1. Introduction
As well known, the integer and fractional quantum Hall effects (IQHE and FQHE) appear in a quasi-two dimensional electron system under a strong magnetic field perpendicular to the 2D electron channel the thickness of which is extremely thin [1] -[17] . Only the ground state along the z-direction of Figure 1 is realized actually for a low temperature and so we can treat the system as a 2D electron system. The confinement of the Hall resistance
at IQHE is extremely accurate and then the confined resistance is employed as the resistance standard [18] . The IQHE and FQHE are observed in various materials namely Si, GaAs, graphene and so on. The QHE appears independently of materials and is caused only by many electrons in a thin film. The Hall resistance is the ratio between Hall voltage and electric current. In the IQHE the Hall voltage is larger than about 10−4 Volts and the diagonal (potential) voltage is less than 10−11 Volt. Also in the FQHE the Hall voltage is extremely large compared with the potential voltage. Therefore this asymmetry of x and y directions in Figure 1 should be taken into consideration in the investigations of QHE. Consequently the total Hamiltonian of many electrons should be composed of three kinds of interactions namely the strong magnetic field interaction, the Coulomb interactions between electrons, and the electric field produced by the Hall voltage. However, many theories ignore the electric field along the Hall voltage. We take account of the electric potential along the y-direction in Figure 1.
We have developed the theory of Tao and Thouless [19] [20] and have found out the most uniform configuration of electrons in the Landau orbitals which yields the minimum expectation value of the total Hamiltonian 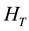 [21] -[25] . Since the Coulomb interaction depends only upon the relative coordinate between two electrons, the
[21] -[25] . Since the Coulomb interaction depends only upon the relative coordinate between two electrons, the 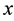 component of the total momentum is conserved in the Coulomb transition. Because of the momentum conservation and the most uniform configuration, the number of the allowed transitions takes the local maximum at the specific filling factors
component of the total momentum is conserved in the Coulomb transition. Because of the momentum conservation and the most uniform configuration, the number of the allowed transitions takes the local maximum at the specific filling factors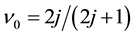 ,
, 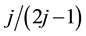 ,
, 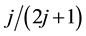 ,
, 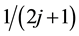 ,
, 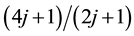 ,
, 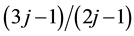 ,
, 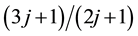 ,
, 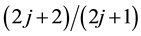 and so on. The transitions produce the binding energy of the electron pair. The larger the number of transitions, the pair energy is lowered. If the filling factor
and so on. The transitions produce the binding energy of the electron pair. The larger the number of transitions, the pair energy is lowered. If the filling factor  deviates from the specific filling factors
deviates from the specific filling factors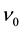 , many Coulomb transitions are forbidden. The forbidden mechanism yields the energy gap at the specific filling factors
, many Coulomb transitions are forbidden. The forbidden mechanism yields the energy gap at the specific filling factors . Thereby, the Hall confinement appears at the specific filling factors. Thus the present theory can explain the FQHE well without any quasi-particle [21] -[26] .
. Thereby, the Hall confinement appears at the specific filling factors. Thus the present theory can explain the FQHE well without any quasi-particle [21] -[26] .
The spin-polarizations of FQHE are obtained by V. Kukushkin, K. von Klitzing, and K. Eberl [27] . They clarified the magnetic field dependence of the polarization under fixing the filling factors. Although their experiments are rather old, the polarization curves versus magnetic field give us the very important knowledge. The experimental polarization-curves have the wide plateaus and small shoulders.
There are many spin-arrangements in the most uniform configuration of electrons in the Landau orbitals. These spin-arrangements have the same minimum-expectation-value of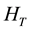 . That is to say many electron states with various spin-arrangements are perfectly degenerate. Therefore, we should exactly diagonalize the residual Coulomb interaction. We examine the partial Hamiltonian composed of the strongest and second strongest interactions between electrons. Then we have succeeded to diagnalize the Hamiltonian exactly. The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experimental data. Recently J. K. Jain has written the article [28] and compared the composite fermion (CF) theory [29] -[44] with the Haldane-Halaperin (HH) hierarchy theory [45] [46] . Also he summarized the composite fermion theory and showed the theoretical results on the spin-polarization of FQH states. We compare the polarizations by the CF theory with that by our theory in Section 5.
. That is to say many electron states with various spin-arrangements are perfectly degenerate. Therefore, we should exactly diagonalize the residual Coulomb interaction. We examine the partial Hamiltonian composed of the strongest and second strongest interactions between electrons. Then we have succeeded to diagnalize the Hamiltonian exactly. The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experimental data. Recently J. K. Jain has written the article [28] and compared the composite fermion (CF) theory [29] -[44] with the Haldane-Halaperin (HH) hierarchy theory [45] [46] . Also he summarized the composite fermion theory and showed the theoretical results on the spin-polarization of FQH states. We compare the polarizations by the CF theory with that by our theory in Section 5.
