Development and Validation of a High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Method for Quantitative Analysis of Saxagliptin ()
1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex disease mainly caused by impaired beta cell function and insulin resistance [1] . It is the most common form of diabetes comprising of 90% to 95% of all diabetes cases [2] . Oral antidiabetic drugs, along with diet and exercise, can help to control T2DM-associated hyperglycemia in adults [3] . Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors are a class of oral antidiabetic agents which increase circulating concentrations of the incretin gastrointestinal hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. The incretins are rapidly released after meals and stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion. Glucagon-like peptide-1 also inhibits glucagon secretion, thereby attenuating postprandial glucose excursions. The DPP-4 inhibitors improve glycaemic control by blocking the rapid inactivation of incretins, mainly glucagon-like peptide-1 [4] . All the DPP-4 inhibitors are orally available and are rapidly absorbed. Within 5 min of administration, they exhibit significant inhibition of plasma DPP-4 activity [5] . Saxagliptin is an oral anti-hypoglycemic agent and it belongs to selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class [6] . It is chemically known as (1s,3s,5s)?2?[(2s)?2?amino?2?(3?hydroxy?1?adamantyl) acetyl]?2?azabicyclohexane?3?carbonitrile [7] . Saxagliptin has been shown to be beneficial in glucose management as well as in the achievement of glycated hemoglobin goals (HbA1c < 7%) [1] .
Several analytical methods have been developed for quantitative analysis of Saxagliptin in bulk and pharma- ceutical formulations like UV?spectrophotometric method [8] , ion-pairing spectrophotometric method [9] , Reverse Phase-High Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) method [10] , RP-HPLC with fluorescence detection method [11] , etc. Ultra performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method has been developed for quantification of Saxagliptin in rat plasma [12] . Liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for simultaneous analysis of Saxagliptin and its major metabolite [13] . However, so far there are no reports on High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic method for quantitative analysis of Saxagliptin in both active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and marketed tablet formulation. Hence the present study was focused for the development and validation of an efficient HPTLC method for the estimation of Saxagliptin.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Drugs
Saxagliptin (API) was obtained as a gift sample from Mylan laboratories Ltd. (Hyderabad, India). Onglyza (Saxagliptin-5 mg) tablets were purchased from Bristol-Myers Squibb (USA). Solvents like Chloroform and Methanol were purchased from SD fine chemicals Ltd. (Mumbai, India).
2.2. Equipment
It consists of an applicator of model LINOMAT-5 and a scanner (CAMAG, Switzerland) with UV detector. The data was monitored and processed using WINCAT software. The sample was loaded on to the TLC plates by Hamilton Rheodyne injector syringe of 100 µL (CAMAG) and the plate was developed in twin trough chamber (20 × 20).
2.3. Standard Solution Preparation
Standard stock solution was prepared by dissolving 10 mg of Saxagliptin in 100 mL of methanol to obtain a solution with final concentration, 100 µg/mL.
2.4. Sample Preparation
Ten tablets of ONGLYZA were weighed and finely powdered. An accurately weighed powder equivalent to 10 mg was taken to 100 mL volumetric flask and dissolved in 50 mL Methanol and finally volume was made up to the mark with the Methanol to obtain a concentration of 100 µg/mL. This solution was sonicated for 10 min and filtered. Filtration is done to remove the excipients and to avoid clogging of sample applicator syringe.
3. Development of a Method
For the optimization of an HPTLC method, several mobile phase compositions were tried as developing solvent systems, they are shown in Table 1.
4. Method Validation
The developed method was validated for various parameters like linearity, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantification (LOQ), accuracy, precision and robustness according to ICH guidelines.
![]()
Table 1. Optimization of mobile phase.
4.1. Linearity
Different concentration solutions of Saxagliptin like 400, 600, 800, 1000 and 1200 ng/spot were applied on the TLC plate from the standard stock solution. After the development the TLC plate was scanned under UV at 222 nm and the peaks were recorded using WINCATS software version 1.4.3. The calibration curve was obtained by plotting peak area vs. concentration, using linear regression model. According to ICH guidelines, an acceptance criterion of linearity for an analytical method is correlation coefficient should be not less than 0.998.
4.2. LOD and LOQ
The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) of Saxagliptin by the developed HPTLC method were calculated using the following formulae, respectively.
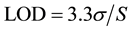
where σ is the standard deviation of the response and S is the slope of the calibration curve.
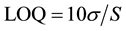
where σ is the standard deviation of the response and S is the slope of the calibration curve.
4.3. Accuracy
Accuracy is calculated as the percentage of recovery by the assay of known added amount of analyte in the sample, or as the difference between the mean and the accepted true value, together with the confidence intervals. As per ICH guidelines accuracy should be assessed using a minimum of nine determinations i.e., three replicates at three concentrations across the specified range of the procedure. Three different levels (50%, 100% and 150%) of standard solutions were added to a pre-analyzed sample and were analyzed for % recovery of Saxagliptin. Acceptance criterion is the mean % recovery should not be less than 98% and not more than 102%.
4.4. Precision
ICH guidelines recommend that repeatability should be assessed using a minimum of nine determinations covering the specified range of the procedure (i.e., three replicates of three concentrations) or using a minimum of six determinations at 100% of the test concentration. It can be determined by measuring repeatability, intermediate precision and reproducibility. Three different concentration solutions of standard Saxagliptin were applied to the TLC plate and the chromatograms were recorded. The precision of an analytical procedure is usually expressed as the variance, standard deviation or coefficient of variation of a series of measurements and the acceptance criterion is % RSD of the peak areas should not be more than 2.0%.
