Emulating a System Dynamics Model with Agent-Based Models: A Methodological Case Study in Simulation of Diabetes Progression ()
1. Introduction
Systems science methodologies have received increased attention in recent years in response to elevated pressures to more accurately represent complexity and actual behaviors of large-scale systems such as healthcare delivery markets. However, in the current state-of-practice of system science modeling, there exist few examples of methodologies to translate models from one type to another. Moreover, there is little guidance regarding the amount of complexity required to emulate the actual system being modeled. This situation limits the ability to approach systems science models of complex systems simultaneously from the perspectives of multiple methodologies. Our objectives here are two-fold. First, we focus on the translational barrier separating system dynamics and agent-based simulation (ABS) models. We demonstrate by example a methodology to develop a parsimonious ABS model of diabetes mellitus type 2 disease progression (ABSDM2). We show how basic elements of a validated system dynamics (SD) model of diabetes type 2 (SDDM2) can be transferred into the ABS domain in order to mimic the elementary dynamics of a health system in multi-agent space. Our baseline ABSDM2 model is referred to here as the uncoupled model because stocks and flows are assigned levels and rates according to static parameters unrelated to age, obesity and health behavior dynamics. The second objective is to formulate a principled approach to systematically enlarge model complexity to better account for available health system data, while at the same time constraining the growth of complexity of the models beyond their ability to adequately explain more data. We accomplish this objective by carefully defining a simple hierarchy of parameterized models of increasing depth or detail. The entire model system consists of three child model types, each of which have a different nesting relationship to a parent uncoupled model, as illustrated in Figure 4. Each child model inherits the basic structure of the uncoupled model, but adds model detail in different ways by focusing on different factors. Estimating parameter values for the four models was accomplished with the assistance of a global search procedure (simulated annealing).
In evaluating parameterized ABSDM2 models, we not only measure the extent to which they reproduce target behaviors as stocks and flows, but also examine the time histories of specific state variables in terms of their interpretability in light of observed trends in health status and health behavior in the SDDM2 model. These state variables (i.e., elderliness, obesity prevalence, healthy behaviors) are not quantitatively fitted to data measuring similar quantities; however, they do play a role in determining diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2) progression. We pursue these objectives in the healthcare domain by examining the progression of DM2 in the general US adult population from 1980 to 2000. The next sections describe SD and ABS methodologies in some detail followed by a detailed description of the ABSDM2 model. After describing the methodology used to fit model hierarchy parameters to the outputs of the SDDM2 model, results are presented and explained with an emphasis on determining which factors are required to adequately reproduce the outputs of the SDDM2 model. The methodology is further illustrated with a counterfactual example. We conclude with a few general observations.
2. Systems Science Methodologies
The US adult healthcare system is an example of a large-scale complex system that is amenable to systems science approaches to analytics. Systems science methods “are designed to address complexity, that is, change over time, nonlinear relationships, bidirectional relationships (feedback loops), time-delayed effects, and emergent properties of the system―phenomena that are observed at the system level but cannot usually be causally linked to a single individual component of the system.” [1] . Two important members of this family of methodologies are agent-based simulation and system dynamics modeling.
A fundamental dynamic in healthcare delivery systems is the behavioral interaction between patient and physician (provider). This basic interaction can itself be further analyzed for various dynamic behaviors, predispositions, intervention choices, etc. A generalization beyond the patient-provider interaction has diverse additional components as described in Figure 1. The figure, itself a more detailed elaboration of the workflow defined in [2] , shows behaviors, influences, and other elements of a healthcare “knowledge core” which can be called out as modules and parameters in an individual simulation model. Each interaction between agents has its own characteristics, and modeled actions to be taken. Because many aspects of the healthcare system are not known in detail, the ABS must be constructed modularly in order to allow testing many different component models. This is done quite naturally by defining a family of embedded models that proceeds from the conceptually simple to more complex models.
A SD model is an aggregated description of a complex dynamic system consisting of a causal structure un-
![]()
Figure 1. High-level modeling flow of healthcare delivery.
dergirded by “an interlocking set of differential and algebraic equations” [3] . Causal factors, other influences and inputs are integrated and refined by the analyst in the form of stock and flow diagrams in order to capture the essential causal structure of the system. The flows between stocks not only denote direction of causality, but outline complex feedback loops of the system. There are many software packages available to implement SD models.
