Keywords
Expectations Hypothesis, Foreign Exchange Markets, Monetary Model, Uncovered Interest Parity Condition

1. Introduction
The exchange rate is an important macroeconomic instrument fundamental to analyze the relationship between macroeconomic variables such as interest rates, changes in money supply, real output, prices, or the balance of payments, across countries. The exchange rate can also be considered as an asset traded in financial markets (see Hansen and Hodrick [1] , Fama [2] , Obstfeld and Rogoff [3] , Backus, Foresi and Telmer [4] or more recently Ang and Chen [5] ). This implies that its price dynamics are determined by future market expectations on macroeconomic fundamentals, and also under no-arbitrage conditions, by the relationship between international asset markets and the effects of perceived risks on these markets by international investors.
This paper studies exchange rate determination as the result of the interaction between financial and macroeconomic variables between open economies. Our model is based on rational expectations and absence of arbitrage opportunities. The model explicitly considers the effect of time-varying terms that measure departures from market efficiency in the foreign exchange market and from the expectations hypothesis in international bond markets. These terms can be interpreted as variables measuring the existence of risk aversion in the foreign exchange market, liquidity preferences reflected in the term structure of domestic and foreign interest rates, and ex-ante profitability opportunities reflected in imbalances between international bond markets with the same maturity. This approach is motivated by portfolio balance theories; portfolio balance theorists argue that risk aversion is the predominant motive in investors’ choice between domestic and foreign currency securities. This implies that assets in different markets are not perfect substitutes since investors require a risk premium for investing on the risky market.
The conclusion of our model is that the exchange rate is mainly forward looking. We observe that the failure of the forward exchange rate in predicting the next period spot exchange rate is due to the presence of imbalances in the risk premium between international bond markets with different maturities. These imbalances are reflected, in equilibrium, in differences between the realized differential in international interest rates and the implicit differential obtained from the international term structure of interest rates.
Our theory on exchange rate determination has an immediate applicability to monetary policy. The effects of unanticipated movements in monetary policy between economies differ depending on the term structure of international interest rates. The imbalances in international bond markets have an impact on monetary policies; in particular we observe that the existence of a premium on the foreign short-term bond higher than that on its domestic counterpart tempers the need of monetary measures by the foreign monetary authority. This is done by providing an alternative tool for boosting real output.
The closest contributions to our paper are Obstfeld and Rogoff [3] , that observe that the nominal exchange rate is an asset, and hence, propose asset pricing models for exchange rate determination based on future market expectations; Engel and West [6] that study the forecasting ability of present value models and link them to macroeconomic fundamentals such as interest rates, money supply, real output or expected inflation; Engel, Mark and West [7] that also present evidence that exchange rates are primarily determined by changes in expectations and show that these series incorporate news about future macroeconomic fundamentals; and finally, Chen and Tsang [8] that discuss an empirical model for exchange rate determination based on macro-finance fundamentals. In their model, the exchange rate is the result of the interactions between the risk premium on international bond markets and the foreign exchange market. These authors capture expectations about future economic conditions and systematic risks in the currency markets by applying the Nelson-Siegel [9] latent factor model extracted from the cross-country yield curve.
The article is structured as follows. Section 2 sets the theoretical framework by introducing the equilibrium conditions in asset markets and analyzes the effect of departures from the expectations hypothesis for determining the exchange rate in equilibrium. Section 3 extends this theory to analyze exchange rate determination as a result of simultaneous equilibrium in the monetary and output markets. The section also explores the effect of macroeconomic policies affecting money supply, interest rates and prices on the determination of the exchange rate. Section 4 concludes.
2. Theoretical Framework
We assume two open economies, domestic and foreign, with a floating exchange rate system between their currencies. Interest rates are determined from the interaction between financial and macroeconomic factors and in particular from the clearing of domestic and foreign zero-rate bond markets. In this model supply and demand forces eliminate instantaneously the existence of arbitrage opportunities in asset markets (international debt markets and foreign exchange market). Investors operating in these markets hold rational expectations with respect to the future performance of assets. There is perfect capital mobility between economies implying an infinite free flow of capital to take advantage of investment opportunities arising in both debt markets. Prices fully reflect available information implying market efficiency but make allowance at the same time for the presence of a risk premium derived from investors’ risk aversion. We assume three periods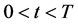 , time 0 corresponds to the current period, time t denotes the future short term and time T the future long term. We identify the long run exchange rate with an exchange rate where both foreign and domestic economies are in equilibrium; no shocks to the system happen at time T.
