Using Fuzzy Theory in %GR&R and NDC of Measurement System Analysis ()
1. Introduction
In the 1980s, Motorola in the United States created a set of techniques known as Six Sigma to improve quality management systems. Subsequently, this technique was successfully adopted by major enterprises such as General Electric, producing benefits including reduced costs, and gradually leading a new wave of thinking about quality across the globe [1] . Companies have participated in quality certification such as ISO9000 to strengthen operations, systems, product quality, corporate image, and international marketing, at the same time as winning more orders and enhancing competitiveness [2] . Chen [3] explained that in order to produce high quality products, good quality management systems are indispensable. Therefore, quality systems such as ISO9001:2000 and TS 16949 have become the major quality system management standards for both traditional and high-tech industries and crucial performance indicators [4] .
In quality management, measurement techniques can be used to determine whether a product meets certain specifications and safety requirements; thus, measurement techniques are effective tools for increasing product quality [5] . A good measurement system is critical to the entire manufacturing process. During the measurement process, an evaluation of the measurement equipment is carried out to assess whether the equipment is suitable for use with the measurement system. Therefore, establishing the quality of measurement produced by the measurement system and measurement equipment is of particular importance [6] .
As the precision and accuracy of different types of measurement equipment have increased, companies have developed various methods for measuring quality. The objective of the analysis of measurement methods is to find the total variation between measurement methods, widely referred to as the measurement uncertainty [7] . If the measurement analysis during the manufacturing and testing process is biased, the measurement results will be unreliable [8] , jeopardizing the survival of the firm. Therefore, a sophisticated measurement system is needed to manufacture products that meet the quality requirements of customers. Here, equipment variation (EV) plays a critical role. Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility (GR&R) is used to identify the sources of variation in the measurement process. In this process, smaller measurement errors indicate effective process control [9] . Therefore, only measurement systems with acceptable GR&R can correctly measure product safety and specifications. At present, enterprises use the Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) Reference Manual in TS 16949:2009 to develop factory measurement systems and assess GR&R acceptability. MSA tests the measurement capability and quality of measurement equipment, ensuring that the quality of measurement systems is maintained. A study by Pai [10] assessed the relationship between different tasks as a basis for improving the effectiveness of the measurement system and carrying out preventative and corrective maintenance. Ensuring that a measurement system is correctly applied in the production process is critical to quality inspection [11] . Conversely, poor precision of the measurement system will lead to poor product quality and impairment of consumer rights [12] .
The introduction of QS 9000/TS 16949 certification and Six Sigma has ensured that quality control personnel now pay more attention to measurement systems and GR&R [13] . In recent years, industry personnel involved in quality-related work have applied GR&R analysis of measurement variation as judgment criteria, generally using the standards set out in the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and MSA manuals to assess whether measurement systems are capable. This study attempts to integrate fuzzy theory and proposed a new method to calculate %GR&R and then compare the %GR&R calculated according to the methods in MSA manual and that calculated from the proposed method. Itaims to propose method to determine the %GR&R and NDC that can reflect the measurement system variance. For that, managers can apply the proposed method to decide whether a measurement system is capable and acceptable. Managers, therefore, can discover measurement system problems as early as possible and take necessary actions to correct the system. The research steps are showed in Figure 1.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Measurement of Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility
Mandel’s [14] research looked at variability in GR&R, defining repeatability as the variance in measurement results for repeated tests on the same material within a single laboratory, and reproducibility as the variance in measurement results for repeated tests on the same material in different laboratories. GR&R is therefore applied to compare the capability of different laboratories.
Research by Montgomery and Runger [9] found that measurement systems play a critical role in helping or-
ganizations improve quality. Therefore, a successful measurement system should provide effective techniques for dealing with process variation (PV) and be able to establish the causes of variation. Measurement systems use GR&R to analyze the sources of measurement variation and quantify the variation. Tsai [15] used the X-bar- R chart to analyze GR&R. This method pairs standard deviation over the entire range to obtain the GR&R measurement variation. The X chart is used to show variation in measurement capability or whether measuring equipment is able to identify variation between items, while the R chart is used to explain measurement errors or the measurement capability of operators, referred to as gauge repeatability.