The SD approach to modeling healthcare for chronic conditions is already fairly mature (e.g., see [4] -[6] ). Behaviorally significant states of diseases such as DM2 have previously been represented at a resolution appropriate for a SD model; here we build upon this work, focusing our efforts on behavioral and cognitive issues, albeit rudimentary, which have received scant attention in previous attempts to model DM2 and other chronic conditions. To demonstrate some of the advantages of policy simulation using agent-based simulation, we translated a well-known SD model of DM2 [7] into an agent-based model, and augmented the basic model with behavioral and cognitive components.
An ABS model is a “collection of autonomous decision-making entities called agents. Each agent individually assesses its situation and makes decisions on the basis of a set of rules” [8] . Instead of presenting an aggregated view of a complex system, it disaggregates the system, populating it with individual entities from the bottom-up, thereby allowing the system-level behavior to emerge from interactions among individual agents. The ABS approach benefits greatly from adopting principles of object (agent)-oriented design.
The ABS paradigm can provide a general framework to simulate healthcare systems by adhering to a more disciplined approach to ABS design methodology. Our ABS model for healthcare delivery systems relies on increasingly recognized ABS strengths [9] [10] including: 1) ability to capture and measure emergent behavior of complex systems (bottom-up instead of top-down); 2) fewer required distributional assumptions regarding times to transition between states; 3) allowance for local interactions between individual agents―non-homogeneous effects of diffusions; and 4) ability to handle health disparities and geographic variation at unprecedented resolution. It also incorporates most features on the recently formulated SIMULATE checklist, including systems, interactions, understanding, loops, agents, time and emergence [11] .
It is increasingly being recognized that SD and ABS approaches are complementary methodologies sharing a great deal of mutual ground in the kinds of systems for which they provide suitable modeling architectures [12] . SDM and ABS modeling domains converge if systems being modeled contain large numbers of active objects with at least limited agency, internal or private states, and discrete external behavior. In examining correspondences between SD and ABS approaches, one set of investigators concluded that ABS “is more general and powerful because it enables to capture more complex structures and dynamics,” and that it “provides for construction of models in the absence of the knowledge about the global interdependencies.” [13] . This is consistent with our position because we use a smaller number of structures to capture mean and covariance structures in time series health data. For example, it has been recently demonstrated how the often-used Bass diffusion model in aggregate SD models can be mimicked by a simple disaggregated ABS model where the locus of diffusion is at the individual level, and that can easily be generalized to more complex types of diffusion in order to capture multiple social influence states, heterogeneity and social structure [14] .
3. Agent-Based Simulation Implementation Approach
We elected to adopt modern software engineering best practices and methodologies that are grounded in mathematical systems theory to develop an ABS model that is robust, scalable and modular. Accordingly, we selected the Discrete Event System Specification (DEVS) formalism, itself a simulation framework derived from systems theory that defines a system as a mathematical object and provides strong guarantees for reproducibility and model verification [15] -[17] . Although DEVS has been implemented primarily as a discrete event simulation engine, it is general enough to be cast as an agent-based orientation. We used a Java implementation of the “adevs” framework to develop the models introduced in this paper1.
Many existing agent-based simulation environments are founded on an underlying discrete time model as an approximation of continuous time, e.g., events and agent updates occur at equal-step discrete time intervals (e.g., the positive integers). The risk in adopting the discrete time approach is that it can trigger systematically inaccurate behaviors, diverging from the “correct” solution as the resolution of an ABS model is decreased [18] . Furthermore, there is little formal guidance concerning appropriate fixed time steps for a discrete time model in a given problem space. In order to avoid the possibility of divergent behavior we designed our ABS models such that events are scheduled in a continuous time frame, often resorting to random draws from continuous distributions such as the exponential distribution to define a time advance for scheduling a change of state. We expect that discrete event scheduling in continuous time may be particularly critical for handling diffusion of innovations or beliefs through social networks, which may diverge considerably if the fixed time step is too long. Additionally, true discrete event updating allows for asymmetric updating of agent profiles to be implemented naturally, thus avoiding scheduling issues arising from simultaneous updates of multiple (or all) agents. Although it is perfectly legal for agents to update simultaneously in discrete simulation time, logically they must update according to a strict sequence. Determining a proper update sequence is an open problem in discrete simulation. Random update orders are sometimes used to avoid systematic bias, but they are still vulnerable to introduction of additional uncertainty into simulation execution.
4. ABS Model of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
We investigate systems science methods in order to illuminate the fine-grained dynamics of public healthcare systems. Two leading methodologies in this space are SD and ABS [19] . We build upon our research in translating a simple workforce model from an SD formalism to an ABS model [18] . First, in order to study similarities and differences between ABS and SD in the healthcare domain, we developed a basic ABS model of diabetes using an agent-oriented DEVS framework in order to reproduce the outputs of the SDDM2 model described in [7] . We selected this particular diabetes SD model because its acceptance within the healthcare simulation community and extensive validation with historical time series data. In our initial ABSDM2 there is only one agent class―the individual or diabetes patient. The model is designed in such a manner as to allow additional agent classes, e.g., primary providers, secondary providers, hospitals and payers, to be added at a later time. However, in order to address current objectives, a single agent class is sufficient.
