Usefulness of an Anisotropic Diffusion Method in Cerebral CT Perfusion Study Using Multi-Detector Row CT ()
1. Introduction
Cerebral perfusion studies using X-ray computed tomography (CT) have become increasingly important for management and/or prognostic prediction of stroke patients [1] . CT perfusion studies can be performed with the dynamic acquisition of sequential CT sections in cine mode during the intravenous administration of iodinated contrast material using a standard spiral CT scanner or multi-detector row CT (MDCT) [2] [3] . However, radiation exposure during CT perfusion study is a serious problem and is one of the hurdles preventing this procedure from becoming widespread [4] . One of the methods for reducing the radiation exposure is to reduce the X-ray tube current of CT and/or to make the time for X-ray exposure as short as possible. Previously, we proposed a method for reducing the radiation dose in cerebral CT perfusion studies by using a variable scan schedule [5] . However, reducing the X-ray tube current and/or shortening the X-ray exposure time can cause an increase of the statistical noise in the dynamic images, leading to deterioration of the accuracy of the perfusion parameters calculated from the dynamic images [5] .
To reduce image noise, various filtering techniques have been devised [6] . In linear spatial filtering such as Gaussian filtering, the content of a pixel is given the value of the weighted average of its immediate neighbors. This filtering reduces the amplitude of noise fluctuations, but also degrades sharp details such as lines or edges, and the resulting images appear blurred and diffused [6] . This undesirable effect can be reduced or avoided by designing nonlinear filters, the most common technique being median filtering. With median filtering, the value of an output pixel is determined by the median of the neighboring pixels [7] . This filtering retains edges, but results in a loss of resolution by suppressing fine details. Perona and Malik [8] developed a multiscale smoothing and edge detection scheme based on anisotropic diffusion (AD), which is a new concept for image processing. Their AD method overcomes the major drawbacks of conventional spatial filtering, and significantly improves image quality while preserving spatial resolution [8] - [10] . The purpose of this study was to present an application of the AD method to cerebral CT perfusion studies using MDCT for improving the accuracy of perfusion parameters and to investigate its usefulness and feasibility in reducing radiation exposure.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
Six patients with cerebrovascular disease [3 males and 3 females; age, 69.0 ± 5.7 (mean±standard deviation) years] participated in this study. The details of the patients are described in [5] . Informed consent was obtained from each patient after a detailed explanation of the purpose of the study and scanning procedures. Following a standard protocol for CT perfusion study, continuous (cine) scans (1 sec/rotation ×60 sec) consisting of four 5-mm-thick contiguous slices were acquired after an injection of iodinated contrast material (300 mgI/mL, 30 - 40 mL) into a peripheral vein through a 20-gauge catheter with an injection velocity of 4 mL/sec, using an MDCT scanner (LightSpeed QX/i, GE Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan) with a tube voltage of 80 kVp and a tube current of 200 mA. The 60 images obtained in each of the four slices were defined as “original images”. New image data were generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 2 sec or 3 sec. The thinned- out images were then interpolated by linear interpolation to generate the same number of images as originally acquired. We call the images generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 2 sec and linear interpolation “2-sec-interpolated images”. Similarly, we call the images generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 3 sec and linear interpolation “3-sec-interpolated images”.
2.2. Anisotropic Diffusion (AD) Method
The interpolated images were processed by the AD method. We call the 2-sec- and 3-sec-interpolated images processed by the AD method “2-sec-AD images” and “3-sec-AD images”, respectively. Figure 1 illustrates how the thinned-out, interpolated and AD images were generated from the original images.
