Large Scale Desalination: A Comparative Cost Affective Economic Analyses of Nuclear, Gas and Solar Powered Plants ()
1. Introduction
Water is probably the most important commodity affecting the livelihoods of the majority of the populations on the Earth. In due course, water will be at the central stage of a worldwide crisis that may consume millions of lives. It is imperative to find the least expensive and most productive approach to largely produce water in order to satisfy the future needs of the Earth’s inhabitants. Not much literature is written on direct solar energy for the purpose of producing drinking water, not on a large scale anyway.
The nuclear, gas and solar energy schemes differ in the technique to produce energy [1] [2] , however, there are few viable options to produce drinking water. In this paper only the Multi-Stage-Flash (MSF) system is considered for the desalination of seawater [3] . MSF uses a process in which seawater is heated, evaporated and then condensed to produce drinking water. For the nuclear and gas plants, the water, on average, is heated to boiling temperature, 100˚C - 105˚C, to increase the percentage of the evaporated water, which in turn increases the percentage of condensed water. However, the downside, in this case, is that increasing the heated water temperature, in the long run, lowers the efficiency of MSF system, and reduces the span of the system’s lifecycle. This increases cost and lowers its investment potential. The direct solar heat, on the other hand, heats the seawater in long parallel ducts (Figure 1) to a reasonable temperature subject to the location and seasonal temperature variations. In Saudi Arabia the water collectors’ temperature averages about 80˚C for the solar-heated seawater during the days of the summer months [4] . The average temperature difference between the seawater and the seaside ground surface fluctuates for nights and days, winters to summers periods, 30˚C to 50˚C, respectively [4] . This increases the evaporation and condensation during the summer period, however, the temperature interval separating the lows and highs during the rest of the year is enough for the production of large amounts of drinking water [3] [4] .
In Saudi Arabia a large number of gas-powered seawater desalination plants are operating, being built, or planned. Due to the scarcity of water in the Arabian Peninsula, Saudi Arabia may rely on seawater desalination for a long time to come. However, it is worth mentioning that in the long run, although not economically proven feasible, some believe that nuclear energy may be the most reliable for producing and desalinating electricity and sea water, respectively [5] [6] .
The data can be divided into informational data such as the cost of energy, operation and maintenance (O & M) per million joules (MJ), and the cost of construction is also the same. This information is used to calculate the total cost per million joules (TC/MJ) of energy [1] . Maintenance includes energy, labor, parts and other indirect costs. Construction includes, for nuclear power, nuclear reactors, turbines, heaters, all other required plant’s concrete chamber(s), compressors, gauges and monitors; for gas power, all of the above are included, excluding the nuclear reactor and adding the gas-based electric turbines [7] .
![]()
Figure 1. The tide-based seawater desalination system (Ashry, Mohammed H., Csrea Press, 2013).
Defining the Parameters
The data for the nuclear and gas energy based plants are extracted from US energy production costs between 1995 and 2011. The previous three years are the result of a regressive inflation based extrapolation [1] [2] . However, the solar powered plant’s data are entirely inflation-based extrapolated estimates [7] . TC/MJ is utilized for two purposes:
a) To calculate the profit under the assumption that the initial cost is financed. In this case the cost of the first year is multiplied by 2000 to obtain the present worth (PW) of the financing money for the establishment of two Giga Joules energy-plant for the production of drinking water. The annual payment (AP) and the future worth (FW) of the borrowed money are calculated at the bottom of Table 1 or each of the industrial sectors; however, only Table 1 will be discussed, since all the figures and the table follow the same mathematical procedure, except for the solar energy where the data are extracted entirely, as mentioned above, from inflation based data, and which is the main subject of this paper. The total cost of two Giga Joules energy-plant will be used as the present worth of the project to estimate and gauge their future value over twenty years. The first year, 1992, will be used to calculate the present worth-value to finance the project. The financing data will be used purely for comparative purposes with the actual data and its estimates to emphasize the viability of the marketing future of the desalination industry.
