Assessing the Relative Efficiency of Health Systems in Sub-Saharan Africa Using Data Envelopment Analysis ()
1. Introduction
Health is now seen as a component of human capital the same way as education and nutritional status [1] -[4] . According to these authors, everyone has an initial health stock that depreciates with age, but can be maintained or even appreciated by combining individual health care and education, and according to the time available. Moreover, according to a study by the World Bank (World Bank, 1993) at least four reasons support the assertion that a healthy individual is more productive and contributes more to economic growth.
・ Health limits the loss of production because of the impact of disease on labor.
・ It allows exploiting the natural resources that were largely inaccessible because they are located in infested areas.
・ It increases the rate of school attendance and allows children to assimilate better the lessons learned.
・ Finally, health frees for other purposes, resources that would have served otherwise to provide care to the sick.
The impact of health on the well-being and overall health of a country probably justifies the huge investments of the states in this area. Indeed, in 1990, global spending on health was evaluated at $1700 million [5] with more than 1000 billion from states; representing 60% of the total. In developing countries (Africa, Asia, Latin America), these costs were estimated at $170 billion, 50% funded by the states.
The role and the importance of health systems in the success of health outcomes are now well established. The issues that remain to investigate are, among other things, why some health systems can be considered more effective than others, and what explain the differences in countries’ health systems.
The purpose of this paper is to shed some more light on this issue that, to our knowledge, has received little attention in the literature. This relative paucity of literature on the subject is associated, according to some authors (for example, [6] or [7] ), to the challenges posed by the comparison of different health systems because, inter alia, of the following reasons:
1) The definition of health proposed by the World Health Organization (WHO) is, according to [8] , useless for all practical purposes, “a perfect state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, not just the absence of disease or illness”.
2) There are many measures of health status (see, for example, [6] or [9] ), especially if we compare individual health indicators, such as “health utilities index” that, as argued by [7] , are unfortunately based on functional capacity concepts rather than on performance.
This second argument should be tempered because, since 2000, a bold demarche for developing a composite index measuring the performance of health systems was conducted by the World Health Organization [10] . It’s an index that determines the overall performance of a health system based both on the level of progress of each country with respect to a number of objectives and on the distribution of the health conditions in the population. Five criteria are generally used for this purpose: 1) The general health; 2) The distribution of this health condition; 3) The responsiveness of the health system; 4) The distribution of responsiveness; 5) The fairness of financial contributions. Unfortunately, as pointed out by [11] , the quality of this synthetic indicator, as well as composite indexes calculated by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) namely, the Human Development Index (HDI) or the Human Poverty Index (HPI), is often questioned by statisticians and economists, both in the mathematical formulation as well as in the reliability of the statistics used.
In this paper, we compare and attempt to provide an explanation on the inefficiencies of health systems of 35 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Our comparative analysis of health systems is based on the concept of efficiency obtained through Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). This concept is related to the production function that shall be defined as the technical interrelationship which results in the maximum output for a combination of production factors and a given technology. This is somehow the ability of each country to transform its sanitary inputs in health outputs [12] . Beyond this definition, this function is also conceived as a frontier or a standard of comparison for assessing efficiency. In other words, the health system of a country will be considered efficient when the combination of outputs and inputs is located on the frontier.
Several reasons justify the appropriateness of the DEA in this study.
1) The popularity of this technique in the field of health lies in its ability to take into account the specificities of the sector such as the complexity of the technology (multi-product/multi-factors) and the absence of true price both for the outputs and for the inputs [13] .
2) It’s suggested for the analysis of complex or non-profit organizations such as public services. As pointed out by [14] , it’s close to the work of Leibenstein of X-inefficiency. Indeed, with DEA we can also characterize an output lying inside the Pareto optimal production frontier by stipulating that the hidden inefficiencies come from two sources: 1) the externalities inherent in the economic system or, more generally, to the political and social environment and 2) the non-apparent production factors or not taken into account by the model and thus related to the company’s management [15] .
Note that the DEA method was applied in health sector by many other authors, including [16] - [18] . However, in these applications, the analysis is usually at the micro level, that is to say, at the hospital level. The objective is then to evaluate the performance of a hospital in comparison to others [16] . This comparison is sometimes made depending on the status: not-for-profit versus for profit private organizations [17] [18] . It also happens to compare, according to their seniority, the practice of physicians within the same hospital [19] .
Our study differs from previous at least on two points:
1) Our analysis is at a more macro level since we compare different countries’ health systems, and not within the same country. We seek to build an international production frontier in the health sector. For each country, we consider all hospitals as a single production unit.
2) In addition, this study is, to our knowledge, one of the first uses of the DEA method to compare health systems of countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
The rest of this article is organized as follows: Section 2 is devoted to the presentation of the DEA method. In Section 3, we present our results of the evaluation of the technical efficiency of the health systems of 35 countries of sub-Saharan Africa. Thus evaluated, the efficiency depends on the specific environment of each country. To provide explanatory elements of the efficiency scores of the different countries, we establish a relationship between the level of efficiency and certain strategic or environmental variables. Our concluding remarks are provided in Section 4.