Montgomery and Runger [16] followed their earlier study [9] by using a nested design model and factorial design, in addition to GR&R and confidence interval estimation of parameters for measurement variation, to show the main weaknesses of modified ANOVA. Mandel [17] followed up previous research to assess the influence of inspectors, environment, and equipment on variation in reproducibility. Variation in measurements for the same materials, but using different inspectors, different equipment, and different measurement systems is calculated. Measurement system variance is defined as the mean square of the measurement system variationminus the mean square of variation within measurement systems divided by the number of repeated measures. Therefore, measurement system variance plus repeatability variance produces the reproducibility variance. This definition can be used for both discrete and continuous measurement results. Subsequently, Mandel [18] used this definition to calculate the repeatability variance and reproducibility variance of an actual measurement system for discrete data.
Reilly [19] defined accuracy as how closely a measurement value obtained by an instrument confirms the actual value of the sample. Repeatability is calculated by repeat measures on the same sample. The precision of an instrument is calculated by the consistency of its results across multiple measures. Reproducibility is the consistency when measuring the same sample at different times, or by different operators, or by different instruments (but using the same model). De Bievre [20] defined repeatability as the measurement precision obtained using the same operator, measurement system, and location for the same test object and material. In contrast, reproducibility looks at the measurement precision when different measurement systems at different locations are used for the same test object and material. Jorgensen [21] showed that types of measurement variation include bias, stability, and linearity, demonstrating that the categories of measurement variability are suitable for anX-bar-R chart. However, when plotting the graph, it is first necessary to observe whether the measurement systems are controlled, have sufficient discrimination power, and have no system errors following repeat measures. Research by Al-Refaie and Bata [22] pointed out that GR&R used to assess measurement capacity during the manufacturing process is a form of variance analysis. Repeatability analysis shows variation in measurement capacity, while reproducibility analysis shows whether measurement variation factors are present.
Research by Dolezal et al. [23] found that when calculating the GR&R model, if the inspectors are fixed, the use of a mix effects model is more appropriate. In addition, Burdick et al. [24] included measurement method factors in the original GR&RANOVA model. Finally, Dolezal et al. [23] produced a similar conclusion: assuming there are not too many inspectors, the mix effects model produces better outcomes. Pan [25] proposed three methods to estimate GR&R: ANOVA, classical GR&R, and long form. In this study, ANOVA provides a more accurate estimation of variance, since it is able to estimate the interaction effects between factors. In contrast, classical GR&R and long form are unable to estimate the interaction effects between variables.
Assuming inspectors and parts both have fixed effects, Wang and Eldon [26] used a bootstrapping nonparametric approach to statistical inference to estimate the GR&R point estimates and confidence interval. Bootstrapping uses data resampling to estimate statistical distribution. Pan [27] used Montgomery and Runger’s [16] estimated measure variation confidence interval to carry out a simulated comparison of the length of the confidence interval for variation among a sample size of parts (n), number of inspectors (p), and replicate measures (k). The results of the simulation show that given the same npk combination, it is recommended that more inspectors be allocated to the measurement. If the number of inspectors is fixed, more samples should be taken, reducing the number of repeated combinations.
Fang and Wang [28] showed that traditional GR&R and the long form method can allow onsite inspectors with no statistical background to quickly analyze the quality of the measurement system. However, it cannot provide accurate measurement when the effects of inspectors and parts interact. Therefore, they proposed a revised estimation model that corrects the failure of traditional GR&R and the long form method to account for the interaction between inspectors and parts. Fang et al. [29] used a simulation to verify the findings of Fang and Wang [28] . The study found that the accuracy and precision of the measurement variation is proportional to the number of combinations. At the same time, with a fixed combination of parameters, increasing the number of inspectors within measurement parameters increases the accuracy and precision of measurement variation.
Fang et al. [30] followed up the work of Fang and Wang [28] and found that the variance estimation obtained by both traditional GR&R and the long form method both have a large deviation from the true value. Therefore, they proposed three revised models. Asides from being closer to the true value, these models also provide more precise and accurate measurement than traditional GR&R and the long form method. Of these, the MLFN2 variance estimation is closest to ANOVA. Fang et al. [31] and Fang et al. [32] proposed unbiased estimators for traditional GR&R and the long form method. The proposed estimators are used for situations where interaction effects between inspectors and parts are either present or absent. The research found that the first consideration increased the number of inspectors, followed by the number of parts, and finally the number of repeated measures. In addition, at least three inspectors are required to ensure that variance and mean square error is not too large. Lyu and Chen [33] used a generalized linear model (GLM), iterative weighted least squares (IWLS), andrepeatability variance to develop a statistical method for calculating variance between measurement systems, which is used to calculate the reproducibility variance. A simplified table provides a reference for actual operation in industry.
