Effects of Pitavastatin on the Intima-Media Thickness of the Carotid Artery in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: The Pitavastatin Efficacy Study on Surrogate Markers and Imaging for Stroke (PESSMIST) ()
1. Introduction
Hyperlipidemia is one of the risk factors for cerebrovascular diseases [1] [2] , and the carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) is a well-known indicator of stroke risk [3] . Statins are therapeutic drugs used to treat hyperlipidemia, and are also known to reverse the progression of the carotid IMT [4] -[7] .
There have been many reports about the clinical effects of statins for the prevention of primary and secondary strokes [8] -[10] . Pitavastatin is a strong statin that was developed in Japan. It has been commercially available in Japan and some other countries since 2003. Some studies have investigated the clinical effects of pitavastatin in patients with acute coronary syndrome or heart failure [11] -[13] . One report demonstrated that pitavastatin provided effective carotid IMT control for patients with subclinical carotid atherosclerosis [14] . However, the clinical preventive effects of pitavastatin for patients with ischemic stroke have not been reported. A randomized head-to-head comparison of statins, including pitavastatin, showed no differences in their reduction of low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and adverse reactions [15] . Therefore, we conducted a prospective, open label, clinical case-control study to determine the beneficial effects of pitavastatin for Japanese patients with cerebral infarction and hyperlipidemia. The first purpose of this study was to compare the features of stroke patients with and without hyperlipidemia. The second purpose was to examine the effects of pitavastatin on the carotid IMT in patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia using carotid ultrasonography. The carotid IMT in the patients without hyperlipidemia was examined in the same manner and used as a control.
2. Study Population
The inclusion criteria in this study are that the patient was diagnosed to have a cerebral infarction and could regularly visit the out-patient clinic. The exclusion criteria were the presence of severe systemic diseases. The patients were consecutively enrolled in the study. Each patient’s consent to be included in the study was obtained prior to the enrollment.
The pitavastatin group included 20 Japanese patients diagnosed with cerebral infarction and hyperlipidemia without previous statin intake. Their age ranged from 34 to 84 years (mean 69.3 years old). There were 12 males and eight females. Cerebral infarction was diagnosed based on the clinical and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings, with lacunar infarctions diagnosed in 14 patients, atheromatous infarctions in five patients and a cardiogenic embolism in one patient, according to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) stroke criteria [16] [17] . Hyperlipidemia was defined as an abnormally high serum total cholesterol (TCho) and/or LDL-C level. Antiplatelet agents were given to all but three patients. The patient with a cardiogenic embolism was given an anticoagulant. The other two patients who did not receive antiplatelet agents included one asymptomatic patient with a mild lacunar infarction and one patient complicated with an unruptured cerebral aneurysm diagnosed by MR angiography. Eight patients were complicated with primary hypertension, which was controlled using calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers. No patient was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus or renal failure. Two patients had a past history of a malignant tumor, but these tumors were not active during the study period.
The control group included the 22 patients diagnosed to have a cerebral infarction without hyperlipidemia. Their age ranged from 68 to 86 years old (mean 75.5 years old). There were 10 male and 12 female patients. Among the control group patients, 19 were diagnosed to have lacunar infarctions and three were diagnosed to have atheromatous infarctions. All control group patients were treated with antiplatelet medication. Thirteen patients were complicated with primary hypertension, which was controlled using calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers. Three patients were diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, which was well controlled with medical therapy. One patient had a past history of a malignant tumor, which was inactive.
3. Methods
The patients in the pitavastatin group received 2 mg of pitavastatin (Livalo®, Kowa, Japan) once a day after dinner. This medication was continued for all patients during the study period, because there were no significant side effects due to pitavastatin intake. The blood chemistry, carotid ultrasonography, brain MR image and angiography findings, as well as the clinical symptoms, were examined before and after the initiation of the pitavastatin treatment. Carotid ultrasonography was examined by experienced sonographers using a Prosound α10 device (Aloka, Japan) and a 5 MHz linear probe. The mean and maximum carotid IMT were measured. Brain MR images and angiography were acquired by experienced radiological technologists using a 1.5 Tesla MR machine (Symphony, Siemens, Germany). These technologists were not aware of the medications being used by the patients. The control group comprised patients that received no statins, and they were assessed using the same modalities as those used for the pitavastatin group.
