Mineragraphic Study of Manganese Ore Deposits of Kandri, Mansar, Beldongri and Satak Mines, Nagpur District (Maharashtra) Central India ()
1. Introduction
Manganese ore deposits of the study area are a part of M.P.-Maharashtra belt of Central India and this belt is encountered with Mesoproterozoic Sausar Folded Belt [1] [2] . The Precambrian rocks of Sausar belt [3] contain the largest and richest manganese ore deposits of India which are highly deformed and subjected to low-high grade metamorphism and this metamorphic grade in the Sausar supracrustal rocks varies from greenschist to upper amphibolite facies with gradual increase in the grade of metamorphism from east-southeast to northwest [4] [5] . The study area is situated in southern part of this belt and lies about 40 - 45 km away from Nagpur Station. In Nagpur District four manganese mines viz, Mansar, Kandri, Beldongri and Satak are selected for mineragraphic studies. These are working manganese mines, in which Mansar, Kandri, and Beldongri are underground mines and Satak is the opencast mine. Braunite, bixbyite, jacobsite, hollandite and hausmannite are observed as a predominance manganese mineral of these mines. Detailed studies of this area are described by [6] in his classic memoire and [7] carried out the mineralogy of the study area and proposed his view. In the study area, systematic mineragraphic study of manganese ore was not carried out by earlier workers. This area was investigated only with regard to their structural and geological setting. The mineralogy of manganese ores of adjacent area such as Gumgoan mine and Tirodi mine has been investigated by many researchers. [8] carried out the mineralogy, paragenesis and genesis of gondite rocks and associated ore deposits around the study area. The mineralogy of other parts of M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt is investigated by many workers. [9] -[15] suggested that the paragenesis of manganese minerals is associated with the gondites rocks of Nagpur District.
With the help of these works, the authors are trying to establish the mineralogy of manganese ores of Kandri, Mansar, Satak and Beldongri area of Nagpur District, (Maharashtra) Sausar Belt. The mineral chemistry of study area is helpful to establish textural relation and paragenesis which will be helpful to delineate the phase equilibrium condition of the manganese ore and host rocks of this area.
2. Geology
The study area is occupied by a major structural feature (synclinal basin). The host rocks of the area are Precambrian metasediments and schistose rocks of Sausar Groups i.e. known as “Sausar Series” [6] . These Sausar series (Figure 1) are regionally metamorphosed and comes under the low grade (green schist) to high grade (amphibolites) facies. In Central India, the location of the study area occurs in southern part of central portion of Sausar Folded Belt. In this area four important formation and stages (Table 1) are proposed by different workers [6] [16] [17] which are based on field observation and present lithology. According to their proposal these formations are Mansar formation (Schistose rocks and gondites/manganese ore), Chorbaoli Stage (Quartzite) and Bichua (Dolomitic marble). But these workers proposed the stratigraphy of whole belt. Apart from these, [3] [18] -[21] proposed a local stratigraphy of the study area. According to the recent stratigraphy (Table 1) of the area, the basement are made up of biotite genesis which is known as Tirodi Biotite Gneisses and the litholog unit interpreted as a conglomerate horizon by some earlier workers, near the contact of the granite gneiss and the Sausar Group in Mansar-Kandri area,has been reinterpreted to be of tectonic origin [3] . Mansar formation are rich in mica schist, muscovite-biotite-schist with sillimanite, intercalations of manganese ore horizon with gondite rocks, Chorbaoli formation are formed by the quartzite, quartz-schist, quartz muscovite schist with sillimanite tabloids and Bichua Formation occur as dolomitic marbles with calc-silicate and schistose bands and sillimanite bearing quartz biotite-granulite. All the above formations are intruded by pegmatite and quartz vein.
3. Material and Methods
A total of 40 samples were collected from the different selected mines of study area, out of which 32 samples were finally selected for the mineragraphic studies. These mineragraphic microscopic studies of ore samples were conducted by polished blocks under the reflected light of microscope. Prepared ore blocks were examined
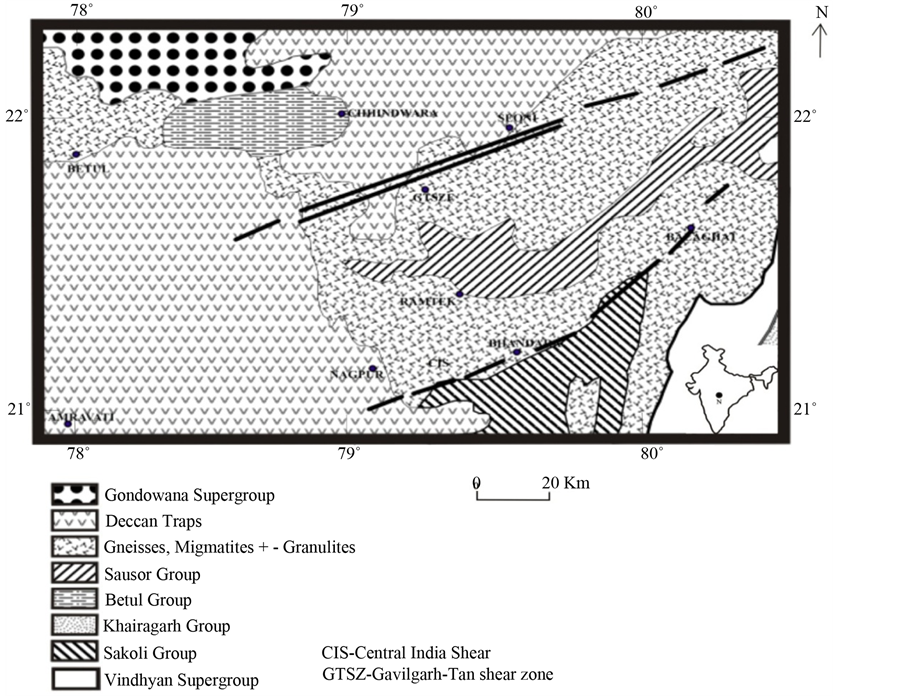
Figure 1. Generalised geological map of study area (Nagpur) in Central India, India. After Chattopadhyay and Ghosh [22] . Inset: Map of India showing position of study area (N = Nagpur).