2.2. ISO/TS 16949 Quality Management System
TS 16949 provides internationally universal and proven technical specifications for the automobile and precision industries, covering the operating requirements for the quality systems of both manufacturers and suppliers. Before the establishment of TS 16949, all suppliers of parts and services in the automobile industry had to obtain quality system certification for each country or region they supplied, for instance EAQF in France, AVSQ in Italy, QS 9000 in the United States, and VDA-6 in Germany.
Reid [34] highlighted that the difference between quality certification across different countries and regions lies in the different methods and tools used to obtain targets, but that the requirements are largely the same. Therefore, in 1996, automobile industry associations in various European countries joined with the AIAG in the United States to establish the International Automotive Task Force (IATF).The main objective of the IATF is to coordinate between the different quality specifications of members (members include the German Association of the Motor Industry (VDA), the French Automobile Manufacturers Committee (CCFA), AIAG in the United States, the French Vehicle Equipment Industries Association (FIEV), and the Italian Association of the Automotive Industry (ANFIA)) to integrate the methods and tools used in different quality systems. IATF members and the three leading American carmakers, General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler, jointly announced that suppliers must obtain ISO/TS 16949:2002 certification to guarantee product quality. In addition, AIAG in the United States announced that ISO/TS 16949:2002 would replace the widely used QS 9000 quality standard. As a result,
all suppliers involved in the manufacture or maintenance of parts in the automotive industry were required to use the ISO/TS 16949 automobile industry quality management system. Aside from the automotive industry standards in the ISO 9001quality management system, ISO/TS 16949 also contains five core tools: 1) advanced product quality planning (APQP); 2) production parts approval process (PPAP); 3) measurement system analysis (MSA); 4) failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA); and 5) statistical process control (SPC). These five core tools make the ISO/TS 16949quality management system more rigorous.
The basic framework of TS 16949:2002 is based on ISO9001:2000. The process is used as the basic framework, looking at process management models formed by a series of interactions and relationships during the conversion of inputs to outputs. This management model is the process management from receiving an input to producing an output, and continued maintenance of the PDCA cycle during process management. Continued reductions in variation are achieved to ensure that outputs achieve customer satisfaction, while also strengthening the organization’s quality control system [35] .
2.3. Measurement System Analysis
MSA uses statistical and diagrammatic methods for experimental design and statistical analysis of measurement system error to assess variance in measurement systems, allowing an assessment of the variance in individual measurement equipment and inspectors, and providing a basis for the management of measurement equipment systems [36] . A core tool of the ISO/TS 16949 quality management system is MSA. The main objective is to collect important input and output data from the process, estimate the reliability of the data, and analyze which aspects of inspectors, machines, materials, methods, or the environment produce variations. The analyzed data is then used as a reference for future improvements. Therefore, the main reason for the use of MSA is that the variation caused by inspectors, machines, materials, methods, or the environment can be controlled within a reasonable range and variations between products can be identified.
Equipment qualification, equipment calibration, and MSA are all within the scope of measurement system evaluation. Each of these methods aims to evaluate the reliability of the measurement system and establish the stability of the manufacturing process and benefits from improvement. This study summarizes frequently used evaluation methods for measurement systems according to type and function, as shown in Table 1.
If the errors produced by inspectors or measurement equipment in measurement systems are large, the reliability of the data recorded in the manufacturing process needs to be reconsidered. An ideal measurement system should have an error rate that is statistically zero [7] , but such an ideal measurement system does not exist given the limitations of existing measurement equipment. Currently, three questions are associated with measurement. The first is whether the measurement system produces stable statistical appraisal within a given period. Measurement systems are used in the stability and reproducibility of measurement equipment. Second is whether the measurement system produces adequate item discrimination. Item discrimination is not 1/10 of traditional tolerance specifications, but is 1/10 of the overall process 6σ. Third is measurement error or variation. Can statistical consistency be achieved within a certain range to allow use for control or process analysis? When calculating errors in instrument measurement systems, we can distinguish between accuracy and precision. Accuracy measures the difference between the measured values and the actual values, while precision measures the variation in values when using the same equipment for repeated measures of the same parts. In contrast, precision is the repeatability using different measurement systems, which in this case refers to reproducibility because different measurement systems are used. The MSA Reference Manual [37] proposes three techniques for determining re-
![]()
Table 1. Evaluation methods of measurement systems.
peatability and reproducibility: the range method, the average and range method, and the ANOVA method.
