1. Introduction
We often face situations in which our initial assumptions are revised as we gather more information, such as when we read a news item in a newspaper. Imagine the headline is Mother kills son with heroin overdose. Without knowing much more, one might judge that the mother’s behavior is extremely morally wrong. What if reading further the news item states that the son was suffering from Huntington’s disease and his mother decided to give him a lethal injection, would your moral judgment of the mother’s behavior change? What if the article concluded that the mother was arrested and charged with manslaughter, would this signal another revision in your moral judgment? The main objective of this study is to examine whether moral judgments are revised with more information, and how they are revised as a result of the order of information that enables updating of knowledge of the scenario. In addition, the influence of consequences is also considered, and here too, the severity of the consequences of the scenarios is manipulated to examine their effect on moral judgment. Finally, because the present study also includes scenarios based on genuine news items, a second focus of investigation is whether moral judgments are sensitive to the veracity of the scenarios (i.e. fabricated or genuine) under scrutiny.
1.1. Order
Although not common in the moral judgment domain, there is work indicating that judgments are sensitive to the order in which information is presented ( Austin, Ruble, & Trabasso, 1977 ; Feldman et al., 1976 ; Petrinovich, & O’Neill, 1996 ; Sinnott-Armstrong, Mallon, McCoy, & Hull, 2008 ; Wiegmann, Okan, & Nagel, 2012 ). Wiegmann et al. (2012) point out two types of order effects (Primacy & Recency effects; Sequential effects). First, developmental studies show that the first and last items of information presented in a moral scenario lead to the most extreme moral judgments ( Austin et al., 1977 ; Feldman et al., 1976 ). Second, in the adult domain work has shown that if the first scenario in a sequence of multiple scenarios involves an action that is judged to be strongly prohibited, then this leads to more severe moral judgments generalize to other moral scenarios ( Petrinovich & O’Neill, 1996 ; Wiegmann et al., 2012 ). If however the critical action in the first scenario is judged to be permissible, then moral judgements for all subsequent scenarios are lenient ( Wiegmann et al., 2012 ). Crucially, both types of order effects have only been demonstrated with variants of a single scenario, namely the Trolley problem ( Foot, 1967 ). This is a moral scenario adapted from a thought experiment devised to explore a philosophical principle known as the doctrine of double effect (DDE). The DDE broadly asserts that it is prohibited to perform a bad act intentionally to bring about a good outcome, but it is permissible to do a good act intentionally that will bring about a bad outcome. In the original scenario a group of potholers that includes a fat man get stuck in a cave because the fat man blocks the entrance. The water level is rising, so by trapping the others inside the cave, the fat man is sure to drown them. Either they use a stick of dynamite to blow the fat man out of the entrance, but killing him in the process, or all five of them drown. Variants of this scenario have been used in psychological research on moral judgments to examine a variety of phenomena, including factors that will attenuate as well as increase the severity of moral judgments, and what is deemed a permissible action.
Taken together, this work suggests that order effects do impact on moral judgments, but only for a very specialist type of moral scenario. To address this issue, and to extend the work focused on examining order effects in novel ways, the present study frames moral scenarios within the context of reading a news item from a newspaper. The motivation for this is to contextualize the manipulation of order of presentation of information within an everyday type experience. Thus, the study manipulates the sequence order of a headline, main story, and conclusion of a moral scenario (typical order, atypical order, random order). Prediction 1: If primacy effects bias moral judgments, then the first item of information presented, regardless of what it is, will generate the most severe judgment compared with the second and last item in the sequence. Prediction 2: If people adjust their moral judgments as knowledge of the moral scenario is updated, then when information in the sequence implies that the morally dubious action is permissible, followed by information that implies that the action is prohibited, moral judgments should be adjusted upwards (from less severe to severe). When information in the sequence implies that the morally dubious action is prohibited, and is followed by information that implies the action is permissible then moral judgments should be adjusted downwards (from severe to less severe).
