Construction of a Simple Rectum Model Using Image Guidance in Prostate Patients Treated with 3D Conformal Radiotherapy ()
1. Introduction
Prostate carcinoma is the most common malignant and potentially curable tumour in males in western country and the most frequent cause of cancer death [1] [2] . Conformal radiotherapy techniques, such as Three-Dimen- sional Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT) and Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), allow dose escalation to the prostate and reduced side effects [3] - [5] . Rectal toxicity represents the most important side effect of prostate irradiation and impacts significantly on quality of life [6] - [9] . The analysis of the dose-volume histograms (DVH) of the rectum has been performed and some constraints have been proposed [10] - [17] . Author correlated the investigation constraints with late rectal bleeding in order to keep the risk of developing Grade 2 or worse toxicity as low as possible using different definitions for the rectum [18] - [20] . Most of these investigations that aimed at finding reliable constraints were built on 3D-CRT toxicity data and did not take into account information/guidance from on-board imaging systems, the latter being a technology not available at the time of collection of most data. In fact, internal motion between fractions can significantly influence dose accumulation over a course of treatment [21] - [24] . In this respect, a standardized IGRT protocol associated with a dietary regimen aimed at decreasing the volume of faeces and gas in the rectum can limit the inter- and intra-fraction prostate motion [25] . The surrounding normal tissues can be spared by reducing margins thus offering further opportunity for dose escalation [3] [4] .
In a previous analysis [26] , we have obtained Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans in six patients and assumed that those performed during the first week of treatment were representative of the whole treatment course. Both the arithmetical mean of the dose-volume histograms and the DVH of a geometrical model of the Average Rectum (AR) were in accordance within ±5% and usually lower than the DVHs of the planning CT (pCT) scans, thanks to the dietary regimen. The aim of the present evaluation is to extend the same analysis to 20 patients in order to corroborate our preliminary results. To compare the DVHs arising from the different ways of handling the rectum contours we have used the Lyman Kutcher Burmann Normal Tissue Complication Probability (NTCP-LKB) model [27] with the parameter values proposed by the QUANTEC (Quantitative Analysis of Normal Tissue Effects in the Clinic) [16] group. Finally, to obtain indications on how the daily filling of the rectum could impact on toxicity, we have also studied the time distributions of the CBCT scans and compared the cumulative DVH points at the dose values taken from the QUANTEC group.
2. Materials and Methods
A retrospective analysis on twenty clinical Stage I or II prostate cancer patients referred to our Radiation Oncology Unit between April 2008 and February 2010 was performed. The patients were instructed to follow a dietary regimen in order to reduce intestinal gas and to ensure an empty rectum both at the planning CT scan and at each treatment session. The diet was prescribed in combination with a daily mild laxative (1000 mg magnesium oxide) to be taken every night before going to bed [26] . Patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Patients were treated in the supine position using 18 MV photons produced by an Elekta Synergy® S linear accelerator (Elekta, Crawley, UK) with an integrated 3D CBCT verification system. All patients received a dose of 76 Gy in 38 fractions (66 Gy were given to the prostate plus SVs (CTV1) and 10 Gy to the prostate only (CTV2)) using a 6-field 3D conformal technique. Treatment plans were developed using Pinnacle 8.0 m® (Philips Medical Systems, Cleveland, OH). Our treatment dose-volume hard constraint for the rectum was that no more than 25% of its volume had to receive a dose of 70 Gy (V70 ≤ 25%). As additional soft constraints no more than 60% of the rectal volume had to receive 40 Gy (V40 ≤ 60%) and no more than 50% of the rectal volume had to receive 50 Gy (V50 ≤ 50%).
All patients were scored according to the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group scoring criteria (RTOG/
![]()
Table 1. Patients’ characteristics.
EORTC), both for acute and late toxicity (Table 2).
Patients were examined weekly during the course of treatment, 8 weeks after treatment, every 4 months for the first 2 years and every 6 months afterwards. At each follow-up visit, physical examination including a digital rectal exam was performed and a questionnaire was used to collect information about urinary, anorectal morbidity and sexual function. The average follow-up was 35.3 months (range 12 - 58).