, time 0 corresponds to the current period, time t denotes the future short term and time T the future long term. We identify the long run exchange rate with an exchange rate where both foreign and domestic economies are in equilibrium; no shocks to the system happen at time T.
The notation is the following. Let 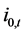 and
and 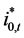 be domestic and foreign interest rates outstanding between period 0 and t, continuously compounded;
be domestic and foreign interest rates outstanding between period 0 and t, continuously compounded;  is the spot nominal exchange rate defined as units of foreign currency per unit of domestic at time t and
is the spot nominal exchange rate defined as units of foreign currency per unit of domestic at time t and  is the corresponding forward price determined at time t. An increase in S means an appreciation of the domestic currency. The expressions in small letters are logs of spot and forward prices. The expression
is the corresponding forward price determined at time t. An increase in S means an appreciation of the domestic currency. The expressions in small letters are logs of spot and forward prices. The expression  denotes the expectation of the log of the spot exchange rate conditional on the information set
denotes the expectation of the log of the spot exchange rate conditional on the information set ; this set contains all the information available at time 0. The tilde symbol denotes differences between variables measured for the foreign and domestic markets, e.g.
; this set contains all the information available at time 0. The tilde symbol denotes differences between variables measured for the foreign and domestic markets, e.g. .
.
2.1. Exchange Rates in Equilibrium
Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market is given in the short run by
 (1)
(1)
and in the long run by
 (2)
(2)
with  and
and  time-varying risk premiums that measure the level of international investors’ risk aversion to the foreign currency compared to the domestic currency at periods 0 and t, respectively. This condition is the so-called risk-adjusted uncovered interest parity condition and accommodates the presence of a time-varying risk premium in efficient markets. The existence of this term is widely documented in the literature on the term structure of interest rates, see Campbell and Shiller [10] , Fama and Bliss [11] , Diebold, Rudebusch and Aruoba [12] or Cochrane and Piazessi [13] , amongst others; or on empirical statistical tests of the unbiasedness of the forward exchange premium, see for example Fama [2] , or discussions in Domowitz and Hakkio [14] , Cumby [15] , Frankel [16] [17] , Frankel and Froot [18] , or more recently Obstfeld and Rogoff [3] or Bekaert, Wei and Xing [19] .
time-varying risk premiums that measure the level of international investors’ risk aversion to the foreign currency compared to the domestic currency at periods 0 and t, respectively. This condition is the so-called risk-adjusted uncovered interest parity condition and accommodates the presence of a time-varying risk premium in efficient markets. The existence of this term is widely documented in the literature on the term structure of interest rates, see Campbell and Shiller [10] , Fama and Bliss [11] , Diebold, Rudebusch and Aruoba [12] or Cochrane and Piazessi [13] , amongst others; or on empirical statistical tests of the unbiasedness of the forward exchange premium, see for example Fama [2] , or discussions in Domowitz and Hakkio [14] , Cumby [15] , Frankel [16] [17] , Frankel and Froot [18] , or more recently Obstfeld and Rogoff [3] or Bekaert, Wei and Xing [19] .
The assumption of no-arbitrage in financial markets implies no-arbitrage in the foreign exchange market. The no-arbitrage condition is
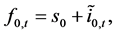 (3)
(3)
with  the forward exchange rate. The no-arbitrage condition corresponding to the international debt market is
the forward exchange rate. The no-arbitrage condition corresponding to the international debt market is
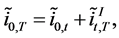 (4)
(4)
with 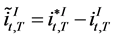 the differential in implicit forward rates obtained from the corresponding foreign and domestic yield curves. This condition is also called international term structure of interest rates. Other related articles studying exchange rate dynamics from no-arbitrage arguments are Hansen and Hodrick [1] , Fama [2] , Backus, Foresi and Telmer [4] or more recently Ang and Chen [5] .
the differential in implicit forward rates obtained from the corresponding foreign and domestic yield curves. This condition is also called international term structure of interest rates. Other related articles studying exchange rate dynamics from no-arbitrage arguments are Hansen and Hodrick [1] , Fama [2] , Backus, Foresi and Telmer [4] or more recently Ang and Chen [5] .
