Distorted Factor Markets, Government Intervention, and Excess Capital Accumulation: The Case of China ()
1. Introduction
Since the economic reform initiatives in December 1978, the Chinese economy has experienced a real annual growth rate of per capita GDP of 8.8%, a performance that makes China the most rapidly growing economy in the world during this period. However, in contrast with the fast economic growth, household consumption levels are very low. According to Figure 1, at the beginning of the economic reform period, household consumption’s share of GDP was around 50%, which is lower than that of developed countries, yet it has declined sharply since the 1990s. Meanwhile, investment spending has been strong until recently. In particular, household consumption’s share of GDP has been smaller than that of gross capital formation since 2004, indicating the possibility of excess capital accumulation during the rapid economic growth period.
To address the issue of how the Chinese economy can maintain high growth, low consumption, and high in- vestment simultaneously, I focus on China’s imperfect competition factor markets and government intervention.
After Deng Xiaoping’s Southern Tour in 1992, China accelerated the economic reform process, thus moving
![]()
Figure 1. GDP using the expenditure approach. Data indicate the share of each element in GDP. Source: China Statistical Yearbook [9] .
toward a fully fledged market economy. China’s factor markets, however, remain extremely imperfectly competitive. First, the labor market is far from perfect competition in China. The compensation of employees’ share of GDP is lower than that of developed countries, and the share has been declining rapidly since the 2000s (Figure 2). A number of papers argue the underpayment of wages in China. For example, Fleisher et al. [1] claimed that, on average, the wage of highly educated workers was about 7.5% of their marginal productivity in 2000, and the wage of less educated workers was about 19.2% of their marginal productivity. Other papers that discuss the underpayment of wages in China include Dong and Putterman [2] -[4] , Fleisher and Wang [5] , Jefferson and Rawski [6] , Parker [7] , and Yang and Zhou [8] .
In financial markets, because of the undeveloped legal system, creditor and shareholder protection is weak in China (Allen et al. [11] ). Managers may, therefore, focus more on firm growth than maximizing shareholder wealth, for example, by spending free cash flow on unprofitable projects rather than paying dividends to shareholders, resulting in overinvestment. As shown in Figure 3, the share of household dividend in GDP is very low compared with developed countries, indicating the underpayment of capital revenue in China. Adding the under- payment of labor revenue, imperfect factor markets lead to abundant internal reserves among Chinese corporations. In fact, according to the China Statistical Yearbook [9] , self-fundraising’s share of total investment financing was 52% in 1995, rising to close to 70% in 2011, implying there are huge internal reserves being held by Chinese corporations (Figure 4). In previous research, Barnett and Brooks [12] concluded that the heavy reliance on self-financing from profits, combined with weak governance of Chinese corporations, may accelerate capital investment as managers reinvest earnings and expand assets and market share, rather than focus on maximizing the enterprise value to shareholders. Knight and Ding [13] argued the importance of retained earnings and informal funds for all types of ownership. In particular, individually owned enterprises relied on such funding for over 95% of investment, and even state-owned enterprises raised at least 60% in this way. Both the studies using macro data and those using micro data indicated that the internal reserves of Chinese corporations have played an important role in capital investment. Guariglia et al. [14] used a panel of 79,841 Chinese firms over the period 2000-2007 and found that the availability of internal finance represents a binding constraint for the growth of private firms, especially those operating in coastal regions, with negligible foreign ownership. Furthermore, Poncet et al. [15] used firm-level data for China from the Oriana dataset over the period 1998-2005 and found that private Chinese firms competing directly with numerous state-owned enterprises in the same province/industry depend more strongly on their internally generated funds for their investment and appear more credit constrained, which impedes their growth. Ding et al. [16] examined the efficiency of the capital investment of Chinese enterprises using a firm-level dataset of 100,112 firms over the period 2000-2007 and found that overinvestment is observed for all types of firms, and that the free cash flow hypothesis provides a good explanation of China’s overinvestment in the most efficient and most profitable private sector, while in the state sector, overinvestment is attributable to the poor screening and monitoring of enterprises by banks. In another study, Yang and Guariglia [17] used 1168 listed firms from 1999 to 2010 and
![]()
Figure 2. Compensation of employees’ share of GDP. Sources: 1992-1999 is from data of flow of funds of China: 1992-2004 [10] , and 2000-2009 is from China Statistical Yearbook [9] .
