Work and Income Sharing in a Rural Economy: Effect on Economic Growth and Welfare ()
Keywords
Work and Income Sharing, Rural Economy, Endogenous Growth Model, Welfare in Developing Countries, Technology Adaptation

1. Introduction
Work and income sharing (WIS) is a common practice in many developing countries [1] . The practice is widely observed in harvesting and transplanting in the rice producing communities of South and Southeast Asia. In the Philippines the traditional harvest sharing system (hunusan) obligates rice farmers to accept the wishes of any villager to participate in harvesting; a fixed amount (traditionally one-sixth) of rice harvested by that villager is given as payment [2] . Similar systems are observed in Indonesia [1] [3] , Bangladesh [4] and Thailand [5] .
A high dependency on hired labor is not a traditionally held view on small subsistence farms. However, in the above regions, hired labor as a percent of total labor requirements typically exceeds 50 percent [2] . Lacking modern technology and custom services for transplanting or harvesting hired labor is used for peak labor demand (seasonal) activities. The custom is that family members do not perform this work; instead it is hired out. The payment for this labor is a sharing of the output among the hired laborers. While there is no consensus on why these villagers exchange labor without fully utilizing family labor, the literature provides some insight.
Takahashi [6] provides a theoretical explanation for this practice in the Philippines under shared tenancy contracts with landlords. With harvest sharing and mutual employment contracts, tenants maximize their output share at the expense of landlords. However, pointing out that harvest sharing is equally prevalent among small scale owner-farmers (not tenants) in West Java, Hayami and Godo [2] question the applicability of Takahashi’s theory to understand the practice of harvest sharing.
Scott [7] explains traditional rural economy customs in Southeast Asia in the context of a “subsistence ethic” by which social systems are designed to secure minimum subsistence for all community members. Under this principle, better-off members in the community have an obligation to offer employment opportunities to poor members. This moral oriented view of the traditional rural community has been challenged by some who claim that individuals maximize self-interest even in a rural economy [8] .
Hayami and Kikuchi [9] argue that two economic conditions can lead to risk sharing among farmers in a rural community. First, with low levels of agricultural technology, crop yields are not highly affected by whether the farmer works hard on his/her own fields or the work is performed by hired or exchange laborers. Second, farmers use WIS as a form of income insurance in a region where crop yields vary widely due to highly variable rainfall and frequent insect infestations. Thus, in the absence of insurance instruments (crop insurance, forward markets, well-functioning credit markets, or viable off-farm employment opportunities), WIS can insure against production risk [9] .
In this paper we consider WIS in the context of “endogenous technological change” models with expanding variety [10] [11] . Here the intermediate goods sector which develops and produces growing varieties of intermediate inputs is the source of economic growth. We employ an expanding variety model because the innovation in rural areas of developing countries is typically not of the quality-ladder type model in which the latest technology replaces older ones completely and immediately. Modern seed varieties are often hybridized with local seeds and it is common to see traditional farming methods and inputs coexisting with modern ones [2] .
Our model divides the intermediate goods sector into the “local adaptation stage” and the physical production stage. The “local adaptation stage” includes all activities, other than the physical production of intermediate goods, necessary to introduce the new input variety to the rural area. The scope of the local adaptation stage is larger than that of the R&D activity; it includes R&D, planning for production and distribution, land and infrastructure adjustment for new intermediate variety. Innovations in rural agriculture are mainly dependent on transfers of agricultural technology, including crop varieties, pesticides, fertilizers, machinery and irrigation systems, to different environments. This occurs through adaptive research and infrastructure improvements rather than through innovations within the area [12] .
In economic growth models, agriculture is typically incorporated in the context of structural change in which the economy shifts from agricultural to industrial as growth occurs [13] , or agricultural productivity growth provides the basis of take-off for the industrialization [14] . While these illustrate the transition from agricultural to industrial economy, our model focuses on the effect of WIS on economic growth and welfare in a rural economy. Our motivation comes from the fact that many of rural areas in developing countries remain agrarian-based even after considerable productivity and economic growth such as Green Revolution in Asia [15] .