Table 1. Generalized Stratigraphy of Study area after Chattopadhyay, et al. (2003).
under the reflected light of microscope with the help of air and oil immersion lenses and powder X-ray diffraction technique was use to confirm the present minerals. X-ray diffraction analysis was conducted by XPERTPRO PHILIPS in Jadavpur University, Kolkata. This technique was used on operating current 40 kv-30 ma and results were obtained on 2θ positions in the form of peaks.
4. Mineralogy of Manganese Ore
4.1. General Statement
Braunite is recorded in all polished blocks of manganese ore. On the basis of textural evidence of manganese ore of Tirodi mine, [9] has been concluded that braunite has a wide distribution in all the grades of metamorphism and all manganese ore horizon of different formation. Braunite is recorded in all samples of manganese ore of the study area. Bixbyite, hausmannite and jacobsite are followed braunite. Vredenburgite (Figure 2) are spotted in few polished block of manganese ore. Braunite, bixbiyte, and jacobsite are the high grade metamorphic minerals. Pyrolusite, hollandite and manganite are identified as low grade metamorphic minerals. Exsolution of hausmannite (Figure 2) in jacobsite and braunite also occur in manganese ore of Nagpur manganese mines and they have been introduced by higher pressure temperature condition. The interstitial space between braunite (Figure 3) is filled by secondary oxides of manganese. Second generation braunite has replaced all the primary metamorphic minerals and secondary pyrolusite and psilomelane (Figure 4) has also invaded and replaced them abundantly. Pseudo-colloform textures (Figure 5) are observed in manganese mines of Nagpur. Pseudo-colloform textures are formed by the alteration of jacobsite to psilomelane along the grain boundary of braunite. This texture is already reported by [11] in Gumgoan-Ramdongri manganese mines. Replacement texture and relict texture are common between braunite, bixbyite, hausmannite and jacobsite. In polished block of Mansar and Satak manganese ore, amorphous braunite (Figure 6) minerals are recoded. Mostly amorphous braunite ore minerals occur as veinlet. Along the margin of these braunite veins, psilomelanes also occur. In few blocks these amorphous braunite also contain tiny shaped or vein shaped jacobsite. Tiny shaped and needle shaped Iron bearing minerals like hematite and ilmenite are spotted. According to the Roy [11] these iron bearing mineral which are associated with manganese minerals, are metamorphic minerals. The mineral paragenesis of the study area is concluded on the basis of the detailed study of polished blocks of manganese ore samples. In
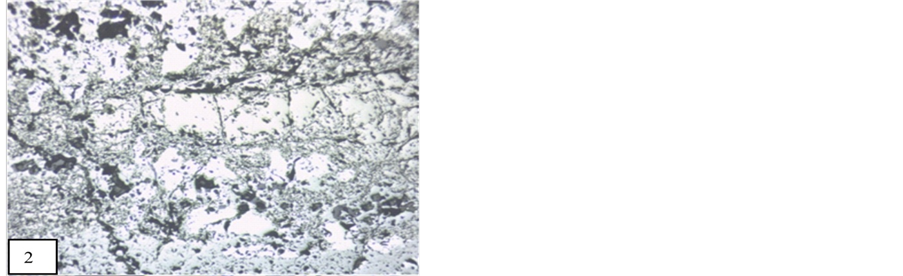
Figure 2. Exsolusion texture (vredenburgite) between hausmannite and jacobsite (4×), M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
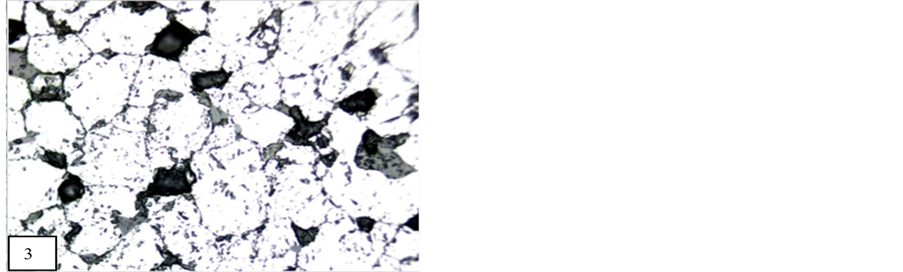
Figure 3. Interstitial filling of psilomelane between the grain of braunite (20×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
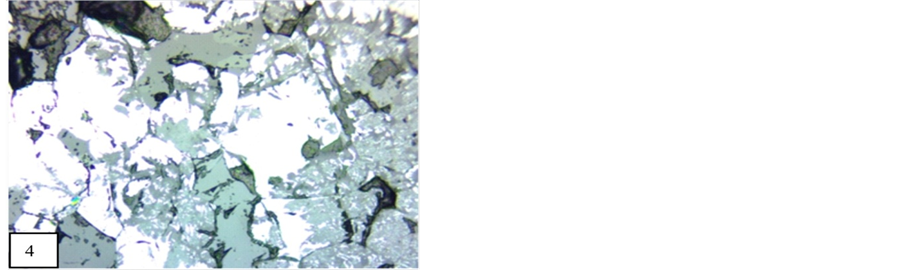
Figure 4. Psilomelane and pyrolusite are replacing braunite (20×). M.P-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
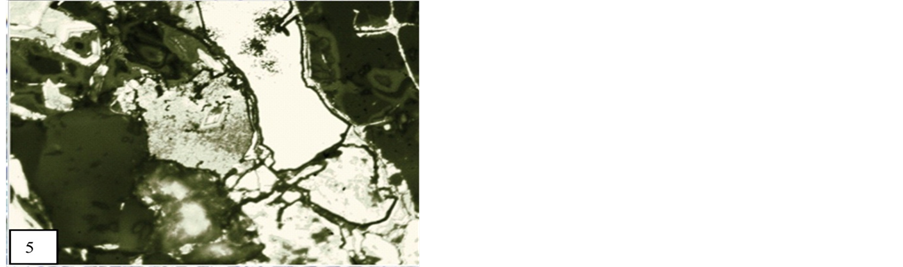
Figure 5. Psedo-colloform texture between jacobsite, braunite and psilomelane (oil immersion lens 50×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).

