Restricted Daily Feeding of Liquid Meal Reduces the Motivation of Rats to Get Food ()
1. Introduction
It has been established that various physiological functions in rats are regulated by the circadian pacemaker, which is located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus and is entrained by the light-dark cycle [1] . Moreover, it is also known that these physiological functions are modified by restricted daily feeding (RF), in which food supply is restricted to a fixed time each day [2] [3] . Particularly well documented are the prefeeding peaks in adrenocortical activity [4] and locomotor activity [5] [6] . The prefeeding peaks are not entrained by the light-dark cycle and do not depend on the SCN [7] . RF can reset the phase of peripheral molecular oscillation without the participation of SCN clock function [8] . Based on these findings, the prefeeding peaks are believed to be an expression of endogenous circadian oscillation that is entrained by RF and whose pacemaker is located somewhere outside the SCN.
On the other hand, the motivation to get food seems to be important in the developing of the prefeeding peaks [9] . Previously, we reported that feeding liquid meal to rats placed under RF attenuates the prefeeding peak in adrenocortical activity compared with the situation in rats fed solid meal under RF [10] . Furthermore, masticatory dysfunction was reported to affect the central nervous system [11] [12] . Masticatory dysfunction impaired memory and learning ability [11] . We reported that placing an incisal cap affects plasma corticosterone levels in the rat, indicating that occlusal disharmony affect hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis [12] . These studies suggest that mastication affects the motivation to get food. To corroborate this hypothesis, we carried out experiments in the present study to determine whether there was a difference between locomotor activities of rats subjected to RF of liquid meal (LM rats) and those of rats subjected to RF of solid meal (SM rats).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Male rats of the Wistar strain were bred and reared in animal quarters, in which environmental conditions were controlled as follows: temperature, 22˚C ± 1˚C; humidity, 60% ± 5%; and a 12-h light:dark cycle (lights on from 06:00 to 18:00). Light intensity at the cage surface was approximately 100 lux. Just after delivery, body weights of all pups were measured to standardize the weight of each litter. The size of each litter was adjusted to 6 males until weaning. Rats were fed commercial pellet rat chow (MF, Orient Yeast Co., Tokyo, 3.6 Kcal/g) and tap water ad libitum, unless otherwise stated. All experiments were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals at Hokkaido University Graduate School of Dental Medicine.
2.2. Measurement of Locomotor Activity
At 3 months of age, each rat was transferred to a separate cage, and their spontaneous locomotor activities were continuously monitored by an Animex (Animex III, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), as described previously [13] , and analyzed using a Chronobiology Kit (Stanford Software Systems, Stanford, CA, USA). This instrument measures changes in capacitance of a resonance circuit installed beneath a cage. The amount of activity was expressed as counts per 15 min, which were recorded when the animal moved.
2.3. Experimental Procedures
Twelve male rats bred from 2 mothers on the same day were used in this study. At the beginning of the experiment, the 12 rats were divided into two groups. During ad libitum feeding for 2 weeks, the 12 rats were supplied with solid meal (MF). After ad libitum feeding, RF was carried out for 18 days in such a way that rats had free access to meal and water only from 1000 to 1200 hours. During RF, rats in one group (LM rats) were supplied with diet that consisted of MF powder mixed with water in a blender at a ratio of 1:4 (w/v), dispensed through a graduated feeding tube (Dyets Inc., Bethlehem, PA, USA), and rats in the other group (SM rats) were supplied with solid meal (MF). Body weight and the amount of food intake were measured at 16:00 of each day during the experiment.
2.4. Analyses of Activity Rhythm
Locomotor activity of each rat was determined every hour, and the averaged locomotor activities of each rat during ad libitum feeding (1 week), the first week of RF, and the second week of RF were calculated. Furthermore, relative locomotor activity of each rat during RF was defined as follows.
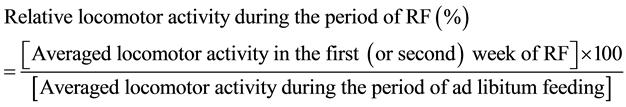
Data were analyzed using SPSS Version 10 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post-hoc Bonferroni testing were used for comparisons between groups. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
Table 1 shows changes in body weight in the LM rats and the SM rats during the experiments. The weights of LM rats and SM rats did not significantly differ at any stage of the experiments.