Next we observe the experimental data [27] in more details. Then we find small shoulders on the curves of the polarization versus magnetic field. The small shoulders appear at the middle between two wide plateaus. This property is similar to the famous feature in the spin-Peierls effect [47] . The spin-Peierls effect is caused by the lattice distortion with the period doubling the unit cell. The sum of spin-energy and distortion-energy (namely total energy) becomes lower than that without distortion. We applied the distortion to the intervals between Landau orbitals in the previous works [48] [49] where the magnitude of distortion was treated to be a fixed value. However the magnitude should be determined by minimizing the total energy in each field strength. Accordingly the magnitude of distortion depends on the field strength. The minimizing of the total energy needs a very complicated program and a long cpu-time. In this article we succeed to make the Mathematica program with parallel computation. The calculated results show the Peierls instability and the polarization curves are in better agreement with the experimental data than the previous results.
2. Fundamental Properties
A typical quantum Hall device is illustrated in Figure 1 where the current flows along the x-direction and the magnetic field 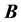 has the z-direction, namely
has the z-direction, namely![]() . In the absence of the Coulomb interaction between electrons, the Hamiltonian of a single electron is given by
. In the absence of the Coulomb interaction between electrons, the Hamiltonian of a single electron is given by
![]() . (1)
. (1)
Therein ![]() is the potential along the z-direction confining electrons to the thin conducting layer. The potential
is the potential along the z-direction confining electrons to the thin conducting layer. The potential ![]() has large potential difference between both ends,
has large potential difference between both ends, ![]() and
and ![]() as in Figure 2. In the right hand side of Equation (1),
as in Figure 2. In the right hand side of Equation (1), ![]() is the electron momentum and
is the electron momentum and ![]() is the effective mass of electron, the value of which differs from material to material. The value of
is the effective mass of electron, the value of which differs from material to material. The value of ![]() in GaAs is about 0.067 times the free electron mass.
in GaAs is about 0.067 times the free electron mass.
The eigen-value problem of ![]() is solved and the single-electron wave function
is solved and the single-electron wave function ![]() is expressed as
is expressed as
![]() (2)
(2)
where ![]() the Landau level number,
the Landau level number, ![]() the wave function of the ground state along z-direction,
the wave function of the ground state along z-direction, ![]() the Hermite polynomial of
the Hermite polynomial of ![]() -th degree and
-th degree and ![]() is the normalization constant. Also
is the normalization constant. Also ![]() is given by
is given by
![]() . (3)
. (3)
The eigenenergy is given by
![]() , (4)
, (4)
where ![]() is the ground state energy along the z-direction and
is the ground state energy along the z-direction and ![]() is the potential energy in Figure 2.
is the potential energy in Figure 2.
Next let us consider the many electron system. The total Hamiltonian is given by
![]() , (5a)
, (5a)
where ![]() is the total number of electrons and
is the total number of electrons and ![]() is the single particle Hamiltonian:
is the single particle Hamiltonian:
![]() . (5b)
. (5b)
The eigenstate of ![]() is described by
is described by ![]() which is specified by the set of Landau
which is specified by the set of Landau
![]()
Figure 2. Potential ![]() along the y-direction.
along the y-direction.
level numbers ![]() and momenta
and momenta![]() . The expectation value of the total Hamiltonian is expressed by
. The expectation value of the total Hamiltonian is expressed by![]() :
:
![]() , (6)
, (6)
where ![]() is the expectation value of the Coulomb interaction. Hereafter we call
is the expectation value of the Coulomb interaction. Hereafter we call ![]() “classical Coulomb energy”. We separate
“classical Coulomb energy”. We separate ![]() into two parts
into two parts ![]() and
and![]() .