![]()
Figure 3. Income from properties’ share of GDP. Sources: 1992-1999 is from data of flow of funds of China: 1992-2004 [10] , and 2000-2009 is from China Statistical Yearbook [9] .
found that overinvestment is positively and significantly related to positive free cash flow, resulting from firms’ agency costs.
Furthermore, local government officials have strong political incentives to promote local economic growth in China. A growing body of economic literature has argued that the Chinese central government rewards and punishes local officials on the basis of their economic performance to motivate them to promote their local economy. For example, Blanchard and Shleifer [18] compared the political incentives of local governments that lead to different economic performance in China and Russia. Zhou [19] , [20] argued that promotion tournaments, as an incentive system governing Chinese local officials, are a possible source of China’s miraculous growth. How- ever, they are also the root of many profound and pressing problems for the Chinese economy. Li and Zhou [21] found that the likelihood of the promotion of provincial leaders increases with their positive economic performance, while the likelihood of termination decreases with their economic performance. Zhang and Gao [22] re- vealed a positive impact of both term limits and rotation of governors across provinces on local economic growth. However, as local government officials encourage corporations to invest in order to stimulate GDP
![]()
Figure 4. Sources of funds for investment in fixed assets in China. Data indicate the share of each source to total funds. Source: China statistical yearbook [9] .
growth, this ultimately leads to inefficient investment during the rapid growth process. Chen et al. [23] found that political connections significantly reduce investment efficiency in SOEs (state-owned enterprises), but do not find such evidence in non-SOEs. Moreover, Chen and Lou [24] indicated that the turnover of local governors results in more investment expenditure and lower investment efficiency; the turnover frequency is positively related to investment volatility. The influence is stronger in state-owned enterprises.
Only a few papers discuss the inefficient economic growth in China in a general equilibrium model. Zou [25] built a growth model where social planners derive positive utility from both consumption enjoyed by the people and capital stock owned by the state, and found that the capital stock is larger than the modified golden rule stock in the steady state. Gu [26] also built a simple growth model and found that when labor is extremely underpaid, despite the existence of the underpayment of capital revenue, the capital stock will be over accumulated, exceeding its golden rule level.
In contrast with existing theories of economic growth, this paper develops a simple growth model in which both financial markets and labor markets are distorted, and the government intervenes in corporate management activities. As corporate governance is imperfect, profits from the underpayment of factor revenues are accumulated as internal reserves. In addition, because of the pressure to overinvest from local officials, managers invest in capital excessively. The main finding of this paper is that the model can explain high economic growth, low consumption, and high investment simultaneously, which have occurred within the Chinese economy since the 1990s, implying the inefficiency of economic growth. The contribution of this paper is to attempt to explain the inefficiency of rapid economic growth with excess capital accumulation in China in a general equilibrium framework that embeds distorted factor markets and government intervention, which has not been done in previous research.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the model. Section 3 presents a quantitative analysis. Section 4 provides a conclusion.
2. The Model
I develop a continuous-time, closed-economy model assuming there are only two groups of agents, namely households, having 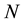 members, and managers, having
members, and managers, having 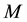 members. The total population in this economy is
members. The total population in this economy is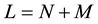 . I assume population growth is constant. Each member of households and managers offers one unit of labor to the firms in each period.
. I assume population growth is constant. Each member of households and managers offers one unit of labor to the firms in each period.
2.1. Underpayment of Wages
As discussed in the introduction, there is strong evidence supporting the underpayment of wages in China. One of the most obvious reasons is monopsony labor markets. The main purpose of this model is to produce an overaccumulation of capital; therefore, I do not explicitly exhibit the microfoundations of monopsony1. Instead, the underpayment of wages is expressed as a percentage of labor wage as follows
 (1)
(1)
where 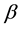 is the degree of underpayment of wages and
is the degree of underpayment of wages and  is the marginal productivity of labor.
is the marginal productivity of labor.
2.2. Imperfect Corporate Governance and Government Intervention
Technology is given by
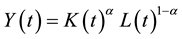 (2)
(2)
where  is the capital share.
is the capital share. 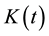 and
and 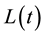 represent capital stock and labor input, respectively. I assume there are two kinds of capital in this economy,
represent capital stock and labor input, respectively. I assume there are two kinds of capital in this economy,  owned by the households, and
owned by the households, and 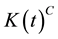 owned by the corporations. Therefore, the production function can be rewritten as
owned by the corporations. Therefore, the production function can be rewritten as
![]() (3)
(3)
where ![]() and
and ![]() are the total labor input of households and managers, respectively. Dividing both sides of Equation (2) by
are the total labor input of households and managers, respectively. Dividing both sides of Equation (2) by![]() , I obtain the per capita product function
, I obtain the per capita product function
![]() (4)
(4)
where ![]() is the household’s share of the total population. I define
is the household’s share of the total population. I define ![]() and
and
![]() , indicating that the corporations’ capital is owned equally by both households and managers.
