Multiserver Multichannel Real-Time System with Limited Maintenance Facilities under Maximum Load ()
1. Introduction
Real-time systems (RTS) are defined as those for which correctness depends not only on the logical properties of the computed results, but also on their temporal properties. In RTS, a calculation that uses temporally invalid data may be useless and sometimes harmful―even if such a calculation is functionally correct. Examples include industrial automation, traffic control, aerospace, robotic, intelligence and defense system, telecommunication and distributed process control, just to name a few.
Several researchers ([1] -[3] ) have proposed a number of classic priority algorithms for scheduling real-time tasks on a single processor. The problem of minimizing the number of processors in multiprocessor computer system executing real-time tasks is studied in [4] .
Different scientific communities are treating RTS problems. During last three decades several meta-heuristic methods, such as Tabu Search [5] , Simulated Annealing [6] and Greedy Randomized Adaptive Search Procedure [7] are developed. Good surveys on Artificial Intelligence and real-time decision problems (RTDP) are given in references [8] -[11] .
The use of analytical methods of queueing theory [12] and stochastic processes [13] has significant benefits in developing RTS.
We will focus on RTS with a zero deadline for the beginning of job processing. In these RTS, jobs are pro- cessed immediately upon arrival, if there are available servers. That part of the job which is not processed immediately is lost forever, since queueing of jobs or their parts are not allowed. The particular interest in such RTS is aroused by military intelligence problems involving unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), which demonstrate a very high efficiency in many local conflicts. It is proved that the non-mix policy of never relieving an operative server maximizes the availability of a multiserver single-channel RTS involving preventive maintenance and working in general regime with any arrival pattern under consideration and constant services and maintenance times ([14] [15] ). This policy appears to be optimal for any finite time interval, and not only for infinite horizon. Multiserver (identical servers) and multichannel (identical channels) RTS [16] [17] (with limited and unlimited number of maintenance facilities respectively), working under maximum load regime were treated as finite source queues. Two-dimensional birth-and-death processes [18] [19] were applied in analysis of a multiserver RTS (with ample and limited number of maintenance teams respectively) with two different channels operating under a maximum load regime, when both service and maintenance times are exponentially distributed. In [20] the results of [18] for 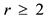 different channels operating under a maximum load regime were extended. Optimal assignment probabilities maximizing availability of RTS (with ample and limited number of maintenance teams respectively) with large number of servers and two channels were obtained [21] [22] . Amultiserver and multichannel RTS with identical servers and channels and ample maintenance facilities, working in general regime with exponentially distributed service, maintenance, jobs inter-arrival and duration times were treated as Markov chains [23] in order to obtain various performance characteristics. The researchers [24] [25] obtained moments of RTS with ample and limited maintenance facilities respectively. In [26] RTS with preemptive priorities policy were considered. In [27] the RTS with exactly one job in each channel was studied. The researchers [28] computed analytically (for exponentially distributed service times) and via Cross Entropy [29] -[31] simulation approach (for generally distributed service times) optimal routing probabilities for RTS with ample maintenance facilities.
different channels operating under a maximum load regime were extended. Optimal assignment probabilities maximizing availability of RTS (with ample and limited number of maintenance teams respectively) with large number of servers and two channels were obtained [21] [22] . Amultiserver and multichannel RTS with identical servers and channels and ample maintenance facilities, working in general regime with exponentially distributed service, maintenance, jobs inter-arrival and duration times were treated as Markov chains [23] in order to obtain various performance characteristics. The researchers [24] [25] obtained moments of RTS with ample and limited maintenance facilities respectively. In [26] RTS with preemptive priorities policy were considered. In [27] the RTS with exactly one job in each channel was studied. The researchers [28] computed analytically (for exponentially distributed service times) and via Cross Entropy [29] -[31] simulation approach (for generally distributed service times) optimal routing probabilities for RTS with ample maintenance facilities.
This work extends the models [27] [28] as follows. The RTS under consideration assumes the constant number of jobs, specific for each channel. We compute analytically steady-state probabilities of this system, its availability, loss penalty function and other performance characteristics.
The paper is organized as follows: in Section 2 describes the model; Section 3 provides steady state probabilities; Section 4 presents various performance measures; Finally, Section 5 summarizes our results.
2. Description of the Model
We consider a multiserver RTS consisting of N identical servers that provide service for requests of real-time jobs arriving via rdifferent channels required to be under nonstop surveillance. There are exactly 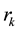
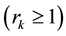 , k = 1, ∙∙∙, r requests of real-time jobs in k-th channel at any instant (there are no additional job arrivals to the busy channel), and therefore
, k = 1, ∙∙∙, r requests of real-time jobs in k-th channel at any instant (there are no additional job arrivals to the busy channel), and therefore  servers at most are used to serve the i-th channel (with others being on stand-by or providing the service to another channel or in maintenance or waiting for maintenance) at any given time. Thus,
servers at most are used to serve the i-th channel (with others being on stand-by or providing the service to another channel or in maintenance or waiting for maintenance) at any given time. Thus,
the total number of operating servers in the system is at most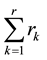 .