The set-up verification procedure, acquisition protocol and off line organ motion analysis have been extensively discussed in a previous report [26] . Briefly, CBCT scans were used in a routine online bone-anatomy- based setup protocol. CBCT images were transferred to Pinnacle for off-line organ motion analysis [28] . The rectum outlines were used to obtain a mean DVH for each patient (
) by averaging the DVHs of the rectum as they appeared in every CBCT scan. A geometrical model of the rectum, representative of the whole treatment, referred to as “Average Rectum” (AR), was obtained from the contours delineated on the CBCT scans and was used to calculate the corresponding DVH (DVH
AR). In addition both averaging methods were restricted to the first five CBCT scans only, representing the first week of treatment, and the corresponding DVHs were calculated (
5> and DVH
AR5, respectively).
To assess the influence of the dietary protocol on our results and to investigate the possibility of making reliable predictions on rectum position using data collected in the first week only we have compared DVHpCT,
5>,
, DVH
AR5 and DVH
AR, using the NTCP-LKB model to reduce the above mentioned DVHs into numbers. The following QUANTEC-recommended parameters for late effects [16] (95% confidence intervals) were used in the calculation of NTCP-LKB (NTCP-QLKB): n = 0.09; m = 0.13 and TD
50 = 76.9 Gy.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated to measure how NTCPpCT, NTCP
, NTCP
, NTCPAR5 and NTCPAR, which are the NTCP values calculated from DVHpCT,
5>,
, DVH
AR5 and DVH
AR respectively, were pairwise related. To estimate the differences between medians of the NTCP distributions, i.e. to assess whether samples from NTCP
pCT, NTCP
, NTCP
NTCP
AR5 and NTCP
AR came from populations with the same distribution, we used the Wilcoxon Rank Sum test applying the continuity correction.
QUANTEC [16] reports that VD, the volume receiving doses up to a specified threshold D, is not significantly associated with rectal toxicity for D ≤ 45 Gy and provides dose-volume thresholds, with conventional fractionation up to 78 Gy, which are more restrictive than our planning constraints: V50 < 50%, V60 < 35%, V65 < 25%, V70 < 20% and V75 < 15%. Being widely accepted, the QUANTEC dose checkpoint values were used to describe the time behaviour of the relative volumes using the Gamma Distribution for the frequency of the relative rectum volumes at each QUANTEC dose value.
![]()
Table 2. RTOG/EORTC toxicity score.
Therefore data of the percentage rectal volumes, have been collected from all DVHs of all the patients, both at the dose values corresponding to our constraints and at those of the QUANTEC constraints.
The Gamma Distribution was chosen, as data were positive and right-skewed. A wide distribution means high variability in the rectum volume receiving doses equal or higher than the chosen checkpoint value along the treatment course. On the contrary a narrow distribution means that the volume stays roughly the same. In the case of optimal treatment reproducibility, the curve becomes a Dirac’s The Gamma Distribution parameters were estimated with a maximum likelihood estimator. For each patient and for each dose level (dose), the dis-
tributions were plotted superimposing the QUANTEC constraint (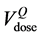 ) and the percentage volume correspond-
) and the percentage volume correspond-
ing to the same dose level in DVHpCT ( ) and in DVHAR (
) and in DVHAR (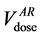 ). These results were then employed to ana-
). These results were then employed to ana-
lyze how many patients had CBCT rectal volumes percentage outside the confidence interval established (95%), i.e. the fraction of CBCT scans whose percentage rectal volumes, for each patient and QUANTEC dose-bin, sta-
tistically exceeded 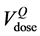 (1 − p > 0.05). The p value is, in fact, the integral of the gamma distribution up to
(1 − p > 0.05). The p value is, in fact, the integral of the gamma distribution up to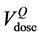 .
.
This information has then been then qualitatively related to the follow up data.