1.2. Consequences
The philosophical doctrine of consequentialism and DDE has influenced the interests of researchers in the moral judgment and reasoning domain. This may help explain why consequences of actions on moral judgments has been of explored in such detail by many researchers (e.g., Borg et al, 2006 ; Waldmann et al., 2012 ) as compared to say, the order of information on judgments. Essentially consequentialism and DDE posit that consequences and intentions should be the basis on which moral judgments are made. Whether this should be used as a benchmark for appropriately evaluating the rationality of moral judgments is still up for debate ( Parfitt, 2011 ; Waldmann et al., 2012 ). Nevertheless, what is clear is that people attend to details concerning the consequences of actions (or inaction in some cases) on the victim when making moral judgments. For instance, Borg et al.’s (2005) study manipulated a variety of factors that included: 1) the numerical consequences of an action (small vs large number of people/objects) that either resulted in 2) harm (active) or enabled harm to happen (passive), either 3) intentionally or unintentionally, on 4) people or objects. Borg et al.’s (2005) found that moral judgments (is it wrong?) and judgments of action (would you do it?) revealed a highly nuanced understanding of consequences, and sensitivity to the intentionality behind an action described in a moral scenario.
Rather than examining the consequences of actions on the victim as is typical in studies of moral judgment and reasoning, the focus of the present study is to consider the impact on moral judgments when the consequences to the perpetrator of the morally dubious action are manipulated. Often, the media is highly biased in the focus of details reported such that often the main story and conclusion concern the perpetrator rather than the victim ( Dowler, Fleming, & Muzzatti, 2006 ). Therefore, consistent with this, and keeping with the general theme of the study which is to simulate the kinds of processes that are experienced while processing actual real life news items, the consequences experienced by the perpetrator of the morally dubious action were either severe or not severe. For example, referring to the illustration at the start of this induction, the severe consequence would be The police discovered what the mother had done, and arrested and charged her with manslaughter. She is now in prison and is psychologically traumatized, and the not severe consequence would be The courts looked favorably on the mother and she was never charged. After a period of grieving, the mother was able to be at peace with her decision. As discuss, work in the moral judgment domain shows that people are sensitive to signals of the prohibitedness or permittedness of the morally dubious actions ( Wiegmann et al., 2012 ). On this basis, this study examined prediction 3: When all content of the scenario is held constant (i.e. headline, main story), and regardless of presentation order of Conclusion, if people are sensitive to the consequences of actions, moral judgements should be more severe when the conclusion contains details of severe consequences (prohibitedness) for the perpetrator than no severe consequences (permittedness).
1.3. Veracity and Dumbfoundness
As said, the aim of the present study is to simulate real world experiences in which moral judgments are likely to be adjusted as a result of exposure to further information about the morally dubious action referred to in the scenario. However, the possibility of adjustment can be called into question if one assumes that the underlying basis on which moral judgments are made is unconscious. That is to say, the processes that govern our moral judgments may be predominantly emotionally driven and inaccessible to conscious reflection ( Greene et al, 2001 ; Haidt, 2001 ). One demonstration of this is moral dumbfoundedness. Simply put, this refers to situations in which people judge a scenario as morally wrong, but cannot provide a good rationale to support their judgment. The reason for this failure is that explanations are shown to be post-hoc rationalisations because all rational bases on which severe moral judgments can be made have been removed from the scenario. For instance, one such scenario that generates moral dumbfoundedness refers to a family that decide to eat their pet dog after having gone on holiday and tasted the local delicacy which was cooked dog; they suffer no consequences as a result. Another scenario that reliably generates moral dumbfoundedness refers to the actions of two siblings that go on a hiking trip and decide to have sex with each other. Regardless of being told in both scenarios that there were no negative consequences resulting from the morally dubious actions described, participants typically judge these scenarios as morally wrong ( Haidt, 2001 ; Haidt & Hersh, 2001 ). The idea being here that moral outrage is founded on emotional signals that aren’t supported by rational thought, and so the individual has difficulty providing reasoned arguments for their moral judgment.