The AIAG [38] Measurement Systems Analysis Reference Manual includes GAL, GTS, and GRR. When evaluating measurement systems, it is necessary to first estimate precision and accuracy. Since there is currently no statistically perfect measurement system, the reliability of the data obtained will affect the results of process capability analysis, ANOVA, regression testing, hypothesis testing, experimental design, and control charts. Therefore, before gathering data, we must first analyze the overall measurement system. This analysis will focus on the methods, equipment, and inspectors used, determining whether the overall measurement system is within an acceptable range.
Pan [25] divided measurement errors into: 1) measurement equipment: measurement errors called by a lack of precision in measurement equipment; 2) inspectors: measurement errors caused by lack of training for inspectors or operational differences; and 3) environment: measurement errors caused by the measurement environment not meeting the requirements, including factors such as pressure, temperature and humidity, and weight. Therefore, factors causing errors in measurement systems are not limited to measurement equipment. Each element of a measurement system can cause errors. Therefore, in order to produce precise measurement systems, error factors must be reduced [39] .
2.4. Fuzzy Theory
Fuzzy theory refers to the fuzzy conceptualization of certain data. Uncertain information is made more precise through an approximate reasoning process [40] . Fuzzy mathematics was first proposedby Lotfi A. Zadeh [41] , a cybernetics expert at the University of California, Berkeley in an article published in the journal Information and Control. Fuzzy theory has become a frequently discussed and applied approach in a range of disciplines. Fuzzy theory is mainly applied to solving the fuzzy phenomena that exist in the real world, with the objective of dealing with concepts that are somehow vague, for example, partial, uncertain, imprecise, or random concepts, and rigorously quantifying these concepts into data that can be processed by computers [42] .
A crisp set is a very clearly defined set, without any fuzzy areas. Therefore, a characteristic function of a crisp set can be expressed as, if not 0, then 1. Conversely, in order to express the fuzziness of fuzzy sets, a membership function of between 0 and 1 must be used to represent the degree of membership to the set [43] . An abstract concept such as a “cold” can be viewed as a fuzzy set, with a membership function used to express the degree of the cold, in contrast to a traditional dichotomy. The degree of membership is represented by an actual value in the closed interval [0, 1]. Therefore, a value of 1 indicates complete membership of the fuzzy set representing “colds,” while 0.7 indicates that the degree of membership to the set is 0.7. Therefore, this method can be used to make abstract concepts such as “perception” and “hope” more precise and flexible.
In order to distinguish between crisp and fuzzy sets, this study sets fuzzy sets as Ã. For example, if the crisp set A is defined as {x is equal to b}, when x is equal to b, its membership degree of set A is 1. However, when x is not equal to b, its membership degree of set A is 0, as shown in Equation (1):
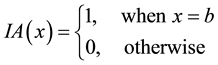 (1)
(1)
Conversely, if the fuzzy set à is defined as {x is approximately equal to b}, when x is equal to b, its membership degree of set à is 1. However, when x is a value close to b, its membership degree of set à is between 0 and 1, as shown in Figure 2. Therefore, crisp sets are a special case of fuzzy sets.
Commonly found membership functions of fuzzy sets include trapezoidal membership functions, triangular membership functions, and bell membership functions. This study uses the triangle membership function (a,b,c) shown in Figure 1, with a, b, and c representing the three points of the triangle on the x axis, with the horizontal coordinates indicating any possible x value, while the longitudinal coordinates indicate the membership degree of value x to set Ã. This value is between 0 and 1, defining the triangle membership function as follows:
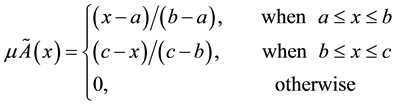 (2)
(2)
In practical application in industry and academia, since there are many possible shapes for membership func-
![]()
Figure 2. Membership function of fuzzy set Ã.
tion, the choice of membership function will depend on the practical considerations of decision-makers.
However, the fuzzy concepts in mathematics proposes a fuzzification process of turning numbers into functions of fuzzy numbers and carrying out expansion of fuzzy relations on crisp sets. Therefore, the use of fuzzy control involves determining the operating range based on the size of the measurement values. Therefore, the semantic value is an expression of the membership function of the fuzzy set. When a crisp value is observed, this will correspond to the membership function of the domain and obtain the membership function of the inputs.
