1. Introduction
During the last years a mathematical law, discovered more than a hundred years ago, gave new insights into the quality of public health data. Operational inefficiencies, systemic flaws and even fraud can be detected easier. This tool is called the “first-digit law” or “Benford’s law” [1] . It explains the distribution of statistical frequencies in naturally occurring data sets. It is based on the observation that some numbers occur more frequently than others in many real life data sets.
The exact mathematics of Benford’s law are beyond our article, but we would like to show that its intuitiveness is easy to understand. A small city with 100 pregnant women needs to double (to grow 100%) until the first-digit in the number of pregnant women will be replaced by a “2” (e.g. 200) as the first number. The number of pregnancies then needs again to grow 50% for the 3 and again at least 25% for the 4, until it ends up with 400 - 499 pregnancies. This shows that it is much easier―meaning here more frequent―to reach the lower numbers than the higher ones. This fact is addressed in Benford’s law.
Benford’s law was in recent years used to detect widespread fraud in big datasets (e.g. for the Greek economy [2] ) and so gained more popularity than before. Our objective was the application of this law to the data, which are published for the world’s Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR). MMR is one of the most important numbers for obstetrics and the sustainable development of vast regions of the world. It is important for public health and provides the basis for various political decisions, which affect mothers and children worldwide. We investigate whether MMR is really such a robust parameter as it is often accredited to be and whether Benford’s law either shows the reliability of the figures we have for MMR or detects possible anomalies.
2. Methodology
Benford’s law states that the probability of a leading occurring number 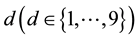 can be calculated following the equation:
can be calculated following the equation:
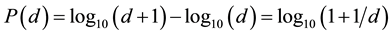 [3]
[3]
This distribution shows that the number “1” occurs as first or leading number is much more common than all other numbers―in around 30.1 %of the cases; the number “2” in 17.6%, the number “3” in 12.5%, the number “4” in 9.7%, the number “5” in 7.9%, the number “6” in 6.7%, the number “7” in 5.8%, the number “8” in 5.1% and the number “9” in around 4.6% [3] .
All expected frequencies for the second, third and fourth number can be calculated too [4] . The probabilities of their occurrence (now for the numbers 0 - 9) is for the second digit between 12% for the “0” and 8.5% for the “9” and the fourth digit than is approaching an almost uniform distribution of 10% [5] .
When natural demographic data cover more than two orders of magnitude, have no artificial cut-off point and provide five data in each group then they are likely to satisfy the law of Benford well [6] -[8] .
Deviating and non-conforming data are suspicious of systemic data challenges, arbitrary assignment of numbers, irregularities, psychological considerations, errors or fraud.
Benford’s law was applied to the data internationally available for MMR. Due to its widespread usage in organizations worldwide we used the data published in the UNICEF’s survey “The State of The World’s Children”. The reports of 2012 and 2014 were evaluated. They show adjusted data from 2008 and 2010 [9] [10] . To examine whether the deviation between the observed numbers and the expected numbers after the Benford law for first digits is at random or not we used the Chi-square test with an alpha value of 0.05, 8 degrees of freedom. Our null hypothesis (H0) was, that the numbers are correct (H1: There is a flaw in the numbers and they are not correct).
3. Results
1) The data of Unicef reports “The State of The Worlds Children” from 2012 and 2014 [9] [10] :
180 countries (2012: 172) were reviewed and all data concerning MMR were counted for the frequency of the occurrence of all numbers from 1 - 9 in the first position. Results of the expected and the observed values are summarized in Tables 1-3.
2) Graphical comparison of the observed and expected data:
Figure 1 shows the visual impression for the observed numbers plotted against the expected numbers in blue for Benford’s law.
3) The calculation of significance:
Chi-square for the Maternal Mortality Rate is 21.08 for 2008 and 19.97 for 2012. The cut off value for a chi- square distribution with eight degrees of freedom and a level of significance of 0.05 (alpha = 0.05) is 15.51 [11] [12] .