Figure 6. Vein texture in braunite and psilomelane replacing the boundary of braunite (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
study area two types of minerals are identified. These identified minerals are categorised as a primary minerals and secondary minerals.
4.2. Primary Minerals
In Nagpur braunite, bixbyite, hausmannite, jacobsite and vredenburgite are primary minerals which are associated with host rocks gondites, quartzite, schist, marble and calc-silicate gneisses. In the study area primary manganese minerals are considered as most probably initial sedimentary manganese ore or metasediment which are laterally metamorphosed. The influx of hydrothermal to colloidal solution might be derivatives by dissolution of the metamorphic manganese and the supergene might be due to mobilization both of metamorphic and colloidal manganese [23] .
4.2.1. Braunite: 3(MnIII, FeIII)2O3, MnIISiO3
Braunite occurs as dominant mineral of manganese ore deposits of Nagpur. It is categorised as lower oxides high temperature and pressure manganese minerals [24] . It also contains iron and silica. Braunite occurs as subhedral mineral, but due to the replacement of pyrolusite, and alteration of bixbyite and hausmannite, it occurs as anhedral minerals. Braunite occurs in two generations. The first generation occurs in intergrowth with hausmannite (Figure 7) and also intimately associated with the vredenburgite, bixbyite and other primary minerals of this suite. The second generation veins the earlier minerals like vredenburgite, manganite (Figure 8) etc. and occur interstially in them [9] . In study area braunite mainly associated with manganese silicates which represent metamorphic origin. According to [7] such braunite are metamorphic origin.
1) Optical properties The first observation was made under the analyser out condition. In the presence of oil the colour of braunite will be dark grey but in air braunite appear light grey in colour with red internal reflection. One set cleavage is present. [25] described the reflection behaviour of braunite. According to him braunite appear greyish-white with a brownish tinge (quite similar to galena in strongly dimmed light), rather moderate reflection. Braunite has low reflectivity, weak plechroism, weak anisotropic in oil.
2) Etch reaction On etching of braunite with HCL (Con.), HNO3 (Con.) and H2SO4 (Con.) gives negative result but with SnCl2 (Sat.) shows strong etching. When braunite is etched with H2O2 (Dil. 20%) show slow effervescence along fractures but there is no stain.

Figure 7. Braunite, hausmanite and manganite occur as a band and exsolusion of braunite and hausmannite present (4×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
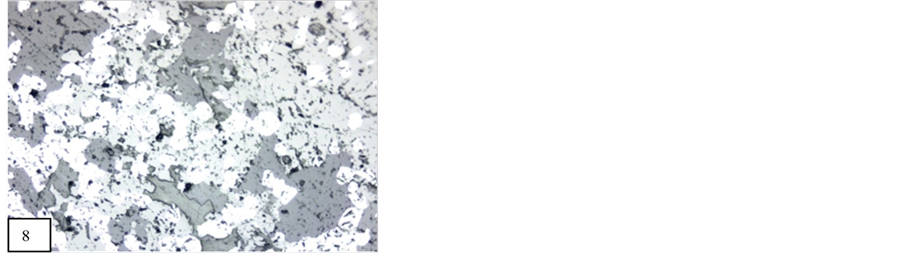
Figure 8. Braunite occur with manganite and gangue (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
4.2.2. Bixbyite: (Mn, Fe)2O3
Bixbyite is recorded as commonly occurring intergrown with braunite and hausmannite. Bixbyite probably crystallize in tetragonal system. Bixbyite recorded as nuclei (Figure 9) and near the boundary of the braunite minerals. Free bixbyite (Figure 10) is also spotted in ore block of the study area and confirmed by the XRD analysis. They occur as well-developed crystals with square and rectangular outline. Bixbyite occur along with braunite and garnet. Bixbyite is characteristically formed at high temperature metamorphic zone. Relict texture of bixbyite (Figure 9) in braunite depict about the origin of bixbyite. Braunite is formed by the original sediments of the iron oxide, silica and manganese hydroxides, which react with iron oxides to form bixbyite [26] .
1) Optical properties Under microscope bixbyite is non-pleochroic and isotropic mineral. Bixbyite is biscuit coloured with a tinge of green in oil and yellowish grey in air. The reflectivity of bixbyite is higher than braunite. The grains of bixbyite are rounded and oval in shape. Some grains of Bixbyite contain lamellar twinning. According to [27] the different grains are cemented by thin films of iron oxide (haematite). Part of the iron oxide is coarse grained and recrystallised and such hematite exhibits lamellar twinning.
4.2.3. Jacobsite: MnFe2O4
Jacobsite occur in isometric system. In study area jacobsite occur as a free grain or exsolusion texture with braunite and hausmannite, i.e. known as vredenburguite (Figure 2).
1) Optical properties Under microscope jacobsite is non-pleochroic and isotropic mineral. Jacobsite is brownish grey and sometimes with a faint yellow tint in air and dark green tinge observable in oil. Some varieties are isotropic and others feebly anisotropic. In all polished block jacobsite occur as a idiomorphic grains. Jacobsite also show exsolution texture. These exsolution textures are formed as hausmannite with jacobsite and jacobsite with magnetite (Figure 11).