As a further qualitative comparison, an empirical cumulative distribution function of the quantities NTCPpCT, NTCP
, NTCP
, NTCPAR5 and NTCPAR sampled on the 20 patients was calculated. Moreover we calculated the probability of having zero complications when the model adopted for the calculation of NTCPs of each patient was NTCPpCT, NTCP
, NTCP
NTCPAR5 and NTCPAR, respectively. This was given by the product of the individual probabilities of having zero complications:
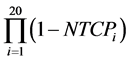
Statistical calculations were performed using the Mathematica8 (Wolfram Research, Inc. 100 Trade Center Drive, Champaign, IL 61820-7237, USA) and R version 2.15.1 (R Core Team, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
3. Results
Four patients (20%) developed G2 acute gastrointestinal toxicity, no G3 acute or late toxicities were recorded. Only two patients (50%) among those experiencing G2 acute toxicity presented co-morbidity and risk factors like diabetes, hypertension, and haemorroids (Figure 1). The Gamma Distributions of the rectum volumes at the QUANTEC dose levels were found to be highly variable among the patients depending on daily rectum filling. However, a trend towards smaller volumes as the treatment progressed was observed in most patients. As an
![]()
Figure 1. Gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity incidence.
example, in Figure 2 we show the Gamma Distribution plots relative to the percentage rectum volume receiving 65 Gy or more for two patients. The dashed vertical line represents the relative volume corresponding to the 65
Gy constraint specified by the QUANTEC ( ), the dotted and continuous vertical lines are the relative vol-
), the dotted and continuous vertical lines are the relative vol-
umes corresponding to 65 Gy in the DVH of the rectum in the pCT 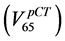 and in the AR (
and in the AR (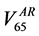 ), respectively.
), respectively.
In the plot on the left (Figure 2(a)) a medium width distribution, corresponding to a fairly satisfactory repeat-
ability of the rectum position is shown. Both 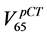 and
and 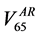 are below
are below 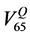 so the treatment plan would have
so the treatment plan would have
been acceptable from the QUANTEC viewpoint and remained so during the treatment. In the plot on the right
(Figure 2(b)) a slightly wider distribution is pictured, but in this case 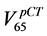 is higher than
is higher than ![]() while
while ![]() is
is
much lower. This is an example of a treatment plan that would fail acceptance criteria based on the QUANTEC hard constraints, which drifted towards an acceptable treatment thanks to the dieting regimen.
Inspecting all the distributions we have found that both ![]() and
and ![]() were lower than the QUANTEC
were lower than the QUANTEC
constraints in 17 of the 20 patients (90%); ![]() and
and ![]() were lower than
were lower than ![]() and
and ![]() in 9 of the 20 pa-
in 9 of the 20 pa-
tients (50%) and in 15 of the 20 patients (75%), respectively. ![]() was always below
was always below![]() .
. ![]() were always
were always
below the QUANTEC thresholds but in one patient, whose ![]() was slightly above
was slightly above![]() .
.
From the CBCT scans, our results indicate that, considering the p-value, 15 patients (75%) had the percentage
rectal volumes within![]() ; 14 (70%), 11 (55%) , 13 (65%) and 20 (100%) patients had the percentage rectal
; 14 (70%), 11 (55%) , 13 (65%) and 20 (100%) patients had the percentage rectal
volumes within![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() , respectively.
, respectively.
The percentage of DVHpCT rectal volumes is almost always higher than the corresponding
5>,
, DVH
AR5 and DVH
AR suggesting that the dietary regimen was adequately followed during the treatment course. Small differences (with the exception of one patient) are evident comparing
5> with
and DVH
AR5 and DVH
AR (data not shown).
In Table 3 the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients among all NTCPs, are displayed. All the coefficients relating NTCPpCT to the other indices are <0.5, indicating a weak correlation between the DVH of the pCT and the other DVHs. On the other hand, the coefficient between NTCP
and NTCP
as well between NTCPAR5 and NTCPAR were 0.883 and 0.865, respectively, showing a substantial correlation.