.
Each channel has its own specifications and conditions, etc., and therefore different kinds of equipment and inventory are needed to serve different channels.
A server providing service for the k-th channel is operative for a period of time 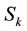 before requiring
before requiring  hours of maintenance.
hours of maintenance. 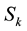 and
and 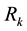 areindependent exponentially distributed random variables with parameters
areindependent exponentially distributed random variables with parameters 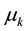 (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) and
(k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) and 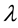 respectively.
respectively.
It is assumed that there are K 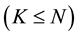 maintenance teams available to repair (with repair times
maintenance teams available to repair (with repair times 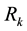 being i.i.d.r.v.) the servers. Thus, a shortage of maintenance facilities is possible. In that case the server waits for maintenance. This server is assigned to the k-th channel with probability
being i.i.d.r.v.) the servers. Thus, a shortage of maintenance facilities is possible. In that case the server waits for maintenance. This server is assigned to the k-th channel with probability 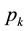 (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r). It receives the appropriate kind of maintenance (equipment, programming, etc.), and therefore cannot be sent to another channel. Assignment probabilities
(k = 1, ∙∙∙, r). It receives the appropriate kind of maintenance (equipment, programming, etc.), and therefore cannot be sent to another channel. Assignment probabilities 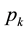 may depend upon inventory conditions. They also can be used as control parameters. The duration
may depend upon inventory conditions. They also can be used as control parameters. The duration 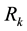 of repair is exponentially distributed with parameter
of repair is exponentially distributed with parameter![]() , and does not depend on the channel. After maintenance, the server will either be on stand-by or serving the channel it was assigned to.
, and does not depend on the channel. After maintenance, the server will either be on stand-by or serving the channel it was assigned to.
The system works under a maximum load (worst case) of nonstop data arrival to each one of r channels. This kind of operation is typical in high performance data acquisition and control systems, such as self-guided missiles, space stations, satellites, etc.
If, during some period of time of length T, there is no available server to serve one of the jobs, we will say that the part of the job of length T is lost.
Queues of jobs or their parts cannot exist in RTS, nevertheless they can be fitted into a framework of finite source queues, while using a dual approach of changing the roles between jobs and servers.
3. Steady State Probabilities
Denote: ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() the state of the system, where
the state of the system, where ![]() (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) is a number of fixed servers assigned to the k-th channel (obviously
(k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) is a number of fixed servers assigned to the k-th channel (obviously![]() ), and
), and ![]() the corresponding steady state probability. There are
the corresponding steady state probability. There are ![]() states in total.
states in total.
The above RTS can be presented as a closed Jackson queuing network (Figure 1) consisting of N customers (N servers of the RTS), r + 1 nodes (r channels and maintenance station of the RTS) with ![]() servers at k-th node (
servers at k-th node (![]() jobs in the k-th channel of the RTS) (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) and K servers at r + 1-th station (K maintenance teams of the RTS). The network has transition probabilities
jobs in the k-th channel of the RTS) (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) and K servers at r + 1-th station (K maintenance teams of the RTS). The network has transition probabilities ![]() (assignment probabilities of the RTS) from r + 1-th node to k-th one (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r), and transition probabilities from k-th station to r + 1-th are equal to 1. Other transition probabilities are equal to 0. Service times at the network stations (operating and maintenance times of the RTS) are exponentially distributed. The customers of the network cannot leave it and cannot come to it from outside. Thus, the network is a closed Jackson network by definition.
(assignment probabilities of the RTS) from r + 1-th node to k-th one (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r), and transition probabilities from k-th station to r + 1-th are equal to 1. Other transition probabilities are equal to 0. Service times at the network stations (operating and maintenance times of the RTS) are exponentially distributed. The customers of the network cannot leave it and cannot come to it from outside. Thus, the network is a closed Jackson network by definition.
From the description of the RTS as a closed Jackson network we obtain ([12] [32] ) that the steady-state prob
abilities ![]() are given by the following:
are given by the following:
Theorem 1: A real-time system with N servers, K ![]() maintenance crews, r
maintenance crews, r ![]() different chan- nels operating under a maximum load regime with
different chan- nels operating under a maximum load regime with ![]() jobs in k-th channels at any instant, and exponentially
jobs in k-th channels at any instant, and exponentially
distributed operating and maintenance times (with parameters ![]() (for the k-th channel (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r)) and
(for the k-th channel (k = 1, ∙∙∙, r)) and ![]() respectively) has following values of the steady-state probabilities
respectively) has following values of the steady-state probabilities
![]() , (3.1)
, (3.1)
![]() , (3.2)
, (3.2)
where ![]() is a state of the RTS,
is a state of the RTS, ![]() is number of fixed servers of the RTS in the k-th channel and
is number of fixed servers of the RTS in the k-th channel and ![]() (k = 1,∙∙∙,r).