Equilibrium in asset markets is completed by equilibrium on international bond markets. We assume a domestic and a foreign market for bonds; each market trades a short and a long term bond. Investors can freely invest in both markets for both maturities. To assess the relation between interest rates in equilibrium we compute the return between time 0 and t of each investment; for simplicity we consider a face value of one monetary unit for each bond. For the domestic short term bond this is given by  and for the long term bond by
and for the long term bond by , with s and l denoting short and long term investments, respectively. If
, with s and l denoting short and long term investments, respectively. If 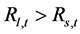 we observe a preference for the short term bond in the domestic market; this can be identified with the existence of a preference for liquidity in the market. In order to make the long term bond attractive the market demands a risk premium. Operating with these expressions and using no-arbitrage arguments we observe that in equilibrium domestic interest rates satisfy that
we observe a preference for the short term bond in the domestic market; this can be identified with the existence of a preference for liquidity in the market. In order to make the long term bond attractive the market demands a risk premium. Operating with these expressions and using no-arbitrage arguments we observe that in equilibrium domestic interest rates satisfy that  with
with . The implicit forward interest rate can be interpreted as the maximum value at which investors are still willing to hold domestic long term bonds compared to domestic short term bonds, that is, it is the value that makes
. The implicit forward interest rate can be interpreted as the maximum value at which investors are still willing to hold domestic long term bonds compared to domestic short term bonds, that is, it is the value that makes . Similarly, if
. Similarly, if  the relation between interest rates is the same as before but with
the relation between interest rates is the same as before but with . The short term bond offers a premium compared to the long term bond. This can be identified with the existence of risk aversion to the short term. The implicit forward interest rate reflects the minimum value at which risk averse investors are still willing to hold short term investments in the domestic bond market compared to investing in the long term domestic bond. For values of
. The short term bond offers a premium compared to the long term bond. This can be identified with the existence of risk aversion to the short term. The implicit forward interest rate reflects the minimum value at which risk averse investors are still willing to hold short term investments in the domestic bond market compared to investing in the long term domestic bond. For values of  different from zero we observe departures of the expectations hypothesis of the term structure of interest rates. Assuming the same equilibrium condition for the foreign bond market we obtain the following expression for the differential in international interest rates in equilibrium;
different from zero we observe departures of the expectations hypothesis of the term structure of interest rates. Assuming the same equilibrium condition for the foreign bond market we obtain the following expression for the differential in international interest rates in equilibrium;
 (5)
(5)
with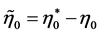 . The sign of this parameter is very important for determining investor sentiment on international bond markets. If
. The sign of this parameter is very important for determining investor sentiment on international bond markets. If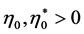 , both domestic and foreign short term bonds offer a higher yield than the corresponding long term bonds. The quantity
, both domestic and foreign short term bonds offer a higher yield than the corresponding long term bonds. The quantity  can be interpreted as an ex-ante expected excess return between short term markets. To show this we calculate the return that an international investor expects at time 0 from investing on the foreign bond market between t and T. At time 0 she expects to invest
can be interpreted as an ex-ante expected excess return between short term markets. To show this we calculate the return that an international investor expects at time 0 from investing on the foreign bond market between t and T. At time 0 she expects to invest  units of domestic currency that will yield a gross expected return of
units of domestic currency that will yield a gross expected return of  in domestic currency. This strategy is expected to be more profitable than investing in the domestic bond market if the previous return is higher than
in domestic currency. This strategy is expected to be more profitable than investing in the domestic bond market if the previous return is higher than  obtained from investing one unit of domestic currency in its own debt market at time t. Taking logs and using suitable approximations, the foreign strategy is more profitable than the domestic one if
obtained from investing one unit of domestic currency in its own debt market at time t. Taking logs and using suitable approximations, the foreign strategy is more profitable than the domestic one if
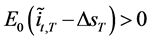 (6)
(6)
with . Now, applying (2) to
. Now, applying (2) to  and
and  and using conditions (4) and (5) we observe that
and using conditions (4) and (5) we observe that
 (7)
(7)
From (5), it follows that the term  is the expected excess return from investing on the foreign bond compared to investing on the domestic bond. Further, taking expectations at time 0 in expression (2), we have
is the expected excess return from investing on the foreign bond compared to investing on the domestic bond. Further, taking expectations at time 0 in expression (2), we have
 (8)
(8)
Expressions (7) and (8) show that under the risk-adjusted uncovered interest parity condition the best predictor of the risk premium on the foreign exchange market is the excess return expected at time t in the international bond market, that is,
 (9)
(9)
Interestingly, we obtain a condition similar in spirit to the uncovered interest parity condition. Investors’ expectations on the exchange rate risk premium  are a consequence of the expected excess return in the international short term bond market. That is, investors expect a movement of the exchange rate risk premium at time t that offsets the expected excess return on the corresponding international bond market.
