Optimal Environmental Policy under Endogenous Terms of Trade and Economic Growth ()
1. Introduction
In the last two decades many studies have tried to explain the existing trade-offs among economic growth, international trade, and the environment (see, for example, [1] -[3] ). However, from a theoretical perspective, their main results were based on economic models in which the terms of trade were defined as an exogenous variable. Therefore, the analysis of such trade-offs under endogenous terms of trade represents a missing subject in the economic literature. In this framework, the present analysis departs from previous ones in the modeling of the optimal environmental policy when we deal with both endogenous terms of trade and economic growth. Then, working in a simple representative agent model, we allow for the possibility that the domestic economy might be big enough to modify its terms of trade, where the latter are indirectly delineated by means of the price of an aggregate consumption good. Hence, as long as emissions of a global pollutant, coming from the production process of a pollution-intensive good, affect negatively the quality of the environment and, therefore, the utility of the economic agents, we find that the optimal policy represents a pollution tax on production.
2. The Basic Model
Let us assume that there are two traded goods in the world and that the domestic economy is completely specialized in the production of one of them, a pollution-intensive good, which can be consumed, invested, or traded overseas1. Moreover, it has the power to modify the international price of its exported good and, therefore, the terms of trade. Finally, it is assumed that trade is balanced, which rules out the possibility of lending or borrowing from abroad. Preferences: the instantaneous utility function of the representative agent is defined as: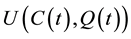 , where C represents an aggregate consumption good, i.e., a subutility function of the consumption of both domestic and imported goods, and Q denotes a stock variable measuring the quality of the environment. Furthermore, it is assumed that the utility function is increasing and strictly concave in both of its arguments, i.e.,
, where C represents an aggregate consumption good, i.e., a subutility function of the consumption of both domestic and imported goods, and Q denotes a stock variable measuring the quality of the environment. Furthermore, it is assumed that the utility function is increasing and strictly concave in both of its arguments, i.e., 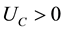 ,
,  ,
, 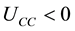 ,
,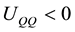 . Finally, we assume that the sign of the cross-partial derivative between consumption and environmental quality,
. Finally, we assume that the sign of the cross-partial derivative between consumption and environmental quality, 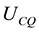 , is ambiguous. This conveys the possibility of a “win-win” outcome when both the equilibrium growth rate increases and the environment improves. Production and Environmental quality: The production process is modeled as a linear function of the stock of physical capital,
, is ambiguous. This conveys the possibility of a “win-win” outcome when both the equilibrium growth rate increases and the environment improves. Production and Environmental quality: The production process is modeled as a linear function of the stock of physical capital, . On the other hand, given the negative effect that domestic emissions generate on the quality of the environment, the latter is defined as:
. On the other hand, given the negative effect that domestic emissions generate on the quality of the environment, the latter is defined as: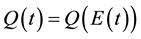 , where E stands for the total amount of emissions. Hence, assuming, for simplicity, that the emission level (in units of measurement) is proportional to the production level, i.e.,
, where E stands for the total amount of emissions. Hence, assuming, for simplicity, that the emission level (in units of measurement) is proportional to the production level, i.e., 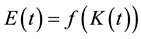 , we can express
, we can express 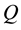 as:
as:
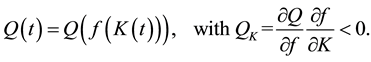 (1)
(1)
This implies that the quality of the environment is a decreasing function of the stock of capital. Note that as we focus on steady-state situations and not on the dynamic properties of the economy, the introduction of more realistic functions and pollution-abatement activities does not affect qualitatively the main results of our analysis2.