With the AD method, smoothing is formulated as a diffusive process and is suppressed or stopped at boundaries
![]()
Figure 1. Illustration of generating the thinned-out, interpolated and anisotropic diffusion (AD) images from original images. The thinned-out images were generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 2 sec or 3 sec. The thinned-out images were then interpolated by linear interpolation to generate the same number of images as originally acquired (interpolated images). We call the images generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 2 sec and linear interpolation “2-sec-interpolated images”. Similarly, we call the images generated by thinning out the original images at an interval of 3 sec and linear interpolation “3-sec-interpolated images”. The interpolated images were processed by the AD method to generate the AD images. We call the 2-sec- and 3-sec-interpolated images processed by the AD method “2-sec-AD images” and “3-sec-AD images”, respectively.
by selecting locally adaptive diffusion strengths [8] -[10] . This process can be formulated as follows, assuming no sinks or sources [8] -[10] :
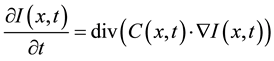 (1)
(1)
where 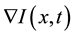 represents the magnitude of the image gradient at x. The variable t is the process-ordering parameter; in the discrete implementation it is used to enumerate iteration steps [9] .
represents the magnitude of the image gradient at x. The variable t is the process-ordering parameter; in the discrete implementation it is used to enumerate iteration steps [9] . 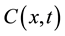 represents a diffusion function which controls the diffusion strength. In this study, we used the following function given by Tukey’s Biweight as
represents a diffusion function which controls the diffusion strength. In this study, we used the following function given by Tukey’s Biweight as 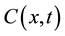 [11] :
[11] :
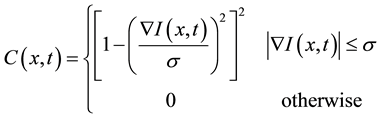 (2)
(2)
where  is the scale parameter. In this study, we chose a value for the scale parameter
is the scale parameter. In this study, we chose a value for the scale parameter 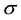 so that it begins rejecting outliers at the “robust scale”
so that it begins rejecting outliers at the “robust scale” 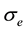 [11] . The “robust scale”
[11] . The “robust scale” 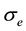 is given by [12]
is given by [12]
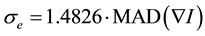 (3)
(3)
where MAD denotes the median absolute deviation and the constant is derived from the fact that the MAD of a zero-mean normal distribution with unit variance is 0.6745 = 1/1.4826.
Numerical implementation of Equation (1) was performed in a standard manner by substituting partial deri- vatives with the appropriate discrete sample differences of the image data. Details of the discretization of Equation (1) can be found in Perona and Malik [8] and Fischl and Schwarz [13] .
2.3. Generation of CBF, CBV and MTT Images
According to the indicator dilution theory [14] for intravascular contrast agents, the time-dependent concentration of the contrast agent in the volume of interest (VOI) [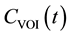 ] is given by [15]
] is given by [15]
 (4)
(4)
In Equation (4), 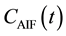 is the time-dependent concentration of the contrast agent in a feeding artery.
is the time-dependent concentration of the contrast agent in a feeding artery. 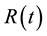 is the residue function which is the relative amount of contrast agent in the VOI in an idealized perfusion experiment, where a unit area bolus is instantaneously injected [
is the residue function which is the relative amount of contrast agent in the VOI in an idealized perfusion experiment, where a unit area bolus is instantaneously injected [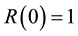 ] and subsequently washed out by perfusion [
] and subsequently washed out by perfusion [![]() ]. It is known from Equation (4) that the initial height of the deconvolved time-concentration curve equals the cerebral blood flow (CBF). In this study, the CBF value was obtained from the maximum value of the deconvolved time-concentration curve. There are several possible approaches to calculating CBF from Equation (4) by deconvolution [16] [17] . In this study, we adopted an algebraic approach based on singular value decomposition (SVD) [16] [17] , which was robust against statistical noise. The details of this approach have been described elsewhere [16] [17] . When using SVD in deconvolution analysis, the elements in the diagonal matrix obtained by SVD were set to zero when they were smaller than the threshold value given beforehand. In this study, the threshold value was taken as 0.2 [16] [17] . We generated the CBF images by applying this approach pixel by pixel. The arterial input function [
]. It is known from Equation (4) that the initial height of the deconvolved time-concentration curve equals the cerebral blood flow (CBF). In this study, the CBF value was obtained from the maximum value of the deconvolved time-concentration curve. There are several possible approaches to calculating CBF from Equation (4) by deconvolution [16] [17] . In this study, we adopted an algebraic approach based on singular value decomposition (SVD) [16] [17] , which was robust against statistical noise. The details of this approach have been described elsewhere [16] [17] . When using SVD in deconvolution analysis, the elements in the diagonal matrix obtained by SVD were set to zero when they were smaller than the threshold value given beforehand. In this study, the threshold value was taken as 0.2 [16] [17] . We generated the CBF images by applying this approach pixel by pixel. The arterial input function [![]() ] was obtained from the middle cerebral artery using fuzzy c-means clustering [18] .