Figure 1 shows averaged relative locomotor activities of 6 LM rats during the light period and the dark period. The relative locomotor activities of the LM rats in the hours of 10 - 11, 11 - 12 and 13 - 14 were significantly higher in the second week of RF than in the first week of RF (F1,10 = 5.348; p = 0.042, F1,10 = 7.309; p = 0.024, and F1,10 = 21.756; p = 0.001, respectively) (Figure 1(a)). On the contrary, the relative locomotor activities of the LM rats in the hours of 23 - 0, 0 - 1 and 3 - 4 were significantly lower in the second week of RF than in the first week of RF (F1,10 = 8.164; p = 0.017, F1,10 = 3.961; p = 0.047, and F1,10 = 38.023; p < 0.001, respectively) (Figure 1(b)).
![]()
Table 1. Changes in body weight in the LM rats and the SM rats.
Data are expressed as means ± SE (n = 6); LM rats, rats supplied with liquid meal; SM rats, rats supplied with solid meal; RF, restricted daily feeding.
![]()
Figure 1. Averaged relative locomotor activities of rats subjected to RF of liquid meal (LM rats) during the light period (a) and dark period (b). Solid bars and open bars express the data of averaged relative locomotor activities in the first week of RF and second week of the RF, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SE (n = 6). ★★p < 0.01 and ★p < 0.05 vs. the first week of RF.
Figure 2 shows averaged relative locomotor activities of 6 SM rats during the light period and the dark period. The relative locomotor activities of the SM rats in the hours of 10 - 11, 13 - 14 and 14 - 15 were significantly higher in the second week of RF than in the first week of RF (F1,10 = 6.500; p = 0.026, F1,10 = 23.713; p = 0.001, and F1,10 = 18.177; p = 0.002, respectively) (Figure 2(a)), and there was no significant difference between the locomotor activities during the dark period in the first week and second week of RF (Figure 2(b)).
Figure 3 shows averaged relative locomotor activities of 6 LM rats and 6 SM rats during the light period and the dark period in the second week of RF. The relative locomotor activities in the hours of 10 - 11, 13 - 14 and 14 - 15 during the light period were significantly higher in the SM rats than in the LM rats (F1,10 = 4.476; p = 0.049, F1,10 = 5.194; p = 0.048, and F1,10 = 12.311; p = 0.013, respectively) (Figure 3(a)), and the relative locomotor activities in the hours of 18 - 19, 19 - 20, 20 - 21, 23 - 0 and 0 - 1 h during the dark period were also significantly higher in the SM rats than in the LM rats (F1,10 = 36.001; p < 0.001, F1,10 = 8.138; p = 0.024, F1,10 = 20.056; p = 0.001, F1,10 = 10.063; p = 0.014, and F1,10 = 6.124; p = 0.027, respectively) (Figure 3(b)).
Figure 4 shows representative double-plotted records of locomotor activities of an LM rat (a) and an SM rat (b).
4. Discussion
The present study indicated that the pattern of locomotor activity of rats subjected to RF of liquid meal was different from that of rats subjected to RF of solid meal.
The strength of the prefeeding peak in locomotor activity during the light period became greater in both LM rats and SM rats as the RF procedure advanced (Figure 1(a) and Figure 2(a)). However, the strength of the prefeeding peak in locomotor activity of LM rats was significant smaller than that in locomotor activity of SM rats (Figure 3(a)). The anticipatory prefeeding peak in locomotor activity is the expression of feeding-associated circadian rhythm, the nature of which has been intensively studied [4] . The built-up process of the prefeeding peak found in the present study is actually the process in which the feeding-associated circadian rhythm entrains to the feeding cycle [7] . However, the fact that the prefeeding peak in LM rats was significantly smaller than that in SM rats indicated that the feeding-associated circadian oscillation that developed by feeding with liquid
![]()
Figure 2. Averaged relative locomotor activities of rats subjected to RF of solid meal (SM rats) during the light period (a) and dark period (b). See the legend of Figure 1 for details.