4.1. Model Structure
The SDDM2 model incorporates seven stocks or diabetes states: normoglycemic, undiagnosed prediabetes, diagnosed prediabetes, undiagnosed uncomplicated diabetes, diagnosed uncomplicated diabetes, undiagnosed complicated diabetes, and diagnosed complicated diabetes. The distinction between undiagnosed and diagnosed states is important because health behavior presumably can be affected by diagnosis. A total of eighteen flow rates govern the dynamics of the model, including the possibility of transiting to death from any stock. Most state transitions are progressive, but there is the possibility of recovery from prediabetes. Stocks and flow rates are depicted in Figure 2 from [7] . An unpublished report by the same authors [20] contains a more detailed description of the input data to the SDDM2 model; this data was used to calibrate our ABSDM2 models.
In order to ingest stock and flow information into our ABSDM2 model, we abandoned the “tanks with liquid” metaphor from SD theory, disaggregating each stock into a population of discrete individuals, agents or patients, each with an internal state indicating their degree of DM2 [13] . The idea here is to substitute agent states for stocks. Instead of estimating continuous flow rates at global levels of abstraction, time delays for individual agents are drawn from probability distributions in order to determine when agents transition from one state (stock) to another. Mean delay time in ABS models is analogous to flow rate in SD modeling. Although any continuous distribution could be used to model delay time, for simplicity we selected the exponential distribution.
Three other important state variables were introduced into our ABSDM2 model hierarchy: obesity (true or false), healthy behaviors (true or false) and elderly (true or false). Taking all combinations of these variables, every patient agent was initialized into one of eight possible obese/behavior/elderly states. We defined several transitions between the four compositional obesity/health-behavior states as shown in Figure 3. The obesity/health-behavior state transition model is unique to the ABSDM2 modeling system and is not represented in the original SDDM2 model. The state names from left to right are healthy/not-obese, not-healthy/not-obese, not-healthy/obese, and healthy/obese. Since only a single transition may be scheduled for future enactment, if more than one is possible, the transition time associated with the lowest random draw is selected. For example, the next transition from not healthy/not obese (~H~O) is min (t2, t3). Since asynchronous updating was imple-
![]()
Figure 2. Stock and flow diagram for diabetes mellitus type 2 model (modified from [7] ).
![]()
Figure 3. Obesity-health behavior state transition model with formulas for expected transition times.
mented in the ABSDM2 model, random state transition times are used instead of state transition probabilities executed at constant time intervals. Furthermore, state variables can dynamically influence state transition times, i.e., disease state and behavior are coupled. Most significantly, these states are allowed to affect the disease condition trajectory; for example, sudden onset of obesity or crossing the elderly threshold can retroactively speed up the transition time for disease progression, just as adoption of healthy behaviors can slow disease progression midstream. An HO state change leads to a call of the disease state method where a revised transition time is computed. If the re-calculated transition time has already been exceeded, then disease state change will occur at the current time tick.
Figure 3 confirms that expected times to transition between H and ~H depend critically on the individual agent intent to perform healthy behaviors. Obesity transitions are merely lag functions. Actual time transitions are random draws from exponential distributions that utilize fitted model parameters β1, β2, δ1 and δ2. In addition, the state transition model requires two conditional probabilities for initialization: the probability that an individual engages in healthy behaviors given they are obese, and the probability that an individual engages in healthy behaviors given they are not obese. The initial obesity fraction of the adult population is given in [20] . Consequently, the obesity-health behavior state transition model possesses six adjustable parameters.
