Comparative Organics Remediation Properties of Nanostructured Graphene Doped Titanium Oxide and Graphene Doped Zinc Oxide Photocatalysts ()
1. Introduction
The organic decontamination in water is generally achieved by combination of chemical, physical [1] - [6] and biological techniques [7] -[12] . The organic such as petroleum oil (combination of volatile organic, naphthalene, toluene, type A oil, etc.) is remediated from water using various surfactants, sorbent, flocculants―bioremediation and occasionally in situ burning methods [13] -[16] . Though, each technique has its own benefits and disadvantages, however, the remediation is related to chemical and physical properties of water as well as related remediation technique. The residues of the oil remain in water while remediated using most of the techniques except bioremediation, which has its own numerous drawbacks [17] [18] . Recently, our group has completed extensive remediation of several organic compounds including oil using TiO2 and ZnO based nanostructured materials in immobilized and colloidal dispersion compounds, where the chemicals were remediated using the UV-vis and visible radiation of light [19] -[23] . The remediation is certainly dependent on the formation of free radical (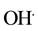 and
and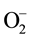 ), nature of the nanostructured based materials TiO2 and/or ZnO and doping of transition metal [24] [25] . Besides, our group has effectively remediated number of chemicals (toluene, methylene orange (MO), naphthalene etc.), using photocatalyst nanocomposite materials in visible radiation of light [19] -[21] .
), nature of the nanostructured based materials TiO2 and/or ZnO and doping of transition metal [24] [25] . Besides, our group has effectively remediated number of chemicals (toluene, methylene orange (MO), naphthalene etc.), using photocatalyst nanocomposite materials in visible radiation of light [19] -[21] .
The use of transition metal as well as non-metal dopants in TiO2 photocatalyst is to narrow the bang gap which could increase photocatalytic activity in the visible light [26] -[30] . The sol-gel technique of photocatalyst synthesis allows to control and manage chemicals homogeneously and processed reaction conditions for yielding nanosized metallic oxide photocatalysts [31] [32] . The graphene doped TiO2 has revealed remediation of organics in the visible light. Yang Yang et al. have shown remediation of ZnO nanowires where iron doping was prepared on the seeding layer [20] -[22] . Further, Udom et al. have used silver dopant in seeding layer to manufacture ZnO nanowires for remediation of several organic compounds [21] . Yang Yang et al. doped the ZnO seeding layer before the growth of ZnO nanowires [21] [23] .
The present paper is devoted to understanding qualitatively and quantitatively the remediation properties by graphene-ZnO nanowires, graphene-TiO2 nanocomposite, and comparing the outcomes with graphene-TiO2 nanoparticles and commercial photocatalyst TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. The nanowires were synthesized using the graphene with seeding photocatalytic nanomaterials (different sizes) in zinc nitrate and hexamine. The graphene-ZnO nanowires, graphene-TiO2 nanocomposite, and compared the outcomes with graphene-TiO2 nanoparticles nanostructured materials were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. The doping of graphene onto TiO2 in both nanoparticles and nanowire structure is studied due to unique properties of graphene. The remediation of MO and naphthalene in water was studied quantitatively and qualitatively. In our experimental set up, initiatives have been taken to pass radiation on light on a reaction chamber from both top to bottom ends, separately, and remediation has been studied as a function of time (hours). The remediation experiments were completed using both nanostructured materials in immobilized substrates (example: petri discs) as well as in nanoparticles in colloidal form. The colloidal/suspension particles after remediation were removed using centrifuge, and the filtered water was tested using UV-vis measurements. In design of our experiments, the factors have been considered in estimating the influence of individual variable and their interaction to organize maximum number of experiments.
The MO remediation is shown in Figure 1 using G-TiO2 nanostructured material. The schematic has revealed how G-TiO2 produces radical with the use of water molecule and oxygen. The free radicals 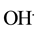 and
and 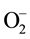 were created when light interacted with G-TiO2 nanostructured materials. The pollutants were oxidized and finally broke into carbon dioxide (CO2) and H2O molecules. The stepwise remediation of pollutant is given in Equation (1)-(7). Further, Figure 1 shows schematic of reaction of G-TiO2 for remediation of MO.
were created when light interacted with G-TiO2 nanostructured materials. The pollutants were oxidized and finally broke into carbon dioxide (CO2) and H2O molecules. The stepwise remediation of pollutant is given in Equation (1)-(7). Further, Figure 1 shows schematic of reaction of G-TiO2 for remediation of MO.