. ![]() is composed of all diagonal parts and
is composed of all diagonal parts and ![]() is constructed only by the off-diagonal elements as follows:
is constructed only by the off-diagonal elements as follows:
![]() , (7a)
, (7a)
![]() . (7b)
. (7b)
Because the Coulomb interaction depends upon only the relative coordinate, the total momentum of the x-direction is conserved in this system as follows:
![]() (8)
(8)
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the initial momenta and
are the initial momenta and ![]() and
and ![]() are the final momenta via
are the final momenta via![]() . All the electrons
. All the electrons
in the ground state of ![]() exist in the lowest Landau levels
exist in the lowest Landau levels ![]() for a filling factor
for a filling factor ![]() because
because
electrons can take up- and down-spin states. If the electrons with the momenta ![]() distribute most uniformly in the Landau orbitals, the classical Coulomb energy takes the lowest value. Thereby the many-electron state becomes the ground state of
distribute most uniformly in the Landau orbitals, the classical Coulomb energy takes the lowest value. Thereby the many-electron state becomes the ground state of![]() . The momenta
. The momenta ![]() are determined by each centre positions
are determined by each centre positions ![]() namely
namely ![]() as in Equation (3). For any filling factor, we can find only one electron- configuration with the minimum energy of
as in Equation (3). For any filling factor, we can find only one electron- configuration with the minimum energy of![]() . The proof has been done in Ref. [21] . The residual Hamiltonian
. The proof has been done in Ref. [21] . The residual Hamiltonian ![]() acts between two electrons. All the initial states with the momenta
acts between two electrons. All the initial states with the momenta ![]() are
are![]() ,
,
![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() where the symbols
where the symbols ![]() and
and ![]() indicate up and down spins, re-
indicate up and down spins, re-
spectively. The final states are![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are the final momenta via the interaction
are the final momenta via the interaction![]() . Now we consider the Coulomb transitions of only between the degenerate ground states of
. Now we consider the Coulomb transitions of only between the degenerate ground states of![]() . The ground states have the most uniform configuration. Therefore the electron- configuration of the final state is equivalent to that of the initial state. So the final momentum set is the same as the initial one. Then we obtain
. The ground states have the most uniform configuration. Therefore the electron- configuration of the final state is equivalent to that of the initial state. So the final momentum set is the same as the initial one. Then we obtain ![]() or
or![]() . The case of
. The case of ![]() is removed because the diagonal matrix elements of
is removed because the diagonal matrix elements of ![]() are zero. Accordingly the final momenta become
are zero. Accordingly the final momenta become
![]() (9)
(9)
Even if Equation (9) is satisfied, the initial state is identical to the final state for the same spin direction of the two electrons. Therein the transition matrix element is zero. Accordingly non-zero matrix elements are
![]() (10a)
(10a)
![]() (10b)
(10b)
where![]() . We examine following three cases:
. We examine following three cases:
Case A:![]()
![]() (11a)
(11a)
Case B:![]()
![]() (11b)
(11b)
Case C:![]()
![]() (11c)
(11c)
Figure 3 shows the case A.
This transition is equivalent to the following process: the spin at site 1 flips from up to down, and the spin at site 2 flips from down to up without changing the momenta. Thus the Coulomb transition of the case A is equivalent to a spin exchange process which is described by the interaction![]() . Therein
. Therein ![]() is the spin transformation operator from down to up-spin state and
is the spin transformation operator from down to up-spin state and ![]() is the adjoint operator of
is the adjoint operator of![]() . Another Coulomb transition given by Equation (10b) is equivalent to
. Another Coulomb transition given by Equation (10b) is equivalent to![]() . Accordingly Coulomb transition between sites 1 and 2 is
. Accordingly Coulomb transition between sites 1 and 2 is
![]() (12)
(12)
where ![]() was already defined by Equation (11a). In this Coulomb transition, the classical Coulomb energy of the initial state is exactly equal to that of the final state.
was already defined by Equation (11a). In this Coulomb transition, the classical Coulomb energy of the initial state is exactly equal to that of the final state.
Next Figure 4 shows the case B.
Coulomb interactions in Cases B and C are equivalent to the following spin exchange interactions where ![]() and
and ![]() are the coupling constants defined by Equation (11b) and (11c), respectively.
are the coupling constants defined by Equation (11b) and (11c), respectively.
![]() (13)
(13)
Let us study two examples of ![]() and 2/5. The most uniform configuration is in Figure 5(a) and Figure 5(b). The spin-states are numbered sequentially from left to right as shown by green color. It is noteworthy that the site-number of spin is different from the orbital number. At the
and 2/5. The most uniform configuration is in Figure 5(a) and Figure 5(b). The spin-states are numbered sequentially from left to right as shown by green color. It is noteworthy that the site-number of spin is different from the orbital number. At the![]() , the strongest interaction acts between the nearest electron pairs which has the coupling constant
, the strongest interaction acts between the nearest electron pairs which has the coupling constant![]() . The second strongest interaction has the coupling constant
. The second strongest interaction has the coupling constant ![]() as shown in Figure 5(a). At
as shown in Figure 5(a). At![]() , the strongest and the second strongest interactions have the coupling constants
, the strongest and the second strongest interactions have the coupling constants ![]() and
and ![]() as shown in Figure 5(b).
as shown in Figure 5(b).