] was obtained from the middle cerebral artery using fuzzy c-means clustering [18] .
The cerebral blood volume (CBV) was given by the following formula:
![]() (5)
(5)
From the central volume principle [14] , the mean transit time (MTT) was obtained by the equation:
![]() (6)
(6)
The CBV and MTT images were generated by applying Equations (5) and (6) pixel by pixel, respectively.
2.4. Evaluation and Statistical Analysis
To quantitatively evaluate the usefulness of the AD method, we drew 5 regions of interest (ROIs) of approximately 300 mm2 on each slice level of the CBF, CBV and MTT images, i.e., a total of 20 ROIs. The positions of the ROIs were as follows: 1) white matter of right frontal lobe, 2) white matter of right temporal lobe, 3) white matter of left frontal lobe, 4) white matter of left temporal lobe and 5) basal ganglia. When drawing ROIs, large blood vessels were carefully excluded. We calculated the correlation coefficients between the perfusion parameter values obtained from the original and AD images for the above 20 ROIs using linear regression analysis. For comparison, we also calculated the correlation coefficients between the perfusion parameter values obtained from the original and interpolated images. Bland-Altman plots [19] were also generated. Furthermore, the mean and standard deviation (SD) of the perfusion parameter values in the white matter were obtained, and the coefficients of variation (CVs) were calculated from SD/mean.
The statistical comparisons of the correlation coefficients and CV values were performed using the paired Student t test. P values less than 0.05 were considered to be significant in all statistical analyses.
3. Results
Figure 2 shows typical examples of the CBF images generated from original, interpolated and AD images. The upper left, middle and right panels show the CBF images generated from the original, 2-sec-interpolated and 3-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while the lower left, middle and right panels show those generated from the original images processed by the AD method, 2-sec-AD and 3-sec-AD images, respectively. Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the cases of CBV and MTT, respectively. As shown in Figures 2-4, the statistical noise was reduced by using the AD method while preserving spatial resolution for all cases.
Figure 5(a) and Figure 5(b) show typical examples of the correlation (upper panel) and Bland-Altman plot (lower panel) between the CBF values obtained from the original and 2-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while Figure 5(c) and Figure 5(d) show those between the CBF values obtained from the original and 2-sec-AD images, respectively. Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the cases of CBV and MTT, respectively.
![]()
Figure 2. Typical examples of the cerebral blood flow (CBF) images generated from the original, interpolated and AD images. The upper left, middle and right panels show the CBF images generated from the original, 2-sec-interpolated and 3-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while the lower left, middle and right panels show those generated from the original images processed by the AD method, 2-sec-AD and 3-sec-AD images, respectively.
![]()
Figure 3. Typical examples of the cerebral blood volume (CBV) images generated from the original, interpolated and AD images. The upper left, middle and right panels show the CBV images generated from the original, 2-sec-interpolated and 3-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while the lower left, middle and right panels show those generated from the original images processed by the AD method, 2-sec-AD and 3-sec-AD images, respectively.
