumen at (0%, 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) by weight of bitumen, the tensile strength ratio and the retained stability index are determined. For both tests, 0.3% zycotherm addition gave the highest value. TSR is increased from 85.67% to 100.85% and RSI is increased from 67.57% to 89.72%. However, when the modification system is changed and the basalt are modified with zycotherm dilution, which is applied to aggregate at (0%, 1%, 3% and 5%) by weight of aggregate, tensile strength ratio and retained stability index are determined. It is inferred that 3% zycotherm addition gave the highest value. TSR is increased from 85.67% to 90.43% and RSI is increased from 67.57% to 99.75%. From the above test results, it is obtained that the addition of zycotherm causes the tensile strength and
![]()
Figure 1. RSI of mixtures made with limestone aggregate after zycotherm dilution added to aggregate.
stability reduction after conditioning samples to be decreased to minimum.
Zycotherm is effective on basalt aggregate much more than on limestone, because it chemically changes the surface property of basalt and a hydrophobic nanolayer is produced. All the above findings support that using zycotherm to a great extent decreases the moisture susceptibility and increases the hot mix asphalt pavement service life. Asphalt binder performance tests performed on samples contain zycotherm (0%, 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.5%) by weight of bitumen. The test results show that no significant effect on properties of asphalt binder is produced to change the grade of asphalt. However, the results of DSR and BBR tests show that improvements in (G*/sinδ, G* sinδ , stiffness and m-value) especially after addition of 0.5% zycotherm, greatly increase the resistance to rutting and resistance to fatigue, and low temperature cracking prohibition is obtained.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the scientific research fund of Faith University under the project number p50101301 y (3190). The authors are very grateful to the university council to provide this support.