are a consequence of the expected excess return in the international short term bond market. That is, investors expect a movement of the exchange rate risk premium at time t that offsets the expected excess return on the corresponding international bond market.
Expression (9) also reveals that for 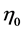 and
and  of equal magnitude the departures of the expectations hypothesis in each market cancel out and the uncovered interest parity condition holds. In this case, the international term structure of interest rates is still an unbiased predictor of the actual interest rate differential and there is no expected excess return to be made a priori by investing in different bond markets. The difference between realized and implicit interest rate differentials is due to the occurrence of unexpected shocks to the financial system, as shown in (5).
of equal magnitude the departures of the expectations hypothesis in each market cancel out and the uncovered interest parity condition holds. In this case, the international term structure of interest rates is still an unbiased predictor of the actual interest rate differential and there is no expected excess return to be made a priori by investing in different bond markets. The difference between realized and implicit interest rate differentials is due to the occurrence of unexpected shocks to the financial system, as shown in (5).
2.2. Exchange Rates under Departures from Equilibrium
To study the exchange rate under departures from asset market equilibrium we analyze the impact of a shock to the financial system on the international bond market. A similar analysis can be carried out by studying the impact of the shock to the foreign exchange market. The shock is defined as
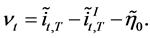 (10)
(10)
This condition together with the no-arbitrage conditions (3) and (4) yield
 (11)
(11)
with  and
and . Operating with this expression we observe the following contributions to the short run exchange rate:
. Operating with this expression we observe the following contributions to the short run exchange rate:
 (12)
(12)
This expression shows that the exchange rate is, as recent literature has highlighted, forward looking. This literature refers to models in which the exchange rate is primarily determined by changes on market expectations, see Engel, Mark and West [7] . These authors view the exchange rate as an asset price, and therefore, make use of asset pricing models to determine the exchange rate. In these models, see Obstfeld and Rogoff [3] , Engel and West [6] or more recently Chen and Tsang [8] , the exchange rate is driven by a present discounted sum of expected future fundamentals. In our model, the exchange rate depends on the forward price, but more importantly, it depends on the difference between realized and implicit interest rate differentials. This spread incorporates the effect of different risk premium terms corresponding to the short and long term in the domestic and foreign bond markets, and the occurrence of shocks to these markets. These factors can produce a change in market expectations on the equilibrium exchange rate and on the foreign exchange market risk premium.
Expression (12) also rationalizes the existence of carry trade strategies. These strategies are given by short positions in the low interest rate country used to invest in the high interest rate country with the expectation of observing an appreciation in the latter currency. For the sake of exposition, assume that the high interest rate country is foreign, assume also that , and rewrite (12) as
, and rewrite (12) as
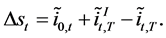 (13)
(13)
This formula predicts the profitability of these strategies when the shock to the international bond market produces an unanticipated increase in the realized interest rate differential large enough to offset the implicit interest rate differential at time t and the initial difference of interest rates at time 0. Otherwise, the foreign currency (high interest rate) will depreciate.
The next section analyzes the implications of accounting for the difference between international interest rates differentials in the determination of the exchange rate and real output using monetary models.