In Table 4, the results of the Wilcoxon Rank Sum test among all NTCPs, are shown. We found that the null hypothesis (zero difference between the medians) could not be rejected (p-value > 0.05) only for the couples (NTCPAR5, NTCPAR) and (NTCP
, NTCP
). For all the other couples of samples, with the possible exception of the couple (NTCPpCT, NTCP
), the p-values indicate that the difference between the corresponding medians is statistically significant. This finding agrees with the previous partial results.
Figure 3 shows the estimated cumulative distribution of the NTCP-QLKB values calculated from the DVHpCT,
,
, DVH
AR5 and DVH
AR in our patient population. NTCP data are binned at 0.001 intervals. NTCP
AR and NTCP
AR5 display a shift towards left corresponding to smaller values. This indicates that using these DVHs in calculating NTCP, a lower incidence of Grade ³ 2 late rectal toxicity is predicted with respect to the NTCPs calculated from the other DVHs. In addition, the values obtained on the 20 patients (maximum NTCP
AR ~ 11%) are smaller than those predicted from QUANTEC (Grade ≥ 2 late rectal toxicity inferior
![]()
Figure 3. Estimated cumulative distributions of NTCP-QLKB values calculated from the DVHs of pCT,
,
, AR5 and AR in the entire patient population.
to 15%) and of about the same order for the probability of Grade ≥ 3 (10%). This is consistent with the fact that the percentage volumes obtained for AR are smaller than the thresholds accepted in the QUANTEC review, as well.
The values of the probability of having zero complications ranged range from a minimum of 12% for NTCPpCT to maximum of 26% for NTPCAR.
4. Discussion
In the last years, different studies have shown that dose escalation to the prostate can improve clinical outcomes
![]()
Table 3. Pearson’s correlation coefficients among the NTCP values calculated on the corresponding DVHs.
![]()
Table 4. Wilcoxon Rank Sum test, comparing two related samples in order to assess whether their population mean ranks differ.
[3] [4] but may increase the risk of rectal toxicity [29] . A number of consistent results on dose-volume effect and rectal bleeding appeared in literature and most of them confirmed the rectum behaving prevalently as a serial organ. In particular, significant correlations between late rectal bleeding and the fraction of rectal volume receiving more than 40 - 60 Gy (V40-V60: intermediate dose) and more than 65 - 75 Gy (V65-V75: high dose) have been reported [10] - [17] [30] - [34] .
The QUANTEC group published a review analyzing dose-volume data from multiple centers using the LKB NTCP model. Dose-volume constraints were established for conventional fractionation up to 79.2 Gy, considered as conservative and starting from 3D treatment planning. Following these constraints, the probability of Grade ≥ 2 and Grade ≥ 3 late rectal toxicity is expected to decrease to < 15% and to < 10%. In the above mentioned papers patients were asked to keep their rectum empty during therapy, but the specific role of a diet on the radiobiological parameters has not been extensively investigated yet, even though the benefit of a dietary protocol in combination with an IGRT protocol is well assessed in literature [25] and confirmed by our previous results [26] .
In our previous investigation, we proposed a method to evaluate the dose delivered to the rectum during the course of treatment using the information of an off-line definition of organ volume using a commercial linear accelerator with an integrated CBCT scanner [26] . We verified on 6 patients that, taking into account only the volumes corresponding to 4 dose points (V40, V50, V60 and V70), that both DVHAR and
could describe the average behaviour of the rectum during the treatment course. We also observed that DVH
pCT appeared higher than the other DVHs in all six patients and we interpreted it as a proof of the need to stress the diet and bowel cleaning, probably not yet optimal at the beginning of the treatment. It remained to be cleared which of the two DVHs should be used to best predict rectum toxicities and whether the CBCT scans performed during the first week of treatment could be taken as representative of the whole treatment. In this paper, the aim was to confirm the importance of a “diet-IGRT” combination and to try to find an answer to the above questions.