Another well-known fact about rural economies in developing countries is that R&D activities are largely performed by public institutions [12] [16] . This may be due to some form of market failure such as nonrivalry or nonexcludability of knowledge, ideas and products created by R&D activities [17] . With these market failures it is not possible for private agents to appropriate through market pricing the full social benefits arising from R&D activities; hence, without government intervention suboptimal R&D levels result. The nonrival or nonexcludable nature of knowledge is typically specified as “knowledge spillovers” in endogenous growth models [18] . The high dependency on public institutions for agricultural R&D in developing countries requires special attention. Activities in the local adaptation stage in our model, other than R&D, such as land and infrastructure improvements also provide positive externalities to the rural economy. These positive externalities from the local adaptation stage take the form of knowledge spillovers from new seed varieties and benefits from local infrastructure improvement. With existence of positive externalities we show that volatility in either sector would enlarge the gap between the optimal and the market-equilibrium growth rate; the practice of WIS alone will approach, but never reach the optimal growth rate. This result helps explain the prevalent intervention of public institutions in agricultural R&D in developing countries.
The basic features of our endogenous growth model are described in the next section. We then derive the market-equilibrium growth rate in the steady state with WIS. Our ensuing welfare analysis elaborates the impact of WIS on the rural economy and the policy mix necessary to achieve optimal growth. We conclude with a summary of the results.
2. Market Structure and Production Shocks
In Figure 1 we show the basic components of our rural economy model. It is composed of the final and intermediate goods sectors. The final good sector is agriculture in which many farmers produce nondifferentiated goods in competitive markets. Agriculture productivity growth occurs through the provision of a greater variety in intermediate goods used in production. The intermediate goods sector supplies horizontally differentiated inputs such as crop varieties, fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, tools and machinery invented outside of the region.
In the intermediate goods sector there are two stages: the local adaptation stage and the production stage. The former stage includes R&D, planning for production and distribution, land and infrastructure adjustments for new intermediate varieties while the latter stage provides the intermediate goods. Nonfarm labor is an input in both stages. Because all intermediate goods are differentiated and imperfect substitutes, each intermediate good firm exploits positive profit. In the local adaptation stage positive externalities can deter the intermediate goods sector from appropriating the full social benefits from the local adaptation activities.
Differentiated intermediate goods are used together with farm labor and land in agriculture. The greater the variety of intermediate goods, the greater the productivity of agriculture. The supply of farm labor is from nonfamily members for the case with WIS, and from family members without WIS. Both family and nonfamily laborers receive a wage rate equal to value of the marginal product of labor. If the farmer is a tenant, the payment for land is made to the landlord; otherwise the payment remains with the owner farmer. In either case the rent is equal to the value of marginal product of land.
Lastly, consumers earn rents and wages in either agriculture (farm labor) or in the intermediate goods sector (nonfarm labor); their income can either be saved or used to purchase food. Savings are invested in the intermediate goods sector.
In each period agriculture experiences farm-specific cyclical production shocks that are based on climate and biological conditions. The logarithm of output from farm i in period t has a disturbance term lnθit with the following property.
Assumption 1. , and
, and  for all i,
for all i, ; and
; and 
 where m is the number of farms, ωi is the weight based on size for farm i, and κ is a measure of production shock diversity. We assume κ > 1, thus allowing for diversity in production shocks. If however κ = 1, there is no diversity and hence no opportunity to reduce risk through WIS.
where m is the number of farms, ωi is the weight based on size for farm i, and κ is a measure of production shock diversity. We assume κ > 1, thus allowing for diversity in production shocks. If however κ = 1, there is no diversity and hence no opportunity to reduce risk through WIS.
Here we assume that innovations in the disturbance term are not serially correlated. This assumption will lead

Figure 1. Market structure and production shocks in a rural economy.
to the logarithm of gross regional product (GRP) following a random walk process in equilibrium which coincides with empirical studies of the gross product and other macroeconomic time series [19] .