There exists little guidance with respect to nominal computational models for intent formation and change in the agent-based simulation literature. Accordingly, we selected a parsimonious approach in keeping with our model development effort as a whole by defaulting to a linear model. The intent to engage in healthy behaviors in our model hierarchy is derived from a simplified implementation of the Theory of Planned Behavior, a popular qualitative account of intent formation. Intentis calculated using a linear weighted combination of the strength of a randomly selected inherent individual attitude with respect to healthy behaviors (0 ≤ A ≤ 1), a randomly selected individual social influence parameter (0 ≤ α ≤ 1) and the perceived normative behavior of one’s peer group. This latter factor gauges the consistency of social influence on the individual. Every agent is embedded in a random social network where each agent begins a simulation run with a constant number of contacts. The contact list grows and shrinks randomly as agents die and new agents are added to the network. Contacts for new agents are determined by random draw. Social influence develops from the strength of belief that a preponderance of contacts in an agent’s social network is engaging in healthy lifestyle behaviors. The number of contacts for each agent is a user-selected variable in the model; the default number is set at five. Agents notify their contacts immediately whenever they experience a change of healthy behavior status, but agents only assess behavior norms in their contact list periodically―an exponentially distributed variable with a mean of 0.25 years. In the current version of the model, social influence due to perceived norms (0 ≤ S ≤ 1) is simply the proportion of contacts engaging in healthy behaviors. Behavioral intent (0 ≤ I ≤ 1) is then equal to
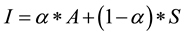 , (1)
, (1)
where (1 − α) is positive individual susceptibility to social influence. Independent influences on diabetes state are simply combined multiplicatively to calculate the mean value of the actual transition time μijk from state i to state j in transition mode k as
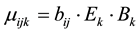 , (2)
, (2)
where the bij are eighteen (minus one degree of freedom)baseline mean transition times as depicted in the stock and flow diagram in Figure 2. Multiplicative factors for elderliness (Ek) and obesity (Bk) are given by
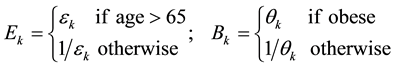 (3)
(3)
and εk, θk > 0 are model parameters that must be estimated from data. They proportionally increment or decrement by a constant factor adjustments to exponentially-distributed mean transition times in order to accommodate obesity and elderliness. Equivalently, these parameters arithmetically add or subtract adjustments to log mean transition times. Our motivation for proportional adjustment was to first try the simplest available method to implement the model. Elderliness and obesity factors are subscripted by k which denotes an element belonging to the set of transition modes M = {onset, progression, recovery, death}. Following the convention in [20] , the threshold for transition to elderly was set at age 65. Actual transition times are stochastic variables, the values of which are determined by random draws from an exponential distribution where the mean value is equal to the mean baseline transition time. For example, the actual time to transition from undiagnosed prediabetes to normoglycemia is an exponential random draw where the mean value is baseline recovery time X elderly recovery factor X obesity recovery factor. Adjustment factors Ek, Bk in excess of unity increase time to transition, whereas a value less than unity decreases time to transition. In the full agent-based model a total of 17 adjustable parameters are baselines for actual transition times, eight parameters specify adjustments for elderliness and obesity, and another six parameters are required to calculate the six obese/behavior state transition times and probabilities in Figure 3.
The SDDM2 model is actually quite detailed, containing multiple exogenous influences to the model in the form of 40 constant inputs and eleven complete time series inputs obtained from real data. These counts omit costs and unhealthy day calculations which were not replicated in our models. Some of these inputs represent details of diabetes care not included in our models, such as healthcare access, diabetes testing fractions, managed care fractions, and ability to adopt healthy lifestyles or self-monitor. Note that some of these quantities are difficult to estimate from external data sources because they measure internal cognitive states, e.g., ability to adopt healthy lifestyles. The constant and time series inputs account for 40 + 11 × 20 = 260 fixed parameters in the SDDM2 model. By way of contrast, the only time series inputs in our models were new adult rate and transition time for diagnosed pre-diabetes switching on at the 15th year. The new adult rate was represented as a piecewise linearized time series from 1980 to 2000. Constant inputs to our models included initial stock levels, and initial obese, healthy behavior and elderly proportions. Instead of using a large number of inputs to capture model dynamics, we sought to reproduce outputs of the SDDM2 model by adjusting a smaller number (31 in the full agent-based model) of adjustable parameters to minimize the discrepancy between our model outputs and the SDDM2 outputs.
4.2. Initial Age Distributions
Elderliness (age > 65) of agents is an important determinant of diabetes state transition rates in the SDDM2 model. In order to determine when an agent crosses the elderly threshold, the agent class needs to keep track of its age from the beginning of a simulation run. We sought to fix the initial ages of agents in the seven stocks by random draws from a continuous distribution. We first attempted to fit the data to a lognormal age distribution, but a two-parameter Weibull provided much better fit to the grouped age data from the US census. Table 1 summarizes intermediate calculations and final values for the Weibull parameters for each stock. Age group proportions were first estimated for each stock using data from the online-only appendix Table A1 in [21] . These estimates are for 1988 to 1994; more precisely, they represent the probability of each stock given an age group. After retrieving base rates for the age groups from 1980 US census data and the initial probabilities for each stock from [22] , Bayes theorem was used to compute conditional probabilities for each age group. A normalization step was required to ensure that all probabilities summed to unity. Finally, grouped age data was fit to the Weibull distribution in order to obtain smooth distributions for initial age. The scale and shape parameters are shown here in the far-right column of Table 1.
