Effect of Sevelamer Hydrochloride on the Serum Calcitriol Concentration in Hemodialysis Patients ()
1. Introduction
Secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) associated with hyperphosphatemia and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) are known to play central roles in the pathological state of CKD-MBD (chronic kidney disease-min- eral and bone disorder) [1] . Hyperphosphatemia is one of risk factors for vascular calcification [2] , and associa- tions with cardiovascular complications and shortening of life expectancy have been reported based on epidemi- ological studies of CKD patients [3] [4] . Favorable bone mineral metabolism and prevention of cardiovascular complications may be possible by performing phosphorus management at earlier stages of CKD, and guidelines that recommend appropriate phosphorus management have been prepared recently [5] - [7] .
It is no exaggeration to say that phosphate binders, along with restriction of ingestion of phosphorus-con- taining foods [8] and phosphorus removal by dialysis therapy [9] , are essential to properly managing phosphorus. The phosphate binders that can currently be used in Japan are roughly divided into two categories: calcium-con- taining phosphate binders and calcium-free phosphate binders. Calcium-containing phosphate binders have long been used worldwide, but based on the results of recent research there is concern that they may cause low-turn- over bone disease and vascular calcification as a result of the calcium load [10] , and the calcium-free phosphate binders, sevelamer hydrochloride and lanthanum carbonate, were developed in view of this drawback. Favorable serum-phosphorus-lowering actions [11] [12] and the possibility of an ameliorating effect on the life expectancy of elderly dialysis patients [13] [14] were demonstrated, and one after the other they have been applied clinically in Japan as well as abroad.
Based on its mechanism of action, sevelamer has strong affinity for bile salts in addition to directly binding phosphorus in the gastrointestinal tract [15] . When sevelamer binds bile salts, absorption into the body of fat- soluble substances that should ordinarily be dissolved by the bile salts and absorbed may be inhibited. Active vitamin D, which plays an important role together with phosphate binders in the management and treatment of CKD-MBD, falls into the category of these fat-soluble substances, and there has even been a report of a de- crease in the bioavailability of an oral calcitriol preparation in an experiment in which SH was used in Beagle dogs [16] . However, while there has been a report of a similar study in which healthy humans were the subjects [17] , there has never been a report of a study that investigated whether SH actually inhibits the absorption of an oral calcitriol preparation in vivo in hemodialysis patients, who are important treatment targets both clinically and in reality. The purpose of the present study was to compare the serum 1-25(OH)2D concentrations when the phosphate binder was switched from LC to SH in subjects who were hemodialysis patients being treated for CKD-MBD with oral calcitriol.
2. Methods
2.1. Patients and Procedure
The hemodialysis (HD) patients attending our clinic who were being treated for CKD-MBD with a phosphate binder and oral calcitriol (Rocaltrol capsules 0.25 μg, 0.5 μg, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Tokyo) were candidates of this study. The aims of the study were explained to the candidates, and after obtaining the consent of the patients themselves to participate in this study, we were careful to protect their personal information. Exclusion criteria were: inability to comply with regular ingestion of the drugs for any reason, a past history of an adverse event during treatment with a phosphate binder, a past history of digestive tract resection or cholecystectomy, and be- ing an SHPT patient in whom control with cinacalcet hydrochloride was impossible. We constantly checked for the development of adverse events or side effects during the observation period, and if there was a problem, immediately took measures to deal with it, such as discontinuing ingestion, drug therapy, etc., and recorded it. The Institutional Review Board of the Matsushita Nephrology Clinic approved all study protocols (A0002), and they were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines regarding ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Informed consent was obtained from all of the subjects being in- formed about the study.
The study design was a retrospective study. The phosphate binders lanthanum carbonate (Fosrenol tablets; 250 mg, 500 mg, immediately after each meal, Bayer Yakuhin, Osaka: abbreviated LC below) and sevelamer hydrochloride (Renagel tablets; 250 mg, immediately before each meal, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Tokyo: abbre- viated SH below) were each taken orally in that order for 4 weeks, and the dose of oral calcitriol during that pe- riod was maintained constant. Oral calcitriol was taken immediately after each meal, and the blood 1-25(OH)2D concentration (pg/ml; Japan Medical, Yamanashi Prefecture) 12 hours later was measured after taking each of the phosphate binders for 4 weeks and used as the primary endpoints. The treatment of SHPT consisted of ad- justing the parathyroid hormone level (wPTH) with the dose of cinacalcet hydrochloride (Regpara tablets 25 mg, 75 mg, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Tokyo; abbreviated CH below) to achieve the target level of 35 - 140 pg/ml.