One of the many criticism that has been levelled at work of this kind is that the scenarios are artificial (as with the Trolley problem), and so participant’s moral judgments in response to them do not necessarily reflect the kinds of judgments that are often made when they can bring relevant knowledge to bear on helping them judge the scenario ( Musschenga, 2009 ; Sauer, 2012 ). The present study uses the Dog and Incest scenarios, along with four stories based on genuine new items from national newspapers, in order to compare patterns of moral judgments for fabricated and genuine moral stories. Thus, the study tests prediction 4: If people are sensitive to the veracity of the scenario, then the pattern of moral judgments for fabricated and genuine moral stories should differ.
2. Experiments 1a and 1b
2.1. Methods
2.1.1. Design and Materials
Experiment 1a was carried out in a lab setting in which participants were provided with a questionnaire comprised of 36 pages with six moral scenarios. They were required to make moral judgments at their own pace in a quiet isolated room. Two of the moral stories were adapted from the Dog story and Incest story mentioned in the introduction section (fabricated stories). The four other scenarios were based on news items from UK National newspapers (broadsheets, and tabloids) over a period of two months (August 2014-October 2014). Initially 8 news items were selected, but these were rated by two independent raters from the Dynamic decision-making (DLDM) lab (www.magdaosman.co.uk) on criteria concerning tone, controversy, and sensitivity. Based on the agreement of the raters the 8 items were reduced to 4, which then were used in the present study (genuine scenarios). The headline of each of the four stories based on genuine news items that were used in the present study is: Mother kills son with heroin overdose (as referred to in the introduction); Parents turn their own children in to the police for vandalism; Woman lies under oath to save her husband from a crime he did commit; Woman abandons her baby in the toilet. In addition, two other raters from the DLDM lab were asked to classify the sets of conclusions for each of the moral scenarios according to whether they had severe consequences for the perpetrator, or no severe consequences, there was 100% agreement on all 6 moral stories (severe-consequence conclusion, no-severe consequence conclusion). Informed consent was acquired from every participant before they could continue with the main part of the study.
On each page participants were presented either with the headline, the main story, or the conclusion for a given scenario (See Table 1).
The Headline was always presented so that at face value, a clearly prohibited action was described in the simplest possible terms. For the main story mitigating or permissible’ details were presented, and for the conclusion for half the group the details signalled that the morally dubious action was prohibited, and for the other half, the details signalled that the action was permissible. For all conditions, the scenarios were presented randomly, but for each scenario the headline, main story, and conclusion, were presented together consecutively in order (typical) or random (random). The word length of the headline across scenarios ranged between 5 - 16, for the main story the word length ranged between 36 - 43, and for the conclusion the word length ranged between 23 - 34. In addition to this manipulation, half of the group were presented with scenarios in which a severe consequence was experienced by the perpetrator(s) (severe-consequence conclusion), or no severe consequence was experienced (no-severe consequence conclusion). For each item of information participants were presented (i.e. headline, main story, conclusion) they were asked to Please indicate your moral judgment on the following scale according what you think about the actions of the (the perpetrators were detailed here corresponding to each scenario), and responded on a scale ranging from 1 not at all morally wrong, to 7 extremely morally wrong. At the end of the questionnaire, participants were asked to judge for each scenario whether they thought it was fabricated or genuine, which was used as an index of participant’s sensitivity to the veracity of the scenarios. Thus participants were randomly allocated to either: typical-order-no-severe-consequence (N = 12), typical-order- severe-consequence (N = 12), random-order-no-severe-consequence (N = 12), random-order-severe-consequence
![]()
Table 1. Fabricate and genuine moral scenarios that were included in Experiment 1a and Experiment 1b.
(N = 13). A total of 49 participants (19 Males) with a mean age of 19 (SD = 1.4) responded to an email advertisement to take part in the experiment. They were predominately students from across different departments at Queen Mary University of London.