b) The actual total of the varying inflation-based cost [8] will be calculated by tallying the cost of the first year, 1992, plus the aggregate portions greater than the 1992-magnitude, for the duration of the time series to 2011. With the exception of the nuclear sector, both the gas-based and the direct sun-radiation energy-based sectors fluctuate above and below the 1992 magnitude, due to many factors which will be discussed later. The future value of the actual total cost is displayed in Row 25, under the heading “Actual Total Project Cost/Million Joules, (ATC/MJ)”, in Table 1, for the three sectors, respectively, where 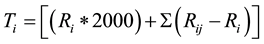 for
for 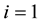 and
and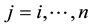 ; where
; where 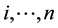 stands for the magnitudes of 1992-2011. These values for the three sectors are also solely as reference and for comparative purposes. The actual market rates’ time series values for the three sectors, “revenue data” (
stands for the magnitudes of 1992-2011. These values for the three sectors are also solely as reference and for comparative purposes. The actual market rates’ time series values for the three sectors, “revenue data” (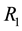 ,
, and
and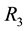 ), will be estimated using the first order autoregressive model (FOA) to estimate
), will be estimated using the first order autoregressive model (FOA) to estimate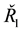 ,
, 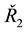 and
and 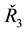 [9] . The actual and estimated values will be utilized to run a variance ratio test of the random walk hypothesis of both variances (Table 2),
[9] . The actual and estimated values will be utilized to run a variance ratio test of the random walk hypothesis of both variances (Table 2), 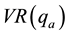 and
and , where
, where 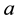 stands for actual and
stands for actual and 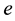 for estimated. This is employed to assess the viability of the energy producing schemes including the solar seawater desalination. The data in turn can be evaluated using the variances and data fluctuations of the three energy schemes. The objective is to forecast the viability of the solar energy for seawater desalination. The notion that annual changes in the cost of energy-projects including desalination are equivalent to changes in stocks’ earning yields is adopted to facilitate the process. The stocks of the involved manufacturing businesses are rising due to people’s growing need for drinking water. The increasing cost of seawater-desalination projects is due to both the rising cost of the energy and the emergence of numerous and diverse advances in desalination technology that have not been extensively tested, despite its competitive market. Energy projects for water desalination are investments known for its high return, however the risk associated with such projects adds to the uncertainty of the seawater desalination ventures in general. Solar seawater desalination eliminates this uncertainty [4] . The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of the desalination of seawater through direct solar energy is an asset that someday will provide the world with most of its drinking water.
for estimated. This is employed to assess the viability of the energy producing schemes including the solar seawater desalination. The data in turn can be evaluated using the variances and data fluctuations of the three energy schemes. The objective is to forecast the viability of the solar energy for seawater desalination. The notion that annual changes in the cost of energy-projects including desalination are equivalent to changes in stocks’ earning yields is adopted to facilitate the process. The stocks of the involved manufacturing businesses are rising due to people’s growing need for drinking water. The increasing cost of seawater-desalination projects is due to both the rising cost of the energy and the emergence of numerous and diverse advances in desalination technology that have not been extensively tested, despite its competitive market. Energy projects for water desalination are investments known for its high return, however the risk associated with such projects adds to the uncertainty of the seawater desalination ventures in general. Solar seawater desalination eliminates this uncertainty [4] . The cost-effectiveness and efficiency of the desalination of seawater through direct solar energy is an asset that someday will provide the world with most of its drinking water.
2. Application Analysis
The schemes employed are intended to test for the most appropriate energy based process for global mass water-production. In this paper, the total per energy cost of the construction, operation and maintenance is subject to changing inflation, depreciation, and rate changes in the cost of material due to constantly changing technology. However, the cost is actually an investment, part of which is earnings to investors; which maybe a cost to the project’s owners hoping to make a profit on the long run. There are three parties involved here, the manufacturers, for whom the project is revenue, the banks or investors providing the loan, and the owners operating or leasing the finished project for profit. The first year’s Cost/MJ of energy is used as the base value to calculate the present value of the investment. The financing uses this value to calculate the annual payment and future value of the investment after twenty years with a 3% interest rate, purely for economic comparison purposes. The calculated future values (FW), as shown in Table 1, for the solar case, with annual principle payment AP1,
FW ranges from 7% to 9% of the actual annually changing per energy cost (Table 3). This indicates a successful endeavor despite the low interest rate. The solar desalination actual cost of the energy is lowest in comparison to the nuclear and gas powered methods. However, that is not necessarily enough to appreciate this scheme. The cost of such technique may be higher in other countries. Nations in the northern and southern hemisphere may not have enough solar radiation to generate enough heat, not to mention the sea-side ground elevation relative to seawater level [4] . Nations near the equator especially in desert areas may not have the appropriate geography to employ such approach, and altering the landscape maybe too costly.
3. Technical Analysis
This paper employs a number of analytical procedures and processes in order to reach an outcome that is gauged from different perspectives through diverse analyses. The following explains the process in an easy to read and understand scheme.