We examine the third strongest interaction at![]() . Therein another electron is inserted as seen in Figure 5(a). Therefore the interaction between the third nearest electrons becomes weak by the screening effect of the inserted electron in between the pair. At
. Therein another electron is inserted as seen in Figure 5(a). Therefore the interaction between the third nearest electrons becomes weak by the screening effect of the inserted electron in between the pair. At ![]() the third strongest interaction acts between the electrons placed in the fifth nearest orbitals where another electron is inserted as in Figure 5(b). Therefore the interaction
the third strongest interaction acts between the electrons placed in the fifth nearest orbitals where another electron is inserted as in Figure 5(b). Therefore the interaction
![]()
Figure 3. Equivalence of specific Coulomb transition and spin exchange interaction for case A.
![]()
Figure 4. Equivalence of specific Coulomb transition and spin exchange interaction for case B.
becomes weak by the screening effect of the interposing electron. Consequently the most effective interaction is obtained for ![]() as;
as;
![]() (14)
(14)
This Hamiltonian yields the quantum transition between the degenerate ground states. We take account of the Zeeman interaction and get the most effective Hamiltonian as
![]() (15)
(15)
where ![]() is the effective g-factor, B is the magnetic field,
is the effective g-factor, B is the magnetic field, ![]() is the electron spin operator of the z-direction and
is the electron spin operator of the z-direction and ![]() is the Bohr magneton. The Hamiltonians for
is the Bohr magneton. The Hamiltonians for ![]() and
and ![]() are given by
are given by
![]() (16)
(16)
![]() (17)
(17)
These three Hamiltonians can be exactly diagonalized by using the method of Ref. [50] .
3. Diagonalization of the Most Effective Hamiltonian for FQH States
We introduce a new mapping from a spin state to a fermion state. The down-spin state ![]() is mapped to the vacuum state
is mapped to the vacuum state ![]() and the up-spin state
and the up-spin state ![]() is mapped to the fermion state
is mapped to the fermion state ![]() where
where ![]() is the creation operator. Thereby the spin operators
is the creation operator. Thereby the spin operators![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are mapped as;
are mapped as;
![]() . (18)
. (18)
Many electron states are mapped to the many fermion states where the multiplying order of the creation operators is the same as the order of the up-spins:
![]() (19)
(19)
where the operators ![]() and
and ![]() satisfy the anti-commutation relations. The spin operators
satisfy the anti-commutation relations. The spin operators![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are mapped to the products of the fermion operators as follows:
are mapped to the products of the fermion operators as follows:
![]() (20a)
(20a)
![]() (20b)
(20b)
![]() . (20c)
. (20c)
It has been verified in Ref. [50] that the mapping ((20a), (20b), (20c)) is isomorphic.
Accordingly Hamiltonian Equation (15) is equivalent to the following form:
![]() . (21)
. (21)
We can exactly solve the eigen-value problem of ![]() by introducing new operators
by introducing new operators ![]() and
and![]() :
:
![]() , (22)
, (22)
where ![]() is the cell number. Thereby the Hamiltonian (21) becomes
is the cell number. Thereby the Hamiltonian (21) becomes
![]() , (23)
, (23)
where ![]() is the total number of cells given by
is the total number of cells given by ![]() (
(![]() is the total number of electrons). We apply a Fourier transformation to Equation (23) and obtain as
is the total number of electrons). We apply a Fourier transformation to Equation (23) and obtain as
![]() , (24)
, (24)
where
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,![]() . (25)
. (25)
In Equation (24) the term with one value of ![]() is expressed by the following matrix:
is expressed by the following matrix:
![]() . (26)
. (26)
This matrix has two eigen-values ![]() and
and ![]() which are given by
which are given by
![]() . (27)
. (27)
We introduce new annihilation operators ![]() and
and ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() . (28)
. (28)
Hamiltonian (24) is expressed by making use of ![]() and
and ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() . (29)
. (29)
Thus we have succeeded in diagonalizing the original Hamiltonian (15).
4. Spin-Polarization
The electron-spin polarization ![]() is defined by the thermodynamic mean value as follows:
is defined by the thermodynamic mean value as follows:
![]() (30)
(30)
where ![]() is the thermal average and the minus sign comes from the negative charge of electron. All the eigen-states are specified by the set of the numbers
is the thermal average and the minus sign comes from the negative charge of electron. All the eigen-states are specified by the set of the numbers![]() . The eigen-energy for
. The eigen-energy for ![]() is
is
![]() and the energy for
and the energy for ![]() is zero. The Boltzmann factor is
is zero. The Boltzmann factor is ![]() for
for ![]() and
and
![]() for
for ![]() where
where ![]() is the Boltzmann constant and
is the Boltzmann constant and ![]() is the temperature. Accordingly, the probability of
is the temperature. Accordingly, the probability of ![]() is
is![]() . Then the thermal average is obtained as follows;
. Then the thermal average is obtained as follows;
![]() . (31)
. (31)
Substitution of Equation (31) into Equation (30) gives![]() . Because the
. Because the
momentum interval is extremely small, the electron-spin polarization is expressed by the integration as
![]() . (32)
. (32)
Similarly we obtain the spin-polarization at the filling factors of 3/5 and 4/7 as follows:
![]() . (33)
. (33)
The calculated results are shown in Figure 6 which are in good agreement with the experimental data.