We used CarbostarÒ-P as the dialysis solution. The electrolyte concentrations (mEq/L) after preparing the di- alysis solution are: Na+, 140; K+, 2.0; Ca2+, 3.0; Mg2+, 1.0; Cl−, 111; HCO3−, 35; citrate3−, 2.0. Blood was col- lected before hemodialysis at the start of the week (M-W-F pattern: on Monday; Tu-Th-Sa pattern: on Tuesday), and each of the parameters was measured. The following 11 parameters [units] were measured: 1-25(OH)2D [pg/ml], 25(OH)D [ng/ml], corrected Ca [mg/dl], P [mg/dl], whole PTH (wPTH) [pg/ml], pH, 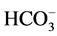 [mEq/l], base excess (BE) [mEq/l], total cholesterol (T-Chol) [mg/dl], non-HDL-cholesterol (non-HDL-Chol) [mg/dl], and triglyceride (TG) [mg/dl]. The pH,
[mEq/l], base excess (BE) [mEq/l], total cholesterol (T-Chol) [mg/dl], non-HDL-cholesterol (non-HDL-Chol) [mg/dl], and triglyceride (TG) [mg/dl]. The pH,  , and BE measurements were made in the laboratory of our clinic with a GASTAT-602i blood gas analysis unit (Techno Medica, Yokohama), and the other parameters were meas- ured at a testing center (BML, Yamanashi Branch, Yamanashi Prefecture). wPTH was measured with an IRMA kit (DS Pharma Biomedical, Osaka).
, and BE measurements were made in the laboratory of our clinic with a GASTAT-602i blood gas analysis unit (Techno Medica, Yokohama), and the other parameters were meas- ured at a testing center (BML, Yamanashi Branch, Yamanashi Prefecture). wPTH was measured with an IRMA kit (DS Pharma Biomedical, Osaka).
2.2. Statistical Analysis
We performed paired t-test to compare the results of each of the tests when the switch had been made from LC to SH. And we also performed a gression analysis to assess the relationship between wPTH and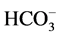 . The test results are expressed as mean values ± standard deviation. When we compared the test results according to phosphate binder, we added the difference between the means and the 95% confidence interval, and when the significance level (p value) was less than 5% (p < 0.05), we concluded that a statistically significant difference existed. We used the JMP8 software program (JMP Japan, Tokyo) to perform the statistical analysis.
. The test results are expressed as mean values ± standard deviation. When we compared the test results according to phosphate binder, we added the difference between the means and the 95% confidence interval, and when the significance level (p value) was less than 5% (p < 0.05), we concluded that a statistically significant difference existed. We used the JMP8 software program (JMP Japan, Tokyo) to perform the statistical analysis.
3. Results
No adverse events or side effects that appeared to be attributable to oral LC or SH were observed during the study period, and all of the subjects completed the entire 8-week study period. There were 35 males (76%) among the 46 subjects, and 16 subjects (35%) were diabetic. The subjects’ age was 65.3 ± 10.8 years, and their dialysis vintage was 113.7 ± 65.4 months (Table 1). The daily dose of calcitriol prescribed, which was constant throughout the study period, was 0.32 ± 0.11 μg.
The changes in test results, which are reported as “LC group ® SH group, units, p value,” were: 1-25(OH)2D, i.e., the primary endpoint, 19.9 ± 9.0 ® 14.2 ± 8.1 pg/ml, p < 0.001, and with a difference and [95% confidence intervals] of −5.7 pg/ml and [−2.8, −8.5], had significantly decreased in the SH group, but the difference in 25(OH)D values (22.1 ± 12.4 ® 25.9 ± 10.6 ng/ml, p = 0.143) was not significant. The results for the drug taken during this period were: CH 16.3 ± 23.8 ® 15.7 ± 23.6 mg/day, p = 0.160, and the difference was not significant; the results for the two phosphate binders were: LC 1443 ± 671 mg/day and SH 3897 ± 1888 mg/day. The results of bone mineral metabolism tests were: corrected Ca, 9.6 ± 0.7 ® 9.6 ± 0.7 mg/dl, p = 0.918; P, 4.4 ± 1.3 ® 4.7 ± 1.6 mg/dl, p = 0.135; and wPTH, 65.9 ± 41.2 ® 61.5 ± 42.2 pg/ml, p = 0.080, and none of the differences were significant. The test results for impact on acid-base equilibrium were: pH, 7.34 ± 0.03 ® 7.33 ± 0.04; p < 0.05, 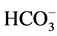 , 22.5 ± 2.4 ® 20.3 ± 2.4 mEq/l, p < 0.001; and BE, −2.8 ± 2.3 ® −4.8 ± 2.6 mEq/l, p < 0.001, and significant worsening of the acidosis in the SH group was observed in the results for all 3 parameters. The test results for lipid metabolism were: total cholesterol, 157.3 ± 31.4 ® 135.3 ± 27.0 mg/dl, p < 0.001 and non- HDL-cholesterol, 110.3 ± 26.8 ® 85.3 ± 19.7 mg/dl, p < 0.001, and significant decreases were observed, but the difference in triglyceride values, 101.8 ± 80.8 ® 101.6 ± 84.2 mg/dl, p = 0.975, was not significant (Table 2).
