1. Introduction
The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) describes the relationship between income per capita and environmental degradation as an inverted U-shape. At initial stages of economic development and low income per capita, environmental degradation increases with income because increased production leads to pollution. Eventually, the environmental problems are redressed as demand for environmental quality increases with rising income.
Since the initial EKC study by [1] , a number empirical EKC studies have been published [2] - [9] . Theoretical EKC models that have been developed to help motivate the EKC have included infinitely-lived agent models ( [10] [11] ) and overlapping generation models ( [12] ). [13] develop the Green Solow Model, an extension of the Solow model including a resource constraint.
[14] approach the EKC from a consumer standpoint and assumes increasing returns to pollution abatement. These authors derive conditions for a turning point or the point at which pollution degradation is maximized. The present study provides a utility maximizing theoretical framework motivating the EKC model. Theoretical parameters are linked directly to the typical empirical parameters of the reduced form empirical EKC model. Linking theoretical parameters to the typical empirically estimated parameters is relevant for devising policy and future EKC studies.
2. Theory
Consider agent 1 in the upstream country (U) and agent 2 in the downstream country (D). The utility of agent 1 is a general function of their consumption and pollution,
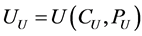 (1)
(1)
and the downstream agent utility is a function of their consumption and pollution,
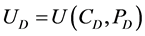 (2)
(2)
Utility is quasi-concave in C and P for upstream and downstream agents. Pollution in the upstream country is a function of consumption 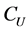 and environmental effort
and environmental effort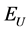 ,
,
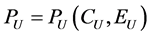 (3)
(3)
where 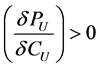 and
and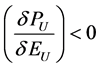 .
.
Pollution in the downstream country is a function of consumption and environmental effort in the downstream country, plus the fraction of upstream pollution that travels downstream,
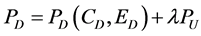 (4)
(4)
where 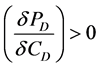 and
and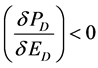 .
.
Income  is spent on consumption
is spent on consumption  and environmental effort
and environmental effort  Prices of
Prices of 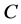 and
and 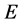 are normalized to 1 in the income constraint
are normalized to 1 in the income constraint
 (5)
(5)
where![]() .
.
In a specified utility function, agent ![]() maximizes
maximizes
![]() (6)
(6)
where ![]() is the constant marginal disutility of pollution assumed equal to one. Upstream utility
is the constant marginal disutility of pollution assumed equal to one. Upstream utility
![]() (7)
(7)
where ![]() is the marginal disutility of pollution assumed equal to one. Upstream pollution is a quadratic function of consumption and environmental effort in upstream and downstream countries,
is the marginal disutility of pollution assumed equal to one. Upstream pollution is a quadratic function of consumption and environmental effort in upstream and downstream countries,
![]() (8)
(8)
Substituting the pollution function into the utility function utility![]() . For notational convenience let
. For notational convenience let ![]() and
and![]() . To ensure that the reduced form utility function is concave, assume
. To ensure that the reduced form utility function is concave, assume ![]() and
and ![]() which in turn require the parameter restrictions
which in turn require the parameter restrictions ![]() and
and![]() .
.
The upstream agent chooses consumption and effort to maximize utility, subject to the budget constraint![]() . The adding-up conditions on the solutions to this problem require the further parameter restriction that
. The adding-up conditions on the solutions to this problem require the further parameter restriction that ![]() 1. Optimal consumption and effort levels in the upstream country are
1. Optimal consumption and effort levels in the upstream country are
![]() (9)
(9)
![]() (10)
(10)
In general ![]() or
or
![]() (11)
(11)
Again ![]() represents marginal disutility of pollution in the downstream country, assumed equal to one.
represents marginal disutility of pollution in the downstream country, assumed equal to one.
Pollution in the downstream country is
![]() (12)
(12)
where ![]() represents the fraction of upstream pollution that flows downstream. For simplicity, assume
represents the fraction of upstream pollution that flows downstream. For simplicity, assume ![]() so that all upstream pollution flows downstream. Substituting (8) into (12) expresses downstream pollution as a function of upstream and downstream consumption and environmental effort,
so that all upstream pollution flows downstream. Substituting (8) into (12) expresses downstream pollution as a function of upstream and downstream consumption and environmental effort,
![]() (13)
(13)
The potential of diminishing returns to pollution with respect to consumption and environmental effort is preserved from the A&L model.
Substituting (13) into (11) the utility of the downstream citizen is a function of their own consumption and environmental effort as well as upstream consumption and environmental effort,
![]() (14)
(14)
subject to the constraint on income,![]() . As above, impose the parameter restrictions
. As above, impose the parameter restrictions![]() ,
, ![]() , and let
, and let ![]() and
and![]() .
.
Treating ![]() and
and ![]() as constants and solving for optimal consumption and environmental effort in the downstream country yields
as constants and solving for optimal consumption and environmental effort in the downstream country yields
![]() (15)
(15)
![]() (16)
(16)
Substituting (9), (10), (15), and (16) in the downstream pollution function
![]() (17)
(17)
and combining like terms and simplifying yields
![]() (18)
(18)
Equation (18) requires the further restriction ![]() and
and![]() .
.
The estimated EKC model follows
![]() (19)
(19)
where ![]() is BOD per capita,
is BOD per capita, ![]() is upstream income,
is upstream income, ![]() is downstream income, and
is downstream income, and ![]() are coefficients to be estimated.
are coefficients to be estimated.
Linking the theoretical model with the empirical model, the second order marginal effects of consumption and effort on utility for the upstream country ![]() and
and ![]() and downstream country
and downstream country ![]() and
and ![]() can be derived from the following:
can be derived from the following:
![]() (20)
(20)
![]() (21)
(21)
![]() (22)
(22)
![]() (23)
(23)
Solving for ![]() in terms of
in terms of![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() yields
yields
![]() (24)
(24)
The parameter ![]() is unknown. The parameter
is unknown. The parameter ![]() can take any positive value as long as
can take any positive value as long as![]() . Let
. Let
![]() . Once
. Once ![]() is solved, the following expression can solve for
is solved, the following expression can solve for![]() :
:
![]() . (25)
. (25)
The parameters ![]() and
and ![]() can be solved using
can be solved using ![]() and
and ![]() in a similar manner.
in a similar manner.
Although this model is somewhat restrictive, this appears to be the first attempt to link a theoretical model of an EKC with an empirical model. This is important because the underlying causes of an EKC are debated. Some EKC theorists believe citizens make “greener” consumption choices as they grow richer, while other theorists believe the EKC is a reflection of harsher environmental regulations in higher income countries. The EKC empirical estimates can derive underlying second order effects of consumption and effort on utility. Results may offer insight into how consumers value consumption and effort and where their income should be spent.
3. Conclusion
This paper investigates downstream dependence in an EKC for water pollution. The question this paper addresses is whether downstream pollution can be redressed with income growth in the upstream country. A theoretical model is developed that relates theoretical parameters directly with the typical empirically estimated parameters of the reduced form EKC model. Theoretical parameters for upstream and downstream county consumption and environmental effort are derived. Future EKC studies may benefit from employing the theoretical model proposed in this paper to help devise appropriate policy for various pollution indicators.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Jeff Peterson, John Crespi, and Henry Thompson for comments.