(k = 1,∙∙∙,r).
We will use the following notations:
1) ![]()
![]()
and
2) ![]() the probability that
the probability that ![]() fixed servers are assigned to the k-th channel
fixed servers are assigned to the k-th channel![]() .
.
Then, using Theorem 1, we obtain:
![]() ,
,
![]() (3.3)
(3.3)
where![]() ,
,![]() .
.
4. Performance Characteristics
After the text edit has been completed, the paper is ready for the template. Duplicate the template file by using the Save As command, and use the naming convention prescribed by your journal for the name of your paper. In this newly created file, highlight all of the contents and import your prepared text file. You are now ready to style your paper.
In this section we show how to obtain some useful performance characteristics of the RTS under consideration.
Each server can be in one of following states:
(i) busy (serving a job of one of the channels);
(ii) in maintenance;
(iii) on stand-by (for one of the channels);
(iv) waiting for maintenance.
Each job of k-th channel ![]() can be in one of two positions:
can be in one of two positions:
(i) in service;
(ii) out of service.
Keeping in mind that ![]() is a number of fixed servers assigned to the k-th channel
is a number of fixed servers assigned to the k-th channel![]() , we can repre-
, we can repre-
sent the number of channels and servers in different positions in terms of![]() , namely:
, namely:
Number of fixed servers is![]() ;
;
Number of fixed servers serving the k-th channel (also a number of jobs served in the k-th channel) is
![]() ;
;
Number of fixed servers on stand-by for the k-th channel is![]() ,
,![]() ;
;
Number of broken servers is![]() ;
;
Number of broken servers in maintenance is![]() ;
;
Number of broken servers waiting for maintenance is![]() .
.
Now we can obtain corresponding average values (performance characteristics):
![]()
for average number of fixed servers assigned to the k-th channel,![]() ;
;
![]()
for average number of fixed servers in the system;
![]()
for average number of busy servers serving the k-th channel (of jobs served in the k-th channel),![]() ;
;
![]()
for average number of nonserved jobs in the k-th channel,;
![]()
for average number of busy servers in the system (average number of jobs in service);
![]() for average number of broken servers;
for average number of broken servers;
![]()
for average number of broken servers in maintenance;
![]()
for average number of broken servers in maintenance assigned to the k-th channel, k = 1, ∙∙∙, r;
![]()
for average number of broken servers waiting for maintenance;
![]()
for average number of fixed servers on stand-by assigned to the k-th channel,![]() ;
;
![]()
for average number of fixed servers on stand-by in the system;
![]()
for average rate of servers arriving from maintenance;
![]()
for average rate of servers arriving from maintenance and assigned to the k-th channel,![]() ;
;
![]()
for average time spent on stand-by by server assigned to the k-th channel, ![]() (Little Theorem);
(Little Theorem);
![]()
for average time of server assigned to the k-thchannel being fixed, k = 1, ∙∙∙, r(Little Theorem).
![]()
is an average number of jobs served in the k-th channel(k = 1, ∙∙∙, r) at any given moment.
It follows from (3.3) that
![]() (4.1)
(4.1)
![]()
for average number of nonserved jobs in the k-th channel, k = 1, ∙∙∙, r.
The use of RTS relies on the principle of availability. We will introduce therefore several definitions.
Definition 4.1: For a channel (with ![]() jobs inside) operating under maximum load regime, the average availability is given by the following formula
jobs inside) operating under maximum load regime, the average availability is given by the following formula
![]() .
.
Definition 4.2: For a multichannel system (number of channels![]() ) operating under maximum load regime, the average system availability is given by the formula
) operating under maximum load regime, the average system availability is given by the formula
![]() .
.
Another important characteristic is an average loss penalty (or operation cost) of system operation in equilibrium during time unit.
Definition 4.3: Let ![]()
![]() be the cost of time unit during which one job in k-th channel is out of ser-
be the cost of time unit during which one job in k-th channel is out of ser-
vice (penalty). Then formula
![]()
represents average loss penalty function.
We also have the following important relationship between system availability and its loss penalty function, namely for ![]()
![]() (4.3).
(4.3).
5. Conclusion
We presented a multiserver multichannel real-time system working in maximum load regime with the shortage of maintenance teams. The system consists of r different channels with exactly ![]() jobs in k-th channel. We obtained analytically the steady state probabilities and various performance measures, providing complete description of this system. These analytical results could be used immediately without long simulations by researchers and practitioners. Our next goal is to find the optimal routing probabilities, maximizing the system availability.
jobs in k-th channel. We obtained analytically the steady state probabilities and various performance measures, providing complete description of this system. These analytical results could be used immediately without long simulations by researchers and practitioners. Our next goal is to find the optimal routing probabilities, maximizing the system availability.