3.1. The Methodology
The total annual cost per million joules (TAC/MJ) for nuclear, gas and solar seawater desalination industries is employed as the main actual variable as the industrial investments’ annual revenues; Table 1 is a demonstration of the solar industry’s activity.
![]() utilizing
utilizing![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() , for the industries mentioned above, respectively. The data is utilized to assess the viability of solar seawater desalination as a continuous source of drinking water. The actual data is estimated using the first order autoregressive model Equations (1)-(6) (Table 1) [9] [10] . Equation (7) is used to test for the stability and deviation of the explained and unexplained autoregressive model’s variations between the actual and estimated variances (Table 1). Then using Equations (8)-(11), the variance ratio (VR) is calculated to test for the random walk hypothesis (Table 2). Finally, Equations (8) and (13), the heteroscedasticity asymptotic variance (HAV) and 15, the consistency form, to test for the market-earnings consistency, in this case growth or a bubble (Table 2). Equation (16) tests the estimated variables and variances for investment risks for the three industrial sectors. The equations mentioned above are listed in the order they are employed as follows:
, for the industries mentioned above, respectively. The data is utilized to assess the viability of solar seawater desalination as a continuous source of drinking water. The actual data is estimated using the first order autoregressive model Equations (1)-(6) (Table 1) [9] [10] . Equation (7) is used to test for the stability and deviation of the explained and unexplained autoregressive model’s variations between the actual and estimated variances (Table 1). Then using Equations (8)-(11), the variance ratio (VR) is calculated to test for the random walk hypothesis (Table 2). Finally, Equations (8) and (13), the heteroscedasticity asymptotic variance (HAV) and 15, the consistency form, to test for the market-earnings consistency, in this case growth or a bubble (Table 2). Equation (16) tests the estimated variables and variances for investment risks for the three industrial sectors. The equations mentioned above are listed in the order they are employed as follows:
![]() (1)
(1)
where ![]() the values vector represented by the industrial return at time t. “
the values vector represented by the industrial return at time t. “![]() ,
, ![]() constants calculated using ordinary least squares model
constants calculated using ordinary least squares model ![]() a noise random variable in the industrial-return variables, averaging zero with a value of 1 for standard deviation in bivariate dependent regression, which maybe more instrumental in economics sensitivity studies; overall can be eliminated in earnings estimates” [10] . Equation (1), puts more emphasis on regressive estimates of the actual values with emphasis on the so called unexplained disturbance (noise) for multivariate regression. This unexplained disturbance, in reality is an error that can be explained by the variation in the deviation of the estimated variance from that of the actual over the regression period. In this case, it is simplified by employing the time series periods and degrees of freedom to factor into the co-variances instead of using expected return coefficients. The coefficients in this equation correlate the independent variables.
a noise random variable in the industrial-return variables, averaging zero with a value of 1 for standard deviation in bivariate dependent regression, which maybe more instrumental in economics sensitivity studies; overall can be eliminated in earnings estimates” [10] . Equation (1), puts more emphasis on regressive estimates of the actual values with emphasis on the so called unexplained disturbance (noise) for multivariate regression. This unexplained disturbance, in reality is an error that can be explained by the variation in the deviation of the estimated variance from that of the actual over the regression period. In this case, it is simplified by employing the time series periods and degrees of freedom to factor into the co-variances instead of using expected return coefficients. The coefficients in this equation correlate the independent variables.
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
(for solar desalination![]() )
)
If![]() , 1 then
, 1 then![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , respectively.
, respectively.
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
Equation (5) can be employed for estimating variance of two variables, where ![]() are the variances of the separate industries however our case requires Equation (7) due to the extreme fluctuations of our industrial variables. Equation (2) estimates the actual variables’ for two variables. In this process, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, the noise’ standard deviation is 1, and averaging zero which allows economists to exclude the disturbance, in this case, when estimating revenue. However, Equation (1) is more appropriate where the unexplained deviation is formulated by manipulating Equation (7). For example, Equation (6) is an example of a partial correlation coefficient where
are the variances of the separate industries however our case requires Equation (7) due to the extreme fluctuations of our industrial variables. Equation (2) estimates the actual variables’ for two variables. In this process, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, the noise’ standard deviation is 1, and averaging zero which allows economists to exclude the disturbance, in this case, when estimating revenue. However, Equation (1) is more appropriate where the unexplained deviation is formulated by manipulating Equation (7). For example, Equation (6) is an example of a partial correlation coefficient where ![]() correlates the independent variables
correlates the independent variables ![]() and
and ![]() a correlation coefficient for a third variable is utilized to compensate for the significant disparities in magnitude between the separate variables, So for
a correlation coefficient for a third variable is utilized to compensate for the significant disparities in magnitude between the separate variables, So for![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() (6)
(6)
or vise-versa for the variance and correlation coefficients.