4.3. Implementation in DEVS Framework
The agent model comprises five classes to separate clusters of agent characteristics and behaviors. The model diagram in Figure 4 shows inputs, outputs and wiring of the basic objects in the base model. Diabetes state management (movement between stocks) occurs in the Diabetes object, and the current obesity health behavior state (Figure 3) is managed from ObeseBehav. Other classes were developed to maintain specific functions: 1) the Observer collects critical time series output data and writes these data to a file; 2) Age notifies agents when they become elderly and when they are eligible to diagnose for pre-diabetes in 1995; and 3) the Poll object requests at exponentially-determined intervals (mean = 0.25 year) a new assessment of social norms prevalent in its social network from the agent. The assessment is performed by the ObeseBehav object. No communication occurs between Diabetes and ObeseBehav objects in the uncoupled (baseline) model, but behavioral models require the ObeseBehav object to transmit its state to the Diabetes object because state transition times depend on obesity state. Both these objects communicate their states to the Observer at annual intervals. The dark lines breaking the Agent borders (defined by the green dashed lines in Figure 4) communicate state information between agents in the same network in order to obtain updates on changing social norms about healthy behaviors. The agent network superstructure is denoted in the orange box, where agents share information with each other.
![]()
Table 1. Best weibull distribution fits to age groups by stock from US census data.
![]()
Figure 4. Base model diagram for agent-based simulation diabetes type 2 (ABSDM2).
4.4. Optimization of ABSDM2 Parameters
We optimized the values of (up to) 31 adjustable parameters for each agent-based model through application of a global optimization algorithm, simulated annealing [22] [23] while taking goodness of fit of simulation stock counts to SDDM2 model outputs at yearly intervals as the objective function. Annual stock counts were replicated as closely as possible by optimizing the adjustable parameter values over two phases of a simulated annealing procedure. During the initial optimization phase, a population of one-tenth the size of the test population was used to search for a neighborhood likely to contain a near-global minimum in the 31 adjustable parameter space. Since a single run of the model required on average approximately six seconds for the reduced population size, we completed 12,000 iterations for each model type from random initial values. Then, we used the parameter values from the best-fitting model from the restricted population to fine-tune the parameter values during the second optimization phase. The second phase used a full initial population size (0.1 percent of the US population) of 1628 agents (distributed among the seven stocks).
During both optimization phases simulation performance was based on the output of a single run. Since the model is stochastic, it would be most desirable to use a score based on the mean of a random sample of simulation runs. This procedure should reduce search time by achieving noise reduction in the model output. However, it was concluded that the amount of noise generated over a single 20 year simulation run did not justify increasing the wall clock time to complete the optimization runs by an order of magnitude or more.
The new adult entry rate was linearized into three segments using US census data from 1980 to 2000. New agents were generated at a constant rate of one agent per 0.046 days from 1980 to 1990 (2241 agents per year), 0.0412 from 1990 to 1995 (2428 agents per year), and 0.0403 (2479 agents per year) from 1995 to 2000.
4.5. ABSDM2 Model Hierarchy
The SDDM2 model is a large model that closely replicates historical DM2 outcomes data. However, the sheer magnitude of the number of inputs makes it difficult to determine which inputs are really necessary to produce a good fit to DM2 outcomes. It could be argued that large sections of the model are not really required to obtain a reasonably good fit. In developing an agent-based model system for DM2, we intended to systematically test the importance of various parameter types. With this goal in mind, a model hierarchy was created with the baseline (uncoupled) model at the root (Figure 5). The modeling system implemented the 31 adjustable parameters listed in the Appendix. The uncoupled model had seventeen adjustable parameters to replicate the stock and flow dynamics in Figure 2, but it was not connected to calculations for obesity and healthy behaviors. The three child models inherited the seventeen flow parameters from the uncoupled model. The elderly model required four adjustable parameters to modify flow dynamics factors for onset, recovery, progression and death due to aging. The behavior model also required estimates for four diabetes factors, and six parameters associated with the obesity-health behavior state transition model including four transition time parameters and two conditional probabilities. It would be possible to create a behavior + elderly model simply combining estimated parameters from the other three models, using polymorphic inheritance to fill in the values of the adjustable parameters. However,
![]()
Figure 5. Model hierarchy with three offspring from the uncoupled model. Solid arrows indicate parent/child relationship. Dashed arrows denote a conceptual hierarchical relationship but the absence of a parent/child relationship with formal inheritance properties.
this method would not permit elderly, obesity and healthy factors to interact with each other. Therefore, the behavior + elderly model required re-estimation of all fourteen new parameters introduced in the elderly and behavior models.