, indicating that the corporations’ capital is owned equally by both households and managers.
As corporate governance is imperfect, the monopoly profit from the underpayment of wages is not returned to shareholders as dividends, instead it is accumulated as internal reserves. In addition, the managers of corporations experience pressure from local officials to stimulate GDP growth; therefore, they accumulate capital passively2. The transition equation for corporation’s capital is
![]() (5)
(5)
where ![]() is the interest rate and
is the interest rate and ![]() is the depreciation rate.
is the depreciation rate. ![]() is the
is the
monopoly profit from the underpayment of wages. To capture the weak protection to creditors and shareholders
in China, I introduce![]() , which indicates the share of the corporation’s capital income and monopoly
, which indicates the share of the corporation’s capital income and monopoly
profit that is accumulated for the next period. The rest is executive perks enjoyed by the managers3.
I assume the managers do not optimize their consumption; instead, they consume all the revenue in every period
![]() (6)
(6)
where ![]() is the per capita consumption of managers,
is the per capita consumption of managers, ![]() is the labor wage, and
is the labor wage, and ![]() is the manager’s share of the total population.
is the manager’s share of the total population.
2.3. Households
The preferences of the representative household are described by
![]() (7)
(7)
where ![]() is the per capita consumption of the household,
is the per capita consumption of the household, ![]() is the time preference rate, and
is the time preference rate, and ![]() is the intertemporal elasticity of substitution. The household’s budget constraint is given by
is the intertemporal elasticity of substitution. The household’s budget constraint is given by
![]() (8)
(8)
Under the special circumstances described in Section 2.2, distorted factor markets and intervention by gov- ernment, I assume that households do not take the factor prices as given when optimizing their consumption and saving behavior. Therefore, simplifying the first-order conditions for utility maximization, I obtain the following Euler equation
![]() (9)
(9)
where ![]() and
and ![]() indicate differentiation with respect to
indicate differentiation with respect to![]() .
.
3. Quantitative Analysis
In this section, I simulate the model described above. In accordance with the growth literature, I use ![]() for the capital share,
for the capital share, ![]() for the time preference rate, and
for the time preference rate, and ![]() indicating log utility. I set
indicating log utility. I set![]() , which is the household’s share of the total population. As there is less information on
, which is the household’s share of the total population. As there is less information on![]() , the share of the corporation’s capital income and monopoly profit accumulated for the next period, I assume
, the share of the corporation’s capital income and monopoly profit accumulated for the next period, I assume![]() . For the purpose of deriving the dynamics of the variables in this model, I assume the following situation. First, there is 5% underpayment of wages in this economy at year 0,
. For the purpose of deriving the dynamics of the variables in this model, I assume the following situation. First, there is 5% underpayment of wages in this economy at year 0,![]() . Consider a shock that worsens the degree of underpayment of wages from 5% to 15% in year 5. This assumption is consistent with Chinese data as illustrated in Figure 2; that is, the compensation of employees’ share of GDP is lower than developed countries, and has been declining rapidly since the 2000s. There are two possibilities in terms of the households’ response. One is that the households anticipate this deterioration in the degree of underpayment of wages at year 0 in the perfect foresight case. The other is that households do not anticipate this deterioration of the underpayment of wages at year 0; instead, this event occurs suddenly in year 5. I consider both situations in this simulation. The numerical algorithm used here is the relaxation algorithm (Strulik and Trimborn [32] ; Trimborn et al. [33] ).
. Consider a shock that worsens the degree of underpayment of wages from 5% to 15% in year 5. This assumption is consistent with Chinese data as illustrated in Figure 2; that is, the compensation of employees’ share of GDP is lower than developed countries, and has been declining rapidly since the 2000s. There are two possibilities in terms of the households’ response. One is that the households anticipate this deterioration in the degree of underpayment of wages at year 0 in the perfect foresight case. The other is that households do not anticipate this deterioration of the underpayment of wages at year 0; instead, this event occurs suddenly in year 5. I consider both situations in this simulation. The numerical algorithm used here is the relaxation algorithm (Strulik and Trimborn [32] ; Trimborn et al. [33] ).