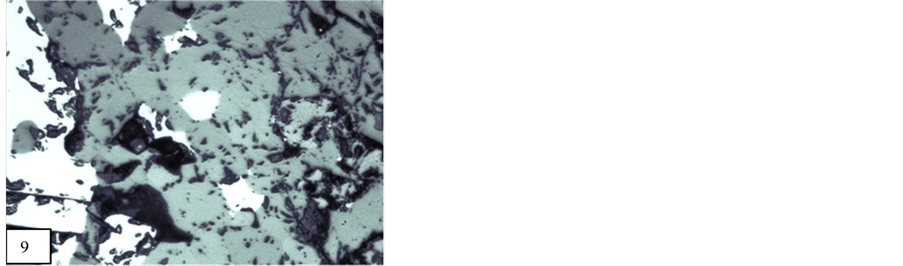
Figure 9. Relics of bixbyite in braunite (oil immersion 50×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
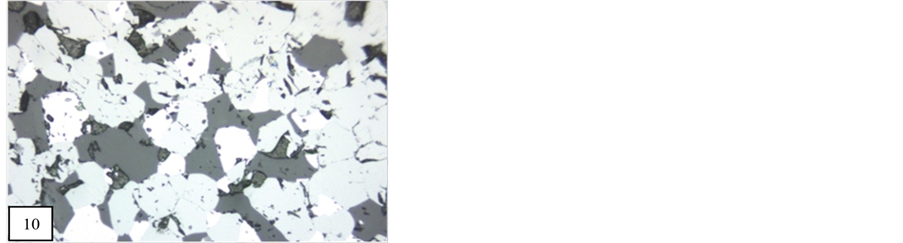
Figure 10. Braunite and bixbyite occur as a free grain (oil immersion 50×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
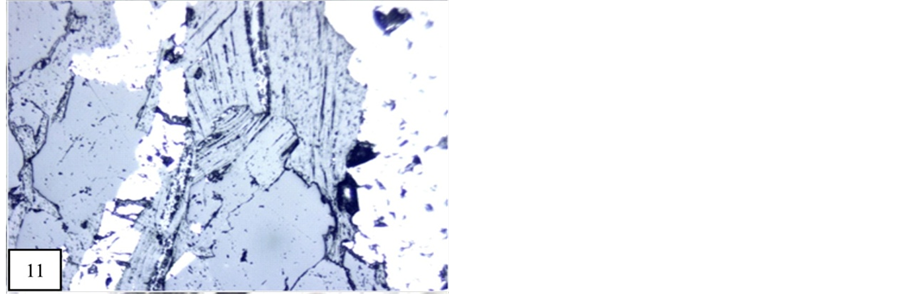
Figure 11. Jacbsite are formed along the fracture of manganite (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
4.2.4. Hausmannite: Mn3O4
Hausmannite occurs with braunite [25] and showing special texture with jacobsite which is known as vredenburgite (Figure 2). In the ore block of study area, hausmannite is spotted as association with bixbyite, jacobsite and braunite (Figure 2 and Figure 7).
1) Optical properties Hausmannite shows strong distinctly pleochroic in shades of grey. Hausmannite is also strongly anisotropic mineral with moderate reflectivity. But reflectivity of hausmannite enhance in the presence of immersion oil. Hausmannite shows exsolution texture with jacobsite (Figure 2). These hausmannite are occur as a lamellar form in jacobsite and vredenburgite. These lamellar hausmannite has no perfect orientation, irregular, bent and contorted.
2) Etch reaction On etching of hausmannite with hydrogen per oxide and sulphuric acid give positive results with dark black tarnishing. On etching with SnCl2 it gives black tarnishing, hausmannite give negative results on etching with hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulphuric acid and FeCl2.
4.3. Secondary Minerals
In Nagpur Secondary minerals are formed by the process of colloidal influx or metasomatism [28] . In Nagpur, psilomelane-cryptomelane, hollandite and pyrolusite are secondary mineral which are occur in less quantity.
4.3.1. Psilomelane-Cryptomelane
Psilomelane is very fine grained. A variety of psilomelane is cryptomelane which shows rhythmic banding. It is found in association with silicates rich in manganese. [29] studied psilomelane specimen (hard, compact and amorphous variety of manganese oxides and after X-ray powder diffraction patterns he concluded that 60% of the specimen is cryptomelane and 30% psilomelane now the term cryptomelane become most widely used for most of the psilomelane. According to [30] psilomelane and cryptomelane have similar physical properties but they have different chemical composition and X-ray powder patterns. Chemically cryptomelane has K2O as one of the essential constituent with minor or no BaO. Psilomelane has vice-versa. It contains BaO as one of the essential constituents with little or no K2O [31] .
1) Optical properties Under reflected light, the colours of psilomelane-cryptomelane are greyish white to bluish grey. In study area the mineral is moderately anisotropic and shows pleochroism which is fairly strong in shades of grey.
2) Etch reaction On etching with potassium cyanide (KCN), potassium hydroxide (KOH), Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3) and tin chloride (SnCl2) give negative results. On etching with hydrogen per oxide (H2O2) psilomelane give some effervescence and in the presence of H2O2 + H2SO4 psilomelane etches strongly brown. But etching with stannous (tin) chloride (SnCl2), it become blackens immediately.
4.3.2. Hollandite: BaR8O16, R = Mn4+ Mainly, Also Mn2+, Fe, Co
1) Optical properties Hollandite crystallizes in tetragonal system. Hollandite is strongly pleochroic mineral and show greyish white to white colour with a precipitated yellow tint. On the observation between cross nicols, hollandite show strong anisotropism but basal sections are isotropic. Some specimens show lamellar twinning similar to that of hausmannite. In the green light, the reflectivity of hollandite depends upon the orientation of grains it measure in range of 28.1% to 29.7%.
2) Etch reaction On etching of hollandite with sulphuric acid and hydrogen per oxide gives positive result. As a result the present twining feature will be more prominent and clear. Hollandite gives negative results on etching with hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and hydrogen peroxides.
4.3.3. Pyrolusite: MnO2
Pyrolusite is secondary manganese mineral which is formed by the alteration of primary manganese minerals and occurs as a crystalline to non-crystalline variety of manganese oxide. Colloform textures are common in pyrolusite. In samples, it is spotted as massive and dendritic in form with containing innumerable gangue mineral. In ore block, replacement textures are formed by the replacement between pyrolusite, silicate and psilomelane (Figure 12).
1) Optical properties Pyrolusite is weakly pleochroic mineral and colour will be yellowish white to white. Pyrolusite has higher reflectivity i.e. 36.3% in green light. Sometimes it shows one set of cleavage. On observing between cross nicols pyrolusite shows distinct anisotropic in shades of grey and light yellow.