3. A Macroeconomic Approach
The above model for exchange rate determination is based on no-arbitrage conditions and market efficiency. The key factors to determine the exchange rate are unexpected changes in interest rate differentials, the underlying risk premium and potential changes on market expectations on the long run exchange rate. This section studies the determination of the exchange rate from simultaneous equilibrium in the monetary and real output markets. The main difference with previous formulations on exchange rate determination is the expression for the short run exchange rate. In our study expression (12) replaces previous models considering the uncovered interest parity condition as one of the building blocks for determining the exchange rate. In this way our model naturally considers the effect of macroeconomic policies producing departures from equilibrium in the determination of the exchange rate.
The above model also has implications for the determination of interest rates. The main theories entertained in the literature are the monetary approach and the Taylor rule. Central banks usually follow Taylor rules to set nominal interest rates. In our model, international interest rates are determined from equilibrium in international zero-rate bond markets. Although both rates are related it is well known that the base rate set by central banks is a lower bound of the corresponding market rate obtained from bond prices. Moreover, the former rate does not correspond to the return on a tradable asset and does not incorporate a risk premium.
To describe the monetary market, and as in Engel and West [6] , we follow the models of Frenkel [20] , Mussa [21] and Bilson [22] , and the versions considering sticky prices introduced by Dornbusch [23] . Both approaches assume that the real demand for money, the log of which is linear in the log of real income and interest rates, can be expressed as
 (14)
(14)
where ,
,  and
and  denote the logs of the nominal quantity of money, the price level, and real income outstanding between time t and T;
denote the logs of the nominal quantity of money, the price level, and real income outstanding between time t and T;  and
and 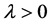 are tuning parameters of the model. The equilibrium in the money market is defined by the condition that states that real money demand equals real money supply. Similarly, equilibrium in output markets is obtained when aggregate output demand is matched by the aggregate real output supplied by both countries. Aggregate output demand is a positive function of disposable income in each country, investment and expenditure by each government. The real exchange rate also has a fundamental role in determining the economy that produces aggregate output. Thus, a depreciation of the real exchange rate implies, in general, an increase in real output by the foreign country. In what follows, we use y to denote both real output demand and supply and assume each output market is in equilibrium. Thus in equilibrium, the monetary model predicts at time 0 that
are tuning parameters of the model. The equilibrium in the money market is defined by the condition that states that real money demand equals real money supply. Similarly, equilibrium in output markets is obtained when aggregate output demand is matched by the aggregate real output supplied by both countries. Aggregate output demand is a positive function of disposable income in each country, investment and expenditure by each government. The real exchange rate also has a fundamental role in determining the economy that produces aggregate output. Thus, a depreciation of the real exchange rate implies, in general, an increase in real output by the foreign country. In what follows, we use y to denote both real output demand and supply and assume each output market is in equilibrium. Thus in equilibrium, the monetary model predicts at time 0 that
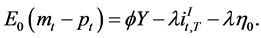 (15)
(15)
The term gauging departures from the expectations hypothesis in the domestic market, 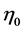 , is a factor to consider by monetary authorities along with the dynamics of prices when designing their monetary offer. For example, if
, is a factor to consider by monetary authorities along with the dynamics of prices when designing their monetary offer. For example, if 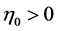 the premium for investing on the domestic short term bond between 0 and t has an effect on the expected money offer. For the foreign monetary market we obtain a similar expression; for simplicity, we assume that
the premium for investing on the domestic short term bond between 0 and t has an effect on the expected money offer. For the foreign monetary market we obtain a similar expression; for simplicity, we assume that  and
and 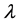 take the same values across countries. Hence, the equilibrium expression between the domestic and foreign monetary markets is
take the same values across countries. Hence, the equilibrium expression between the domestic and foreign monetary markets is
 (16)
(16)
with 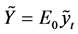 defined as the differential in real output targets.
defined as the differential in real output targets.
