Cardiovascular Reactivity to Short Duration Videos in Adolescents: An Exploratory Study ()
1. Introduction
Using social media websites has become among the most common activities of today’s adolescents. YouTube is certainly one of the most popular of these websites. Its material is extremely diversified and readily available. However, the physiological impact of these short duration videos on adolescents has not been specifically studied.
Cardiovascular (CV) reactivity in real life settings has been examined by several authors (Sausen et al., 1992; Hazlett et al., 1997; Zanstra & Johnston, 2011). A link between emotion and CV reactivity has been many times demonstrated (Anastasiades & Johnston, 1991; Kamarck et al., 2002; Räikkönen & Matthews, 2008). The effects of stress on CV are mediated by the sympathetic component of the autonomic system and include a higher heart beat rate and an increase in the blood pressure. Among others, the physiological reactions associated with fear and anger are well documented. Anxiety produces an increase in heart rate, systolic blood pressure and a low diastolic blood pressure due to a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance. Anger is associated with the same CV characteristics except for the diastolic blood pressure which is increased because of the increased peripheral resistance (Schacter, 1957; Wenger et al., 1960; Martin, 1961). The determinants of stress-induced reactivity in real life have been summarized by Zanstra and Johnston (2011). They are: 1) individual determinants, 2) situational determinants (physical setting), and 3) others such as posture and physical activity.
In this exploratory study, we have focused on a cohort of fourteen and fifteen-year-old adolescents to monitor their cardiovascular changes when exposed to three ecological YouTube videos emotionally charged. Our objectives were threefold: 1) to characterize the cardiovascular effects in adolescents when they watched videos presenting different emotional valence (funny, sad and violent); 2) to determine whether the effects were subject to gender differences; and 3) to determine whether the perception of details was subject to gender differences.
2. Methods
2.1. General Protocol
The research was conducted in accordance with the principles of the American Psychological Association (2000). A written consent was obtained from both the parents and the students after presentation of a summarized written description of the project. The study took place in a French speaking secondary school in Quebec City. All male and female subjects were 14 or 15 years old without any visual (corrected if required) and auditory impairment. Participation was on a voluntary basis and we had no other exclusion criteria. Within 6 hours before the testing procedure, the participants were asked to avoid stressful situations, physical activity, caffeine, cigarettes, alcohol and all drugs.
2.2. Stimuli
The authors selected 5 short YouTube videos for each of the 3 categories. These videos were shown to a group of 5 adults and a consensus was reached on the best sequence for each of the 3 desired emotions. For the funny video, all abusive language was removed from the film sequence in French. The two other segments only had respectively music and music and noise. At the beginning, the participants were asked to relax in the room for five minutes. The following two minutes were used to present a prerecorded set of instructions with a black screen and install the recording cuff on one arm. An extra minute with a black screen was left for the adolescent to get used to the cuff and the setting. During the video, six 0.1-second black screens were added to tell the testers when to make the measurements. These short-duration black screens were barely perceptible to the subjects. The first measurement took place in the middle of the one-minute relaxing time. Between the first and the second, and the second and third YouTube sequences, a relaxing time of two minutes with a black screen was inserted and a measurement was taken in the middle of that period. The optimal timing of the measurements during the YouTube videos was also selected by consensus within the group of five adults according to what they felt would be the images with maximal emotional impact.
Figure 1 summarizes the unwinding of the testing. The first video was a parody of a Mac add. Video 2 presented the story of a little girl cutting her hair in a bathroom to give them to her bald brother coming back home from a chemotherapy session for cancer. The third video was a 45-second segment from the Troy movie in which explicit scenes of violent battles were taking place on a beach. The complete video sequence was created with iMovie. The video was shown to the participants on a 13-inch Macbook Pro computer by two of the authors (JL and JS). All the experiments took place in the same room with the same lighting, table and chair.
2.3. Physiological Monitoring
For each of the six selected landmarks including 3 during the rest periods and one during each of the video sequences, a measurement of the cardiac rate (HR), the systolic (SP) and the diastolic (DP) blood pressure was obtained from an automated one-button blood pressure monitor (Life Source UA-767-Plus). When the 0.1-
second black screen appeared, the tester pressed the button and all the parameters were recorded at the same time.