2) Etch reaction On etching of pyrolusite with hydrochloric acid and nitric acid it gives positive result and become darker. Etching with hydrogen per oxide and sulphuric acid (H2O2 + H2SO4) pyrolusite give dirty grey colour. Pyrolusite gives effervesces without any stain on etching with hydrogen peroxides (20%). On etching with stannous chloride (SnCl2) pyrolusite become blackens immediately with corroded surface.
4.3.4. Hematite
Hematite is an iron mineral and rarely spotted in ore block of manganese. It occurs as a needle or tiny body. Hematite is formed on high temperature and pressure, and depict about high grade metamorphic condition.
1) Optical properties Hematite is non-pleochroic mineral, white in air and bluish in oil. Reflectivity of hematite is 26.5%. Hematite also shows anisotropism in shades of grey. Cleavage and twinning are absent.
2) Etch reaction On etching with all standard reagents hematite give negative results.
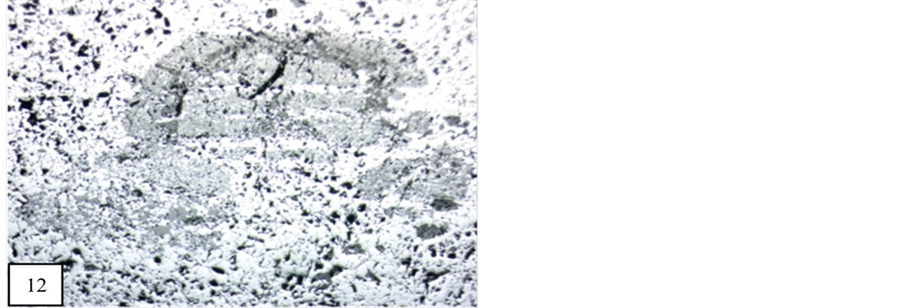
Figure 12. Replacement between braunite, psilomelane and pyrolusite (4×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
5. Result and Discussion
5.1. Microstructure/Texture
The manganese minerals of this area exhibit distinct textures due to the presence of different mineral association. The texture of manganese ore are identified in polished block under the reflected light of microscope which are as follows:
Replacement Texture;
Colloform Texture;
Veined Texture;
Brecciated Texture;
Granular Texture;
Banded Texture;
Crystallographic Intergrowth;
Mutual Boundary Relation.
5.1.1. Replacement Texture
Replacement texture is common in all manganese ore of this area and these replacement textures are observed between different mineral assemblages. Replacement textures are formed between Vredenburgite-Braunite, Jacobsite-Braunite, Mangenite-Braunite, Braunite-Psilomelane, Braunite-Pyrolusite, Manganite-Pyrolusite, Vredenburgite-Psilomelane, Vredenburgite-Pyrolusite, Hollandite-Psilomelane, and Psilomelane-Pyrolusite. These replacement textures are formed along the cleavage, fracture and grain boundary. Temperature, pressure, chemical equilibrium, physico-chemical balance environmental conditions are responsible for replacement textures between minerals.
Vredenburgite and manganite have been invaded by second generation of braunite and this texture is formed along the cleavage plain and grain boundary (Figure 13).
In idioblastic grain of manganite, braunite occur as interstitial mineral (Figure 13).
In this area replacement textures occur between braunite, psilomelane and pyrolusite. Braunite is replaced by psilomelane and pyrolusite is in irregular pattern (Figure 12).
Primary pyrolusite and psilomelane are occur between interstitial spaces of braunite.
Replacement texture between manganite and pyrolusite is formed by the replacement of manganite with pyrolusite which took place along the cleavage plain of manganite.
Vredenburgite are also replaced by psilomelane and pyrolusuite. These whole replacements occur in present lamellae of hausmannite (Figure 14).
Replacement of hollandite by the psilomelane is also observed in ore block of Nagpur manganese mines.
5.1.2. Colloform Texture
Colloform texture is characteristic of supergene manganese ores, specially the manganese ore of MP-Maha-
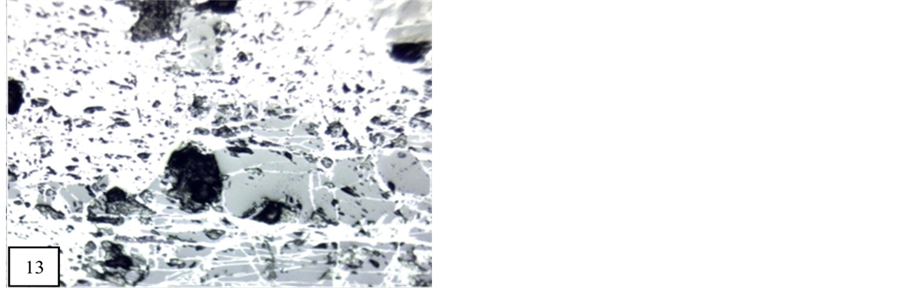
Figure 13. Braunites contain pyrolusite and secondary braunite occur in interstitial space of manganite (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra manganese belt, Nagpur (Central India).
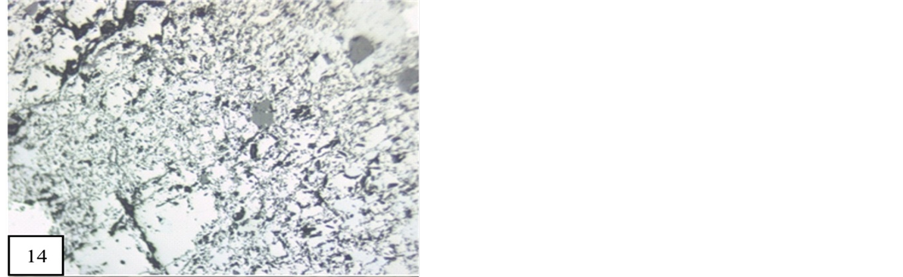
Figure 14. Pyrolusite and psilomelane are replacing vredenburgite (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra Manganese Belt, Nagpur (Central India).
rashtra manganese belt. This texture is formed by the colloidal gels which are precipitate by the present mineral assemblages of host rocks/surrounding rock types. Colloform texture is formed by the psilomelane which is deposited in gangue minerals. This texture shows a series of concentric layer of different manganese ore having a nucleous. Pyrolusite and psilomelane occur as concentric layers. Braunite and gangue minerals are behaved like a nucleous. Pseudo-colloform texture is spotted from the polished blocks of study area (Figure 5).
