Modeling the Surface Ozone Concentration in Campo Grande (MS)—Brazil Using Neural Networks ()
1. Introduction
Surface ozone (O3) is one of the most important pollutants in troposphere. Its concentration in any given area is the result of the combination of its formation, transport, destruction and deposition. The sources of O3 include: 1) photochemical reactions involving its precursors like volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides with natural or anthropogenic origin; 2) downward transport from stratosphere; and 3) long-range (intercontinental) transport of ozone from distant pollutant sources [1] . The increase of precursor emissions due to the economical development of many countries in the world led to the rise of the O3 surface concentrations [2] -[5] . Consequently, a public concern about its negative effects on human health, climate, vegetation and materials has been systematically observed [6] -[8] .
Regarding the human health protection, several studies were implemented to predict the O3 concentrations [9] -[11] . The statistical models are the most commonly used, due to the complexity of the chemical chain reactions that are associated to O3 formation and destruction. In this context, linear and nonlinear models have been applied to predict the concentration of this air pollutant. Multiple linear regression, principal component regression, and quantile regression are, among others, examples of linear models [12] [13] . Conversely, artificial neural networks are the most commonly nonlinear used models [11] [14] -[18] . Evolutionary procedures to determine predictive models have also been applied, which include autoregressive threshold models optimized by genetic algorithms (GAs) and genetic programming models [19] [20] . Moreover, in several research fields GAs were also applied to optimize the data division and the weights or the structure of the artificial neural networks [21] - [24] .
2. Data
Data of daily levels of ozone (O3) were obtained at the Institute of Physics of the Federal University of South Mato Grosso. The measurements performed by Ozone Analyzer are based on the absorption of ultraviolet radiation by ozone molecules. The analyzer is installed near Campo Grande, isolated from any possible local source of ozone. The measurement of ozone concentration is continuously performed every 15 minutes during 24 hours per day.
The arithmetic average values have then been calculated per day and it is assumed that such values are representative of the air pollution in the city of Campo Grande. Data about rainfall, average temperature and relative humidity were obtained from the database of Embrapa Gado de Corte located at Campo Grande.
In this study, we initially perform a descriptive analysis of variables that are subsequently associated with the following parameters: the ozone concentration data; the climatic rainfall variables; the maximum temperature; the relative humidity and the wind speed from the 2004 thru 2010 period.
3. Methods―Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks or ANN can be used to perform several functions such as classification; linear and non-linear regression; association; and mapping tasks [25] -[27] . They may be used in a wide range of applications including adaptive control; optimization; medical diagnosis; decision making; as well as information; signal and speech processing [28] . ANN models are characterized by: 1) a set of processing neurons, also designated as nodes; 2) a pattern of connectivity among neurons; 3) an activation function for each neuron; and 4) a learning rule. The processing neurons are distributed in layers: 1) input or first layer; 2) output or last layer; and 3) hidden layers, between the input and the output layers. The neurons in different layers are linked by synapses, each one storing a weight value. The way that these linkages are done defines the structure of the network. These models were described in further details in references [27] and [29] .
In this study, a feed forward ANN with three layers was applied to predict surface ozone concentrations with five input variables (O3, T, RH, speed, precipitation). A linear function has been used as activation function for the output neuron. Concerning the hidden neurons, four functions were tested: sigmoid, hyperbolic tangent, inverse and radial basis. The early stopping method, i.e. the training procedure is stopped when an increase of validation error is observed, was applied attempting to avoid the over fitting.
Daily data were continually stored and considered all values from January 2004 to December 2010 in this study. The total data has been divided in two parts: a training group within 2/3 of the total data and a test group having 1/3 of the data. For the training and validation of the results, observed data of ozone concentration are then necessary. The program for training and test of ANN were developed using the software MATLAB from Mathworks (www.mathworks.com), 2008 version.
Different net topologies of the Feedforward Multilayer Perceptron were tested aiming the desired map, taking into consideration diverse variations of the number of neurons for the intermediate layers. Since the air temperature, the humidity index, the rainfall precipitation average, the wind velocities and the transport fleet are the main factors influencing the estimative of ozone concentration, their maxima, their minima and the average values were used as input data for the ANN.