, 22.5 ± 2.4 ® 20.3 ± 2.4 mEq/l, p < 0.001; and BE, −2.8 ± 2.3 ® −4.8 ± 2.6 mEq/l, p < 0.001, and significant worsening of the acidosis in the SH group was observed in the results for all 3 parameters. The test results for lipid metabolism were: total cholesterol, 157.3 ± 31.4 ® 135.3 ± 27.0 mg/dl, p < 0.001 and non- HDL-cholesterol, 110.3 ± 26.8 ® 85.3 ± 19.7 mg/dl, p < 0.001, and significant decreases were observed, but the difference in triglyceride values, 101.8 ± 80.8 ® 101.6 ± 84.2 mg/dl, p = 0.975, was not significant (Table 2).
Next, the results for 1-25(OH)2D, the primary endpoint, according to daily dose of calcitriol prescribed (num- ber of subjects, LC group ® SH group, mean difference, [95% confidence interval], p value, daily SH dose pre- scribed) were: calcitriol 0.25 μg group, 34 subjects, 17.5 ± 5.5 ® 13.7 ± 7.1 pg/ml, −3.9, [−6.8, −0.9], 0.012, and 3816 ± 1493, and had significantly decreased, and C 0.5 μg group, 12 subjects, 26.5 ± 13.3 ® 15.9 ± 10.6 pg/ml, −10.6, [−17.9, −3.3], 0.008, and 4125 ± 2797, and had decreased even more, and significantly (Figure 1). The difference in prescribed SH dose was not significant.
4. Discussion
The phosphate binder SH, which is widely used throughout the world, is a polycationic polymer that does not
![]()
Table 1. Characteristics of the study patients.
![]()
Table 2. Clinical characteristics of the patients treated with lanthanum carbonate (LC) and sevelamer hydochloride (SH).
Abbreviations: 1-25(OH)2D, 1-25-dihydroxyvitamin D; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; PTH, parathyroid hormone; HDL, high density lipoprotein.
contain Ca or aluminum (Al). One SH molecule, by ionic binding or hydrogen binding to one phosphoric acid molecule, which has a negative electrical charge in the digestive tract, is excreted in the urine and feces without being absorbed into the body, and is thought to inhibit phosphate absorption [18] . Because SH has the property of not being absorbed by the digestive tract, it is hard to imagine that SH has any direct effect on calcitriol me- tabolism [19] . However, it cannot be categorically stated that SH does not have any impact at all on calcitriol metabolism, especially absorption, etc., mediated by an indirect effect. The inhibitory action of SH on calcitriol absorption that was observed in studies conducted on animals or healthy subjects alone in the past [16] [17] was similarly observed in the results obtained in the present study in hemodialysis patients who were actually being treated clinically. The results according to C prescription group (0.25 μg vs. 0.5 μg) showed that while the 1-25(OH)2D concentration in the 0.5 μg group had significantly decreased in comparison with the 0.25 μg group, no correlation was observed between the decreases and SH doses prescribed. Based on this result, it also ap- peared that the SH dose taken in this study was excessive in terms of the inhibitory effect of SH on calcitriol absorption into the body, but there have been no reports of studies that investigated the effects of the amounts of SH and calcitriol on the serum 1-25(OH)2D concentration in the HD patients. The characteristic of SH as a hy- drocarbon polymer that has strong non-selective affinity for aliphatic polycyclic molecules, i.e., bile acids, vita- min D, and vitamin K [20] , in addition to the possibility that the absorption of fat-soluble substances that should ordinarily dissolve in bile salts and be absorbed into the body is inhibited as a result of SH binding to bile salts
![]()
Figure 1. Changes in serum 1-25(OH)2D in patients switched from lanthanum carbonate (LC) to sevelamer hydrochloride (SH) depending on the dose of oral calcitriol.
[15] can be cited as the mechanism responsible for this action. Furthermore, the acidosis-exacerbating and lipid- lowering actions of SH that have been reported in Japan and abroad [21] [22] were similarly observed in the present study.