4. Results
Table 1 shows the background features of the pitavastatin and control groups at the time of study entry. The mean ages were 69.3 and 75.5 years for the pitavastatin and control groups, respectively, and the age of the pitavastatin group was significantly younger than that of the control group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in sex between the groups. The heights of the patients were not significantly different, however, the body weight and body mass index (BMI) were significantly higher in the pitavastatin group (P < 0.01). The serum TCho, triglyceride (TG) and LDL-C levels were also significantly higher in the pitavastatin group (P < 0.01). The other laboratory findings and blood pressure showed no significant differences between the two groups.
The serum TCho and LDL-C levels had significantly decreased two months after the initiation of pitavastatin treatment (Figure 1, t-test, P < 0.001). The serum triglyceride (TG) and malonyldiacyl-LDL-C (MDA-LDL) levels showed a decreasing tendency at two and four months after the initiation of pitavastatin treatment (not statistically significant). The serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and blood glucose levels, as well as other parameters reflecting the liver and kidney functions, and the microalbumin levels in urine, showed no significant changes during the examination period.
Carotid ultrasonography was performed between two and eight months after the initiation of pitavastatin treatment. The mean and maximum IMT decreased after the initiation of pitavastatin treatment, although the change were not statistically significant (Figure 2). The mean and maximum IMT did not show any significant change in the control group. The right maximum IMT of the pitavastatin group showed a statistically significant decrease compared with that of the control group (P < 0.05). Ultrasonography showed an intermediate signal

Table 1 . The Backgrounds of the pitavastatin and control groups.
*Statistically significant (P < 0.05).
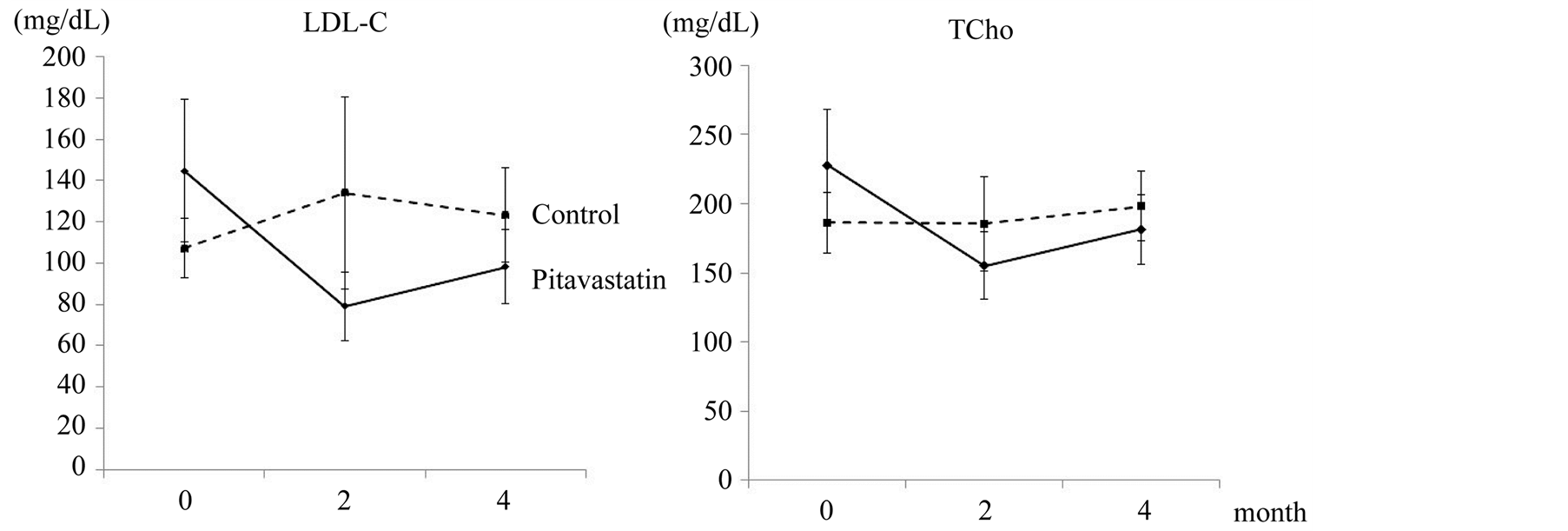
Figure 1. The temporal changes in the TCho and LDL-C levels.