![]()
Figure 3. Averaged relative locomotor activities of LM rats and SM rats during the light period (a) and dark period (b) in the second week of RF. Solid bars and open bars express the data of averaged relative locomotor activities of LM rats and SM rats, respectively. Data are expressed as means ± SE (n = 6). ★★p < 0.01 and ★p < 0.05 vs. LM rats.
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 4. Representative double-plotted records of locomotor activities of LM rats (a) and SM rats (b). The two parallel lines in the actographs indicate the onset and end times of meal supply. Black bars on the abscissa indicate the dark period.
meal was less potent than that in the case of feeding with solid meal.
It has been reported that diet-induced obesity suppressed the prefeeding peak in locomotor activity in rats [14] . This finding can be interpreted as rhythm suppression by high calorie intake during the meal time. Regretfully, amount of liquid or solid meal that was digested by rats was not able to be measured accurately because of dropping of meal in the cage. Therefore, we were not able to calculate the calorie intake in SM rats and LM rats. The difference between the levels of prefeeding locomotor activity of the LM rats and SM rats found in the present study might not be due to the difference between the energy metabolism in the LM rats and that in the SM rats, however, because there was no significant difference between changes in body weights of the LM rats and SM rats during the experimental period. It has been reported that motivation, not the amount of food consumed, seemed to be important in the development and persistence of prefeeding peaks in locomotor activity [9] . Therefore, the results of the present study suggest that RF of liquid meal reduces the motivation of rats to get food during meal time.
It was reported that periodic nutrition supplied with liquid meal established plasma corticosterone rhythm by feeding-associated circadian oscillations [15] . On the contrary, periodic nutrition supply by a parenteral tube failed to produce a prefeeding peak in plasma corticosterone [15] . This study suggested an important role of the oro-gastrointestinal tract, especially oral feeding in formation of the feeding-associated circadian oscillations. Previously, we reported that a prefeeding peak in plasma corticosterone level was detected in LM rats as well as in SM rats, although the strength of the prefeeding peak in LM rats was much smaller than that in SM rats, suggesting that liquid meal attenuated the meal anticipation in the adrenocortical activity in rats subjected to RF [10] . These results and the present result suggest that mastication for digesting solid meal is one of the factors that determine the strength of the feeding-associated circadian oscillation. Further study is needed to examine the role and mechanism of the mastication in establishing of the feeding-associated circadian oscillation.
Several studies have shown that there is a relationship between mastication and brain function, especially spatial memory. Both performance in a radial arm maze task and acetylcholine release in the parietal cortex in aged rats were impaired after extraction of teeth, and it has been proposed that the impairment in spatial memory was due to dysfunction of the central cholinergic system [16] . Furthermore, reduced mastication induced impairment of spatial memory associated with hippocampal neuron loss [17] .
When the RF schedule is imposed, rats learn the time of meal presentation. Therefore, the development and persistence of the feeding-associated rhythm can be regarded as acquisition and retention of memory for time [9] . In addition to spatial memory, the present study and our previous study [10] suggested that there was an important link between mastication-induced stimulation and memory for time in rats subjected to RF.
Other interesting findings in the present study are that the locomotor activity of LM rats during the dark period became suppressed as the RF procedure advanced (Figure 1(b)) and that the level of locomotor activity of LM rats was significantly lower than that of SM rats during the dark period (Figure 3(b)). Many physiological functions are regulated by the SCN in the hypothalamus, the light-entrainable circadian pacemaker, and nocturnal animals such as rats must increase their locomotor activity during the dark period to get food [18] . RF of liquid meal might affect the activity of the SCN, resulting in low locomotor activity during the dark period, the mechanisms of which remain to be studied.
5. Conclusion
It is concluded that RF of both liquid and solid meals affects locomotor activity of rats but that the pattern of locomotor activity of rats subjected to RF of liquid meal is different from that of rats subjected to RF of solid meal in the respects of low prefeeding peak during meal time and suppression of locomotor activity during the dark period.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No. 2546316003).