3. Research Methods
After carrying out MSA, we first calculate the X-bar-R values and make these values independent. Construction of the MSA uses crisp numbers, but errors are still inevitable in the measurement process. These errors are non- sampling errors and cannot be avoided in statistical theory. Therefore, this study regards measurement values as a fuzzy concept where real numbers are used to represent a domain. These measurement values are therefore fuzzy numbers, with fuzzy theory used in MSA. When it is determined that the measurement values are not precise values, fuzzy mathematics is used to replace crisp numbers with fuzzy numbers, with the values also being independent. Then, these two sets of data are compared using GR&R number of distinct categories (NDC).
3.1. Creating the Fuzzy Model
In real life, many problems are uncertain or imprecise. Conventional binary logic may be unable to solve these problems [43] . For the incompatibility between the binary logic in crisp sets and human thought patterns, membership function can provide an appropriate solution [44] . Therefore, the common set produced by the aggregated factors is normally expressed as U, therefore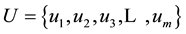 ,with
,with  representing each factor. In the factor set U, either
representing each factor. In the factor set U, either  or
or 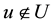 must be established. Therefore, the factor set is a com- mon set. Let
must be established. Therefore, the factor set is a com- mon set. Let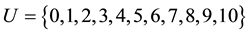 , with each number representing ten samples.
, with each number representing ten samples.
Membership function is the basis for the application of fuzzy sets to actual problems. However, there is still no objective means of determining the membership function [45] . Wu and Chen [46] also clearly pointed out that the definition of the membership function is primarily based on actual experience. Therefore, the process of carrying out independent assessment of a sample to establish the extent to which the measured object belongs to the evaluation set is referred to as fuzzy evaluation for a single sample. For example, the ith factor ui in the sample set is evaluated as having the jth element vj degree of membership rij for the common set. Therefore, the evaluation results can be expressed using the fuzzy set Ri, with Ri the fuzzy subset of evaluation set V, which can also be simply expressed as a vector: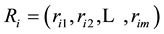 . In addition, to ensure consistency,
. In addition, to ensure consistency, 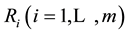 must be a fuzzy set with the same definition. For the ith factor, rij must satisfy the normality condition
must be a fuzzy set with the same definition. For the ith factor, rij must satisfy the normality condition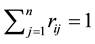 . At the same time, the corresponding factor evaluation set for each factor can be obtained. Therefore, defining the evaluation set Ri for each of the factors as the rows, we can compose the fuzzy matrix.
. At the same time, the corresponding factor evaluation set for each factor can be obtained. Therefore, defining the evaluation set Ri for each of the factors as the rows, we can compose the fuzzy matrix.
1) In this paper, we use linear membership functions since they are more commonly used, and produce a more stable 45-degree angle, making them more acceptable to ordinary readers. An appropriate universal set that contains all data domains is divided into a number of short segments (normally five short segments), and the corresponding data segment for each data item is identified, with the triangle membership function fuzzifying the original data as fuzzy data values [47] .
2) The sample specification tolerance is divided into five intervals, with a positive or negative specification tolerance of 1 mm divided into intervals of 0.02, with a positive or negative interval of 0.02 as v1 = extremely precise; a positive or negative interval of 0.04 as v2 = very precise; a positive or negative interval of 0.06 as v3 = precise; a positive or negative interval of 0.08 as v4 = less precise; and a positive or negative interval of 0.08 as v5 = imprecise. This produces the fuzzy subset for each sample.
The evaluation set represents all the possible evaluations of an object made by the evaluator and is normally represented as V; therefore, 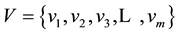 , with
, with 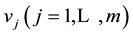 representing each evaluation. Let the interval set
representing each evaluation. Let the interval set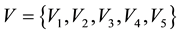 , with V1 = extremely precise, V2 = very precise, V3 = precise, V4 = less precise, and V5 = imprecise.
, with V1 = extremely precise, V2 = very precise, V3 = precise, V4 = less precise, and V5 = imprecise.
Interval I = [a,b] is a special fuzzy number called an interval number. Li [48] pointed out that as a measure is regarded as a fuzzy number, it is first necessary to establish the membership function of that fuzzy number. In this study, measurement data are converted into membership functions to produce special fuzzy numbers, calculated as the membership degree of individual samples multiplied by the median point of the interval set, and defined as the new measurement data. These calculations allow us to obtain the fuzzy numbers for each of the samples, producing a fuzzy measurement record.