Functions like tangent sigmoid type were used as activation for the intermediate layers while functions of linear type were used as activation for the output layer, featuring this neural net as a sort of universal approximator of functions. The data standardization processes were made depending on the kind of activation function in the output layer of the ANN. This procedure is considered necessary.
The MATLAB software offers two forms of data standardization in the interval [−1,1] with average = 0 and variance = 1. The total data were divided in 2/3 considered for training and 1/3 for validation.
Therefore, the following procedure has been systematically applied: the free parameters are randomly created in the beginning of training. Knowing that these initial conditions influence the final result of the training, the network architectures have been trained ten times, after which it is selected the structure presenting the highest value for the determination coefficient r2. This coefficient is calculated from the data of the observed ozone concentration used in the test sample and the respective values estimated by ANN.
Diverse net topologies were trained varying the number of neurons; the activation functions in the intermediate layers; and the numbers of the interactions aiming the desired map. See the principal results expressed in Table 1.
The ozone values estimated by the ANN were compared to the numbers calculated by the accumulated percentage error; to the Average Relative Error (ERM); to the exactitude coefficient of Willmot [30] “d”; and to the performance index “c”. The ERM was calculated from Equation (1).
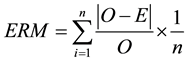 (1)
(1)
where: E is the estimated value and the observed value O.
According to [31] the exactitude or index of Willmott “d” and the trust or performance coefficient “c” are considered to correlate the estimated values with the measured values. The exactitude, related to the detachment of the estimated values in relation to the observed values, is statistically given by the agreement index proposed by Willmott [30] . Their value varies from zero, for total disagreement, to 1, for the perfect agreement. The index is given by Equation (2):
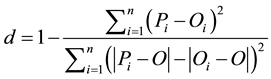 (2)
(2)
In the previous equation Pi is the estimated value; Oi is the observed value; and O is the average of the observed values.
The performance index “C”, presented in reference [31] , evaluates the performance of the different methods of estimation. This index gathers the indexes of precision given by the coefficient of correlation “r”, which indicates the degree of dispersion for the obtained data in relation to the average, i.e. the random error and the agreement “d”. The index “C” is calculated according to Equation (3).
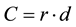 (3)
(3)
Camargo and Sentelhas [31] proposed a criterion to interpret the performance of the estimation methods according to the index “C” presented in the Table 2. A ANN capable of satisfactorily estimate the concentration of surface ozone is obtained after developing and analyzing the training algorithm and the realization of analyses of the available climate data.
This estimation is realized by mapping the relation among the maximum, average and minimum temperature data; the maximum, average and minimum related humidity; the wind speed; the rainfall; the number of automotive vehicles that were counted as new in the period; and the concentration of reference ozone, which is the desired output.
4. Results and Discussions
The selected ANN presents the best performance with the minimum configuration possible. This configuration is composed of one entrance layer within three variables, two intermediate layers having each one 4 and 2 artifi-
![]()
Table 1. Parameters tested in the training of ANN.
![]()
Table 2. Criteria interpretation for the estimative performance of surface ozone concentration.
cial neurons respectively, and one neuron in the output layer. The Sigmoid Hyperbolic Tangent type function was adopted as activation for the neurons in the intermediate layer. Generally the trained nets presented better performances with smaller numbers of cycles. In fact, the ANN selected reached better efficiency after 200 cycles. Beyond this point it has been verified that the nets with more than 200 cycles presented “memorization” problems.
The annual average value is C = 0.81 with a great performance and an annual monthly average of performance equal to 0.79. In Table 3 the values of the performance index (C) and of the average quadratic error (ERM) to the ANN are presented. Lowest values of ERM associated with highest values of “C” indicate the performance of the methodology in the estimative of the ozone concentration from the collected data.
The developed ANN generally presented good performances, except for the data resulting from the month of July, for which the statistic index ERM is equal to −0.32 corresponding to values of “C” that are of very poor performance. Actually, the ozone concentrations presented four months of excellent performance, as shown in the Table 3.