Since agriculture is the economy’s final good sector, the profits of the intermediate good firms fluctuate according to the weighted average production shock . In addition to this shock, which is transferred from agriculture, each intermediate goods producer is exposed to firm-specific Poisson shocks reflecting such occurrences as natural disasters, wars, outbreaks of pests and epidemics. We posit the assumptionAssumption 2. The probability of each intermediate good hit by a Poisson shock in time interval dt is given by λdt, where λ is time-invariant expected arrival rate (also variance) of Poisson shocks.
. In addition to this shock, which is transferred from agriculture, each intermediate goods producer is exposed to firm-specific Poisson shocks reflecting such occurrences as natural disasters, wars, outbreaks of pests and epidemics. We posit the assumptionAssumption 2. The probability of each intermediate good hit by a Poisson shock in time interval dt is given by λdt, where λ is time-invariant expected arrival rate (also variance) of Poisson shocks.
We provide a continuous time frame for Poisson shock in contrast to a discrete cyclical shock. However, our results are invariant to the discrete time frame for both shocks, so that a shutdown can occur only once per period with probability λ. Poisson shocks not only damage the intermediate goods sector, but also damage the agriculture, since a portion of the intermediate inputs cannot be used in agriculture. We also assume that an intermediate goods firm incurs some recovery cost to resume production following the Poisson shock.
3. Steady State Equilibrium
In this section we derive the market-equilibrium growth rate with WIS. This is followed by a look at the welfare effects of WIS on the rural economy.
3.1. Equilibrium with WIS
Agricultural production for farm i in period t has Cobb-Douglas technology as
 (1)
(1)
where, Dit is output, Xit is a productivity indicator of intermediate inputs, Lit is the quantity of farm labor, Tit is land, A is a constant reflecting the choice of units, and θit is the cyclical production shock in period t defined in Assumption 1. The productivity indicator reflects a variety of horizontally differentiated intermediates
 (2)
(2)
where nt is the number of intermediate varieties, xijt is the quantity of intermediate good j used on farm i, and  is a parameter with which the elasticity of substitution between any two intermediate goods is given by
is a parameter with which the elasticity of substitution between any two intermediate goods is given by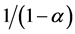 . We assume the availability of a sufficiently large number of intermediates [18] [20] ; thus, the law of large numbers approximates the constant fraction λ of all intermediate inputs not available in steady state. So,
. We assume the availability of a sufficiently large number of intermediates [18] [20] ; thus, the law of large numbers approximates the constant fraction λ of all intermediate inputs not available in steady state. So, 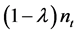 is the number of intermediate varieties available in period t. From Equations (1) and (2) we can show that the demand elasticity for intermediate good j is
is the number of intermediate varieties available in period t. From Equations (1) and (2) we can show that the demand elasticity for intermediate good j is  and the proportion of total agriculture production attributed to the intermediate inputs is
and the proportion of total agriculture production attributed to the intermediate inputs is ;
;  is attributed to farm labor, and
is attributed to farm labor, and  to land
to land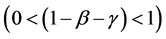 .
.
Now we turn to the profit maximization of intermediate good firms. Intermediate good firms undertake two different activities. First, they engage in local adaptation activities for new varieties of differentiated intermediates invented outside of the region; second, they produce the intermediates. The local adaptation stage cost is an initial cost financed by consumer savings1.
Each firm produces and sells a differentiated intermediate good and enjoys a positive profit by selling its unique variety characterized as an imperfect substitute for other varieties. However, once the Poisson shock causes the operation to shut down, the firm has to spend ζvt to resume production, where  is the damage ratio and vt is the current value of the firm.
is the damage ratio and vt is the current value of the firm.