2.1. The Decentralized Path
Now, since we abstract from any government intervention, each agent perceives the stock of the environment as exogenous, although Q, in the aggregate, varies over time. Therefore, in the second stage of the maximization process, the representative agent, who has already solved his temporal allocation problem, selects the time path for consumption that maximizes3
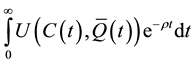 , (2)
, (2)
subject to
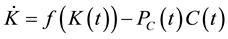 , (3)
, (3)
![]() (4)
(4)
![]() (5)
(5)
where ![]() denotes the social rate of time preferences,
denotes the social rate of time preferences, ![]() indicates that the environment is an exogenous variable, and Pc represents the price of the aggregate consumption good (i.e., a price index). Then, if we define the terms of trade as the relative price of the imported good in terms of the domestic one, Pc will be a positive function of this price4. Also, the market-clearing condition for the economy, (3), implies that the price of the domestic good is normalized to unity5. Therefore, the current-value Hamiltonian, dropping the time arguments, is given by:
indicates that the environment is an exogenous variable, and Pc represents the price of the aggregate consumption good (i.e., a price index). Then, if we define the terms of trade as the relative price of the imported good in terms of the domestic one, Pc will be a positive function of this price4. Also, the market-clearing condition for the economy, (3), implies that the price of the domestic good is normalized to unity5. Therefore, the current-value Hamiltonian, dropping the time arguments, is given by:
![]() , (6)
, (6)
where ![]() denotes the shadow price of capital. Hence, the first order necessary conditions for an optimal (interior) solution include:
denotes the shadow price of capital. Hence, the first order necessary conditions for an optimal (interior) solution include:
![]() , (7)
, (7)
![]() (8)
(8)
These results are quite intuitive. From (7), the static efficiency condition, the shadow price of capital adjusted by the price of the aggregate consumption good must equal the marginal utility of consumption. The dynamic condition (8) is Ramsey’s rule, which requires that the shadow price of physical capital rises at a rate given by the difference between the social discount rate and the marginal product of capital. Hence, if we differentiate totally (7) with respect to time and substitute for ![]() and
and ![]() into (8), the standard condition for the growth rate of consumption can be expressed as:
into (8), the standard condition for the growth rate of consumption can be expressed as:
![]() , (9)
, (9)
where ![]() is the elasticity of the marginal utility of consumption with respect to its argument, the second term inside the brackets captures the effect on consumption of the evolution of the terms of trade, and the last term stands up for the positive or negative effect of a secular improvement in environmental quality on the consumption path. That is, an increase (decrease) in Q increases the marginal utility of consumption, i.e.,
is the elasticity of the marginal utility of consumption with respect to its argument, the second term inside the brackets captures the effect on consumption of the evolution of the terms of trade, and the last term stands up for the positive or negative effect of a secular improvement in environmental quality on the consumption path. That is, an increase (decrease) in Q increases the marginal utility of consumption, i.e., ![]()
![]() , which raises (drops) the incentive to consume and accumulate at all times.
, which raises (drops) the incentive to consume and accumulate at all times.
2.2. The Efficient Path
The social planner’s problem is to select the time path of consumption decisions, assuming Q endogenous, that maximizes the present value of the utility. Formally, the decision maker’s problem, dropping the time arguments, will be to maximize the intertemporal utility function,
![]() , (10)
, (10)
subject to (3), (4), and (5).Therefore, the current value Hamiltonian is given by:
![]() , (11)
, (11)
where the first order conditions for an interior solution are:
![]() , (12)
, (12)
![]() . (13)
. (13)
Then, differentiating totally (12) with respect to time and using (13), we can express the efficient growth rate of consumption as:
![]() . (14)
. (14)
Note that as![]() , (14) and (9) differ only in the term
, (14) and (9) differ only in the term![]() , which shows the adverse effect of
, which shows the adverse effect of
capital accumulation on the environment and, consequently, on the efficient growth path. That is, a higher level of emissions coming from an increase in physical capital decreases the utility associated with a given path of consumption.
2.3. Environmental Policy
In this section we introduce a Pigovian tax-cum-subsidy scheme in order to internalize the environmental externality. Therefore, to calculate this policy, sustainable through a lump-sum transfer, we set up an ad valorem tax or subsidy, ![]() , on production ( with
, on production ( with ![]() if a tax,
if a tax, ![]() if a subsidy) and compute the modified decentralized path. Hence, comparing it with the social path and solving for t we have:
if a subsidy) and compute the modified decentralized path. Hence, comparing it with the social path and solving for t we have:
![]() . (15)
. (15)
From (15), the optimal policy represents a pollution tax on production. This can be expressed as the modified ratio, via the price of the aggregate consumption good, between social marginal benefits, ![]() , and social marginal costs,
, and social marginal costs, ![]() , of reducing pollution.
, of reducing pollution.
3. Conclusions
In this essay we model endogenous terms of trade and economic growth in order to analyze the optimal environmental policy that maximizes social welfare. To accomplish this, we work with an AK model of economic growth and deduce endogenous terms of trade from the price of an aggregate consumption good. Thus, as long as households derive utility from consumption and the environment and pollution is generated through domestic production, we conclude that the optimal policy consists in a pollution tax on production.
There are many additional areas of research that could be pursued. A natural extension would be to admit the possibility that the environment may affect productivity. Another development implies the introduction of a natural resource in the production function.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank an anonymous referee for his valuable suggestions.