5.1.3. Veined Texture
Veined texture (Figure 6) is occurring in manganese mine of Nagpur. In some ore block, manganese minerals occur in form of veins and they are intersected to each other. Vein of amorphous, noncrystalline braunite occur as a vein texture. Psilomelane and pyrolusite are formed on the boundary of these veined mineral. Some gangue and jacobsite also occur as veinlet. In few ore block, replacements of manganese mineral occur along the wall of these veinlet structures (Figure 6).
5.1.4. Brecciated Texture
In all block of manganese, braunite is common ore mineral. Generally these braunite are crystalline and in angular shape. Vacant space of these braunite grains are filled by pyrolusite, psilomelane, bixbyite and gangue material (Figure 3). In few block fractured grains of braunite are cemented with other manganese minerals such as pyrolusite, psilomelane and gangue minerals (Figure 15). But there is no replacement in observed brecciated braunite.
5.1.5. Granular Texture
Granular texture is formed by the crystalline minerals and these minerals are integrown with gangue mineral and intergranular spaces are filled by pyrolusite. In ore block of study area granular texture are formed by the crystalline braunite (Figure 16) which are intergrown in gangue mineral and intergranular spaces are filled by pyrolusite and manganite.
5.1.6. Banded Texture
In the ore block of study area banded texture (Figure 7) is formed between braunite, manganite and gangue minerals. But these braunite do not shows definite crystals outline due to the alteration or replacement. In few ore blocks braunite, bixbiyte and hausmannite are formed in bands and appear as a band texture but grain grains of these minerals are appear as irregular in shapes. The patterns of occurrence of these manganese minerals are give rise as a schistose texture (Figure 7).
5.1.7. Crytallographic Intergrowth
Crystallographic intergrowth is observed between the grains of braunite, jacobsite and hausmannite. These crystallographic intergrowths are also known as exsolution texture. In this texture hasmannite lamellae are oriented in the (III) direction of jacobsite. [32] and [33] describe this texture as exsolution of minor member in the solid solution in the crystallographic directions of the major constituent in the descending temperature. According to
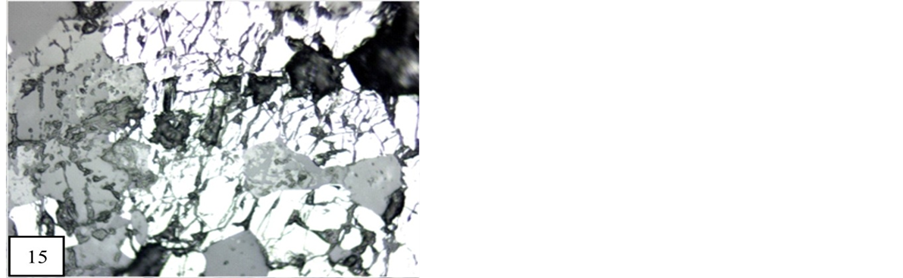
Figure 15. Fractured braunite are cemented by psilomelane, pyrolusite and gangue minerals (20×). M.P.- Maharashtra Manganese Belt, Nagpur (Central India).
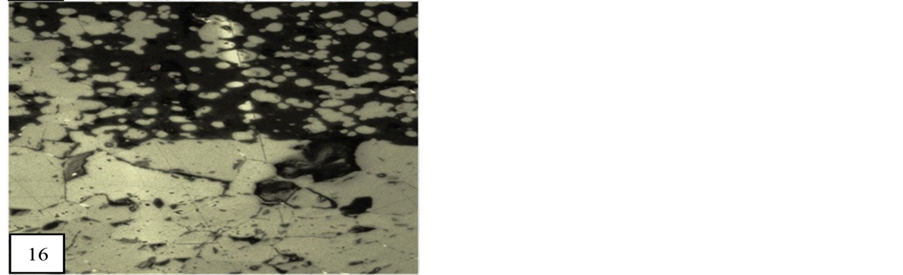
Figure 16. Granular texture is formed by the crystalline braunite (Oil immersion 50×). M.P.-Maharashtra Manganese Belt, Nagpur (Central India).
[34] such exsolution textures are formed at temperature of about 600˚C or lower. Such crystallographic intergrowth is well documented by [9] from Tirodi manganese mine of Balaghat district (Madhya Pradesh).
5.1.8. Mutual Boundary Relations
Mutual boundary (Figure 17) relations are seen only between the mineral of braunite and bixbyite. The contact between braunite and bixbyite are smooth have perfect boundary and there is no replacement between braunite and bixbiyte. On the basis of their preferred orientation and mutual boundary relation, it is suggestive of simultaneous crystallization, but it cannot be regarded as unequivocal evidence [35] . According to [9] the intimate association of these two minerals, a more or less same age relation is suggested by both.
6. Result of Analytical Technique
X-Ray Diffraction analysis of some of the samples confirmed the presence of braunite, bixbyite and rhodocrosite in the ore blocks of manganese of different selected mines. Some associated minerals are also clearly recognized on the XRD spectrum. The position of lowest and highest peak of braunite (d = 4.67542 - 1.6580, Figure 20), bixbiyte (d = 2.70731 - 1.65694, Figure 18) and rhodochrosite (d = 3.661 - 1.76969, Figure 18). The observed peak positions of these minerals showed that they are virtually indistinguishable. Gangue and other minerals which have less quantity of manganese ore such as viz, quartz, orthoclase, anorthite, muscovite, fayalite and almandine are also observed on XRD spectrum which are represented by peaks (Figures 18-23).