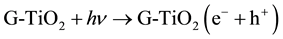 (1)
(1)
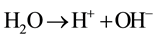 (2)
(2)
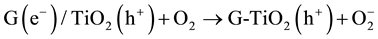 (3)
(3)
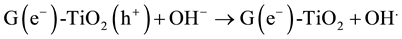 (4)
(4)
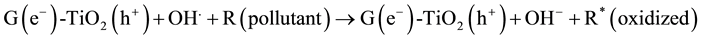 (5)
(5)
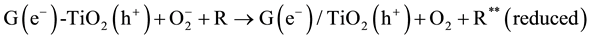 (6)
(6)
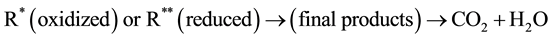 (7)
(7)
![]()
Figure 1. Schematic of remediation of methyl orange using G-TiO2 nanoparticles.
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
The chemicals such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), propanol, titanium (IV) isopropoxide, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), zinc oxide (ZnO) particles, zinc nitrate hexahydrate (Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O), hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA), methyl orange, naphthalene and other reagents were used for the preparation of nanostructured materials and the chemicals were procured from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). The commercial TiO2 P25 was also obtained for comparative remediation studies. The graphene platelets of size < 20 nm in thickness were acquired from Angstrom Materials, a commercial company in USA.
2.2. Synthesis of G-TiO2 Nanoparticles and Nanocomposite
The G-TiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized using mixture of titanium (IV) isopropoxide in propanol solution. Initially, 0.193 gm of graphene (G) was mixed in 20 ml propanol with 30 minutes of sonication with slowly addition of 4 ml of titanium (IV) isopropoxide in round bottom flask. The mixture was stirred for 30 minutes, and later, HCl solution was added drop wise, and the solution to stir for another 24 hours at room temperature. The precipitate was washed using deionized water for removing the unreacted organic residues, later it was centrifuged and dried at 100˚C.
The nanocomposite G-TiO2 was synthesized by using titanium oxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The synthesis was initiated by addition of 6 gm TiO2 (P25) and 0.2 gm of graphene (G) with addition of 70 ml of 10 M NaOH solution. The resulting solution was stirred for 30 minutes and, it was kept at a constant temperature of 150˚C for 48 hrs. The precipitate was washed using 0.1 M HCl solution for several times with an observation that the precipitate showed pH below 7. The precipitate was centrifuged, and dried at 100˚C for 24 hrs. The G-TiO2 nanocomposite was heated at 350˚C for 4 hrs.
2.3. Synthesis of G-ZnO Nanowires
The graphene (G) -zinc oxide (G-ZnO) was synthesized by using Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O, hexamethylenetetramine HMTA and G . Initially 25 mM/l of Zn(NO3)2∙6H2O and HMTA solutions were mixed in deionized water (DI) and 0.1 gm of G was added to the solution, and maintained at 80˚C. Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles with normal size (avg 100 nm) were sonicated in 1 ml of DI water with addition of solution as nucleation sites for the growth of nanowires. The solution was kept at 80˚C for 4 hours, and washed with DI water & ethanol and centrifuged. The samples were dried at 100˚C for 24 hrs.
2.4. Experiment Setup
The photocatalytic activity of materials G-TiO2 nanoparticles (synthesized by sol-gel), G-TiO2 nanocomposite (synthesized by hydrothermal), and G-ZnO nanowire (synthesized by hydrothermal) and commercially available P25 were studied to remediate MO as an indicator. In the process, 0.2 gm of photocatalytic material were coated onto a petri dish with the use of acetic acid & dried at room temperature. Later, it was heated at 200˚C for 30 minutes. 20 ppm of 40 ml MO was added inside the coated petri dishes, and illuminated by light of 30-watt with light intensity of 800 W/m2. The remediated samples were collected from the main remediating samples in an interval of an hour. Attempts were also taken to vary the time interval in some cases in collecting the remediating sample. JASCO V-530 UV-Visible Spectrometer was used to measure the absorbance of MO. Initial concentration was taken as Co at 0 hours. The percentage of concentration ratio was calculated by using Cn/Co with respect to time in hours.
Based on the procedure for MO, the performance of G-TiO2 nanoparticle, G-TiO2 nanocomposite and G-ZnO nanowire were used on naphthalene in water. 30 ppm of naphthalene was used as contaminant in 100 ml of deionised water. 20 mg of sodium dodecyl-sulfonate surfactant was used to enhance the contact of photocatalyst and pollutants.The light intensity of 800 W/m2 generated by 30 watt bulb was used to remediate naphthalene from water. The samples were analyzed using UV-vis spectrum for naphthalene presence in remediated water at 0 and 48 hrs similar to one discussed for MO. The naphthalene has UV-vis absorption at 221 nm, 286 nm and 312 nm. The values at these peaks were considered to determine the percentage (%) of naphthalene in the remediated water samples.