Figure 8 shows the correlation coefficients between the perfusion parameter values obtained from the original and interpolated or AD images for CBF (a), CBV (b) and MTT (c). The closed and open bar graphs show the values obtained from the images without and with processing by the AD method, respectively. “2 sec” and “3 sec” represent the values obtained from the 2-sec-interpolated or 2-sec-AD images and 3-sec-interpolated or 3-sec-
![]()
Figure 4. Typical examples of the mean transit time (MTT) images generated from the original, interpolated and AD images. The upper left, middle and right panels show the MTT images generated from the original, 2-sec-interpolated and 3-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while the lower left, middle and right panels show those generated from the original images processed by the AD method, 2-sec-AD and 3-sec-AD images, respectively.
![]()
Figure 5. (a) and (b) show typical examples of the correlation and Bland-Altman plot between the CBF values obtained from the original and 2-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while (c) and (d) show those between the CBF values obtained from the original and 2-sec-AD images, respectively.
![]()
Figure 6. (a) and (b) show typical examples of the correlation and Bland-Altman plot between the CBV values obtained from the original and 2-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while (c) and (d) show those between the CBV values obtained from the original and 2-sec-AD images, respectively.
AD images, respectively. The error bar represents the SD for 6 patients. As shown in Figure 8, the correlation coefficients deteriorated with increasing thinning-out interval for all perfusion parameters. The deterioration was the largest in MTT. The correlation coefficient for MTT was significantly improved by using the AD method for both cases with thinning-out intervals of 2 sec and 3 sec.
Figure 9 shows the CV values of CBF (a), CBV (b) and MTT (c) in the white matter obtained from the images with various thinning-out intervals. “0 sec”, “2 sec” and “3 sec” represent the CV values obtained from the original images or original images processed by the AD method, 2-sec-interpolated or 2-sec-AD images and 3-sec-interpolated or 3-sec-AD images, respectively. The closed and open bar graphs show the CV values obtained from the images without and with processing by the AD method, respectively. The error bar represents the SD for 6 patients. As shown in Figure 9, the CV values obtained from the images processed by the AD method were significantly lower than those obtained without using the AD method for all cases.
4. Discussion
We previously presented an application of the AD method to improving the accuracy of the CBF images generated from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DSC-MRI) [10] . In the above study, we investigated the usefulness of the AD method using computer simulations and clinical data in comparison with the median and Gaussian filters [10] . Although the median and Gaussian filters also reduced image noise, the accuracy of the CBF values considerably deteriorated. On the other hand, the AD method was capable of reducing the image noise while preserving the quantitative accuracy of the CBF images. We concluded that the AD method will make the CBF images generated from DSC-MRI more reliable [10] . In this study, we presented an application of the AD method to cerebral CT perfusion studies. The present study also demonstrated that the AD method was useful for improving the accuracy of the functional images of CBF, CBV and MTT generated from cerebral CT perfusion studies.
When using the AD method, there are two important parameters that should be determined. One is the scale
![]()
Figure 7. (a) and (b) show typical examples of the correlation and Bland-Altman plot between the MTT values obtained from the original and 2-sec-interpolated images, respectively, while (c) and (d) show those between the MTT values obtained from the original and 2-sec-AD images, respectively.
![]()
Figure 8. Correlation coefficients between the perfusion parameter values obtained from the original and interpolated or AD images in 6 patients. (a), (b) and (c) show the cases of CBF, CBV and MTT, respectively. The closed and open bar graphs represent the data obtained from the images without and with processing by the AD method, respectively. “2 sec” and “3 sec” represent the data obtained from the 2-sec-interpolated (closed) or 2-sec-AD images (open) and 3-sec-interpolated (closed) or 3-sec-AD images (open), respectively. The error bar represents the standard deviation (SD) for 6 patients. *P < 0.05.