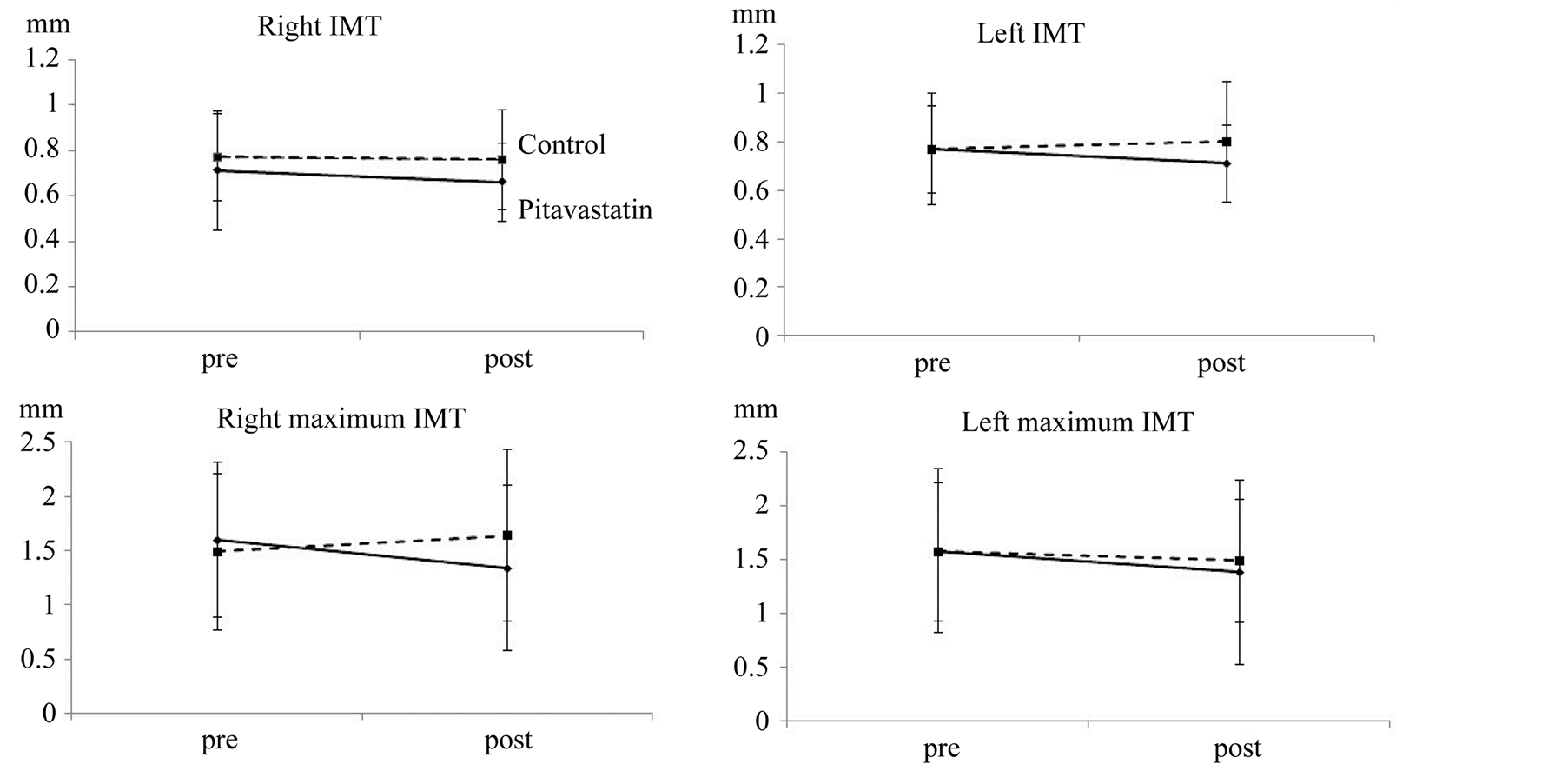
Figure 2. The temporal changes in the right and left IMT.
intensity for most plaques, indicating that the plaques were stable [18] [19] . The ultrasonography signal intensity was not significantly changed during the observation period. Because the intervals of carotid ultrasonography examination were variable, the IMT change per year was calculated to compensate for the variable interval. The change of the IMT %/year were less than zero for the pitavastatin group, and almost zero or higher for the control group (Figure 3). The yearly change of the right maximum IMT was significantly smaller in the patients in the pitavastatin group than those in the control group (P < 0.05).
The observation period in the pitavastatin group ranged from 11 to 52 months, with a mean of 31.6 months. Vascular events or death were not observed during the observation period. The observation period of the control group ranged from 18 to 64 months, with a mean of 41.8 months. The observation period of the control group was significantly longer than that of the pitavastatin group (P < 0.05). One recurrence of cerebral lacunar infarction, one cerebellar hemorrhage and one death due to head injury occurred in the control group during this observation period.