5. Comparison between Present Theory and Composite Fermion Theory
J. K. Jain examined the spin-polarization in the CF theory [28] . He wrote as follows: “For spinful composite fermions, we write![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are the filling factors of up and down spin composite fermions. The possible spin polarizations of the various FQHE states are then predicted by analogy to the IQHE of
are the filling factors of up and down spin composite fermions. The possible spin polarizations of the various FQHE states are then predicted by analogy to the IQHE of
spinful electrons. For example, the 4/7 state maps into![]() , where we expect, from a model that neglects interaction between composite fermions, a spin singlet state at very low Zeeman energies (with
, where we expect, from a model that neglects interaction between composite fermions, a spin singlet state at very low Zeeman energies (with![]() ), a partially spin polarized state at intermediate Zeeman energies
), a partially spin polarized state at intermediate Zeeman energies![]() , and a fully spin polarized state at large Zeeman energies
, and a fully spin polarized state at large Zeeman energies![]() .”
.”
The CF cyclotron energy is proportional to ![]() and the Zeeman energy is proportional to the applied magnetic field
and the Zeeman energy is proportional to the applied magnetic field ![]() as explained in the article [28] . Then the CF energy
as explained in the article [28] . Then the CF energy ![]() is equal to
is equal to
![]() (34)
(34)
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the coefficients. Therein
are the coefficients. Therein ![]() where
where ![]() is the CF Landau level number
is the CF Landau level number![]() . When the filling factor
. When the filling factor ![]() of electrons is samller than 2/3,
of electrons is samller than 2/3, ![]() is expressed by using the CF level number
is expressed by using the CF level number ![]() the number of attached flux quanta
the number of attached flux quanta ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() (35)
(35)
When the sign in the denominator is plus, the effective magnetic field is parallel to the applied magnetic field. So the coefficient ![]() becomes positive. On the other hand the effective magnetic field has opposite direction against the applied field for the minus sign in Equation (35). Then
becomes positive. On the other hand the effective magnetic field has opposite direction against the applied field for the minus sign in Equation (35). Then ![]() is negative. We obtain the sum of the CF cyclotron energy and the Zeeman energy for various CF levels and CF spins. The results are shown in Figure 7 where we find the crossing points between the energies for spin-up and down states. The ratio of the field strengths at the crossing points is 1:4:9:16 and so on. For an example
is negative. We obtain the sum of the CF cyclotron energy and the Zeeman energy for various CF levels and CF spins. The results are shown in Figure 7 where we find the crossing points between the energies for spin-up and down states. The ratio of the field strengths at the crossing points is 1:4:9:16 and so on. For an example ![]() the composite fermions occupy the lowest four levels which are indicated by the bold curves as in Figure 8(a). The ratio of the strength
the composite fermions occupy the lowest four levels which are indicated by the bold curves as in Figure 8(a). The ratio of the strength ![]() and
and ![]() is 1:4:9. Accordingly the spin-polarization depends on the magnetic field strength at zero temperature as in Figure 8(b).
is 1:4:9. Accordingly the spin-polarization depends on the magnetic field strength at zero temperature as in Figure 8(b).
It is noteworthy that the effective field is opposite against the applied field at![]() . Let us compare the spin-polarization of the CF theory with that of the present theory at a finite temperature. Figure 9(a) shows the CF result and Figure 9(b) our result at
. Let us compare the spin-polarization of the CF theory with that of the present theory at a finite temperature. Figure 9(a) shows the CF result and Figure 9(b) our result at![]() . The CF result is different from the experimental data [27] in the low magnetic field region.
. The CF result is different from the experimental data [27] in the low magnetic field region.
Similarly we compare the CF result with our result at ![]() in Figure 10(a) and Figure 10(b). Our theory employs only the normal electrons without any quasi-particle. The partial Hamiltonian with the strongest and second strongest interactions is diagonalized exactly. Then the results are in good agreement with the experimental data. On the other hand the results via the CF theory deviate from the experimental data. Moreover the direction of CF polarization at
in Figure 10(a) and Figure 10(b). Our theory employs only the normal electrons without any quasi-particle. The partial Hamiltonian with the strongest and second strongest interactions is diagonalized exactly. Then the results are in good agreement with the experimental data. On the other hand the results via the CF theory deviate from the experimental data. Moreover the direction of CF polarization at![]() , 3/5, 4/7, etc is opposite against that of normal electrons because the effective magnetic field is opposite against the applied field. But the direction of CF polarization at
, 3/5, 4/7, etc is opposite against that of normal electrons because the effective magnetic field is opposite against the applied field. But the direction of CF polarization at![]() , 2/5, 3/7, 4/9, etc is the same as that of normal electrons. So it is necessary to measure the direction of the polarization especially at
, 2/5, 3/7, 4/9, etc is the same as that of normal electrons. So it is necessary to measure the direction of the polarization especially at![]() , 3/5, 4/7.