The measurement record shows three inspectors coded A, B, and C measuring different samples, as shown in Table 2. Let v1 = the interval median for specification tolerance A; v2 = the interval median for specification tolerance B; v3 = the interval median for specification tolerance C; v4 = the interval median for specification tolerance D; v5 = the interval median for specification tolerance E.
3.2. Research Steps
The MSA average and range method is applied to measurement equipment MX-01 hardness tester and MX-02 micrometer. Three measures for each of the ten samples are taken by the three inspectors, producing 90 data points for XBar and R calculation. Pen [13] [27] stated that the average and range method is most frequently used in industry. On this basis, this study also used the average and range method to calculate GR&R and compare R&R &NDC to evaluate variation in the measurement system.
Research steps:
Step 1: Select ten sample parts and code them to 1 - 10. These sample parts must fully reflect the range of variation in the manufacturing process.
Step 2: Select three inspectors coded A, B, and C.
Step 3: Each inspector carries out random repeated measurement of each sample part three times. Inspectors
![]()
Table 2. Record of measurement outcomes.
Note: A1st: First measurement of inspector; A2nd: Second measurement of inspector A; A3rd: Third measurement of inspector A; B1st: First measurement of inspector; B2nd: Second measurement of inspector B; B3rd: Third measurement of inspector B; C1st: First measurement of inspector C; C2nd: Second measurement of inspector C; C3rd: Third measurement of inspector C.
are not permitted to compare their results. Inspectors A, B, and C will each produce thirty sets of data, giving a total of ninety sets of data.
Step 4: The average and range for the three measurements of each sample part produce a total of ten averages and ten ranges for each inspector.
Step 5: Calculate the sample average for each part. The average and range of each sample part is represented as Rp.
Step 6: Inspectors A, B, and C each produce ten averages, which produce an overall average of![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() , and overall range of
, and overall range of![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() .
.
Step 7: Calculate the ![]() and
and ![]() as shown in Equations (3) and (4).
as shown in Equations (3) and (4).
![]() (3)
(3)
![]() (4)
(4)
Step 8: Repeatability measures EV, with average range multiplied by constant K1, dependent on the number of tests and equal to the reciprocal of![]() ;
; ![]() is dependent on the number of tests (m) and the number of parts multiplied by the number of inspectors (g). As shown in Equation (5),
is dependent on the number of tests (m) and the number of parts multiplied by the number of inspectors (g). As shown in Equation (5), ![]() obtained from the
obtained from the ![]() Table in Appendix C of the 4th edition of the MSA Reference Manual. The MSA Reference Manual shows that for three tests K1 = 0.5908. The reproducibility is measured as the variation between appraisers, AV, calculated as themaximum variation in average between inspectors
Table in Appendix C of the 4th edition of the MSA Reference Manual. The MSA Reference Manual shows that for three tests K1 = 0.5908. The reproducibility is measured as the variation between appraisers, AV, calculated as themaximum variation in average between inspectors ![]() multiplied by constant K2. K2 is determined by the number of inspectors used in the research, and is the reciprocal of
multiplied by constant K2. K2 is determined by the number of inspectors used in the research, and is the reciprocal of![]() . This
. This ![]() is obtained from the
is obtained from the ![]() Table in Appendix C of the 4th edition of the MSA Reference Manual;
Table in Appendix C of the 4th edition of the MSA Reference Manual; ![]() is determined by the number of inspectors (m) and g = 1. As the variation between inspectors also includes EV, this must first be subtracted, as shown in Equation (6). There are three inspectors in this study, thus according to the MSA Reference Manual, K2 = 0.5231, the number of samples is n = 10, and the number of repeat tests is r = 3.
is determined by the number of inspectors (m) and g = 1. As the variation between inspectors also includes EV, this must first be subtracted, as shown in Equation (6). There are three inspectors in this study, thus according to the MSA Reference Manual, K2 = 0.5231, the number of samples is n = 10, and the number of repeat tests is r = 3.
![]() (5)
(5)
![]() (6)
(6)
Step 9: The measurement system GR&R is calculatedas shown in Equation (7).
![]() (7)
(7)
Step 10: Calculating PV. The average range of the sample parts multiplied by constant K3; K3 is determined by the number of sample parts used in the study and is reciprocal of![]() . The MSA Reference Manual shows the value of
. The MSA Reference Manual shows the value of ![]() c, determined by the number of sample parts and subgroups (g=1), as shown in Equation (8). This study has ten sample parts, thus according to the MSA Reference Manual K3 = 0. 3146,
c, determined by the number of sample parts and subgroups (g=1), as shown in Equation (8). This study has ten sample parts, thus according to the MSA Reference Manual K3 = 0. 3146,
![]() (8)
(8)
Step 11: Total variation can be obtained from the square of GR&R plus the square of the part variation (PV), as shown in Equation (9).