The production of intermediate goods follows constant returns to scale technology with nonfarm labor as an input. By appropriately choosing units, the input-output coefficient is  where Hjt is the quantity of nonfarm labor input for production of good j. The profit maximization problem for the firm is then
where Hjt is the quantity of nonfarm labor input for production of good j. The profit maximization problem for the firm is then

where wHt is the nonfarm labor wage. The first-order condition is given as
 (3)
(3)
since demand elasticity for the intermediate good j is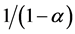 . Then profit for firm j becomes
. Then profit for firm j becomes  . Assuming a symmetric equilibrium (all varieties are equally demanded), profit is
. Assuming a symmetric equilibrium (all varieties are equally demanded), profit is
 (4)
(4)
where, pt and xt are the price and quantity produced for each intermediate good. We now consider the return from investment in an intermediate good firm in the interval dt, the current value of which is vt. Shareholders receive dividends πtdt instantaneously. They also enjoy capital gains of dvt, unless an accident shuts down operations. If an accident occurs during the interval, shareholders incur cost of ζvt to recover the production where ζ is the damage ratio. Probability of an accident is λdt. Thus, we have the following equation:

where rt is the return from investment, and  is
is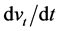 . Ignoring the
. Ignoring the  term, we find that
term, we find that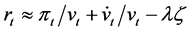 . The investor makes investment decisions at the beginning of period
. The investor makes investment decisions at the beginning of period  given information available at t, so the conditional expectation of return is
given information available at t, so the conditional expectation of return is
 (5)
(5)
In the local adaptation stage the firm can introduce a new intermediate variety by hiring nonfarm laborers. The adaptation velocity function is
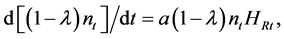 (6)
(6)
where HRt is the number of nonfarm laborers hired for local adaptation stage, and a is a nonfarm labor productivity parameter. The adaptation velocity increases as the number of varieties available in the region  increases. This reflects the positive externalities of local adaptation activities explained previously. The cost of adaptation is
increases. This reflects the positive externalities of local adaptation activities explained previously. The cost of adaptation is . The value of the firm is vt, so that local adaptation activities create
. The value of the firm is vt, so that local adaptation activities create 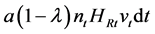 in interval dt. The profit maximization problem for the firm becomes
in interval dt. The profit maximization problem for the firm becomes

Then, market equilibrium with positive economic growth has the condition
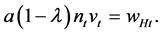 (7)
(7)
Consumers earn wages and rents in the agricultural or intermediate goods sectors, purchase food, and save money which is invested in intermediate good firms. Another source of income is the return from savings (investment). This return can be either consumed or saved. Each period consumers make consumption and savings decisions to maximize utility over an infinite horizon. The optimization problem for consumer i is,
 (8)
(8)
where  is rent
is rent 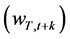 or wage (
or wage (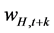 for nonfarm labor and
for nonfarm labor and  for farm labor),
for farm labor), 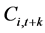 is consumption in period
is consumption in period , and
, and  is wealth at the beginning of period
is wealth at the beginning of period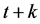 , and
, and  is a common discount factor. The first-order condition is
is a common discount factor. The first-order condition is  in period t. Assuming a constant relative risk aversion (CRRA) utility function so that
in period t. Assuming a constant relative risk aversion (CRRA) utility function so that , the first-order condition becomes
, the first-order condition becomes
 (9)
(9)
where  is the coefficient of relative risk aversion. The next problem is the farmer-consumer selection of the consumption process through WIS. In the steady state equilibrium final good outputs are claimed by each factor in fixed proportions according to the value of their marginal products. Savings, adaptation cost, and income for nonfarm laborers in the adaptation stage are all equalized. This means that the saving rate is a constant, so a fixed portion of individual income is consumed. So, Equations (1) and (2) yield the consumption level process (in logarithms)