![]()
Table 1. Observed values for the Maternal Mortality Rate (found in the reported years 2012/14).
![]()
Table 2. Maternal Mortality Rate - expected values (expected after Benford’s distribution for 2012/14).
![]()
Figure 1. Expected and observed data concerning the frequencies of the first digit for 2008 and 2010 in the reports 2012 and 2014 (the Benford distributions are very similar for the two years, so only one was plotted for the better overview).
For 2008 and 2010 (the reports of 2012 and 2014) chi-square was higher than the cut off value. This had to lead to the rejection the null hypothesis.
The rejection of the null hypothesis means that the numbers observed in the publication are not following Benford’s law in the reports for 2010 and 2014. The deviation from the expected values need an explanation other than chance.
4. Discussion
The first-digit law or Benford’s law was introduced through the so called “forensic accounting” into the scrutinization of data. It monitors whether data sets are of natural origin or not [3] . Data sets being of natural origin, spanning several orders of magnitude and which are not subject to artificial limitations follow (e.g. in socioeconomic and demographic datasets) a distribution of their numbers, which was described as “first-digit law” first by Newcomb [13] , than by Benford [1] .
Surprisingly the knowledge of this statistical relation is not widely used in medicine. In our opinion the first-digit law is an easy to use, valuable and quick tool to identify data-sets in need of closer scrutiny. Additionally this law is accessible to the hard working clinician without thorough knowledge in statistics.
Benford’s law was used by us to scrutinize one of the most important data sets for policy making and programme evaluation in international public health. In the Unicef report “The state of the world’s children” [9] [10] , which is considered by Unicef as fundamental [14] because the data of this report are used by international organizations, programme managers and legislators worldwide [14] , we scrutinized the data for Maternal Mortality Rate. Various organizations rely on the correctness of these data, collected and adjusted through a very important, well known organization with a good reputation. MMR influences many policy decisions on national, regional and international level.
Nevertheless data for MMR in the reports of 2012 and 2014 significantly deviate from the expected values.
Distributions evaluated through the first-digit law and not following the expected distribution are in need of an explanation for their distribution. Benford’s law only states this fact without offering an explanation other than that the reason is not natural and not by chance. Benford’s law shows that a deeper evaluation of the mere fact of a distribution anomaly is needed. The reasons for the anomaly can reach from computational challenges, human errors or systemic operational discrepancies to psychological challenges and deliberate manipulation in the struggle for international funding.
Our reason to write this article and the purpose of this paper was to show that Benford’s law can be an indicator on when to be careful with data, even when they originate from well established sources and put together with care, expertise and experience. Awareness needs to be raised for the importance of a degree of suspicion towards established data sources. Additionally we wanted to show that this is possible even for the not specially trained clinician through this relatively new tool.
Following limitations of our study need to be considered. It was not possible to find the MMR for several countries in the Unicef report, what lowered the number of available data. The Vatican had to be counted as a country even when it has “by definition” no MMR. Some countries might not be considered as “full” countries by some scholars and other places with questionable status were not incorporated in the list of countries. Countries with an extremely low MMR will be much less affected by a deviation of the values, so that the importance of the registered imbalances lies much more on the shoulders of the (usually) poor countries with a high MMR.
All together we have to raise the suspicion, that these important data were not really reliable and accurate during the last years. Our analysis through the Benford distribution showed that data are not only flawed by the well known difficulties in data collection worldwide, which we all appreciate (remote areas, dictatorships, no money to pay the collectors, computer challenges etc. etc.)―but we have to suspect that there might be another systematic flaw to them. This would be well known from other socioeconomic data (e.g. tax evasion [15] ), but is rarely discussed in medicine.
5. Conclusion
International data available for MMR seem not to be as reliable as it is often thought. We should very critically reflect the importance of this finding―especially for future public health planning and funding in resource poor countries.