7. Mineral Paragenesis
Mineral paragenesis is determined by the appearance of manganese minerals in Nagpur mines. [15] suggested “the course of paragenesis of the mineral in the gondites and the associated ore bands of this area, concluded
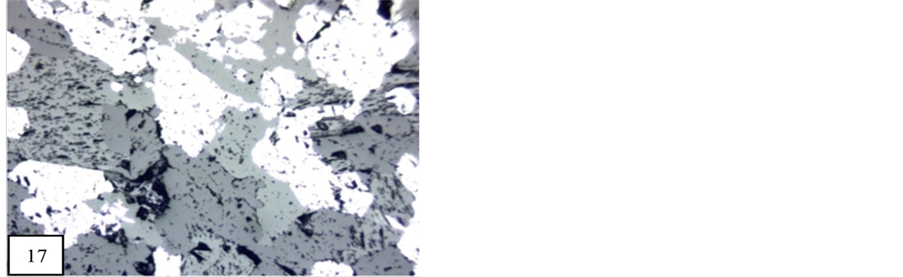
Figure 17. Braunite and bixbyite are showing mutual boundary relation (10×). M.P.-Maharashtra Manganese Belt, Nagpur (Central India).
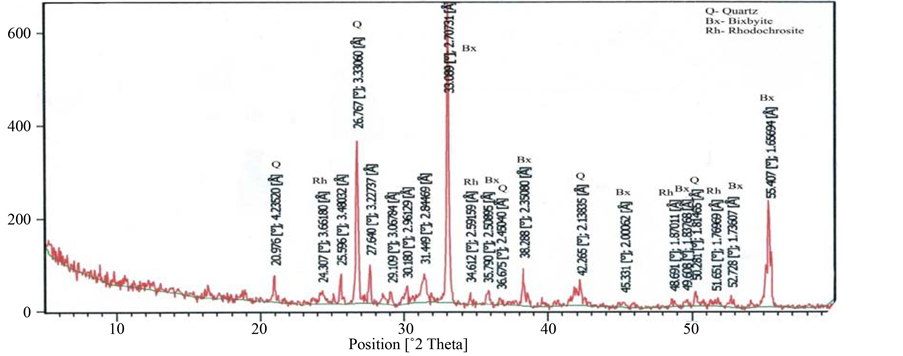
Figure 18. Showing 2θ position of quartz, bixbyite and rhodochrosite (Beldongri mine, Nagpur, Central India).
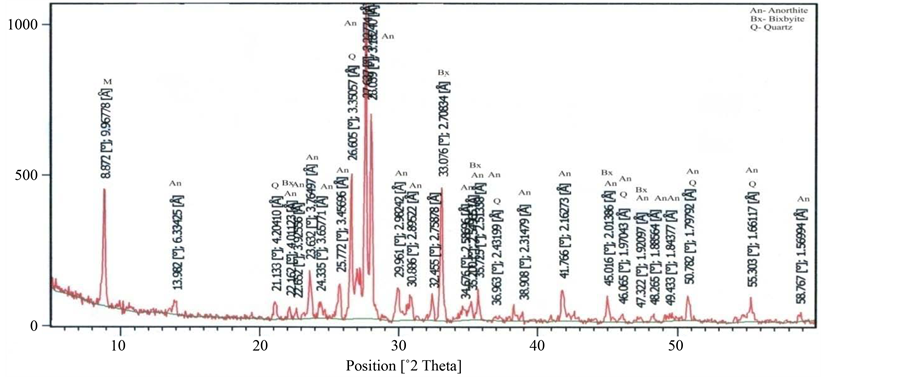
Figure 19. Showing 2θ position of anorthite, bixbyite and quartz (Beldongri mine, Nagpur, Central India).
that the earliest formed manganese oxides were hollandite, vredenburgite and free hausmannite and they were followed by braunite which, was definitely of later origin.” [11] examine the ore blocks of manganese ore of Gumgoan-Ramdongri mine of Nagpur, according to him, Braunite is recorded in all ore block therefore braunite is to be earliest manganese oxides to crystallize and vredenburgite (i.e. intergrowth of two minerals jacobsite
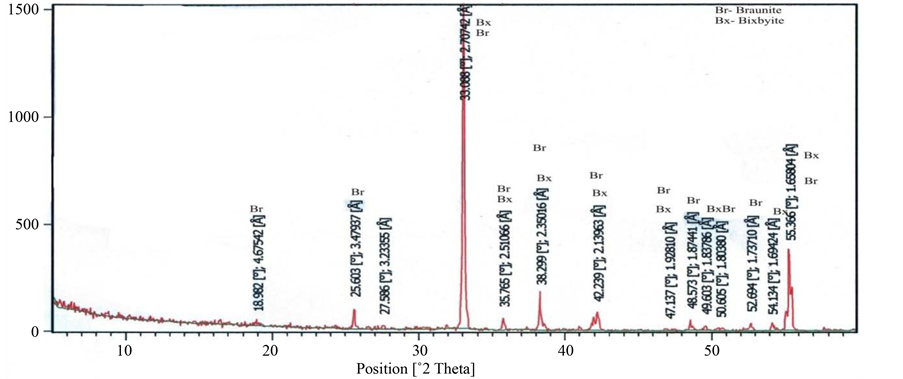
Figure 20. Showing 2θ position of braunite and bixbyite (Kandri mine, Nagpur, Central India).
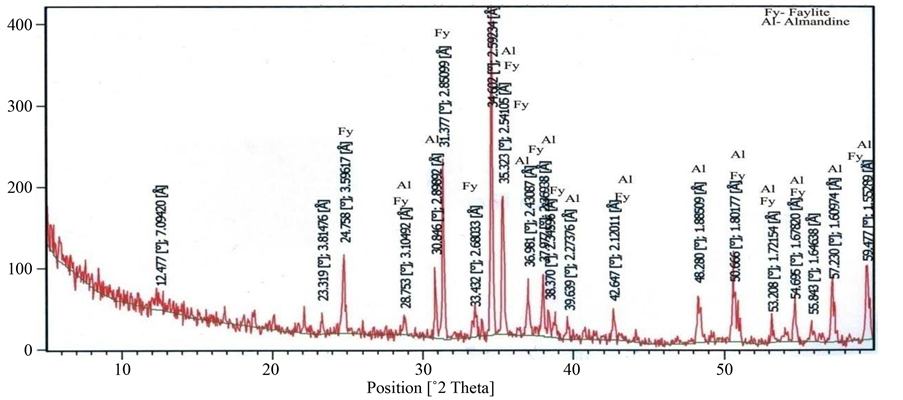
Figure 21. Showing 2θ position of fayalite and almandine (Mansar mine Nagpur, Central India).