is the coefficient of relative risk aversion. The next problem is the farmer-consumer selection of the consumption process through WIS. In the steady state equilibrium final good outputs are claimed by each factor in fixed proportions according to the value of their marginal products. Savings, adaptation cost, and income for nonfarm laborers in the adaptation stage are all equalized. This means that the saving rate is a constant, so a fixed portion of individual income is consumed. So, Equations (1) and (2) yield the consumption level process (in logarithms)
 (10)
(10)
where, g is the expected growth rate of the final good output,  and Si is the volatility indicator
and Si is the volatility indicator . A farmer-consumer can reduce volatility by sharing harvest with other farmers through WIS which is reflected as the value of Si. The present value of expected lifetime utility from the CRRA function is given as,
. A farmer-consumer can reduce volatility by sharing harvest with other farmers through WIS which is reflected as the value of Si. The present value of expected lifetime utility from the CRRA function is given as,

where,  follows the process given by Equation (10). Note that the cardinal value of utility is negative given h > 1. Utility with a higher level of consumption asymptotically approaches zero. Hence, the present value of lifetime utility converges to a finite value. It is easy to show
follows the process given by Equation (10). Note that the cardinal value of utility is negative given h > 1. Utility with a higher level of consumption asymptotically approaches zero. Hence, the present value of lifetime utility converges to a finite value. It is easy to show
 (11)
(11)
We can show that Wi is decreasing in Si. So, the farmer must decrease Si to the minimum level. If farmer i shares harvest with farmer j of the same size, the variance of share for farmer i is 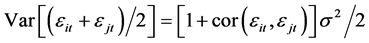 . This expression implies that, except for the perfect correlation case
. This expression implies that, except for the perfect correlation case
 , harvest sharing will strictly lower volatility. Farmers share the harvests until no more is gained from doing so, that is until all farms have perfectly correlated outputs. Therefore, in a rural economy with WIS, all farmers face the identical production shock equal to the weighted average
, harvest sharing will strictly lower volatility. Farmers share the harvests until no more is gained from doing so, that is until all farms have perfectly correlated outputs. Therefore, in a rural economy with WIS, all farmers face the identical production shock equal to the weighted average 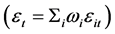 whose variance is
whose variance is  where
where  is degree of diversity in production shocks previously defined.
is degree of diversity in production shocks previously defined.
Therefore, the consumption growth rate and investment returns for all individuals follow the innovation of the weighted average production shock in period t + 1:  and
and . Using this result Equation (9) can be approximated as:
. Using this result Equation (9) can be approximated as: . Using the moment generating function for a normal distribution and taking logs of both sides yields
. Using the moment generating function for a normal distribution and taking logs of both sides yields
 (12)
(12)
Finally, using Equation (6) we can show the factor market clearing condition for nonfarm labor:
 (13)
(13)
where  is the variety adaptation rate
is the variety adaptation rate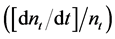 , xt is the quantity of each variety produced in period t, and H is the total number of nonfarm laborers. From Equations (1) to (13)2, we find that the stochastic process of the logarithm of GRP follows a random walk with drift g
, xt is the quantity of each variety produced in period t, and H is the total number of nonfarm laborers. From Equations (1) to (13)2, we find that the stochastic process of the logarithm of GRP follows a random walk with drift g
 (14)
(14)
where  and the drift term g is given by
and the drift term g is given by
 (15)
(15)
The expected growth rate (g) in steady state equilibrium is increasing in nonfarm labor endowment (H) and productivity (a), increasing in the cost share of intermediates in agricultural production (b), increasing in the perceived differentiation of varieties (smaller a), and decreasing in the subjective discount factor (r). Endogenous growth models commonly exhibit these properties [11] . Note that an increase in farm output volatility (σ2) would raise g but an increase in the probability (λ) and damage ratio (ζ) of Poisson shock would lower g. Also from Equation (15), we can derive the necessary and sufficient condition for positive growth,
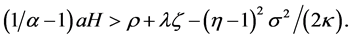
Thus, for the economy to grow it must have sufficient quantities and productivity of nonfarm labor, sufficiently differentiated varieties, a low subjective discount rate, and a low arrival rate and damage ratio of the Poisson shock3. In the following argument we assume the economy has a positive growth rate, so that the above inequality is satisfied.