The effects on the major economic variables are plotted in Figure 5: household consumption, household capital, total net investment, household consumption share of GDP, total consumption share of GDP, total net in- vestment share of GDP, percentage of executive perks to wages, total capital, and GDP. Values for macroeconomic aggregates are detrended and expressed relative to their preshock steady state values. Values for economic rates are expressed in percentage points. In each panel, the aftershock steady state value to which the economy eventually converges is indicated by a red circle. Red solidlines show adjustment dynamics for the perfect foresight case, and the blue dottedlines show adjustment dynamics when the shock hits the economy unexpectedly at![]() .
.
In the perfect foresight case, households adjust their consumption at year 0, indicating that they are eager to smooth consumption and react to the expected lower wages in the future by reducing consumption and initiating an investment spurt today. However, when the shock is realized at year 5, households decrease their consumption, and at the same time, they also start to reduce their capital stock because of the lower revenue. In contrast, because managers have more internal reserves from monopoly profits, they increase their corporation’s capital investment at year 5. Therefore, total net investment increases in year 0, and total capital increases from year 1. The household (total) consumption share of GDP is decreasing, the total net investment share of GDP is increasing, and GDP is increasing. All of these phenomena are consistent with Chinese economic growth since the 1990s. If the shock of the higher degree of underpayment of wages is realized in year 5, the dynamic paths of the model variables are similar to that above, except for the adjustment process of consumption and investment. In this case, consumption and investment stay at their initial levels for the next five years and adjustment com-
![]()
Figure 5. Adjustment paths for the shock of an increase in the degree of underpayment of wages from 5% to 15% coming into effect in year 5. Red solidlines: anticipated at year 0. Blue dottedlines: unanticipated shock. Red circle: the new steady state. Macroeconomic aggregates measured in terms of relative deviation from preshock steady state; macroeconomic rates measured in terms of percentage points.
mences at year 5.
Finally, the welfare analysis is illustrated in Table 1. The preshock steady state consumption equivalent is 1.2728, the consumption equivalent from the preshock steady state to the new steady state under perfect foresight is 1.2565, indicating a 1.28% welfare loss compared with the preshock consumption equivalent. I also calculate consumption equivalents of the case of an unanticipated shock, the case of![]() , and the case of a Ramsey economy. These results are presented in Table 1.
, and the case of a Ramsey economy. These results are presented in Table 1.
4. Conclusions
Since the beginning of economic reform in 1978, China has experienced the most rapidly growing economy in the world. However, the factor markets are still far from perfect competition. As a result, the labor and capital revenues were strikingly underpaid, leading to huge internal reserves among firms. In addition, because of the promotion tournaments, local officials have an incentive to pressure corporations to accumulate capital passively, simulating economic growth.
Based on the findings of previous research, in this paper, I develop a simple growth model that embeds dis- torted factor markets and government intervention. This model can demonstrate high economic growth, low consumption, and high investment simultaneously, which have been presented in Chinese macroeconomic data since the 1990s, implying the inefficiency of Chinese economic growth.
There are, however, several extensions required. For example, this model did not explicitly describe the microfoundations of managers’ overinvestment motivation. In other words, it is necessary to analyze the interaction between local government officials and firm managers. In addition, the origin of the distortion of factor markets is not yet clear and this needs to be investigated empirically and theoretically in future research.
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to Etsuro Shioji, Makoto Saito, Harry Xiao-Ying Wu, Shang-Jin
Note: Column 1 presents the preshock steady state consumption equivalents, column 2 presents the consumption equivalents from the preshock steady state to the new steady state under anticipation, while the consumption equivalents of unanticipated shocks are in parentheses. Column 3 reports the Ramsey economy’s consumption equivalents from the preshock steady state to the modified golden rule.
Wei, Kyoji Fukao, Tokuo Iwaisako, Ryoji Ohdoi, Peng Xu and an anonymous referee for their helpful comments and encouragement. This research is financially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 26885074 and the Suntory Foundation. Of course, any errors are my own.
NOTES
1Bhaskar and To [27] , [28] and Barr and Roy [29] developed simple microfoundation models of monopsony.
2For simplicity, the optimal behavior between firm managers and local officials is not considered in this model. I leave this important issue for future research.
3Kato and Long [30] estimated that executive perks account for 15% to 32% of the total annual compensation of executives in China. Adithipyangkul et al. [31] reported that the median total cash compensation paid to the top three executive officers is 0.30 million RMB, while the median of executive perks (the sum of expenditures for meals, travel, company cars, communications, socializing, and entertainment) is 1.39 million RMB.