parameter σ in Equation (2), and the other is the number of filter operations. Basically, these parameters should be selected by visually comparing different results. The scale parameter σ in Equation (2) is directly related to the gradient magnitude of the image to be kept or smoothed. The selection of this parameter is important and is mainly based on the noise level and edge strength. If the noise level is known, the selection of this parameter is possible from the variance of the image, as suggested by Gerig et al. [9] . If the noise level is not known, a test series with different parameters must be generated and compared. Once selected, the parameter can be kept
![]()
Figure 9. Coefficient of variation (CV) values of CBF (a), CBV (b) and MTT (c) in the white matter obtained from the images with various thinning-out intervals. “0 sec” represents the data obtained from the original images or original images processed by the AD method, while “2 sec” and “3 sec” represent the data obtained from the 2-sec-interpolated or 2-sec-AD images and 3-sec-interpolated or 3-sec-AD images, respectively. The closed and open bar graphs show the data obtained from the images without and with processing by the AD method, respectively. The error bar represents the SD for 6 patients. *P < 0.05.
fixed for acquisitions taken under similar conditions. However, such a procedure is very time-consuming and is not suitable in a clinical setting. In this study, this parameter was automatically selected from robust statistics to estimate the “robust scale” of the image [12] . The “robust scale” is given by Equation (3). Since the scale parameter selected from the “robust scale” worked very well, we believe that this selection can also be applied to cerebral CT perfusion studies.
A second parameter that must be selected is the number of filter operations. The iterated filter operations resulted in a sequence of diffused images, and impressive improvements were obtained from three to five iterations (data not shown). These findings are very similar to those reported by Gerig et al. [9] and our previous results [10] . Therefore, all the results shown here were obtained by fixing the number of filter operations at five.
As previously described, one of the methods for reducing the radiation exposure in cerebral CT perfusion studies is to reduce the X-ray tube current [4] and/or to shorten the X-ray exposure time [5] . Previously, we proposed a method for reducing the radiation dose by using a variable scan schedule [5] . Our previous study [5] demonstrated that to keep the correlation coefficients of all perfusion parameters greater than 0.9, the estimated radiation dose could be reduced to 58.3% with a scan schedule of 10 continuous images and thinning-out interval of 2 sec. The radiation exposure decreased with increasing thinning-out interval. Taking the radiation exposure in the case when using original images as 100%, the radiation dose became 50% and 33% when using thinning-out intervals of 2 sec and 3 sec, respectively. Although increasing the thinning-out interval is useful for reducing the radiation dose, it will cause an increase of image noise, leading to deterioration of the accuracy of perfusion parameters. As shown in Figure 8, the correlation coefficients between the perfusion parameters obtained from the original and interpolated images deteriorated with increasing thinning-out interval. However, the quality of the functional images of CBF, CBV and MTT was visually improved by using the AD method as shown in Figures 2-4. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 9, the CV values of the perfusion parameters in the white matter were significantly improved by using the AD method. These results suggest that the AD method is useful for reducing radiation exposure by decreasing the X-ray tube current [4] and/or by shortening the X-ray exposure time [5] .
Kikuchi et al. [20] reported the usefulness of MTT images for evaluation of the extent of cerebral perfusion reserve impairment in patients with occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Therefore, it is desirable to maintain the reliability of MTT values similar to those of CBF and CBV values. The AD method appears to be useful in this respect, because the correlation coefficient between the MTT values obtained from the original and thinned-out images was significantly improved by using the AD method as shown in Figure 8.
In this study, we used the CV value of perfusion parameters in the white matter as an evaluation parameter (Figure 9). This was mainly because there were no lesions in the white matter and the variation of perfusion parameters with region in the white matter was less than that in the gray matter in the patients used in this study. Furthermore, the perfusion parameters in the gray matter tended to be contaminated by those in the large blood vessels as shown in Figures 2-4.
The present study had some limitations. The number of patients was small, and they had little variation in their cerebral hemodynamic patterns. Few prominent abnormalities of cerebral perfusion parameters were found in these patients. An additional study using more patients with various types of ischemic disease or diseases of the systemic circulation is recommended to enhance the reliability of the present study.
5. Conclusion
Our results suggest that the AD method is useful for improving the accuracy of the functional images of cerebral perfusion parameters and for reducing radiation exposure in cerebral CT perfusion studies using MDCT.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Grant Number: 25282131) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Declaration of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.