, 3/5, 4/7.
6. Spin Peierls Instability in FQH States
When the experimental data [27] of the spin polarization is carefully observed, we can find a small shoulder in the middle of two wide plateaus. This structure resembles the famous mechanism “spin Peierls effect”. R. E. Peierls studied an electron system in a one dimensional crystal and considered the lattice distortion with the period doubling the unit cell. This distortion produces new band gaps and the energy becomes lower than without the distortion. The effect is called spin Peierls effect [47] .
We apply a new distortion for the intervals between Landau orbitals. We change the distance between orbitals in the first unit-configuration longer, that in the second unit-configuration shorter and so on. We call it “interval modulation”. As an example![]() , we illustrate the modulation in Figure 11 where we obtain new four
, we illustrate the modulation in Figure 11 where we obtain new four
ξ η ξ' η' ξ η ξ' η'
![]()
Figure 11. Coupling constants of interactions caused by distortion with double period.
coupling constants![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . The value of
. The value of ![]() is larger than
is larger than ![]() because the
because the ![]() interaction path is shorter than that of
interaction path is shorter than that of![]() . Also,
. Also, ![]() holds.
holds.
We express the distance between nearest Landau orbitals by the symbol ![]() in non-distortion case. The distance becomes
in non-distortion case. The distance becomes ![]() for an odd cell number and the other one becomes
for an odd cell number and the other one becomes ![]() for an even cell number. Then, the classical Coulomb energy
for an even cell number. Then, the classical Coulomb energy ![]() increases. The increasing value per electron is proportional to
increases. The increasing value per electron is proportional to ![]() as
as ![]() where
where ![]() is the constant parameter. We next examine
is the constant parameter. We next examine ![]() -dependence of
-dependence of ![]() and
and![]() . When
. When![]() , the coupling constant
, the coupling constant ![]() is weaker than
is weaker than ![]() because the
because the ![]() interaction path is longer than that of
interaction path is longer than that of![]() . When
. When![]() ,
, ![]() is stronger than
is stronger than ![]() because the
because the ![]() interaction path is shorter than that of
interaction path is shorter than that of![]() . So the
. So the ![]() -dependence in
-dependence in ![]() and
and ![]() is given by
is given by
![]() (36)
(36)
where ![]() is the coupling constant for the non-distortion case and
is the coupling constant for the non-distortion case and ![]() is the proportionality constant. A new dimensionless quantity
is the proportionality constant. A new dimensionless quantity ![]() is introduced as follows
is introduced as follows
![]() . (37)
. (37)
Thereby the coupling constants ![]() and
and ![]() is expressed as
is expressed as
![]() . (38)
. (38)
The increasing classical Coulomb-energy ![]() is also described by the distortion parameter
is also described by the distortion parameter ![]() as:
as:
![]() (39)
(39)
where ![]() is the dimensionless coefficient as
is the dimensionless coefficient as![]() .
.
We calculate the total energy produced by this distortion. Use of the isomorphic mapping namely Equations ((20a), (20b), (20c)) give the spin exchange Hamiltonian for![]() :
:
![]() (40)
(40)
We introduce new operators ![]() and make the Fourier transformation of the operators:
and make the Fourier transformation of the operators:
![]() (41)
(41)
![]() (42)
(42)
where ![]() is the total cell number namely
is the total cell number namely![]() , and
, and ![]()
![]() . Substitution of Equations (41) and (42) into Equation (40) yields
. Substitution of Equations (41) and (42) into Equation (40) yields
![]() (43)
(43)
For each value of![]() , the right hand side of Equation (43) is expressed by the following matrix
, the right hand side of Equation (43) is expressed by the following matrix![]() :
:
![]() . (44)
. (44)
Here we assume that the ratio ![]() is almost equal to the ratio
is almost equal to the ratio ![]() because the interval modulation gives the same effects to
because the interval modulation gives the same effects to ![]() and
and![]() . Then Equation (38) yields the following ratios:
. Then Equation (38) yields the following ratios:
![]() (45a)
(45a)
![]() . (45b)
. (45b)
Four eigen-values of M are expressed by the symbols λ1(p), λ2(p), λ3(p) and λ4(p)![]() . The eigen-energies is obtained by using Equations (45a) and (45b):
. The eigen-energies is obtained by using Equations (45a) and (45b):
![]() (46)
(46)
Then the diagonal form of the Hamiltonian (43) is expressed by the eigen-energies λ1, λ2, λ3, λ4 as:
![]() . (47)
. (47)
The thermal average ![]() is expressed by the eigen-energies as derived in Equation (31).
is expressed by the eigen-energies as derived in Equation (31).