3.2. Welfare Analysis of WIS
In the previous section we showed that farmers share the harvest until no more gain is realized, so that the all farmers face the perfect correlated production shock of  whose variance is
whose variance is  where
where 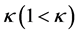 is degree of diversity in production shocks. When WIS is not available, each farm is exposed to the farm-specific production shock (εit) defined in Assumption 1, variance of which is σ2, strictly larger than that with WIS.
is degree of diversity in production shocks. When WIS is not available, each farm is exposed to the farm-specific production shock (εit) defined in Assumption 1, variance of which is σ2, strictly larger than that with WIS.
The community mechanism of risk sharing through WIS, as exemplified by harvest sharing, might also reduce the volatility of investment returns in the intermediate goods sector. Note that a decline in the Poisson arrival rate (λ) or damage ratio (ζ) will raise the expected return from investment in Equation (5). There are at least two paths for risk reduction from the risk sharing principle. First, the principle might facilitate the intermediate good firms to diversify operational sites and, second, provide the flexibility to shift operations in the event of an emergency. These two paths can help avoid a shutdown or decrease damage ratio because production can continue at other sites if one site is shut down.
Welfare improvement through WIS in each sector can be shown using Equations (15) and (11). Substituting g from Equation (15) and  into Equation (11) we find that
into Equation (11) we find that
 (16)
(16)
 (17)
(17)
Because , we have
, we have  Hence, Equation (16) is positive and (17) is negative so that the volatility reduction from either the agriculture (higher κ) or intermediate goods sector (lower λ) is strictly welfare improving in equilibrium. Since market equilibrium is reached when harvest sharing consumes up the diversity of risk in agriculture, Equation (16) implies that additional diversity is necessary to further reduce volatility and improve welfare. The additional diversity of risk (higher κ) could be brought into the system from endogenously growing intermediate varieties such as new seed varieties. Any incremental risk which is only imperfectly correlated with the current aggregate production shock would be converted into volatility reduction through WIS. Therefore, WIS is a mechanism which converts any incremental diversity of risk generated from a new intermediate variety, into volatility reduction, and then into welfare gain.
Hence, Equation (16) is positive and (17) is negative so that the volatility reduction from either the agriculture (higher κ) or intermediate goods sector (lower λ) is strictly welfare improving in equilibrium. Since market equilibrium is reached when harvest sharing consumes up the diversity of risk in agriculture, Equation (16) implies that additional diversity is necessary to further reduce volatility and improve welfare. The additional diversity of risk (higher κ) could be brought into the system from endogenously growing intermediate varieties such as new seed varieties. Any incremental risk which is only imperfectly correlated with the current aggregate production shock would be converted into volatility reduction through WIS. Therefore, WIS is a mechanism which converts any incremental diversity of risk generated from a new intermediate variety, into volatility reduction, and then into welfare gain.
Proposition 1. Work and income sharing (WIS) and the resulting volatility reduction in agriculture or intermediate goods sector are welfare improving. The role of WIS in the endogenous growth model is that it converts any incremental diversity from endogenously growing inputs (e.g., new seed variety) into risk reduction and welfare gain.
Since ∂g/∂λ < 0 from (15) the growth rate is decreasing in the Poisson arrival rate but since ∂g/∂σ2 > 0 it is increasing in cyclical shock volatility. Reduction of Poisson shocks leads to higher expected investment return which contributes positively to economic growth. However, the reduction of the cyclical shock volatility provides consumers (wage and rent earners) with an incentive to reduce their precautionary savings because of greater income stability. This negatively affects economic growth.
Which effect is larger depends on the coefficient of relative risk aversion (h) and on how WIS influences shocks. If the reduction of Poisson shocks is larger than the reduction of the cyclical shocks, WIS tends to lead to a higher growth rate. The less risk averse the consumer the more likely WIS will result in a higher growth rate. The lower the risk aversion (h approaching one) the less motivated the consumer to save for stability and precautionary reasons and therefore, less sensitive to income volatility.