2. Methodology
We apply DEA to assess the performance of health systems of 35 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. In this section, we first present the DEA and then describe our data and variables.
2.1. The DEA Method
DEA is a non-parametric method initially developed by [20] to evaluate the relative efficiency of the decision making units (DMU) of non-profit institutions, or of the public sector which use a group of similar inputs to produce a group of outputs. The DEA method measures the efficiency of a DMU “o” compared with the set of “n” DMUs in a given sample. The aim is to establish a level of relative efficiency θ (0 £ θ £ 1) for each DMU by comparing its input and output quantities with those of other DMUs.
The efficiency in DEA can be characterized in two ways: the input orientation which supposes a minimization of inputs for a given level of outputs and the output orientation which assumes a maximization of the outputs for a given level of inputs. It’s also possible to consider constant or variable returns to scale. Our analysis is based on the input minimization model with the assumption of variable returns to scale.
Indeed, minimizing inputs seems appropriate because:
1) One considers that, as in the case of public services, the services provided by the state to citizens are exogenous.
2) Resource utilization by the countries studied is generally carried out in a difficult budgetary situation.
3) Based on our data, input values are more dispersed than those of outputs. Therefore, minimizing inputs should allow better discrimination of efficiency scores of countries’ health system.
Besides, the assumption of variable returns to scale can be justified by the fact that it is more general, but also because of our data. Indeed, it's difficult to identify scale inefficiencies in aggregate data as is the case in this study. See [21] for a full discussion of the DEA methods.
The model we have estimated is formally expressed below. All annotations are adopted from [21] and [22] .
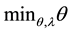 (1)
(1)
Subject to:
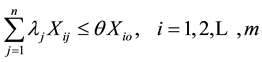 (2)
(2)
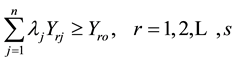 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
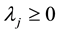 (5)
(5)
where DMUo represents one of the “n” DMUs under evaluation. xio and yro are respectively the ith input and the rth output of the DMUo. s = the number of outputs produced by the DMU; m = number of inputs. θ* (minθ) is a scalar which represents the score of the technical efficiency allotted to the unit under evaluation and is interpreted as the coefficient of the production level attained by the latter. λ is a weighting allotted to DMUs which helps to determine the envelope formed by efficient DMUs (θ = 1).
2.2. Describing the Sample and the Variables
Our data come from the World Bank database [23] . It covers the 1990-1999 periods and involves 35 countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
With aggregated data as ours, we choose as outputs: life expectancy at birth, infant mortality per thousand births and the mortality rate for children under five. These are also some of the outputs generally considered to calculate composite indices measuring the performance of health systems like that of the World Health Organization (WHO, 2000) or of the UNDP (HDI, HPI).
Regarding inputs, like many other authors [16] [17] [19] [22] , we distinguish between labor inputs and capital inputs. The Labor is measured by the number of doctors per 1000 inhabitants. The capital stock is represented by the number of hospital beds per 1000 inhabitants and health expenditures per capita.
To check the sensitivity of our results, we analyze three specifications of the DEA model obtained by different combinations of inputs and outputs (Table 1). The first two specifications differ only on the outputs. In the first model (DEA1), life expectancy at birth and mortality rates of children under five were selected as outputs. In the second model (DEA2), only infant mortality per thousand births was selected as output. Finally, in the third model (DEA3), we select health expenditures as single input.
In the next section, we present the results obtained from these different DEA specifications.
3. Results
First, we present the efficiency scores of the three DEA specifications. Next, like several other authors (e.g. [24] and [25] ) we use, in a second stage, a Tobit regression to analyze the impact of some exogenous factors on the DEA efficiency scores.
3.1. The Efficiency Scores
The efficiency scores are shown in Table 2. They were calculated using DEAP software developed by [26] . The complement to 1 of each efficiency score represents the possible proportional reduction of inputs without any reduction of the output levels. In other words, a country that gets a 90% efficiency score can reduce 10% of its health inputs while maintaining its health outputs at the same level. In light of Table 2, we see that the efficiency scores are sensible to the DEA model specifications. Indeed, with DEA1 and DEA2 models, we observe an average efficiency score around 80%. It’s only 72% with DEA3. With DEA1, 14 countries out of 35 reach a maximum efficiency of 100%. Seven countries are declared efficient with DEA2 and only four countries are found efficient with DEA3 model specification. These declared efficient health systems constitute the frontier or the comparison reference for the other countries’ health system. It is noted, however, that only two countries are found efficient regardless of the type of DEA model specification. Both are countries located in Southern Africa, namely Zambia and Zimbabwe.
3.2. The Determinants of the Efficiency Scores of Countries’ Health System
The observed efficiency scores reflect not only management errors, but also the environmental factors of each country. In what follows, we will try to establish a relationship between the efficiency scores and a number of structural variables associated with each country.