Following the patients during the whole treatment, with the help of the CBCT scans, we were able to check the rectum filling and to assess if patients really followed the diet. All DVH values improve as confirmed by follow-up data which show that 20% of patients present G2 acute toxicity while acute G3 toxicity and late toxicity have been not recorded. Indeed, starting from late toxicity data (zero), our results show that, in the planning CT, QUANTEC constraints were not satisfied in some patients. During the treatment, however, this number decreased thanks to the diet, and the number of CBCT scans respecting dose-volume constraints increased, as shown by the Gamma Distributions. The QUANTEC constraints are more restrictive than those applied in our institute and the fact that in the case of DVHAR they are always satisfied is consistent with our follow-up data showing no late rectal toxicity. The analysis of Gamma Distributions can help us to have off-line information on the reproducibility of the treatment, as well as on the reproducibility of the dietary regimen followed by each patient and, therefore, on the strength of the entire procedure. From Gamma distributions, in addition, we found
that the number of patients with a ![]() lower than
lower than ![]() increases with dose and all
increases with dose and all ![]() values are lower
values are lower
than ![]() ones. This finding well agrees with our toxicity data (zero) and with literature which reports that late
ones. This finding well agrees with our toxicity data (zero) and with literature which reports that late
rectal toxicity is mostly related to the size of the high dose region [10] - [17] [30] - [34] .
The number of patient analyzed is too small to correlate the data for acute toxicity with clinical factors. However, some general considerations can be extracted from Gamma Distributions. The four patients who showed acute toxicity are those with the widest Gamma Distributions, i.e. patients whose treatment was least reproduce-
ble. In addition, three of the four have all ![]() values, but
values, but ![]() higher that
higher that ![]() and at least 30% of the
and at least 30% of the
Gamma Distribution above the QUANTEC constraints. In literature, a correlation between acute and late rectal toxicity has been observed although its nature is not well established [29] [35] [36] . In our small population, the four patients who experienced acute toxicity, did not show late toxicity, and this suggests that among all dose-volume constraints, the V75, which was always respected in the pCT, in all the CBCT scans and in AR, turned out to be the most consistent with the hypothetical correlation between acute and late toxicity.
To further investigate the open questions about the model that best summarizes the rectum movements along the treatment course, we performed a statistical analysis in terms of NTCP. We decided to use the NTCP-LKB model with QUANTEC best estimate parameters because of the low number of patients that doesn’t allow us to make clinical distinctions among them.
The Pearson’s correlation coefficients indicate a substantial correlation between all indices, except for NTCPpCT, with a general positive trend. The Wilcoxon Rank Sum test, however, indicates that the difference between the medians for the couple (NTCPAR5, NTCPAR) and for the couple (NTCP
, NTCP
) is not statistically significant (p-value > 0.05). For the other couples of samples the p-values indicate that the differences are statistically significant (p-value < 0.01), i.e. it is not ruled out the possibility that the rectum behavior during the whole treatment course can be represented by the first treatment week.
To further investigate this, we have then compared the NTCP values with the results of the follw-up. From NTCP distributions (Figure 3), the best predictors for zero late rectal toxicity seem to be AR and AR5 (lower values and narrower distributions). In addition, the highest probability to have no complications on 20 patients is obtained with NTCPAR (26%). These findings suggest that the AR model seems the more consistent with patients’ outcome and that, when the treatment is reproducible along the entire treatment course, which can be verified by CBCT scans, the DVHAR5 well describes the rectum behavior.
5. Conclusions
At the end of our analysis, we conclude that if we concentrate on AR for all patients our results are in a good agreement with QUANTEC assertions and follow-up data. In fact, we obtain that DVHAR always respects QUANTEC constraints and we record no late toxicity in our follow-up data. In addition, when the rectum filling remains reproducible during the entire course of treatment, the DVHAR5 can describe the rectum behavior in the whole treatment. Finally, from the Gamma distributions, and from our toxicity data, we can suggest the V75 as the best predictor of late rectal toxicity. In any case, we are enrolling more patients and performing more statistical analysis to confirm these preliminary results.
Although our analysis has the limit of being extended to very few patients, these preliminary results show that a dietary protocol associated with IGRT technique in order to daily verify the correct dieting behaviour is useful to avoid toxicities on the anterior wall of the rectum.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.