In-Vitro Efficacy of Certain Essential Oils and Plant Extracts against Three Major Pathogens of Jatropha curcas L. ()
1. Introduction
Antifungal activity of some isolated principles from plant extracts may be more effective than some commercial synthetic fungicides. The presence of naturally occurring substances in plants with anti microbial properties have been recognized and tested against a wide range of pathogenic microbes [1] . With the increase of interest in antibiotics plants as a source of potential antimicrobial substances are receiving considerable attention throughout the world. Recently many aqueous plant extracts have been shown to have inhibitory action against some plant as well as human pathogenic microbes. Nowadays some synthetic as well as semi-synthetic antimicrobial agents have been developing, among which very few have broad spectrum activity and most of them are environmentally hazardous in nature. The extensive use of agrochemicals especially fungicides, resulted more carcinogenic risk than other pesticides which may give rise to undesirable biological effects on animals and human beings [2] .
Jatropha curcas is a multipurpose shrub or small tree belonging to the family of Euphorbiaceae [3] . This plant has received increasing interest as a bio-diesel plant since the beginning of the 21st century. The seeds also contain viscous non-edible oil (about 48%) which besides being a source of bio-diesel, can also be used for manufacturing various useful products, candles etc. This valuable plant species have been attacked by various fungal pathogens causing severe loss. Present investigation was carried out to control three major fungal pathogens, viz., Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissl., Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. & Sacc. and Fusarium moniliforme Sheld., isolated from diseased plant parts of Jatropha curcas. C. gloeosporioides is responsible for anthracnose in Jatropha curcas fruit. The disease results in fruit rot and fruit drop and ultimately lead to the yield loss. F. moniliforme caused fruit decay. Alternaria leaf spot disease caused premature defoliation.
Investigations have been carried out with an aim to control the diseases of Jatropha curcas using essential oils and plant extracts of the some selected plant species. Cinnamomum impressinervium Meissn. (Family―Lau- raceae) is a small to medium sized evergreen tree found in evergreen forest of northern state including Sikkim at an altitude between 220 - 1200 m. Leaves are aromatic possessing a strong spicy odour and used as spice in the region. Leaf oil of this species contains high amount of eugenol (88.3%) [4] [5] . Cinnamomum tamala Nees. (Family―Lauraceae), is a medium sized tree distributed in tropical and subtropical Himalayas at the altitudes of 1000 - 2400 m. In India, the tree is cultivated commercially in certain parts of the country for leaf production and essential oils. Leaves and oils are used in flavouring foods, beverages, in perfumery and pharmaceutical industries [6] . Cymbopogon jwarancusa (Jones) schult. (Family―Poaceae) is one of the cultivars developed by CSIR-NEIST, Jorhat (Assam), India. Major constituent of the oil of this species is piperitone (83%) [7] . Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf. (Family―Poaceae), is an important aromatic plant, a source of essential oil and is widely used as a component of ethno-pharmaceuticals in tropical and subtropical countries. The aerial parts of the plant are widely used in folk medicine to treat various health problems [8] . The essential oil of Cymbopogon citratus has antifungal and insecticidal activities [9] . Tithonia diversifolia Hemsley. Gray (Family―Asteraceae) is widely distributed throughout the humid and sub-humid tropics in central and south America, Africa and all Asian countries. Extracts from the leaf of T. diversifolia contain sesquiterpene lactones e.g. tagitinin which possess insecticidal properties [10] . Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don (Family―Apocynaceae) is a medicinal plant grown throughout India and found as an escape in waste places and sandy tracts. The aerial part of the plant contains about 130 different alkaloids from which well-known high value secondary metabolites vincristine and vinblastine are used in chemotherapy to treat diverse cancers, while ajmalicine and serpentine are prescribed for hypertension.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Test Pathogens
The leaves of selected plant species were collected from experimental farm of CSIR-North East Institute of Science and Technology, Jorhat (Assam), India. These were washed 2 - 3 times in tap water and air dried at room temperature (25˚C - 30˚C). The fungal pathogens were isolated from the diseased parts of Jatropha curcas, characterized and were identified through high power microscopy.