![]() (48)
(48)
Then the spin exchange energy is
![]() . (49)
. (49)
We can replace the summation in Equation (49) by the integration because the total number of electrons is a macroscopic value.
![]() (50)
(50)
The total energy per electron is the sum of the classical Coulomb energy and the spin energy as
![]() . (51)
. (51)
Figure 12 shows the classical Coulomb energy for the parameter ![]() in Equation (39) by the dashed black curve. Also the spin-exchange energy
in Equation (39) by the dashed black curve. Also the spin-exchange energy ![]() at
at ![]() is expressed by the red dashed curve.
is expressed by the red dashed curve.
The blue curve indicates the total energy ![]() which has a minimum value at a non-zero
which has a minimum value at a non-zero![]() . Thus the interval modulation occurs actually.
. Thus the interval modulation occurs actually.
The ![]() state are illustrated in Figure 13. These coupling constants yield the
state are illustrated in Figure 13. These coupling constants yield the ![]() Hamiltonian which has the six eigen-values
Hamiltonian which has the six eigen-values![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . Also we obtain the eight eigen-values for the
. Also we obtain the eight eigen-values for the ![]() state.
state.
7. Spin Polarization with Interval Modulation
We have obtained the diagnal forms of the Hamiltonians which have the Peierls instability. The spin-polarization ![]() is given by the integration as:
is given by the integration as:
![]() (52a)
(52a)
![]() (52b)
(52b)
![]() (52c)
(52c)
We numerically calculate the spin-polarization ![]() by the following method: First we search the distortion
by the following method: First we search the distortion ![]() with the minimum total energy for each magnetic field. The searching process is shown in Figure 12 at
with the minimum total energy for each magnetic field. The searching process is shown in Figure 12 at ![]() and
and![]() . Thus we get the distortion value
. Thus we get the distortion value ![]() and the eigen-energies
and the eigen-energies ![]() for each magnetic field strength. The eigen-energies are substituted into Equations (52a), (52b) and (52c) and then the spin-polarization is obtained. The theoretical curve is shown in Figure 14.
for each magnetic field strength. The eigen-energies are substituted into Equations (52a), (52b) and (52c) and then the spin-polarization is obtained. The theoretical curve is shown in Figure 14.
Therein we use the parameter-values![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() for
for![]() . At
. At![]() , the parameter-values are
, the parameter-values are![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . At
. At![]() , the parameter-values are
, the parameter-values are![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() . The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental data as shown in Figure 14.
. The calculated results are in good agreement with the experimental data as shown in Figure 14.
Next we examine the![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() states with the interval modulation. For an example of
states with the interval modulation. For an example of ![]() the most uniform electron-configuration is illustrated in Figure 15.
the most uniform electron-configuration is illustrated in Figure 15.
![]()
Figure 12. Total energy versus distortion parameter![]() .
.
ξ η η ξ' η' η' ξ η η ξ' η' η'
![]()
![]()
![]() (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 14. Polarization of the present theory (red dots indicate the experimental data [27] ).
η ζ η' ζ' η ζ η' ζ'
The interval modulation yields the coupling constants![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() . (53)
. (53)
The ratios between the coupling constants satisfy the following relations;
![]() . (54)
. (54)
We express the spin-exchange and classical Coulomb energies by the same parameter ![]() as
as
![]() . (55)
. (55)
Therein the coefficient ![]() is newly introduced. Using the eigen-values of the matrices, we numerically calculate the spin-polarization curves which are shown in Figure 16.
is newly introduced. Using the eigen-values of the matrices, we numerically calculate the spin-polarization curves which are shown in Figure 16.
Next we examine the spin-polarization at![]() , 7/5, and 8/5. The most uniform electron-configuration and the coupling constants are shown in Figure 17 for two examples of
, 7/5, and 8/5. The most uniform electron-configuration and the coupling constants are shown in Figure 17 for two examples of ![]() and 8/5.
and 8/5.