2.4. Perception Evaluation
At the end of the video exposition, the participants were asked to fill a subjective questionnaire. For each video, they were questioned if they noticed one specific detail: (#1: color of the actor’s shirt; #2: color of a purse; #3 design of the warriors’ helmets). The first two details (colors) were checked by an open questionnaire but we could not do the same with the design of the helmet. We opted for a multiple-choice question with images of five different helmets. They also had to rate each individual sequence on a scale of 1 to 10 as to its value to create the intended emotional situation: humor, sadness and violence. Finally, they were asked if they had ever seen any of the material before.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
For all the data analysis, the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test was used. Comparisons were made for the average cardiac rate and blood pressure before and during each sequence, and the perception of the emotional level ratings by both sexes. The values were considered statistically significant if the p-value was under 0.05.
3. Results
Sixteen males and sixteen females were enrolled in the study. The mean age for each group was respectively 14 and 14.5 years old and the difference was not statistically significant. Figures 2-4 show respectively the mean values of the heart rate, the blood pressure and the median values of the blood pressure. The subjective perception of the emotional intensity of the videos for both sexes is presented in Figure 5.
Testing subject reactions in ecological conditions is one of the most important concerns in current psychological research (Achim et al., 2013). In the present experiment, we aimed to reproduce conditions as close as possible to real life setting by using YouTube sequences. Since we were interested by adolescents’ behavior, all efforts were made to keep the total length of the task as short as possible, in order to avoid any bias related to loss of attention from our young participants. A posteriori analysis of the ratings of the videos by the participants
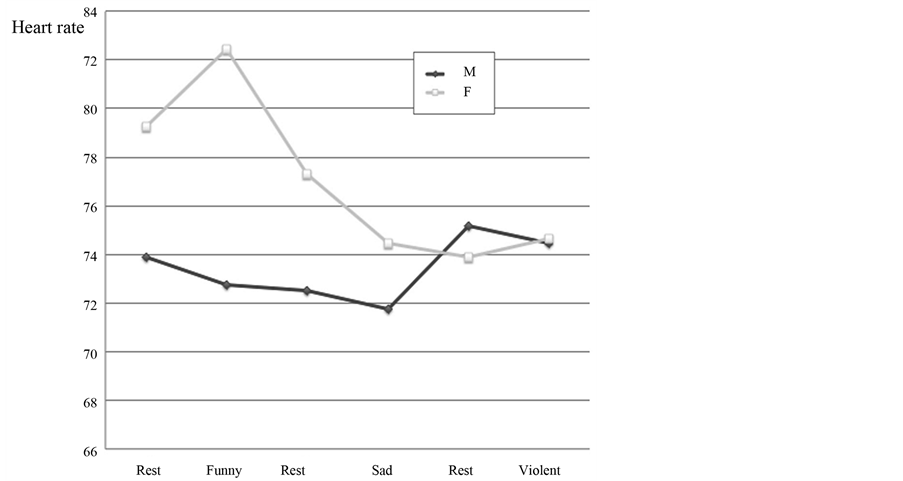
Figure 2. Heart rate (males and females).
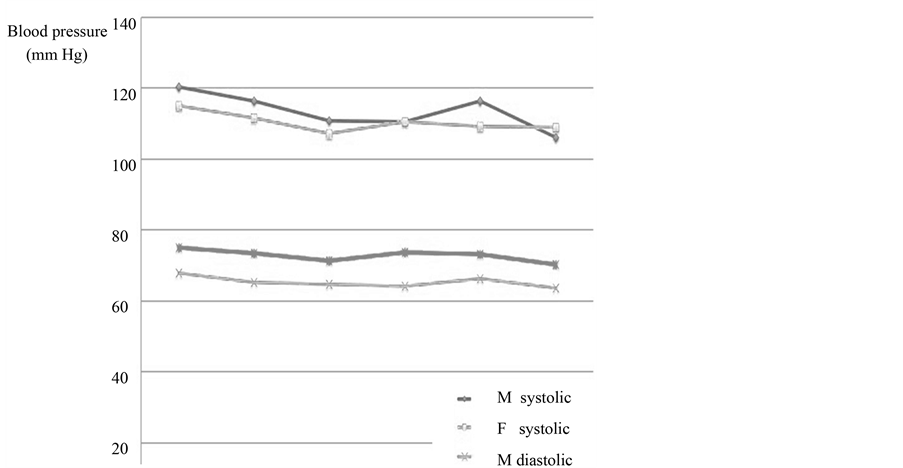
Figure 3. Mean blood pressure (males and females).
confirmed that the selected stimuli were appropriate to elicit the targeted emotions, and therefore, the related physiological changes. Indeed, most of the participants were above 5 out of 10 with all the three median values equal or above 7 for both sexes. While no exclusion criteria were applied in our study, no major psycho-pathology was observed in our subjects from our young participants. A posteriori analysis of the ratings of the videos by the participants confirmed that the selected stimuli were appropriate to elicit the targeted emotions, and therefore, the related physiological changes. Indeed, most of the participants were above 5 out of 10 with all the three median values equal or above 7 for both sexes. While no exclusion criteria were applied in our study, no major psychopathology was observed in our subjects.