![]() (9)
(9)
Step 12: %GR&R is GR&R as a percentage of total variation, as shown in Equation (10).
![]() (10)
(10)
Step 13: NDC. Wheeler and Lyday [49] pointed out that the intervals are the number of non-overlapping 97% confidence intervals that that span the expected product variation, as shown in Equation (11). NDC must be rounded to the nearest integer.
![]() (11)
(11)
Step 14: Repeat steps 4 to 13 according to data from the fuzzy model.
Step 15: Comparison of fuzzification and standard deviation for GR&R and NDC.
4. Case Study
4.1. Case Data Collection
This study looks at the case of a machine tool factory in Taiwan, using the test methods and steps to analyze measurement results and calculate EV, appraiser variation (AV), and GR&R. We carry out tests on the measurement systems and use the results of the analysis to put forward appropriate recommendations, as a basis for industry to determine the %GR&R and as a reference for future research.
In order to obtain variance in a real measurement system, the data gathered in this study were measured during actual processes, as explained below: 1) Using actual production equipment; 2) Personnel were quality personnel or operators who regularly use this equipment; 3) Measurement was carried out using typical measuring tools; 4) Data was collected according to plan; and 5) Three case studies were carried out, each with three inspectors, ten sample parts, and each with three tests.
4.2. Experimental Results and Record
In case study 1, the measurement instrument was a micrometer codenamed MX-02 with an accuracy of obtained values of 0.001 mm. Three inspectors coded A, B, and C were selected, then ten production line guide rod machines were chosen, and the thickness at a certain position was measured. The drawing specification states a thickness of 4.62 mm at this point, with a tolerance range of +0 - −0.035 mm. Each of the three inspectors measured the sample part three times, and the measurement results are recorded in Table 3.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA Reference Manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.0006, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 6.73%. The NDC of 20.904 was rounded to the nearest integer, producing a value of 21.
In case study 2, the measuring instrument was a hardness tester coded MX-01, with an accuracy of obtained values of 1 degree. Three inspectors coded A, B, and C were selected, ten production line hand tool blades were chosen, and the hardness at a certain position was measured. The drawing specification states a thickness of HRC55 at this point, with a tolerance range of +5 degrees - −0 degrees. Each of the three inspectors measured the sample part three times, and the measurement results are recorded in Table 4.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA reference manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.327, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 28.89%. The NDC of 4.672 was rounded to the nearest integer, producing a value of 5.
In case study 3, the measuring instrument was a hardness tester coded MX-01, with an accuracy of obtained values of 1 degree. Three inspectors coded A, B, and C were selected, ten production line tension spindles were chosen, and the hardness at a certain position was measured. The drawing specification states a thickness of HRC48 at this point, with a tolerance range of +5 degrees - −0 degrees. Each of the three inspectors measured the sample part three times, and the measurement results are recorded in Table 5.
![]()
Table 3. Record of measurement outcomes for Case 1.
![]()
Table 4. Record of measurement outcomes for Case 2.
![]()
Table 5. Record of measurement outcomes for Case 3.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA Reference Manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.333, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 28.53%. The NDC of 4.736 was rounded to the nearest integer, producing a value of 5.
4.3. Fuzzy Test Results
In case study 1, each of the three inspectors measured the sample parts three times. Following fuzzification, the measurement results for the fuzzy case are recorded in Table 6.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA Reference Manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.0006, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 8.14%. The NDC of 17.266 was rounded to the nearest integer to produce a value of 17.
In fuzzy case study 2, each of the three inspectors measured the sample parts three times as shown in Table 4. The measurement results following fuzzification are recorded in Table 7.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA Reference Manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.290, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 32.73%. The NDC of 4.071 was rounded to the nearest integer, producing a value of 4.
![]()
Table 6. Record of measurement outcomes for fuzzy Case 1.
![]()
Table 7. Record of measurement outcomes for fuzzy Case 2.
In fuzzy case study 3, each of the three inspectors measured the sample parts three times as shown in Table 5. The measurement results following fuzzification are recorded in Table 8.
After the data were collected, we used the average and range method in the MSA Reference Manual to calculate GR&R, giving a result of 0.276, and a %GR&R for the measurement system of 30.12%. The NDC of 4.463 was rounded to the nearest integer to produce a value of 4.