The coupling constants at ![]() are
are ![]() as in Figure 17. Accordingly the coupling constants and the classical Coulomb energy are re-expressed by using
as in Figure 17. Accordingly the coupling constants and the classical Coulomb energy are re-expressed by using ![]() as follows:
as follows:
![]() (56)
(56)
![]() (57)
(57)
where the new coefficient ![]() takes the value
takes the value ![]() for
for![]() . The doubly occupied orbitals are indicated by the double lines where the electron pair has no polarization because of cancellation by up and down spins. The spin exchange forces act between electrons placed in singly occupied orbitals of Figure 17. That is to say two electrons per four electrons have no polarization at
. The doubly occupied orbitals are indicated by the double lines where the electron pair has no polarization because of cancellation by up and down spins. The spin exchange forces act between electrons placed in singly occupied orbitals of Figure 17. That is to say two electrons per four electrons have no polarization at![]() , four electrons per seven electrons have no polarization at
, four electrons per seven electrons have no polarization at ![]() and also six electrons per eight electrons have no polarization at
and also six electrons per eight electrons have no polarization at![]() . We numerically calculate the spin-polarization curves as in Figure 18.
. We numerically calculate the spin-polarization curves as in Figure 18.
Thus the small shoulders are caused by the Peierls instability as seen in Figure 14, Figure 16 and Figure 18.
The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experimental data.
8. Discussion
In Jain’s scheme the ![]()
![]() state is assigned to the superposition of the IQH state with
state is assigned to the superposition of the IQH state with ![]() and the composite hole (fermion) state with
and the composite hole (fermion) state with ![]()
![]() as mentioned in the Ref. [28] . Accordingly polarization behaviors of the two states resemble that of the
as mentioned in the Ref. [28] . Accordingly polarization behaviors of the two states resemble that of the ![]() state in the CF theory. On the other hand the
state in the CF theory. On the other hand the
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 17. Coupling constants at ![]() and 8/5. Double-line indicates a Landau orbital occupied by electron pair with up and down spins.
and 8/5. Double-line indicates a Landau orbital occupied by electron pair with up and down spins.
polarization behavior of the present theory at ![]() resembles that at
resembles that at ![]() because there are four electrons per unit-configuration in both
because there are four electrons per unit-configuration in both ![]() and 4/7 states. We can calculate the polarization versus magnetic field at
and 4/7 states. We can calculate the polarization versus magnetic field at ![]() and 6/5 by diagnalizing the
and 6/5 by diagnalizing the ![]() matrix (
matrix (![]() matrix for consisdering of spin Pierls effect) as mentioned in Sections 3-7. Accordingly the theoretical predictions at
matrix for consisdering of spin Pierls effect) as mentioned in Sections 3-7. Accordingly the theoretical predictions at ![]() and 6/5 are quite different between the CF theory and our theory. The present author cannot find the experimental curves of the polarization versus magnetic field at
and 6/5 are quite different between the CF theory and our theory. The present author cannot find the experimental curves of the polarization versus magnetic field at ![]() and 6/5. If there are already raw data in experiments, it is preferable to make the curve of the polarization versus magnetic field.
and 6/5. If there are already raw data in experiments, it is preferable to make the curve of the polarization versus magnetic field.
We cannot also find the experimental data of the spin direction. The effective magnetic field in the CF theory is opposite against the applied field for the filling factor![]() . So it is important to measure the direction of the polarization at the filling factors
. So it is important to measure the direction of the polarization at the filling factors![]() , 3/5, 4/7, etc.
, 3/5, 4/7, etc.
9. Conclusions
We have examined the 2D electron system with the total Hamiltonian composed of the three kinds of interactions namely the strong magnetic field interaction, the Coulomb interaction between electrons and the electric potential produced by the Hall voltage. We have found only one electron configuration in the Landau orbitals with the minimum expectation value of the total Hamiltonian for arbitrary filling factor. Up and down spins coexist when the magnetic field is weak. Accordingly there are various spin-arrangements with the same electron configuration. The many states with different spin-arrangements have the same Coulomb energy namely exactly degenerate states. Accordingly we must diagonalize the partial Hamiltonian between the degenerate ground states.
The total momentum along the x-direction conserves via the Coulomb interactions. When the electron 1 placed in the Landau orbital A transfers to the orbital B, the electron 2 placed in the orbital B should transfer to the orbital A because of the total momentum conservation and the relation between momentum and orbital position. We have found the most effective Hamiltonian which is composed of the strongest and second strongest Coulomb interactions. Then we have succeeded to diagonalize the most effective Hamiltonian exactly. The calculated eigen-energies yield the theoretical value of the polarization which has reproduced the wide plateaus on the spin polarization curves. Furthermore we have applied the interval modulation between Landau orbitals and have solved the eigen-equation of the new Hamiltonian. The total energy decreases by the interval modulation. So the modulation appears actually. Thereby the calculated polarization curves have the small shoulders in addition to the wide plateaus. The theoretical results are in good agreement with the experimental data [27] .
Acknowledgements
The author expresses his heartfelt appreciation for encouragement of Professor Masayuki Hagiwara, Professor Koichi Katsumata, Professor Hidenobu Hori, Professor Yasuyuki Kitano and Professor Takeji Kebukawa.