The generally good performance of the ANN is mainly due to the large amount of used data during its training making its learning easier. Another relevant contribution to reach the obtained performance is the fact that different architectures have been tested for the networks, i.e. different number of layers, learning algorithms, number of cycles, etc. Published studies like references [31] and [32] evaluated several architectures for the ANN, obtaining exceptional performances. It has been emphasized is those works that the number of cycles used during the training of the ANN was high, easing its learning and reducing the possibility of memorization occurrence. The memorization effect generally leads the ANN to present good statistic performances, i.e. to a high value of “C” and a low value of ERM basically because the ERM is calculated based exclusively in the sample of the available data. However, the memorization also leads to serious distortions of the spatial ozone concentration calculation making it extremely high or extremely low at certain points.
A direct observation of the values obtained from the ANN, which are exhibited in Table 3, indicates that the effect of memorization does not occur in the process since no severe deviations of the estimated ozone concentration can be noticed.
Analyzing the data of Table 3 it is possible to verify that the average concentrations vary between 10.32 and 29.69 ppb with general decreasing in the months of January, February and March, which correspond to the local rainfall season when it rains basically every day. Conversely, the highest values are systematically evidenced in the months of August, September and October that corresponds to the period used to prepare the soil for the plantation and South Mato Grosso is a highly productive State of crops.
Our results indicate that elevated values for R2 and “d” were obtained. Such results can be directly compared to other studies pointing out previsions for daily ozone concentrations as presented in references [22] and [33] , for which the values of R2 and “d” are (0.60 and 0.86) and (0.61 and 0.78) respectively. The average annual values of R² and “d” obtained in this paper are (0.8796 and 0.923798).
In Figure 1 it is exhibited the graphic comparing the observed and predicted values obtained from the model during the phase of validation. Figure 2 presents the histograms of the residues of the model evaluated in the phase of validation. A good model must have a normal distribution of the residues, i.e. the histogram of the residue must be symmetric typically having the shape of a bell. In order to visualize the performances of the model and of the ANN, the observed and the simulated values have been compared, as shown in Figure 3. This graphic shows a good adjustment of the model to the observed data, equally in the phase of estimation/training as well as in the phase of validation.
To evaluate the fit of the model must perform an analysis of the waste. This analysis can be by the graph of the residual variances of each observation in relation to the values adjusted by the model. A model has set and the graphic with the points closest to zero in the range −2 and 2 (Figure 4). Another chart that is also a good indicator of model fit is the graph of the observed values of the response variable in relation to the values set by the model. The points of this graph should be close, indicating that the fitted values are close to observed values (Figure 3 and Figure 4) [34] .
![]()
Table 3. Statistical indicators for the adjustment between the observed values of the ozone and the estimated values by ANN; monthly average relative error; values of “C” from January of 2004 to December 2010.
![]()
Figure 1. Concentration of observed and predict ozone in the phase of ANN validation.
![]()
Figure 2. Observed and estimated values for the concentration of ozone in the phase of ANN validation.
![]()
Figure 3. Simulation and validation of the observed/trained values.
![]()
Figure 4. Graphics and residual values of deviations observed in terms of adjusted values, the histogram of the response variable for the model of ozone concentration.
5. Conclusion
The use of methods to estimate the surface ozone concentrations provides the average behavior of certain parameters under study, which may become very useful for works concerned with the modeling of air quality. The main results of this specific work lead us to initially conclude that the ANN developed to estimate the ozone concentration reached very good statistic performances. The ANN put into operation returned the spatial concentrations of ozone without the presence of large variances in the resulting estimations. Nevertheless, it is necessary to keep improving the training use of ANN and variations of their architecture in order to obtain better statistic results. Finally, the mean average square error may decrease or even increase depending on the number of variables and the complexity of the resulting ANN architecture. The correlation values can be adjusted according to the data size that is input to the network for calculation. It is important to consider variables that represent further adequately the described environment as well as consider the development of more complex appropriate network architectures that would enable forecast for longer periods.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.