3. Characterization
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction
XRD study of G-TiO2 nanoparticles is shown below in Figure 2. The diffraction peak at 26.51˚ indicates the presence of graphene. The peaks at 24.94, 37.87, 47.88, 54.60, 63.08, 69.26, 74.87, 83.09 degrees indicate the anatase phase of TiO2 in nanocomposite of G-TiO2.
The XRD study of G-TiO2 nanocomposite is shown in Figure 3, which observes the presence of graphene at
![]()
Figure 2. XRD image of G-TiO2 nanoparticles showing the peaks of graphene and anatase (01-075-1537) phase of TiO2.
26.54˚ diffraction peak. The diffraction angle (2θ) at 25.19, 38.08, and 48.01 indicate anatase phase (01-078- 2486) of TiO2 and a 2θ at 27.40, 36.08, and 54.37 indicates the rutile phase (01-075-1748) of TiO2. Based on the length of the diffraction peak, ratio of rutile to anatase phase has been estimated to be 1.32:1, which indicates the material, has relatively added rutile phase than anatase phase.
The XRD image of G-ZnO nanowires is as shown in Figure 4. The peak at 26.49˚ shows the presence of graphene. The peaks in 00-036-1451 in Figure 4, shows the presence of ZnO structure.
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
The surface morphology of G-TiO2 nanoparticles is shown in Figures 5(a)-(d). It reveals the compact particles distribution in the G-TiO2 nanostructured material. A potential explanation for formation for compact particle structure in G-TiO2 is due to dispersion of TiO2 particles on graphene sheets. Figure 5(d) shows the SEM images of G-TiO2 nanoparticle at 500 nm unit magnification. The typical graphene structure is covered by the TiO2
![]()
Figure 3. XRD image of G-TiO2 nanocomposite showing the peaks of graphene and anatase (01-078- 2486) and rutile (01-075-1748) phase of TiO2
![]()
Figure 4.XRD image of G-ZnO nanowire showing the peaks of graphene and (00-036-1451) ZnO
nanoparticle.
We made an attempt to synthesize nanowires for keeping the G-TiO2 seeding layer. However, the G-TiO2 nanocomposite wires were not formed under similar growth condition as indicated by SEM images in Figure 6. However, the G-TiO2 nanostructured has been found similar to one studied in Figure 5.
Figure 7 observes the nanowires structure of G-ZnO. The ZnO nanowires have been found to form on graphene sheets. The sizes of ZnO nanowires coated with graphene were controlled by the size of seeding layer of ZnO. The size of G-ZnO nanowires have been found to be between 200 - 400 nm as shown in Figure 7.
4. Results and Discussion
Figure 8 reveals the degradation of MO using G-TiO2 nanoparticles, G-TiO2 nanocomposite, G-ZnO nanowire and commercially available P25. G-TiO2 nanoparticle observes the improved photocatalytic performance by removing entirely the MO from water solution in less than 5 hours.
Figures 9(a)-(c) show disappearance of UV-vis absorption peaks at 221, 286 and 321 nm from remediated samples. The G-TiO2 nanoparticles have been found to perform better than the G-TiO2 nanocomposite, and G-ZnO nanowires for the decontamination of naphthalene. Based on the experimental investigation, the MO remediation in water using G-TiO2 photocatalytic materials (Figure 9) has been plotted for comparative %Cn/ Co vs time duration (hrs) plots. The similar plots can also be shown with the change of TiO2 nanopartciles to ZnO nanowires using graphene matrix.
![]()
Figure 8.Comparative graph of %Cn/Co vs time of exposure (hrs) for G-TiO2 nanoparticles, G-TiO2 nanocomposite, G-ZnO nanowire and commercially available P25 for methyl orange (MO).
![]()
Figure 9. Comparative graph of %Cn/Co vs time duration (hrs) for G-TiO2 nanoparticles, G-TiO2 nanocomposite, G-ZnO nanowire for naphthalene respectively. (a) G-TiO2 NP; (b) G-TiO2 NC; (c) G-ZnO NW.
5. Conclusion
Sol gel G-TiO2 nanoparticles have superior photocatalytic properties than G-TiO2 nanocomposite (synthesized by hydrothermal), G-ZnO nanowires (synthesized by hydrothermal) and commercially available P25 under visible light. The photocatalytic remediation of both of MO and naphthalene has been faster using G-TiO2 nanocomposite than other synthesized nanomaterials under identical condition. The sol-gel G-TiO2 nanoparticles could find applications for cleaning drinking water.
Acknowledgements
National Science Foundation (NSF) with the grant number 1066649 is greatly acknowledged for financial support. One of the authors, Gunti would like to thank Saumya Sharma and Michael McCrory for SEM and XRD measurements.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.