The change in phosphate binder did not bring about any significant change in wPTH, but we had predicted that wPTH would increase if the 1-25(OH)2D concentration decreased and the acidosis worsened (Table 2). When we examined the before-after differences in wPTH and 1-25(OH)2D, we did not find any significant cor- relation between them, and it appeared that the 1-25(OH)2D levels observed in the results of this study may have been too low to have had an effect on wPTH. When we performed a regression analysis of the before-after dif- ferences in wPTH and HCO3 in order to investigate this from the standpoint of the acidosis, we found that wPTH had significantly increased (DwPTH increase) as the acidosis worsened (DHCO3 decrease) (R2 = 0.324, p < 0.001), and the results were as we had predicted (Figure 2). In addition, there is also a report in regard to lipid metabolism that non HDL-C is unaffected by meals and can serve as a lipid control index in dialysis patients, and that it is a better predictor than LDL-C of the risk of myocardial infarction [23] . The results of the present study also showed significant improvement in response to SH, and that SH is useful in regard to lipid metabol- ism.
The phosphate binder LC, on the other hand, contains neither Ca nor Al, and its clinical use in Japan as a phosphate binder whose source is the rare-earth transition element lanthanum and that forms a strong complex with P was initiated in 2009. It has been reported that since LC has strong P-binding power, efficacy can be ex- pected with small doses, and that it is mainly excreted in bile [24] . The same as in a previous report [17] , the re- sults of the present study, which was conducted on HD patients, showed that LC has no effect on the blood con- centration of calcitriol that has concomitantly been taken orally. However, although LC was thought to have al- most no clinical effects, there is also a report that when LC and calcitriol were taken concomitantly it took longer for calcitriol to reach its peak blood concentration (tmax) than when calcitriol was taken alone [17] , and caution is required when investigating the pharmacokinetics of calcitriol when a single dose is taken.
Drug blood concentration-time curves, which are produced by making frequent serial measurements of the blood concentration of a drug after administering it, and area under the blood concentration-time curve (AUC), in which the curve is bounded by a time axis, are used as indexes of drugs’ in vivo kinetics. In a study of blood concentrations over a 48-hour period after hemodialysis patients received a single oral dose of C (2 μg), its blood half-life (t1/2) was reported to be 38.4 ± 13.6 hours, and the concentration at 12 hours after the dose cor- responded to the portion of the drug blood concentration-time curve in which the concentration was stable and there was little gradient [25] . In the present study, we measured the blood concentration of calcitriol 12 hours af- ter it was taken concomitantly with each of 2 different phosphate binders, and compared the results. When in-
![]()
Figure 2. Correlation of difference of whole PTH and HCO3 switched from lanthanum carbo- nate (LC) to sevelamer hydrochloride (SH).
vestigating pharmacokinetics in detail under ordinary circumstances the assessment should be conducted by preparing a blood concentration-time curve and including such parameters as AUC. However, drawing frequent blood specimens over a long period in dialysis centers that do not have inpatient facilities is unrealistic and en- tails the risk of having a detrimental effect on patients. Consequently, in order to make measurements and evalu- ations in a state in which the blood calcitriol concentration was stable, in the present study we set up conditions in which C was ingested and a blood specimen was collected 12 hours later, a time when the blood concentration was thought to have become relatively stable, under circumstances in which a constant dose of C was repeatedly taken over a 4-week period and the blood concentration of C was in a steady state, i.e., repeatedly rising and falling within a certain range.
The results of the present study showed that SH does not affect the 25(OH)D values of HD patients who take C concomitantly. However, when we investigated its concentration distribution, the patients whose values fell within the range recommended in the K/DOQI guidelines (>30 ng/ml) [26] accounted for no more than approxi- mately 15%, while those whose 25(OH)D level was <15 ng/ml, i.e., a deficiency level, accounted for approxi- mately 25% of the total, and the median value was 19 ng/ml. These results once again confirmed that the 25(OH)D concentrations of HD patients are very low, the same as in previous reports in Japan and abroad.
There have also been previous reports that the 1-25(OH)2D concentrations of HD patients as well as their 25(OH)D concentrations are associated with arteriosclerosis and vascular endothelial function [27] and that tak- ing active vitamin D is associated with a favorable life expectancy [28] , but the reports were based on observa- tional studies, and investigation of a causal relationship by a large-scale randomized controlled study is antici- pated. The 1-25(OH)2D in the body functions as a hormone in the management of bone mineral metabolism in concert with PTH and FGF-23, and calcitriol preparations are drugs that have an important role in managing and treating CKD-MBD in HD patients. The results of the present study showed that when SH and C are taken con- comitantly the C concentration may not be as high as expected, so that we consider caution to be necessary. Faced with these results, in the future it will be necessary to design separate protocols for studies of how to ad- just the oral dose of phosphate binders and the time of C ingestion, etc., and study their pharmacokinetics and precise effects in HD patients.
5. Conclusion
In HD patients, SH significantly reduced serum 1-25(OH)2D concentrations after oral calcitriol administration compared to LH. When we use SH as a phosphate binder with calcitriol for HD patients with CKD-MBD, we should consider the inhibitory effect of SH on oral calcitriol absorption.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.