4.4. Research Results and Discussion
If MSA produces acceptable results, the measurement system is considered reliable. Conversely, unacceptable results indicate that the measurement system has room for improvement. For example, following MSA analysis, if it is discovered that unstable measurement instruments cause instability in the production process, it is not necessary to waste resources changing the production process. Similarly, when a high defect rate for a product is observed, and it is discovered that the reason is excessive EV, if the use of more sophisticated equipment reduces the defect rate or if MSA identifies product design flaws, design changes can be carried out [50] .
Observation of the three cases in the study shows that %GR&R after fuzzification is higher than the original data (see Table 9). The original %GR&R for the three cases was 6.73%, 28.89%, and 28.53%, respectively.
![]()
Table 8. Record of measurement outcomes for fuzzy Case 3.
![]()
Table 9. Comparison of %GR&R and NDC.
However, following fuzzification of the measurement values, %GR&R for the three cases was 8.14%, 32.73%, and 30.12%, respectively.
In practice, if %GR&R is less than 10%, it means that the measurement system is acceptable. If %GR&R is between 10% and 30%, it means that the measurement system is acceptable depending on the application, the cost of the measuring device, cost of repair, or other factors. If %GR%R is greater than 30%, it means that the measurement system is unacceptable and should be improved. In the first case, since the sample part was a key precision part, (as poor tolerance would cause downtime, and make it unusable to the operator), the company stipulates that %GR&R must be less than 10%. Although the value was higher following fuzzification, it was still within the specified range, 10%. The measurement system is acceptable.
In the second and third cases, the original %GR&R of 28.89% and 28.53%, respectively, fell within the edge 30% range, but after fuzzification, exceeded the original 30% range. This diametrically opposite result can act as a reference for assessors. The measurement system should be improved.
The original NDC values for the three cases were larger than 5 and within the specifications. However, fuzzification produced a fall in the NDC values, indicating that the analysis was unable to distinguish between categories with maximum variation. The NDC for the three cases was 21, 5, and 5, respectively. However, following fuzzification of the measurement values, the NDC for the three cases fell to 17, 4, and 4, respectively. In the first case, since the sample part was a key precision part, and while the NDC value was lower after fuzzification, it was still within the specified range. The NDC of 5 for both the second and third cases fell on the edge of the range of 5 or larger; however, following fuzzification it fell to outside of this range, producing a diametrically opposite result. This finding fits with customer complaints of insufficient hardness, and is an important reference for the company.
Finally, this study used the concept of fuzzy theory to test %GR&R and NDC for measurement systems. The results of MSA following fuzzification can help the companies to assess in more depth any uncertainty in measurement systems. In order to ensure that their products achieve good quality, companies need to have accurate measurement systems in place. At present, the industry mostly follows TS 16949 criteria to assess measurement systems and determine whether they are acceptable. Following fuzzification, the measurement systems in the second and third cases are not within an acceptable range and require improvement.
5. Conclusions
This study applies the existing literature to gather measurement data and uses fuzzy theory to process the results. The standards set out in the long form method in the MSA Reference Manual [37] are used for GR&R comparison of measurement systems, assessing the variability of the measurement system on the basis of whether %GR&R can be effectively controlled. The main conclusions of this study as summarized as follows.
1) %GR&R comparison of measurement systems using the standards set out in the long form method in the MSA Reference Manual [37] show completely different results following fuzzification. The original value of %GR&R shows that the measurement system is marginally acceptable in case two and three. However, the fuzzy values of %GR&R show that the variances increase. The measurement system should be improved. There- fore, fuzzy %GR&R is more sensitive. It can effectively detect measurement variance.
2) The measurement capability of the measurement system should be tested regularly. In order to ensure that the analysis results from a measurement system can be used, relevant criteria should be put in place. At the same time, these criterions can be used to grade the measurement capability of the measurement system, providing a reference to the production department when dispatching workers or introducing new products, and preventing the misuse of measuring equipment with poor measurement capability.
3) GR&R comparison of measurement systems using the standards set out in the long form method in the MSA Reference Manual [37] can be used in the trial production stage to produce reasonable criterion for analyzing parts.
4) This study believes that using the %GR&R set out in the MSA Reference Manual as the only criterion for the acceptability of the measurement systems is not an appropriate approach. Assessment of the measurement system should not be based on a single indicator or criterion. NDC for measurement tests under different conditions should also be applied to avoid false positives.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.