Experiment 1b was identical to Experiment 1a with two exceptions. First, participants were recruited in the same way as Experiment 1a, but this time they filled in the questionnaire online. Second, rather than randomizing the order of presentation of the three items of scenarios as was the case in the random conditions in Experiment 1a, to fully test the idea that there are strong recency effects on moral judgments, in Experiment 1b the order was fixed so that half of received the typical-ORDER and the rest received the atypical-order (main story, headline, conclusion). Participants were randomly allocated to one of four conditions: typical-order-no-severe- consequence (N = 22), typical-order-severe-consequence (N = 23), atypical-order-no-severe-consequence (N = 22), atypical-order-severe-consequence (N = 17). A total 84 participants (10 Males) took part. They had a mean age of 21 (SD 6.2). Recruitment was based on responses to an email advertisement sent to the Queen Mary University of London experimental participant pool.
3. Results
Experiment 1a: Analyses were conducted on moral judgments that were collapsed across fabricated scenarios, and collapsed across genuine scenarios. A 2 (type of Scenario: fabricated, genuine) × 2 (consequence: severe, not severe) × 2 (order: typical, random) × 3 (detail: headline, main story, conclusion) ANOVA was carried out. Mauchley’s test indicated that the assumption of sphericity had been violated for Type of scenario, χ2(2) = 7.8, p = .02, therefore Greenhouse-Geisser corrected tests were reported (ε = .9). Also for Type x Detail, χ2(2) = 7.0, p = .03, spherecity was violated, so Greenhouse-Geisser corrected tests were reported (ε = .9).
As observed in Figure 1, there was a clear difference such that moral judgments were more severe overall for fabricated scenarios (M = 5.6, SD =1.0) than genuine scenarios (M = 4.1, SD = .9), F(1, 45) = 100.5, p < .0005,
![]()
Figure 1. Mean moral judgments (SE +/− 1) by scenario type (fabricated, genuine) and detail (headline, main story, conclusion) and condition (typical-no- severe-consequence, typical-severe-consequence, atypical-no-severe-consequence, atypical-severe-consequence) in Experiment 1a.
 = .70. It was also evident that judgments differed according to what item from the scenarios was being judged, F(1.7, 77.5) = 13.6, p < .0002,
= .70. It was also evident that judgments differed according to what item from the scenarios was being judged, F(1.7, 77.5) = 13.6, p < .0002, 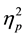 = .43. Overall the conclusion (M = 4.0, SD = 1.2) was judged less severely than either the headline (M = 5.0, SD = .8) and the main story (M = 4.8, SD = .9), though no differences were found between judgments for headlines and main stories (t < 1). There was an interaction such that the order of presentation influenced judgments of particular details, F(1.7, 77.5) = 9.11, p < .0002,
= .43. Overall the conclusion (M = 4.0, SD = 1.2) was judged less severely than either the headline (M = 5.0, SD = .8) and the main story (M = 4.8, SD = .9), though no differences were found between judgments for headlines and main stories (t < 1). There was an interaction such that the order of presentation influenced judgments of particular details, F(1.7, 77.5) = 9.11, p < .0002, 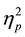 = .17. Judgments were more severe when the headline was always presented first (M = 5.3, SD = .7) than in a random part of the sequence (M = 4.7, SD = .7), but the Main story was judged more severely in a random part of the sequence (M = 5.1, SD = .9) than if it followed the headline (M = 4.4, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). There was also an interaction suggesting that consequences impacted judgments for particular details of the scenarios, F(1.7, 77.5) = 13.6, p < .00002,
= .17. Judgments were more severe when the headline was always presented first (M = 5.3, SD = .7) than in a random part of the sequence (M = 4.7, SD = .7), but the Main story was judged more severely in a random part of the sequence (M = 5.1, SD = .9) than if it followed the headline (M = 4.4, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). There was also an interaction suggesting that consequences impacted judgments for particular details of the scenarios, F(1.7, 77.5) = 13.6, p < .00002, 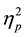 = .23. When there were severe consequences the conclusions were judged more severely (M = 4.8, SD = 1.1) than when there were no severe consequences (M = 3.3, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). Finally, there was an overall main effect, F(1, 45) = 11.2, p < .005,
= .23. When there were severe consequences the conclusions were judged more severely (M = 4.8, SD = 1.1) than when there were no severe consequences (M = 3.3, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). Finally, there was an overall main effect, F(1, 45) = 11.2, p < .005,  = .20, suggesting that judgements were more severe when the consequences were severe (M = 5, SD = .8) than when they were not (M = 4.6, SD = .5).