4.5. Robustness
The robustness of an analytical method is a measure of its capacity to remain unaffected by small but deliberate variations in method parameters and provides an indication of its reliability during normal usage. It was done by changing the mobile phase volume and development time while constantly maintaining the remaining parameters. The acceptance criterion is % RSD of the peak areas should not be more than 2.0%.
5. Stability Studies
To evaluate the stability indicating properties of the developed HPTLC method, forced degradation studies were carried out in accordance to the ICH guidelines and were performed by exposing drug solution to stress conditions like acidic (0.1 N HCl, 1 N HCl), basic (0.1 N NaOH, 1 N NaOH), peroxide (3% H2O2 v/v) and photo induced degradation. The resulting solutions were analyzed for analyte peak and unknown degradants generated by stress induced degradation.
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Optimization of HPTLC Method for Quantitative Analysis of Saxagliptin
After multiple trials an optimized mobile phase was developed for the HPTLC analysis of Saxagliptin. The standard and test samples were spotted in the form of bands of width 8 mm using a 100 µL syringe on precoated silica gel aluminum plate 60 F254 (10 × 10 cm) using a CAMAG Linomat-5 sample applicator. The development was carried out in 20 × 20 cm twin trough glass chamber using Methanol:Chloroform (6:4 v/v) as mobile phase. The saturation time for mobile phase was 20 min. The development time was 20 to 30 minutes. After the development, the TLC plates were air dried and were densitometrically scanned using CAMAG thin layer chromatographic scanner at 222 nm. The chromatograms were recorded using WINCATS software version 1.4.3. The chromatogram of Saxagliptin is shown in Figure 1. This method has shown good resolution of Saxagliptin in both standard and test samples and the Rf value was found to be 0.50 ± 0.02.
6.2. Assay of Saxagliptin in Formulation
The chromatograms of standard as well as test Saxagliptin solutions were recorded and the percentage of drug content was calculated. The percentage assay for Saxagliptin was found to be 98.90%, which lies within the limits mentioned by ICH (98% - 120%). Hence the developed method can be routinely used for the estimation of Saxagliptin in the tablet formulations. The chromatogram of Saxagliptin test solution (sample solution) was shown in Figure 2.
6.3. Method Validation
6.3.1. Linearity
Calibration curve of Saxagliptin was plotted using peak area vs. concentration and was shown in Figure 3.
![]()
Figure 1. Chromatogram of standard Saxagliptin (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Figure 2. Chromatogram of Saxagliptin test solution (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Figure 3. Calibration curve of Saxagliptin.
Linearity was found in the concentration range of 400 - 1200 ng/spot, which was shown by a 3D display in Figure 4. Saxagliptin correlation coefficient value was found to be 0.998. As per ICH guidelines, it lies in acceptable limit and hence the method was found to be linear.
6.3.2. LOD and LOQ
The lowest possible concentration of Saxagliptin that can be detected and quantified by the present method was found to be 7.96 ng/spot and 26.54 ng/spot, respectively. The low values of LOD and LOQ indicates that the method can be used for detection and quantification of Saxagliptin over a very wide range of concentrations in formulations.
![]()
Figure 4. 3D display of Saxagliptin linearity.
6.3.3. Accuracy
Mean percentage recovery values at three different concentrations of Saxagliptin were calculated and the results were shown in Table 2. According to ICH guidelines, the % recovery of Saxagliptin at each level was within the limits of 98% to 102%. Hence, the method was proved to be accurate.
6.3.4. Precision
Intra-day and Inter-day precision data of Saxagliptin was shown in Table 3. % RSD values of Saxagliptin in both intra- and inter-day precision studies were found to be less than 2, which were within the limits mentioned by ICH guidelines. Hence the method was found to be precise.
6.3.5. Robustness
Robustness was done by changing the mobile phase volume and saturation time of development chamber. The data is shown in Table 4.
7. Stability Studies
The standard drug was subjected to acid, base (alkali), oxidation and photolytic degradation studies and their chromatograms were shown in Figures 5-8. Results of Saxagliptin degradation studies are shown in Table 5. These results revealed the suitability of the method to study stability of Saxagliptin in APIs and pharmaceutical dosage forms.
8. Conclusion
The present study was aimed for the development and validation of HPTLC method for the estimation of Saxagliptin in bulk as well as pharmaceutical dosage forms. After performing various trials, a sensitive method was developed and was validated according to ICH guidelines. The method was proved to be sensitive, specific, linear, accurate, precise and robust for the quantitative analysis of Saxagliptin in active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and pharmaceutical dosage forms. It does not suffer from interference from excipients present in
![]()
Figure 5. Chromatogram of acid degraded Saxagliptin (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Table 2. Accuracy study of Saxagliptin.
![]()
Table 3. Intra- and inter-day precision study of Saxagliptin.
![]()
Figure 6. Chromatogram of alkali degraded Saxagliptin (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Figure 7. Chromatogram of oxidation degraded Saxagliptin (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Table 4. Robustness data of Saxagliptin.
![]()
Figure 8. Chromatogram of photolytic degraded Saxagliptin (800 ng/spot).
![]()
Table 5. Saxagliptin degradation studies.
the pharmaceutical dosage forms as well as from the degradants of Saxagliptin resulted from stress-induced degradation studies. Hence this method can be conveniently adopted for quality control analysis and stability assays of Saxagliptin in APIs and pharmaceutical dosage forms.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Mylan laboratories Ltd. (Hyderabad, India) for the kind gift of Saxagliptin Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API).
NOTES
*Corresponding author.