![]() (7)
(7)
In this equation we can see the coefficient of determination ![]() which is a variance ratio used primarily to simplify explaining the variance deviation between the actuals and their estimates, and is instrumental in calculating the noise [10] [11] . In this equation
which is a variance ratio used primarily to simplify explaining the variance deviation between the actuals and their estimates, and is instrumental in calculating the noise [10] [11] . In this equation ![]() and
and ![]() are population degrees of freedom to balance the variance covariance estimates of the ratios. The following Equation (8) is the population variance ratio relating the variables on the basis of their degrees of freedom to accentuate the sampling population variability, where the fluctuation in Equation (9) is examined in relationship to Equation (10), where the sampling
are population degrees of freedom to balance the variance covariance estimates of the ratios. The following Equation (8) is the population variance ratio relating the variables on the basis of their degrees of freedom to accentuate the sampling population variability, where the fluctuation in Equation (9) is examined in relationship to Equation (10), where the sampling ![]() is used to amplify the ratios for the mean sample-calculation of
is used to amplify the ratios for the mean sample-calculation of ![]() Equations (8), (11), and (13)-(15).
Equations (8), (11), and (13)-(15).
![]() (8)
(8)
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10)
(10)
![]() (11)
(11)
![]() (12)
(12)
Equation (12) is a sampling degree of freedoms ratio of the non-heteroscedastic variance. Where Equation (13) is similar to Equation (8) with more emphasis on the heteroscedasticity of the variance variables; in this case, not only is the sampling of the population is important, but also the diversity of the variables.
![]() (13)
(13)
![]() (14)
(14)
![]() (15)
(15)
![]() (16)
(16)
Equations (14) and (15) relate the variance ratios with homoscedasticity and heteroscedasticity, respectively. Equation (16) is the portfolio selection theory formula [10] [12] [13] ; it provides the industrial investment risk assessment employing the variables and variances’ estimates, where![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() represent the industrial percentage coefficients.
represent the industrial percentage coefficients.
3.2. The Abstract Analysis
The solar-heat plant’s maintenance’s cost encompasses cleaning the reservoirs’ walls and surfaces, the condensers and evaporators piping along with the solar fields’ metallic surfaces and concrete inner ducts. The cleaning is done through flush-rinsing the surfaces, ducts and pipes with forced water and using water suctioning to help clear the surfaces and linings of precipitants. The cost is estimated to be $1 per square meter plus $1 per square meter for coating the solar fields’ metal surfaces with less than one millimeter of tar. The total surface area including the ducts and piping is estimated to be 10 Mm2 (million square meters). The total cost = 10 * 1 + 4 (total tar surface-area) * 1 = $14 M; the cost pricing employs the market’s whole-sale maintenance pricing in Saudi Arabia during the late Nineties. The cost per square meter = 14/10 = $1.4 per square meter and the cost of the energy produced = 14ex6/(2.96 * 4ex6) = 1.18 per MW, where the energy produced = ~2.96 MJ/m2 and the heat collectors area is 4 million square meters [4] . The inflation index between 1995 and 2013 has a low of 98 with a high of 148. Using an average approximation we get 2.8 as the annual (consumer price index) average inflation, with the year 1999 as the base index for the actual data in Table 1. Table 3 sums up the results of the analyses of the three industries and their feasibility on the basis of the tests done above.
4. Conclusion
Sadly, as it may be, some sort of a hidden agenda to elicit large profits may be in the works in the minds of many business executives looking to tap into this futuristically very profitable undertaking. Such mind-set is acceptable and encouraged, and eventually mankind will benefit from such unsettling agenda. The analysis above demonstrates that seawater desalination is a viable business sector with a very profitable outlook. The utilization of direct solar energy is a definite plus technically and economically. The low cost of employing solar energy signifies its potential value. Although land cost has never been mentioned in the costing of this example, due to the government control over public land in Saudi Arabia, however, public land throughout the world can be leased at reasonable rates when utilized for public benefits. The low construction and maintenance cost of the solar energy for desalination of seawater outweighs legal, legislative or political obstacles. It is easy to build easy to maintain and unlike the other two options, is not subject to market or political fluctuation and wrangling, respectively.