= .20, suggesting that judgements were more severe when the consequences were severe (M = 5, SD = .8) than when they were not (M = 4.6, SD = .5).
Experiment 1b: The same sets of analyses were performed on moral judgments collapsed across fabricated scenarios, and genuine scenarios. Mauchley’s test indicated that the assumption of sphericity was only violated for Type of scenario x Detail, χ2 (2) = 24.2, p = .005, spherecity was violated, so Greenhouse-Geisser corrected tests were reported (ε = .8).
As with Experiment 1a, in Experiment 1b moral judgments were more severe overall for fabricated scenarios (M = 5.4, SD = .9) than Real (M = 4.4, SD = .8), F(1, 80) = 81.5, p < .00005,  = .51 (see Figure 2). There was also an interaction suggesting that judgments differed depending on the order of presentation and the origin of the scenarios, F(1, 80) = 13.88, p < .0003,
= .51 (see Figure 2). There was also an interaction suggesting that judgments differed depending on the order of presentation and the origin of the scenarios, F(1, 80) = 13.88, p < .0003, 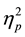 = .15. Judgments were more severe overall when items were presented in a typical order than an atypical order for fabricated scenarios (p < .05). Also, judgments were less
= .15. Judgments were more severe overall when items were presented in a typical order than an atypical order for fabricated scenarios (p < .05). Also, judgments were less
![]()
Figure 2. Mean moral judgments (SE +/− 1) by scenario type (fabricated, genuine) and detail (headline, main story, conclusion) and condition (typical-no- severe-consequence, typical-severe-consequence, atypical-no-severe-consequence, atypical-severe-consequence) in Experiment 1b.
severe overall when the items were presented in a typical order than an atypical order for genuine scenarios (p < .05).
Consistent with Experiment 1a, Experiment 1b showed that judgments differed depending on the particular detail of the scenarios that participants made judgments about, F(1.9,155.4) = 16.3, p < .0003, 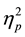 = .17. Overall the conclusion (M = 4.5, SD = 1.0) was judged less severely than either the headline (M = 5.0, SD = 1.0) and the main story (M = 5.0, SD = 1.0), and no differences were found between headline and main story (t < 1). The order of presentation of the details influenced judgments for particular details of the scenario, F(1.9,155.4) = 63.6, p < .0005,
= .17. Overall the conclusion (M = 4.5, SD = 1.0) was judged less severely than either the headline (M = 5.0, SD = 1.0) and the main story (M = 5.0, SD = 1.0), and no differences were found between headline and main story (t < 1). The order of presentation of the details influenced judgments for particular details of the scenario, F(1.9,155.4) = 63.6, p < .0005, 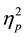 = .44. More specifically, judgments were more severe when the headline was always presented first (M = 5.4, SD = .8) than second (M = 4.3, SD = .7) ? consistent with Experiment 1a, and the main story was judged more severely when presented first (M = 5.6, SD = .8) than when it was presented second (M = 4.3, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). There was an interaction suggesting that consequences effected judgments for particular details of the scenario depending on the order in which they were presented, F(1.9,155.4) = 5.0, p < .01,
= .44. More specifically, judgments were more severe when the headline was always presented first (M = 5.4, SD = .8) than second (M = 4.3, SD = .7) ? consistent with Experiment 1a, and the main story was judged more severely when presented first (M = 5.6, SD = .8) than when it was presented second (M = 4.3, SD = .7). No other comparisons were significant (F < 1). There was an interaction suggesting that consequences effected judgments for particular details of the scenario depending on the order in which they were presented, F(1.9,155.4) = 5.0, p < .01, 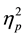 = .1. Specifically, judgments were more severe for headlines presented in a typical than atypical position when the consequences were severe (M = 5.9, SD = .6) than when the consequences were not severe (M = 4.8, SD = .6). No other comparisons were significant (F<1). There was an interaction between consequence and order, F(1, 80) = 11.2, p < .001,
= .1. Specifically, judgments were more severe for headlines presented in a typical than atypical position when the consequences were severe (M = 5.9, SD = .6) than when the consequences were not severe (M = 4.8, SD = .6). No other comparisons were significant (F<1). There was an interaction between consequence and order, F(1, 80) = 11.2, p < .001,  = .12. Judgments in the typical-no-severe- consequences condition were less severe (M = 4.4, SD = .6) than the atypical-no-severe-consequences condition (M = 4.9, SD = .7), and the typical-severe-consequences condition, (M = 5.1, SD = .5) (see Figure 2).