5. Discussion
Our study revealed that the stroke patients with hyperlipidemia were significantly younger than the stroke patients without hyperlipidemia. In addition, the body weight and body mass index (BMI) were significantly higher in the stroke patients with hyperlipidemia than in those without. These results indicate that hyperlipidemia causes metabolic syndrome and stroke at an earlier stage of life. Therefore, the appropriate treatment of hyperli-
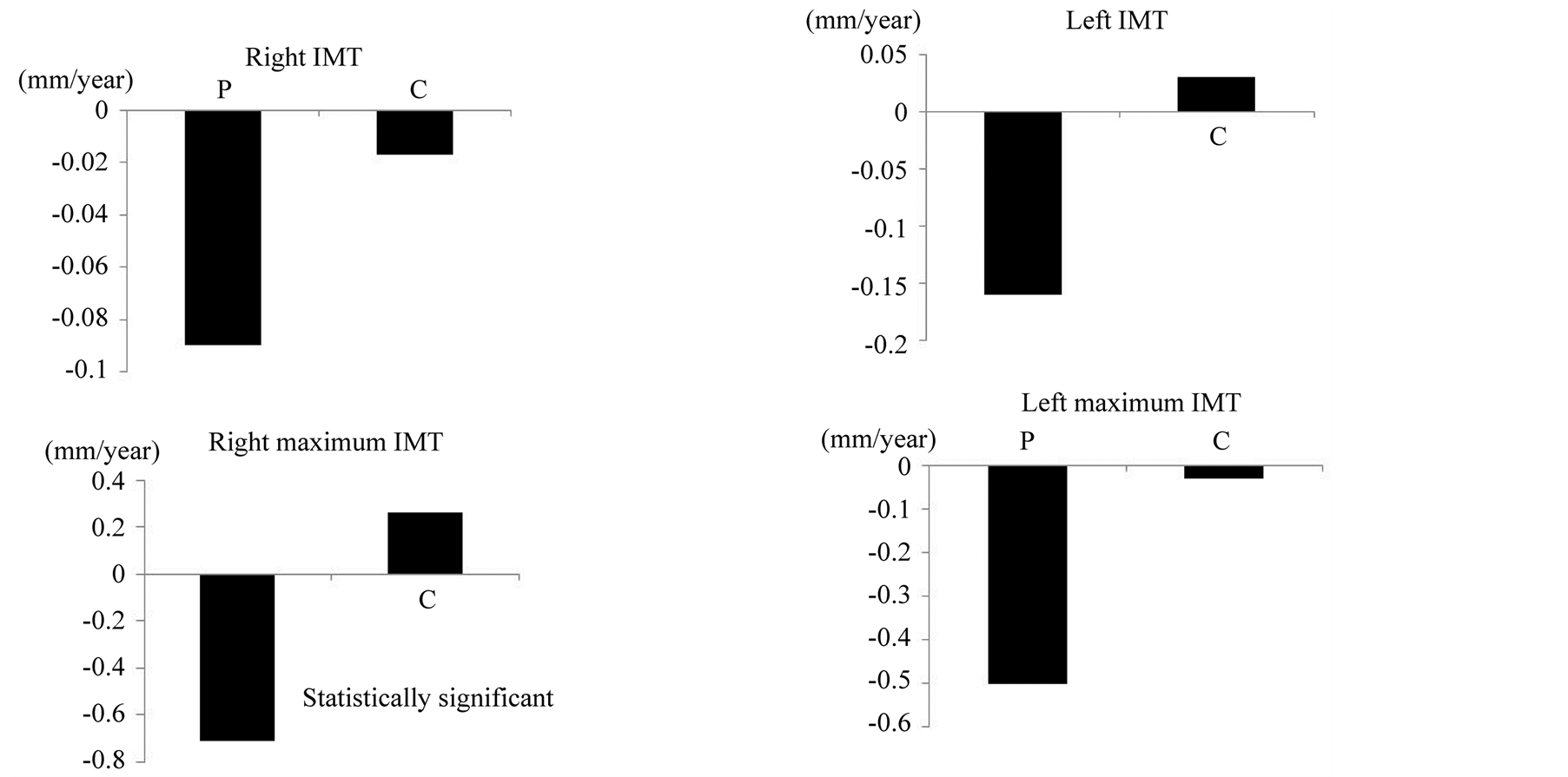
Figure 3. The yearly changes in the right and left IMT.
pidemia could prevent stroke or delay the onset of stroke.