5. Simulation Results
The four ABSDM2 models were optimized to minimize the Chi-Square statistic using GenSA, an R package for generalized simulated annealing [24] . The Chi-Square test was selected as a goodness-of-fit measure instead of ordinary least squares to assign greater weight to low population stocks while somewhat relaxing penalties for proportional errors in high population stocks. The four optimized models were then executed and statistics collected for the 20-year simulated time intervals.
Chi-square goodness-of-fit scores were assessed to ascertain whether adding model parameters significantly improved goodness-of-fit. Results are summarized in Table 2. A total of 160 stock counts were observed over the 20 year run, but only 140 counts can statistically be considered freely-adjustable cells in the data matrix. The uncoupled model had degrees of freedom = (140 − 17) = 123, and the value of the test statistic is χ2(123) = 516.4, p < 0.0001. Therefore we can reject the null hypothesis that the uncoupled model explains the stock count data. In fact, all the models can be rejected under the null hypothesis that the model adequately explains the data. However, we tested to see if the elderly model significantly improves goodness-of-fit by setting the degrees of freedom equal to the six additional parameters estimated from the obtained stock counts, and taking the difference between Chi-Square statistics, i.e., χ2(6) = 516.4 − 496.2 = 20.2, p = 0.003. Similarly, for the behavioral model we have χ2(8) = 516.4 − 328.0 = 188.4, p < 0.0001, and the test statistic for the behavioral + elderly model is χ2(14) = 516.4 − 361.5 = 154.9, p < 0.0001. We therefore conclude that the elderly, behavior and behavior + elderly models each significantly improve the goodness-of-fit over the uncoupled model, thereby providing successively better approximations to the SDDM model.
Another method of assessing model performance is to index the percent improvement in the Chi-Square statistic with respect to the parent model. Since the uncoupled model has no formal parent, we compare its Chi-Square statistic with a zeroth-order model that assumes constant stock levels set at mean values for each stock over the 20-year simulation run. The zeroth model has a Chi-Square statistic equal to 41,104.6; accordingly, the percent improvement over the uncoupled model is 98.7%, a dramatic gain. The percent improvement of the elderly model is small (3.9%), but behavior and behavior + elderly models both register moderately strong percentage improvements, 36.5% and 30% respectively. Again, we confirm that behavior-specific parameters add substantially to model performance, but elderly-specific parameters alone do not.
5.1. Predicted Stock Proportions and Counts
Overall, ABSDM2 models tracked stock proportions in the SDDM2 models quite well. Stock proportions for 20-year runs are plotted for all four models in Figures 6-13. Normoglycemic proportions declined steadily in the SDDM2 model as shown by the solid black line in Figure 6. For the first 15 years of simulation, all four models tracked that proportion reasonably well, although the behavior + elderly model tracked normal populations most closely. However, during the final five years of the run, all four models showed a reversal in the decline, posting real increases in normoglycemic proportions.
The apparent explanation for the increase in predicted normoglycemics is seen in the diagnosed pre-dia- betes stocks shown in Figure 7. The SDDM2 rate increase in this population is quite large compared to the four
![]()
Table 2. Optimization performance of four ABSDM2 models.
![]()
Figure 6. Normoglycemic stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 7. Diagnosed pre-diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
ABSDM2 models. In contrast, pre-diabetes populations escalated less abruptly in the ABSDM2 models immediately following introduction of pre-diabetes diagnosis. A large proportion of the initial diagnosed pre-diabetes populations in the ABSDM2 models likely reverted back to the normoglycemic population after successfully mounting a recovery, although it is difficult to know for certain.
The undiagnosed portion of the pre-diabetes population is shown in Figure 8. Again, the behavior + elderly model tracks this stock proportion better than the other ABSDM2 models. However, all models show a slight dip in this stock after the 15th year. It appears that both elevated diagnosis and recovery from pre-diabetes after 1995 contributed to the predicted rise in the normoglycemic proportion in ABSDM2 models.
Uncomplicated diabetes stock proportion predictions are presented in Figure 9 and Figure 10. Coupling of elderly and health behavior parameters in the behavior + elderly model somewhat elevated the undiagnosed uncomplicated diabetes stock proportion. The proportion of diagnosed uncomplicated diabetes cases steadily declined for all ABSDM2 models, whereas the SDDM2 proportion slowly increased over the 20-year period.