= .12. Judgments in the typical-no-severe- consequences condition were less severe (M = 4.4, SD = .6) than the atypical-no-severe-consequences condition (M = 4.9, SD = .7), and the typical-severe-consequences condition, (M = 5.1, SD = .5) (see Figure 2).
Finally, turning to detection of fabricated and genuine scenarios, given that there were no differences in the accuracy of responses between Experiment 1a and 1b (F < 1), scores were collapsed. The scores were based on accuracy for detecting whether fabricated scenarios were false (out of two), and whether genuine scenarios were true (out of four). A wilcoxon signed rank test revealed that participants were more accurate at judging the genuineas real (M = 45%, SD = 32) than the fabricated scenarios as false (M = 78%, SD = 20), Z = 7.9, p < .0005. This suggests that participants mistakenly judged the fabricated scenarios as genuine more often than the genuine scenarios as fabricated.
4. Discussion
The present study was designed to examine the extent to which moral judgments are adjusted as knowledge of the moral scenario is updated. In addition the study also investigated the effects of order of presentation of specific details concerning a moral scenario (headline, main story, conclusion), the consequences (severe, not severe), and the veracity of the scenarios (fabricated, genuine). Prediction 1 and Prediction 2 were for the large part supported. In both experiments it appeared that there was a primacy effect. In general, the first item of information concerning a scenario was judged most severely (regardless of whether the item signalled a permissible or prohibited view of the morally dubious action). However moral judgements did not remain fixed as information about the scenario changed. There appeared to be a downward adjustment of moral judgments when the headline (signalling prohibited action) was presented first and the main story was presented second (signalling permissible action). There was also a downward adjustment when the headline appeared after the no-severe- conclusion (signally permissible action half the time), and the same adjustment occurred after the main story was presented. More to the point, this suggests that moral judgments are labile, and are adjusted in a systematic way according to what the next item of information signals about how to evaluate the severity of the morally dubious action referred to in the scenario. This also suggests that while there may be a bias in judgment based on the first detail presented, no matter how strong that judgment is people have the capacity to adjust their judgments in systematic ways.
Prediction 3 was also supported. Across both experiments, generally judgments were less severe for groups that received scenarios in which the conclusions indicated no severe consequences for the perpetrator(s) than for groups in which the consequences for the perpetrator(s) were severe. Clearly when reading about scenarios with consistently severe consequences, this sets the tone for the way in which scenarios are judged in general. Furthermore, this study provides further evidence that order effects on moral judgments is generalizable to moral scenarios other than the trolley problem.