2.2. Preparation of the Extracts and Essential Oils
The dried leaves (Catharanthus roseus and Tithonia diversifolia) were ground into powder form, sieved and packaged into polyethylene bags until when needed. 50 g sample of powdered dried leaves were weighed and extracted in Soxhlet extractor with ethanol at 40˚C - 60˚C. Essential oils were obtained by subjecting the fresh leaves to hydrodistillation in clevengers apparatus for 4 hours. Oils were collected in glass vials after removing water traces by sodium sulphate and stored at 4˚C. The extracts and essential oil obtained were assayed against the test organisms to determine the antifungal properties.
2.3. Determination of Antifungal Activity
The retrieved extract was tested for its antifungal activity using Poisoned Food Technique [11] . 20 ml of potato dextrose agar was poured into sterilized petri plates and measured amount of oil sample/extracts were added, allowed them to mix homogeneously and to be solidified. Control growth medium contained equivalent amounts solvent. Fungal disks of 5 mm in diameter from an 8-day-old pure culture were placed in the center of the Petri dish containing medium under aseptic condition, incubated at 27˚C ± 1˚C for 7 days. The experiments were carried out in three replicates per treatment. Growth of each fungal species was observed and recorded after one week of incubation. Percent inhibition was computed after comparison with the control. Percent inhibition of mycelial growth was calculated using the following formula [12] .
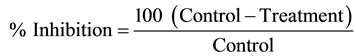
3. Results and Discussion
All the samples showed antifungal activity in-vitro. However, among the essential oils tested Cinnamomum impressinervium exhibited strongest activity at concentration of 1000 ppm (80.0, 78.6 and 80.0 against C. gloeosporioides, F. moniliforme and A. alternate respectively) followed by C. tamala (77.3, 76.8, 78.0), Cymbopogon jwarancusa (73.4, 71.4, 74.0) and C. citratus (67.0, 66.5, 68.6) (Table 1). Catharanthus roseus exhibited stronger activity (72.5, 70.1, 73.0 against C. gloeosporioides, F. moniliforme and A. alternata respectively) in comparison to Tithonia diversifolia (68.6, 66.5, 67.0) (Table 1). It was observed that inhibition percentage of all the essential oils as well as plant extracts increased with the increase in concentration. All the tested plant spe- cies were found to have good antifungal activity.
![]()
Table 1. The inhibitory effects of the samples on mycelial growth of test fungi 7 days after inoculation (percent inhibition).
In present investigation all the tested plants found to be effective against C. gloeosporioides, F. moniliforme and A. alternata. They too showed increasing inhibitory effect on the fungal growth with higher concentration
compared to control [13] while studying the efficacy of 16 plant extracts in controlling the leaf spot in ginger caused by Phyllostica zingiberis found that growth inhibition of fungi increased with increasing concentration of extracts. [14] screened 12 angiospermic plant extracts in and around the same locality of Sonitpur district. Out of these, 6 plant extracts Mikania scandence, Eupatorium odoratum, Cassia sophera, Leucus plunketii, Occimum basilicum and Clitoria ternate were found effective in total inhibition of mycelia growth of S. sclerotiorum.
The inhibition of the growth of the pathogenic fungi is due to the active ingradients predominantly found in the plant [15] . The present investigations are in line with the investigations carried out by other workers [16] who infer that leaf extracts in general have great potentiallity in the control of fungal diseases in commercially important crop plants. It may be concluded that keeping aside the environmentally hazardous commercial fungicides, these leaf extracts could be suitable substitute for controlling fungal pathogens. It may be concluded that keeping aside the environmentally hazardous commercial fungicides, these leaf extracts and essential oils could be a suitable substitute for controlling the fungal pathogens.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.