Proposition 2. Work and income sharing (WIS) and resulting volatility reduction in each sector have opposite effects on economic growth. Reduced volatility in the intermediate goods sector has pro-growth effect, but that in the agricultural sector has anti-growth effect. The former effect tends to be higher as consumers become less risk averse4.
Volatility in agriculture is often thought of as a cause of rural farmers’ preference for low-risk and low-returns in agriculture, which depresses economic growth [21] [22] . Our model supports the similar observation that efforts to reduce risk in agriculture (through WIS in our case) results in lower economic growth rate.
4. Regional Government Policy
4.1. Optimal Growth Rate
Here we explore whether the market-equilibrium growth rate shown in Equation (15) is equal to the optimal rate. Since choosing an economic growth rate is equivalent to choosing resource allocation, the social planner’s optimization problem can be expressed as maximizing the present value of lifetime utility given the resource constraint, so that

Suppose that the social planner can measure the present value of expected lifetime utility from the steady state in period t. Using Equation (11), 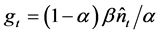 from Equation (10) and
from Equation (10) and , the solution yields the optimal level of growth rate (g*) as
, the solution yields the optimal level of growth rate (g*) as
 (18)
(18)
which is strictly greater than the market-equilibrium growth rate (g) in Equation (15). The difference between the optimal growth rate and the market-equilibrium rate increases as the Poisson arrival rate (l) and damage ratio (ζ) increases. As arrival rate and damage ratio of Poisson shock increase, the expected return from investment decreases and fewer resources are allocated to the local adaptation stage. The difference between the optimal growth rate and the market-equilibrium rate also increases as cyclical shock volatility in agriculture (σ2) increases. An increase in σ2 raises the market-equilibrium growth rate but it also raises the optimal growth rate to a greater extent.
An equally important finding is that the market-equilibrium growth rate is lower than the optimal rate even if the WIS succeeds in virtually eliminating the volatility in the two sectors (l = σ = 0). That is, the practice of WIS alone will approach but will never reach the optimal growth rate. This result is parallel to that from other endogenous growth models with knowledge spillovers effects of R&D and no production shocks [11] [18] . A new finding from our model is that production volatility in either sector will enlarge the difference between optimal and market-equilibrium level of local adaptation and growth rate. Our finding shows that the introduction of production volatilities increases the gap from the optimal level provides an explanation for the prevalent intervention of public institutions in agricultural R&D observed in existing studies [16] .
Proposition 3. The optimal growth rate is higher than the market-equilibrium growth rate. An increase in volatility in either sector would enlarge the difference. WIS alone can approach but will never reach the optimal growth rate.
4.2. Regional Government Policy
Regional governments can realize an efficient allocation of resources and the optimal growth rate through a subsidy on adaptation activity in growth models with positive externalities and no production shocks [10] [11] . Can the regional government achieve the optimal growth rate through the subsidy even in the presence of production shocks? How does the WIS practice by villagers impact policy options?
Suppose the regional government pays a fraction s* of adaptation cost. A subsidy reduces the adaptation cost from 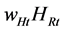 to
to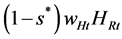 . Then, Equation (7) becomes,
. Then, Equation (7) becomes,
 (7’)
(7’)
Replacing Equation (7) with Equation (7’), we can solve for the subsidy necessary to achieve the optimal growth rate:
 (19)
(19)
where ,
, . Both numerator and denominator are positive, but s* does not have to be less than one. That is, a subsidy alone may or may not realize the optimal rate of growth. More specifically, the subsidy can realize the optimal growth rate, only if production volatility is low enough to satisfy the following condition:
. Both numerator and denominator are positive, but s* does not have to be less than one. That is, a subsidy alone may or may not realize the optimal rate of growth. More specifically, the subsidy can realize the optimal growth rate, only if production volatility is low enough to satisfy the following condition: . Otherwise, volatility must be reduced or diversity in production shocks increased in order to realize the optimal allocation.
. Otherwise, volatility must be reduced or diversity in production shocks increased in order to realize the optimal allocation.