Diagnosis of uncomplicated diabetes in the ABSDM2 models lagged the SDDM2 model, possibly a down-
![]()
Figure 8. Undiagnosed pre-diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 9. Diagnosed uncomplicated diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 10. Undiagnosed uncomplicated diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
stream effect of fewer predicted pre-diabetes cases in the ABSDM2 models.
Due to low proportional representation in the general population, only counts for complicated diabetes stocks are shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12. ABSDM2 models displayed more variability over time compared to nearly flat counts observed in the undiagnosed complicated diabetes stocks from the SDDM2 model. In the diagnosed stock, the SDDM2 model registered slight increases in counts compared to the flat or slightly decreasing counts in the ABSDM2 models. This observation continues the trend of lagging diagnosis rates in the ABSDM2 models compared to the SDDM2 model.
Following the results given in Table 2, the time series plots reveal better qualitative fits for the coupled ABSDM2 models compared to the uncoupled ABSDM2 model. In addition, the behavior model provided better
qualitative matches to the SDDM2 model than the elderly model. However, there was also a consistent pattern of superior qualitative fit to these seven stocks in the behavior + elderly model compared to the behavior model. This observation seemingly contradicts the fact that the behavior model achieved a slightly better quantitative fit compared to the behavior + elderly model in terms of Chi-square goodness-of-fit. We find a possible explanation for this discrepancy in stock counts for the deceased portion of the agent population in Figure 13. Only the last five years of the simulation runs are displayed, but the figure shows the increasing separation among the stock counts for the four ABSDM2 models. Here we clearly see that death counts for the behavior + elderly
![]()
Figure 11. Undiagnosed complicated diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 12. Diagnosed complicated diabetes stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 13. Deceased stock proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 14. Predicted and actual elderly proportions from 1980 to 2000.
model increasingly lag behind the other ABSDM2 model death counts. These deviations can easily account for the slightly poorer fit to the SDDM2 model. As observed in Figure 13, behavior + elderly populations aged more slowly than the other three ABSDM2 models and the SDDM2 model, providing a possible explanation for relative lack-of-fit compared to other ABSDM2 models.
5.2. Population Proportions
Time histories for elderly, obese and healthy behavior sub-populations are shown in Figures 14-16. The reader should bear in mind that our global optimization procedure did not attempt to fit model outputs to the proportions of these outputs as they appeared in the SDDM2 model or in actual census data; nevertheless, the ability of these outputs to track SDDM2 model outputs provides a strong external validation test of the ability of the ABSDM2 models to accurately represent population characteristics for which they were not trained. Although the uncoupled model tracked the elderly population quite well, as expected, the elderly model performed best in terms of closely following actual population proportions for those years (Figure 14). Both quantitatively and qualitatively, the behavior + elderly model tracked obesity according to the SDDM2 model and the census better than the other three ABSDM2 models (Figure 15). Surprisingly, the behavior model posted the weakest performance in tracking actual obesity counts. Most importantly, it did not predict a rise in obesity prevalence. Finally, both behavior and behavior + elderly models distinguished themselves in terms of lower healthy behavior proportions relative to the uncoupled and elderly models, which were not tethered to any meaningful healthy behavior calculations (Figure 16). The healthy behavior trend lines for the two ABSDM2 models with a behavior component were both decreasing and fairly close to each other, although the behavior + elderly model registered a steeper decline in health behaviors from 41.5% in 1981 to 27.7% in 2000.
5.3. Counterfactual Example―The Effect of Increased Social Influence
A counterfactual simulation was performed with the behavior + elderly model in which social influence weight (1 − α) was increased from a uniform distribution over (0, 1) to a uniform distribution over (0.85, 0.95) for all agents. This represents a substantial increase in social susceptibility for most agents in the population. The counterfactual example was executed as a set of twelve independent runs of the behavior + elderly model with high social influence. In Figure 17 we see that greater social influence shifted the healthy behavior trend line
![]()
Figure 15. Predicted and actual obesity proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 16. Predicted and actual healthy behavior proportions from 1980 to 2000.
![]()
Figure 17. Effect of increasing social influence on elderly, obese and health behavior proportions. Confidence intervals were estimated from the twelve runs of the high social influence behavior + elderly model.
about 6% above baseline for the entire 20-year simulation run. Furthermore, obesity prevalence remained at baseline levels until the eighth year, and then gradually slowed, ending at about 4% below the baseline in the final year. Finally, elderly rates were mostly unaffected by changes in social influence, except for a slight increase during the last few years of the simulation. This result could be attributed to falling death rates among the elderly as obesity incidence decreased. This counterfactual example clearly predicts (relative) elevated healthy behaviors with a lagged relative decrease in actual obesity in response to increased susceptibility to social influence. Although these trends were expected, the eight-year lag between the start of healthy behavior change and the beginning of the effect on obesity rate is somewhat more difficult to predict.