In an open economy, monetary policy cannot be taken independently of other countries’ monetary interventions. The previous equation shows that these policies need to account for investors expectations on the long run exchange rate and for the existence of ex-ante profitability opportunities in international bond markets. Expression (16) suggests that for 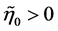 the foreign monetary authority can boost output without the need of large increases in their money stock. For example, for
the foreign monetary authority can boost output without the need of large increases in their money stock. For example, for , the equilibrium condition is
, the equilibrium condition is . In equilibrium, investment opportunities on the foreign short term bond market between t and T attract capital and help to increase real output. A similar argument follows when
. In equilibrium, investment opportunities on the foreign short term bond market between t and T attract capital and help to increase real output. A similar argument follows when ; in this case investment opportunities are in the short term domestic market implying a flow of funds to this economy. The foreign monetary authority needs to react by imposing more aggressive monetary measures. The previous expression also highlights the importance of the risk premium on foreign exchange markets for boosting relative real output between domestic and foreign economies. Thus, under no changes in market expectations on the long run exchange rate, and using (9), we observe that
; in this case investment opportunities are in the short term domestic market implying a flow of funds to this economy. The foreign monetary authority needs to react by imposing more aggressive monetary measures. The previous expression also highlights the importance of the risk premium on foreign exchange markets for boosting relative real output between domestic and foreign economies. Thus, under no changes in market expectations on the long run exchange rate, and using (9), we observe that
 (17)
(17)
The findings of the previous section on the importance of the difference between implicit and realized interest rate differentials have interesting implications for monetary policy. To show this we now consider the exchange rate under departures from equilibrium due to the occurrence of monetary shocks (money expansions/contractions) to the open economy1.
A monetary shock is defined as the difference between the existing real money demand at time t and its conditional expectation. Using the previous expressions, and replacing in (10), we have
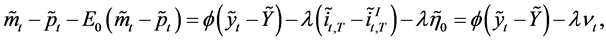 (18)
(18)
that relates monetary shocks to those in output markets and in international bond markets. Now, replacing in (12) we obtain the following decomposition of :
:
 (19)
(19)
with  and
and .
.
The exchange rate can be decomposed into three factors. First, a financial factor given by the forward exchange rate, changes in the risk premium and in market expectations on the long run exchange rate. Second, a real factor given by the unexpected increase in real income differentials between economies, and third, a monetary factor that measures cross-country differences in the shocks to real money supply. This model not only describes the exchange rate in equilibrium but also provides the expression for the exchange rate after changes in monetary and real factors. For example, after relative monetary expansions by the foreign monetary authority and presence of risk aversion given by , the existence of an expected excess return to be made on the foreign short term bond market produces a lower depreciation of the foreign currency than for markets satisfying that
, the existence of an expected excess return to be made on the foreign short term bond market produces a lower depreciation of the foreign currency than for markets satisfying that .
.
4. Conclusions
The exchange rate, modeled as the result of interactions between international asset markets, is forward looking. Our theoretical analysis of the short-run exchange rate highlights the importance of the difference between realized interest rate differentials in international bond markets and the differential predicted by the term structure of interest rates for each economy for determining the exchange rate in equilibrium. This difference is due to the existence of shocks to the international financial system, but more importantly, to imbalances in risk premia between international bond markets. These imbalances have an effect on the spot exchange rate and on the risk premium on the foreign exchange market. These findings also stress the challenges inherent to the choice of the forward exchange rate as an accurate forecast of the spot exchange rate and shed further light on the reasons for the empirical failure of standard regression equations for testing the validity of the uncovered interest parity condition.
Our theory on exchange rate determination has an immediate applicability to monetary policy. The effects of unanticipated movements in monetary policy between economies differ depending on the relation between the term structure of domestic and foreign interest rates and the underlying risk premia in those markets. We observe that the imbalances in international bond markets have an impact on monetary policies. Our model also supports the view that the existence of a premium in the foreign short-term bond higher than that in its domestic counterpart tempers the need of monetary measures by the foreign monetary authority. The risk premium can be interpreted as an alternative tool for boosting real output.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.

1Fiscal shocks or shocks to output markets are more difficult to analyze with our theory on exchange rate determination. It is not clear, for example, that an increase in disposable income by foreign implies a boost of foreign real income. This will also depend on the real exchange rate that determines the relative attractiveness between domestic and foreign products. For these reasons we will not study the effect of shocks to output markets on the exchange rate and assume that both domestic and foreign markets are in equilibrium.