![]()
Table 1. Inputs and outputs of the three different DEA specifications.
The literature distinguishes five main categories of factors that could affect inefficiency in the health system of a country ( [6] [8] [9] [27] - [29] ). These are:
1) Economic variables. These include, among others:
a) The level of economic development as measured by real income per capita calculated assuming purchasing power parity. Indeed, a high income should lead to improved efficiency of the health system. However, it should be noted that the influence of income on health is not as straightforward. It passes through the consumption of goods affecting health (nutrition, hygiene, medical care, education, etc.) The empirical relationship may therefore seem mixed if one also introduces in the regression the variables that characterize the level of consumption of these goods.
b) The extent of poverty and income inequality. Since the poor have limited access to health services, it is ex- pected a positive relationship between inefficiency and the extent of poverty. Similarly, it would be legitimate to think that an unequal income distribution would correspond to a worse health conditions. However, difficult to quantify, the concepts of poverty and inequality are suffering from a lack of universally accepted rigorous definition. Furthermore, there is an abundance of potential indicators for these two related phenomena. As to poverty, because of the lack of satisfactory indicators, either the human poverty index (HPI) or the percentage of the labor force employed in agriculture is used, assuming that the majority of poor are in rural areas. As to inequality in income distributions, the Gini index is often chosen as the relevant explanatory variable.
2) The social and health environment variables. It is assumed that there is a link between the risk of infectious diseases and the quality of the health environment. The frequently used indicators are either the percentage of the population with access to safe water supply or those with access to sanitation services. It is expected a negative correlation between these variables and inefficiency.
3) The parental education. The positive effect of this factor, especially women’s education, was emphasized by Caldwell [27] . Indeed, a higher parent education leads to better child nutrition, finer use of health services and greater attention to hygiene. As variables to characterize the instruction, one retains either the literacy rate or the enrollment rate. The most likely hypothesis is that a low level of literacy or schooling is associated with a low efficiency.
4) The demographic variables. In this case, one often uses the density of the population. The expected relationship between this variable and inefficiency is not a priori obvious. For developing countries, particularly in Africa, two other indicators are used: the percentage of the population below 15 years or below five years. The latter is more relevant because the majority of deaths in Africa occur before the age of five years. So there should be a positive relationship between this percentage and inefficiency.
5) The nature of the political regime. According to the UNDP [30] , democratic regimes achieve higher health outcomes than dictatorial regimes. One often used variable is the Gastil index of civil liberties and political rights provided by the Freedom House.
Taking into account the availability of data, we estimate the following Tobit model:
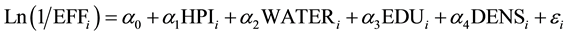 (6)
(6)
where, for country i, EFF = DEA efficiency scores. HPI = the UNPD Human Poverty Index. WATER = percen- tage of the population without access to safe water supply. EDU = the UNPD Education Index. DENS = density of the population.
The results are shown in Table 3.
We observe from Table 3 that the best results, in terms of the significance of the coefficients, are obtained from DEA2 and DEA3 models. Our comments below relate solely to these two models.
We obtain a surprising result with respect to the economic variable used, which is the poverty index (HPI): an inverse relationship between poverty and inefficiency. This somewhat contradictory result is also obtained if we replace HPI by real GDP per capita. Indeed, we found a positive relationship between GDP and inefficiency: it may be possible to spend abundant resources on health while getting very bad results [30] . A more plausible explanation is that the very poor countries are condemned to manage better their health system because they have no other choice. Besides, starting from zero, the relatively limited resources devoted to health can only seem to improve outputs, such as infant mortality.
The health-related variable has the expected sign, but is not significant. The higher is the percentage of the population without access to improved water sources, the greater is the inefficiency.
![]()
Table 3. A Tobit model of the determinants of the efficiency scores of countries’ health system.
***, **, * represent significant coefficients at the 1%, 5% and 10% level respectively.
Our results confirm the role of education as a determinant of efficiency. Indeed, when the level of education rises, the inefficiency decreases.
Finally, with respect to the demographic variable DENS, we found a positive relationship with the inefficiency. A high density leads to an increased inefficiency.
4. Conclusions
Using published data covering the 1990-1999 period, this paper assessed the efficiency of 35 sub-Saharan countries’ health system using the non-parametric technique of DEA. We found that the average efficiency estimates of the countries health system varied from 72% to 84% depending on the combination of inputs and outputs that were considered.
We go beyond this purely descriptive aspect by seeking to identify the factors that can explain the efficiency scores. Our results show that low density of population and the education level contribute to the efficiency of the health system.
To our knowledge, this is one of the first studies using DEA approach to analyzing the efficiency of the health system of countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Additional studies are necessary to understand better and improve the health system of these countries. For example, it would be interesting to extend this study over a longer period. This extension would analyze several sub-periods in order to see the evolution and performance of the health systems. One might also want to make a comparison with other regions. Successful policies of certain countries or regions can inspire others.