Also note that, s* is always increasing in σ2, and increasing in λ when s* < 1. Thus, WIS reduces the level of subsidy even when the subsidy by itself would lead to the optimal growth rate. The minimum level of subsidy is given by  which is strictly less than one.
which is strictly less than one.
Proposition 4. The optimal growth rate can be realized by a subsidy on the local adaptation activity only if the following condition is satisfied: . Otherwise, production volatility must be reduced or diversity in production shocks increased. The subsidy level is decreased with WIS even when the subsidy alone leads to the optimal growth rate.
. Otherwise, production volatility must be reduced or diversity in production shocks increased. The subsidy level is decreased with WIS even when the subsidy alone leads to the optimal growth rate.
5. Conclusions
Work and income sharing (WIS) is a commonly observed custom in the early stages of economic development. It is typically observed in harvesting and transplanting in rice-producing rural communities in South and Southeast Asia [2] . Previous efforts have been made to explain the rationale of this practice. Takahashi [6] interpreted it as a collective effort to maximize farmers’ share in outputs under a share tenancy contract. Other interpretations include the moral economic view of Scott [7] and the social interactions theory by Haymami and Kikuchi [9] . If we interpret the practice in the context of endogenous growth model we uncover an alternative explanation.
Since market equilibrium is reached when WIS consumes up the diversity of risk in each sector in our model, additional diversity is necessary for further volatility reduction. The additional diversity of risk could be brought into the system from endogenously growing intermediate varieties, including new seeds. Any incremental risk which is only imperfectly correlated with the current aggregate production shock would be converted into volatility reduction through WIS. Further, volatility reduction is converted to welfare improvement. Therefore, WIS is a mechanism which converts any incremental diversity of risk generated from a new intermediate variety into volatility reduction and then into welfare gain.
However, WIS and the resulting volatility reduction in each sector have a different effect on economic growth. In the intermediate goods sector WIS has a pro-growth effect through higher investment returns, but in agriculture it has an anti-growth effect through lower precautionary saving motivation.
Positive externalities from local adaptation activity (typically characterized as knowledge spillovers from intermediate varieties and benefits from local infrastructure improvement) lead to sub-optimal local adaptation levels and growth rates of the rural economy. This is consistent with other growth models with positive externalities [10] [11] . An important finding from our model is that the introduction of production volatilities in either sector enlarges the gap from the optimal adaptation and growth rate and that WIS practices alone will approach but never reach the optimal local adaptation and growth rate. This result provides additional insight as to why agricultural R&D in developing countries has been largely performed by public institutions [12] [16] .
While subsidies on local adaptation typically succeed in achieving the optimal growth rate in positive externality models, they may fail to do so in the presence of production volatilities. However, when combined with WIS, a subsidy can lead to the optimal growth rate, when WIS successfully reduces production volatilities. The subsidy level will be smaller when combined with a practice of WIS than the subsidy level which alone is sufficient to realize the optimal growth rate.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Priyodorshi Banerjee, Don Larson, Ian Sheldon, Takao Yurugi and Charity Moore for their helpful comments. We also thank all seminar participants at University of Florida and Ohio State University, but especially, Robert Emerson, Charlie Chern and Naoya Kaneko for their valuable suggestions.
NOTES
1Our results are invariant as to whether a newly founded firm or an existing firm engages in adaptation.

2All mathematical proofs can be obtained from the authors upon request.

3If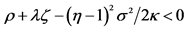 , even a zero endowment of nonfarm labor enables positive growth. Since this is unrealistic we assume that the cyclical volatility is small enough to ensure
, even a zero endowment of nonfarm labor enables positive growth. Since this is unrealistic we assume that the cyclical volatility is small enough to ensure .
.

4This also means the volatility reduction in intermediate goods sector indirectly improves welfare through higher g. That in agriculture directly improves welfare through lower risk while indirectly deteriorates welfare through lower g. However, the direct effect is always greater than the indirect effect.