In addition, by attempting to approximate the type of updating process that may occur in day to day experiences of making moral judgments, participants were shown to have had access to the basis on which their judgments were made, otherwise, they would have been unlikely to adjust their moral in predictable and syste-
matic ways based on incoming evidence. This also suggests that people are likely to be consciously aware of the rationale behind their moral judgments, which presents a challenge to popular theories such as the Haidt’s (2001) Social intuitionist model in which a dualist position is espoused, and in which people are claimed to be, by default, making moral judgments on the basis of unconscious mechanisms. The general dual-process approach has been heavily criticized ( Osman, 2004, 2013, 2014 ), and more specifically, with respect to the Social intuitionist model, various theorists have been critical of this approach on the grounds of conceptual confusion, and the weakness of empirical findings on which the model has been supported ( Huebner, 2011, 2014 ; Teper, Zhong, & Inzlicht, 2015 ). Thus, the evidence from the present study also provides a further challenge to the Social intuitionist model because it suggests that people can spontaneously adapt their moral judgments in line with new consciously processed information, on which their judgments are based.
Are moral judgments special?
A popular position posits that moral judgements are domain specific, and that we have an innate universal moral grammar that equips us with the ability to judge social interactions along moral lines ( Mikhail, 2007 ). This position also implies that moral judgments are made in ways that are unlike other types of judgments (e.g., causal). Alternative to this, the domain-general position posits that processes involved in making moral judgments are no different to judgments of other types ( Gigerenzer, 2010 ; Waldmann et al., 2012 ), and so factors that influence judgments in general (e.g., order of information, belief updating) will also effect moral judgments in the same way. The causal judgment domain is a useful comparison because many have claimed that there is a close correspondence between moral and causal judgments ( Knobe & Fraser, 2008 ; Waldmann et al., 2012 ). Primacy effects, can have a profound impact on causal judgments, (e.g., presenting information first that implies a generative relationship between cause and event [the joint presence, or joint absence of cause and effect) increase causal judgments as compared to cases when information presented first] suggests a preventative relationship [presence of cause or effect, in the absence of the other]) ( Dennis & Ahn, 2001 ). There is also a substantial literature to suggest that causal judgments are revised and updated in accordance with contingency information ( Perales et al., 2007 ). The present study provides evidence to suggest that moral judgments, just like causal judgments, are sensitive to the order (primacy and recency, sequential effect), and to the type of information (severity of conclusion, prohibitedness of actions) on which judgments are based. Moreover, it lends further credence to the idea that moral judgments are likely to be domain general.
Does the veracity of the moral scenario matter?
In the present, when asked to identify which of the 6 scenarios were genuine or fabricated, participants tended to incorrectly judge the fabricated scenarios as genuine. This suggests that participants may have had a bias to judge most of the scenarios as genuine, which distorted the accuracy in favour of genuine scenarios. Nevertheless, judgments were consistently lower for genuine than the fabricated scenarios ( Haidt, 2001 ; Haidt & Hersh, 2001 ), which suggests that while they couldn’t reliably detect them, they did respond differently to them, and treated them as more extreme scenarios. Therefore, this suggests that the content of the moral scenarios is of importance, and perhaps more efforts should be made to draw from genuine day to day moral scenarios that people encounter in order to increase the validity of the studies investigating moral psychology.
5. Conclusion
The present study included two experiments that showed that moral judgments are made in a dynamic fashion in which the severity of moral judgments is adjusted as new information about the scenario is encountered. Overall the findings suggest that the order in which information related to a moral scenario is presented impacts on the severity of the judgments made. In addition, judgments differed depending on whether the scenario was fabricated or from genuine news stories, in the former case judgments were far more severe, suggesting that artificial moral scenarios typically used in psychological research may present a distorted picture of the judgment process when faced with real moral scenarios. Moreover, judgments were also sensitive to the severity of the conclusion. When the morally dubious action was described as permissible, judgments were less severe. Complimenting this, judgments were more severe when the morally dubious action was described as prohibited. Taken together the evidence strongly suggests that people’s moral judgments are flexible, and likely to be accessible to consciousness, because information that is being attended to when forming a judgment is a strong predictor of the direction of change in moral judgments.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Miss Pham for her invaluable contribution to the study. The work that is reported was carried out by Christina Bui Pham and formed part of her final year undergraduate dissertation. The author also wishes to thank William Nelson for his insightful comments and suggestions on an earlier draft.