It was interesting to note that the males’ ratings were higher than the females as to the degree of violence. In contrast, the differences for the sad video were the opposite. Analysis of a possible effect of pre visualization did
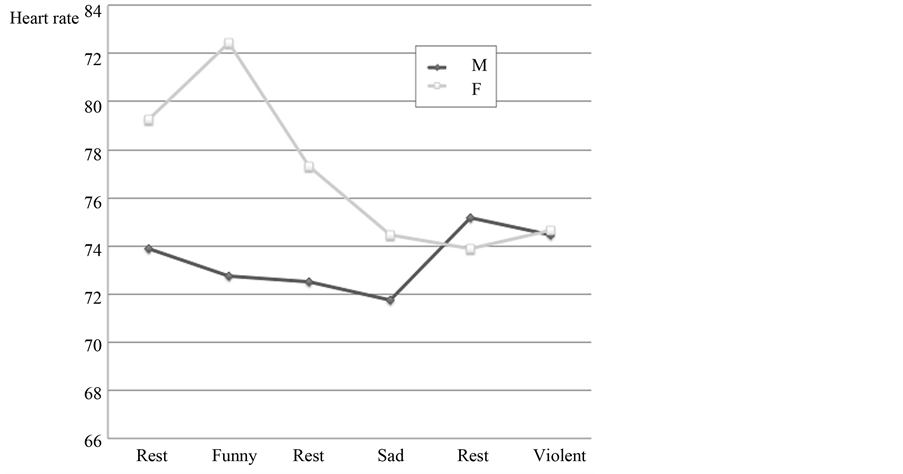
Figure 4. Median blood pressure (males and females).
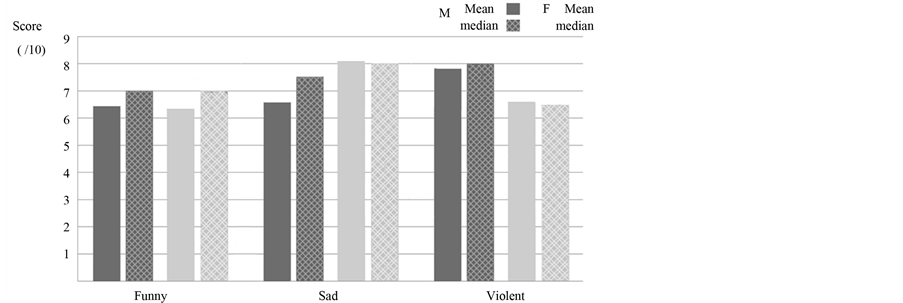
Figure 5. Mean and median perception scores (males and females).
not unveil any significant effect. The larger development of the cerebral amygdala in women at puberty is thought to play a role in the association of emotional significance to sensory experiences (Ruigrok et al., 2013; Goddings et al., 2013; Andreano et al., 2013). As a checkpoint, we investigated to see if the females remembered some details better than the males. Indeed, in 2 out of 3 sequences, they did better than the males. In the sad video, for both sexes, only two students out of 16 had the right answer so the question might have been too difficult. In the last video, the details of the helmet were evaluated through a multiple-choice question including five different helmet pictures. The females still performed better even though the topic and the multiple-choice setting may have helped the males.
The intra-video mean values were compared to the preceding blank screen values for all three parameters in both sexes. The variations in the HR were minimal in both sexes and no statistically significant change was found. The study of the systolic and diastolic blood pressures also revealed minor fluctuations with one exception. The mean SP in the male subjects presented a reduction of 10 mmHg (Table 1) during the presentation of the violent Troy sequence that nearly reached statistical significance (p = 0.067). In this group, we observed an identical 10 mmHg decrease between the systolic pre and post median values. The HR and DP followed a similar pattern without reaching statistical significance. The male subjects rated the video as more violent than the female subjects and this was statistically significant (p < 0.05) (Figure 5). Table 2 shows the results of the identification of a detail in each clip.

Table 1. Mean changes in cardiovascular parameters (males and females).

Table 2. Number of correct answers about details in the videos (/16) (males and females).