Changes in the surrogate markers, such as the serum TCho and LDL-C levels and maximum carotid IMT, were observed a few months after the initiation of pitavastatin. In our study, only the right maximum IMT of the pitavastatin group showed a statistically significant decrease compared with that of control group. However, both the right and left mean and maximum IMT showed a tendency to decrease, although the changes were not statistically significant. In the control group, the right maximum IMT showed an increasing tendency, although the left maximum IMT showed a decreasing tendency. Therefore, only the right maximum IMT showed a significant difference between the pitavastatin and control groups. This may have been because the control group also received antiplatelet and anti-hypertensive drugs, which are beneficial for the carotid IMT. The small number of patients included in the study and the potential for errors in the IMT measurement by ultrasonography may also have led to the lack of significance for the differences between the other variables in the two groups.
There have been many reports of large clinical trials of primary and secondary prevention of cerebrovascular disease using statins [8] -[10] . Most of these studies were conducted in Western countries using the maximum or higher doses of statins, except for the Management of Elevated Cholesterol in the Primary Prevention Group of Adult Japanese Patients (MEGA) study [10] . No large randomized study of the secondary prevention of cerebrovascular disease in the Japanese population using a standard dose of statin has been reported to date. The Japan Statin Treatment Against Recurrent Stroke (J-STARS) study is a large randomized controlled trial of the secondary prevention of cerebrovascular disease in the Japanese population using a standard dose of pravastatin (NCT 00221104) [20] . The J-STARS is currently in progress, and the study is estimated to be completed in 2014. One problem with this study is that the therapeutic drug, pravastatin, is not a strong statin.
In our study, vascular accidents and death were observed only in the control group. However, the control group had a higher median age and longer follow-up than the pitavastatin group, which may account for these events. Although the current study suggested that pitavastatin may be effective for preventing secondary stroke in patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia, a prospective randomized study is required to elucidate the long-term clinical effects of pitavastatin.
Some previous studies reported that rosuvastatin inhibited the progression of the carotid IMT in both Western and Japanese patients with modest IMT thickening and hyperlipidemia [5] -[7] These results were similar to our present results, although our study showed more early changes in the carotid IMT using pitavastatin, while the other study focused on the changes 12 months after beginning the medication.
The present study is associated with some limitations. First, the study was not a randomized controlled trial. The drug group and control group should have the same background in order to definitely evaluate the effects of the drug. That would have required selecting patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia as the control group. Such a study would yield a high level of evidence. However, the failure to treat patients with hyperlipidemia is clinically and ethically inappropriate. Although aggressive LDL-C and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) lowering strategies have been reported to have beneficial effects to prevent stroke in patients without hyperlipidemia [9] , statin treatment for patients without hyperlipidemia is not covered under the Japanese health insurance system. Therefore, the current study selected stroke patients with hyperlipidemia as the target patients for statin medication, and stroke patients without hyperlipidemia as the control patients. Second, the present study selected surrogate markers as the primary end-points. Large randomized studies yield a high level of evidence, but they require a large amount of time and expense. The carotid IMT and serum LDL-C level are sensitive surrogate markers of the risk of stroke [4] [21] . Therefore, these surrogate markers were selected as the end-points in this study, and might also be useful in future, large studies. Third, the study was conducted at single institution, so the patient population was small, and the follow-up period was short. However, significant beneficial changes of the surrogate markers were observed. The study will be continued, and we are recruiting a larger patient population and will report the results of a longer follow-up. Finally, all of the patients in the present study had mild cerebral infarction and were treated in an out-patient clinic. No patients with severe disability or renal failure were included. Most patients had low serum CRP levels and a low carotid IMT. Therefore, the present study just demonstrated the significant protective effect of pitavastatin for Japanese patients with mild cerebral infarction and hyperlipidemia. The effects of pitavastatin on Western patients with severe stroke and hyperlipidemia should therefore be investigated in the future. Although the abbreviation of this study was PESSMIST, this study demonstrated results that should make clinicians “optimistic”, not pessimistic, about the effects of pitavastatin for patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia.
6. Conclusion
A prospective, open label, clinical case-control study was conducted to determine the secondary preventive effects of pitavastatin for Japanese patients with cerebral infarction and hyperlipidemia. The patients with cerebral infarction and hyperlipidemia were younger than the patients with cerebral infarction without hyperlipidemia. The serum TCho and LDL-C levels significantly decreased, beginning from two months after the initiation of pitavastatin treatment. The maximum carotid IMT also decreased after the pitavastatin treatment. These surrogate markers were effective for evaluating the effect of pitavastatin on preventing secondary stroke. Pitavastatin showed beneficial effects for improving these surrogate makers. Although a prospective randomized study is required to reveal the long-term effects of pitavastatin, the current study suggests that it may be effective for preventing secondary stroke in patients with stroke and hyperlipidemia.