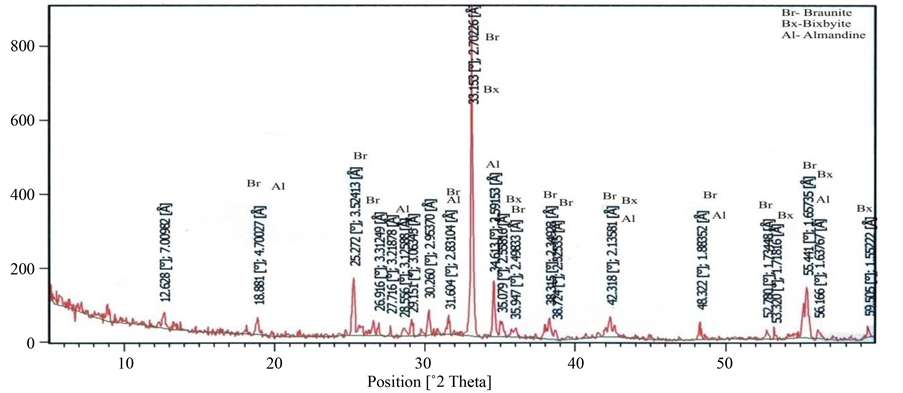
Figure 22. Showing 2θ position of braunite, bixbyite and almandine (Satak mine Nagpur, Central India).
and hausmannite) is spotted in many section of ore block. He also summarised the mineralogy of M.P-Maharashtra manganese belt (Table 2). In the ore block of Nagpur Manganese mines braunite is common mineral which are spotted all ore block and bixbyite are follow to braunite, bixbyite is occur as a relics in braunite. In most of the block bixbyite is recorded on the margin and centre of braunite minerals it behave like a nucleous. But in some block free bixbiyte is also recorded. The occurrence of haumannite is recorded as free minerals or with bixbiyte. The relict of hausmannite is found in bixbiyte. In some polished block hausmannite, braunite and bixbyite occur together and have perfect boundary. They show the mutual boundary relation. Jacobsite occur as a free grain or with hausmannite which is known as vredenburgite. Needle of jacobsite is also recorded from the
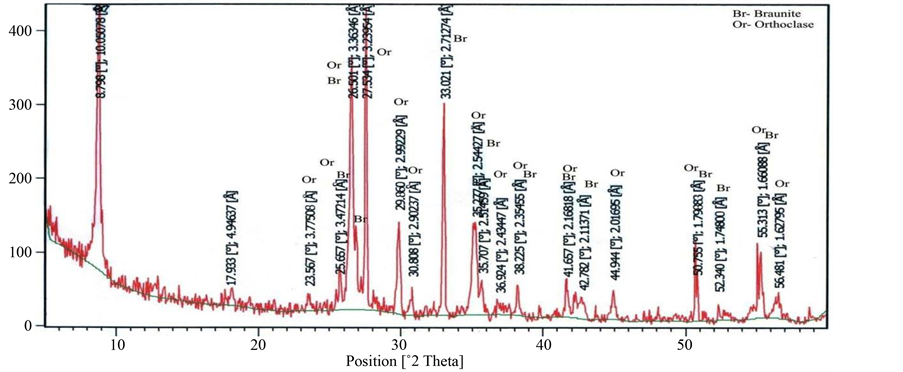
Figure 23. Showing 2θ position of braunite and orthoclase (Satak mine Nagpur, Central India).

Table 2. Paragenesis of Manganese ore minerals in deposits from different metamorphic zones of M.P.-Maharashtra Manganese Belt. After Roy (1963).
polished block of manganese mines of Nagpur. Psilomelane and pyrolusite occur as the interstitial minerals. Hematite and illmenite occur as needle shape which indicates metamorphism. Manganite and pyrolusite tend to crystallize in the interstitial spaces or cavities of cryptomelane. [15] suggested that hollandite, vredenburgite and free hausmannite crystallized simultaneously as the earliest mineral in the suit and they were followed by braunite, manganite, pyrolusite and psilomelane but after observing the textural relationship [11] suggested a different trend of crystallization. According to [11] braunite, which has not replaced or invaded any other mineral of the suite, was evidently the first mineral to crystallize and it was followed by the mix mineral vredenburgite, which under decreasing pressure-temperature condition was split into two phases, hausmanite exsolved in the octahedral direction.
After the examination of textural relationship of pyrolusite and psilomelane, they occur as a secondary minerals. Manganite is also recorded in most of the polished blocks. It has been concluded that these supergene minerals are crystallized due to the colloidal influx. Psilomelane and pyrolusite have been formed widely at the expense of practically all primary minerals in the suite by supergene processes.
8. Conclusion
Manganese ore deposits of study area are characterised by bixbyite and jacobsite which reflect the high temperature and the low pressure condition. In braunite, relics of bixbyite indicate that the bixbyite is formed by the replacement of some elements. The exsolution texture has been found between jacobsite and hausmannite, and the same texture has been reported between braunite and hausmannite. These textures are peculiar characteristics of gondites. Manganese ore deposits of the area occur by metamorphism and colloidal influx. The deposition of gangue minerals on the grain boundary indicates the supergene enrichment. Suggested mineral assemblages of manganese minerals and occurrence of secondary braunite along the margin of hausmannite and manganite are the evidence of retrograde metamorphism.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. L.A.K. Rao, Chairman and Dr. Shahid Farooq, Department of Geology, A.M.U. Aligarh for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work. The authors are grateful to and Dr. Subir Mukhopadhyay (HOD) and their staff member, Jadavpur University, Kolkata for XRD and their valuable guidance and support during the ore microscopy study. The authors are also thankful to Khansa Zaidi, Department of Geology, A.M.U., Aligarh and anonymous reviewer for suggesting necessary corrections in the manuscript. One of the authors, Talat Jawed is grateful to UGC for financial support in the form of a fellowship (MANF).
NOTES
*Corresponding author.