4. Discussion
4.1. Starting Values
In general, the average values of the HR and the BP did not show any major variations throughout the experiment. At the beginning of our test, the SP and DP were rather high and this may be explained by the anxiety of the unknown that the adolescents experienced. Obrist (1981) has showed that active coping tasks that are not physically demanding generate a myocardial reaction. The passive coping tasks tend to generate vascular response patterns. Zanstra and coworkers (2010) have tested students with a Portapres blood pressure monitor. They reported that the period of time before a speech was also characterized by an increase in blood pressure mainly mediated by a myocardial rather than vascular response. This indicates a coping behavior in the anticipatory period. Oyamada et al. (2007) showed three 5-min-long stereoscopic movies on an 80-inch screen to 7 subjects. They found that image presentation elicited autonomic responses that were effective to monitor biomedical effects.
4.2. Intra Emotional Video Values
In our study, we elected to build our three-clip sequence with a black screen in between so they would interfere minimally one with each other. It is hard to tell if the time interval between the short films was long enough. Table 1 depicts the changes that occurred to the parameters after each video exposure. Although all the CV changes did not reach statistical significance in our study, there seemed to be differences between the males and the females. Because the female adolescents were at different points in their menstrual cycle, it is difficult to analyze our results. Pico-Alphonso et al. (2007) investigated the role of estrogens, the hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenocortical activity, and the behavioral profile in individual cardiac autonomic reactivity of 36 adult healthy women exposed to a stress interview and a mental task. Their data confirmed that hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenocortical axis activity (baseline plasma cortisol levels) and the progesterone levels may change the cardiac autonomic activity and stress responsivity. Obviously, the cardiovascular reactivity in our study was not important enough to override the basic physiological changes in the female subjects.
1) Humor The results associated with the funny video were different for the HR in the two sexes. Maybe, the video had more impact on the females. In both groups, the SP and DP went down slightly without reaching statistical significance. It is hard to conclude from the data and maybe a larger cohort would have brought more significant results. Lackner et al. (2013) studied cardiovascular variables during viewing cartoons and non-humorous cartoon-like pictures. Punch elements were associated with tachycardia and increased cardiac output, just the opposite of what we observed.
2) Sadness We could not obtain statistical significance for any of the sad clip values. The absolute changes in the heart rates and the blood pressures did not show any pattern and behaved differently in the 2 groups. It is also hard to draw a definitive conclusion from these results.
3) Violence The near-statistically significant reduction of the systolic pressure following the violent sequence in the males was a surprise. The HR and DP also went down suggesting a reduced sympathetic activity opposite to the expected consequences of anger and aggressiveness. Two possible explanations are suggested. First, there may be latent testosterone-mediated aggressiveness in the 14- and 15-year-old boys that may be controlled for socialization needs. The relaxing effect may come from the combat scenes as a relief for their latent aggressiveness. Second, most of the children in this age group have played with video games where battles are very common. They have experienced fun and relaxation from these games. Watching the movie may have had the same effect as a conditioned reflex. This finding may shed some light on the possible benefits of watching high contact sports such as football, hockey and boxing for the adult males. In his overview of the research on the effects of playing violent video games, Ferguson (2007) stated that his metaanalytic study did not support others’ conclusion that violent video game playing leads to aggressive behaviour. However, playing violent video game was associated with higher visuo-spatial cognition. Recently, Anderson (2014) published an overview of the topic suggesting discrepancies between research results and clinical behavior. This research must be considered as a first step in the exploration of the inner reactivity of adolescents to massive exposure of short videos through Internet-based applications.
While the experimental design of this study does present some limitations, the present approach nonetheless provided interesting insights, which are likely to represent a first step for further studies. Future studies may aim to test each emotional situation separately with a higher number of subjects and measurements, as well as control the hormonal status of female adolescent subjects—with all the difficulties that it may represent when studying a population of this age. Other parameters such as cardiac output and pupillary changes have been used in other studies and may be added to the evaluation. Obviously, a higher number of participants would have helped to reach statistical significance with the systolic blood pressure data.
5. Conclusion
The results of this exploratory study suggest that violent combat scenes in a short video are followed by physiological cardiovascular changes in 14- and 15-year-old male adolescents. We found a near statistically significant decrease of the systolic blood pressure (p = 0.067) and a non-statistically significant decrease of the heart rate and diastolic blood pressure. These results suggest that such activity may be a source of relaxation for the young males. The female subjects did not present the same effects. An extensive study with a more focused protocol, a larger cohort and continuous monitoring is required to confirm these findings.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Doctor Mario Langlais who has allowed and taught us to use the monitoring material.