6. Discussion
In general, the simulation results demonstrate how systematic refinements in an agent-based model can be incorporated to incrementally translate elements of an aggregate population simulation model into a disaggregated individual-level agent-based model in order to increase understanding regarding specific biological, cognitive, behavioral and social mechanisms that are thought to underlie disease and healthcare progression. The simplest uncoupled ABSDM2 model, although not perfect, mimicked the major trends of the SDDM2 model and did a fair job of replicating absolute stock counts representing the seven disease states of DM2. The addition of both behavioral and elderliness factors alone significantly increased the fit of the model to the stock count data, although their combined efficacy could not be demonstrated statistically.
Qualitatively speaking, all ABSDM2 models tracked the counts from most stocks quite well. In the last five years of the simulation, the normoglycemics population was somewhat overrepresented while both pre-diabetes populations were underrepresented. We suspect that this partially due to higher than expected recovery rates from the newly diagnosed pre-diabetes agents, starting in the 15th year. Diagnosed diabetes stocks slightly decreased according to the agent-based model outputs, whereas slight increases were registered in the SDDM2 model.
We should not conclude from the above discussion that system dynamics and agent-based modeling approaches are mutually exclusive. To the contrary, Ip [19] argues that the two approaches are complementary and can be used effectively together to study the same problem. System dynamics approaches to disease modeling are also converging on psychosocial and behavioral factors. For example, [25] introduced constructs representing the ability to socialize and engage in activities, patient participation in care, and cognitive reserve into their quality of life model for diabetes. Indeed, the present study can be situated in the overlap between system science methodology and statistical modeling, where the former is concerned with knowledge synthesis, and the latter with falsification of a null hypothesis [19] . We believe that an appropriate use of statistical modeling is to apply it during development of agent-based models of large-scale systems in order to right-size them for investigation of specific questions and counterfactuals. However, we did not develop an agent-based model from first principles, but instead endeavored to translate the major components from an established system dynamics model in order to foster direct comparison. The development of the SDDM2 model reflects a more data-centric approach in which data-rich inputs ensure a close match between the model and historical time series. In contrast, our more parsimonious approach limits data infusion into the model, thus allowing a minimum amount of model structure and data to approximate time series outputs of the SDDM2 model. The emphasis on systematic addition of data/structure places a premium value on model understanding at the expense of achieving greater predictive accuracy.
There exist substantial limitations to this simulation study. Perhaps the most obvious is the lack of a significant sample size during both the optimization phase and execution of production runs for the purpose of obtaining simulation results. Such a strategy is very desirable given the stochastic nature of the model, but real-time limitations restricted the employment of that strategy here. Future work should be devoted to shortening the clock time to complete a statistically meaningful set of simulation runs. Despite this limitation, the significance of this work as a demonstration of a systems science methodology in healthcare simulation is still evident.
Further details may be appended to the model hierarchy in order to investigate the contributions of additional factors to understanding the dynamics of a diabetes care system. One possibility is to include a feedback loop that not only accounts for the effects of healthy behaviors and obesity on DM2 progression, but potential influences of disease state on intentions to engage in healthy behaviors. One possible mechanism for feedback within the Theory of Planned Behavior framework is the weakening of an agent’s intention to maintain healthy behaviors when advanced progression of the diabetes state erodes their perceived behavioral control and outcome expectancies. Although this model enhancement goes beyond the confines of the SDDM2 model, the strategy of increasing model complexity in the psychosocial domain to account for census data is still sound. Further simulation modeling could also investigate direct effects of sex, race, socioeconomic status or geographic regions on intentions to engage in healthy behavior and their subsequent influences on obesity and DM2 progression.
Acknowledgements
Research sponsored by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program of Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), managed by UT-Battelle, LLC for the US Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725.This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC, under Contract DE-AC05- 00OR22725 with the US Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes.
This manuscript has been authored by UT-Battelle, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725 with the US Department of Energy. The United States Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a non-exclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for United States Government purposes. The Department of Energy will provide public access to these results of federally sponsored research in accordance with the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan).
Appendix
![]()
Table A. Final optimized parameter values for the four models in the ABSDM2 modeling system.
NOTES
1http://web.ornl.gov/~1qn/adevs/.