Reinvestigating the Effect of Money on Output for Taiwan with Additional Robustness ()
1. Introduction
Many economists have applied Granger causality tests to investigate causal relationships among variables since 1969. Thornton and Batten [1] and Kang [2] indicate that the empirical results of the Granger causality are very sensitive to the lag-length chosen criteria in empirical models. To remove the arbitrariness, Hsiao [3] advocates the use of the Akaike’s final prediction error criterion to determine the lag-length applied in many empirical studies. Furthermore, Ozcicek and McMillin [4] summarize the Akaike’s Information Criterion to dominate for the symmetric lag models.
In addition, Keating [5] and Hatemi-J [6] expand the lag-chosen concerns in their empirical study, and the modified AIC designed by Keating [5] is the best for both symmetric and asymmetric lag models in his empirical work. Recently, Hacker and Hatemi-J [7] combine the two lag-chosen criteria to create the Hatemi-J criterion, and he applies a Monte Carlo simulation to investigate the performance of stable and unstable VAR models by employing HJC in choosing the optimal lag order in his study.
We apply VAR models to examine the dynamic relationship between money and output with more robustness concerns. Since different criteria chosen for the optimal lag-length for VAR models might derivate from different results, whether six dissimilar lag-chosen criteria applied in the Granger causality tests will result in similar results is one of the main concerns in this paper. Additionally, while the empirical results are similar by applying different but qualified lag-length chosen criteria, we would regard them as empirical results with the concern of robustness. However, the empirical results might be doubtful, since the empirical results are far from singular when applying several but qualified lag-length chosen criteria.
In this study, the above concerns might induce several worthwhile topics for further research, and there are several question marks shown as follows. What are the important criteria to judge a good model? Should different cases apply different criteria to judge a good model? What are the most important criteria for the lag-length chosen criteria applied in Granger causality tests? Is it certain whether all different sample periods will show the same results? Are there any structure changes which exist during data period?
The empirical results which employed real data might be disturbed by uncertain events, so we use simulated data to reduce the disturbance of empirical studies which resulted from the real data. Therefore, we apply both real data and simulated data to examine whether empirical results will be different by employing different lagchosen criteria for symmetric models and asymmetric models1.
In summary, we design the following robustness concerns for this study as shown below. First, whether our empirical results are sensitive to different lag-length selection criteria, such as AIC2, BIC3, FPE4, SBC5, SIC6 and HJC7? Second, whether the empirical results with concerning asymmetric lag-length would be different from those with concerning symmetric lag-length by using different lag-length chosen criteria? Third, whether the empirical results which used real data will be different from those which used simulated data. Fourth, whether the empirical results tested by short-term data will be different from those tested by long-term data. After concerning the above robustness issue for the empirical study, our empirical results demonstrate that money will still affect output, so policymakers in Taiwan should implement monetary policies with care.
This paper proceeds as follows. Section 1 introduces why we reinvestigate the effect of money on output for Taiwan with more robustness concerns. Section 2 surveys the relevant literature. Section 3 reports the empirical results of this study. Section 4 remarks the conclusion.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Different Lag-Length Criteria
Thornton and Batten [1] and Kang [2] indicate that the empirical results of the Granger causality might be sensitive to the lag-length chosen in empirical models, and we also find several studies which mentioned about lag-length criteria issues in the relevant literature.
Hsiao [8] proposes the FPE criteria, which adopts a stepwise procedure based on Granger’s concept of causality. This criterion is suggested as a practical means to identify the order of lags for each variable in a multivariate autoregressive model. This model seems useful because it could serve as a reduced form formulation to avoid imposing spurious restrictions on the model.
Similarly, the study of Thornton and Batten [1] suggests that based on a standard, classical and hypothesistesting norm, the FPE criterion performs well in selecting lag-length for a model, but the FPE criterion may not conform to all researchers’ prior beliefs about the appropriate trade-offs between bias and efficiency. Unlike Thornton and Batten’s findings [1] , the evidence of Jones [9] reveals that one of the ad hoc methods for laglength determination is found to perform somewhat better than the statistical search methods in correctly assessing the causal relationships between money policy and inflation. These ad hoc methods are non-statistical in nature and include arbitrary lag specifications and rule-of-thumb lag-lengths.
However, the lag terms selected by the FPE criterion are inadequate for the purpose of testing the Granger causality as suggested by Kang [10] . In the Kang’s research, he reveals that the lag terms are selected optimally in the most efficient forecast equations obtained from both univariate variable analysis and transfer function analysis in order to test for the causality between the industrial production and the leading indicator of US data by his new procedure. In addition, he shows that the ARIMA analysis is better than using a pure AR process in the FPE criterion to achieve optimal models. Furthermore, Hall [11] finds considerable gains in the power of ADF tests from estimating p rather than fixing it at some relatively large number (i.e., he concludes that estimating the appropriate lag terms for the ADF tests will obtain power for the tests).
Gredenhoff and Karlsson [12] use simulated data to investigate how sensitive the lag-length estimation procedures are to the true model structure. They show that the commonly used procedure based on equal lag-length together with AIC and HQC8 performs well in most cases. In addition, Ozcicek and McMillin [4] are also concerned about lag-length selection by a Monte Carlo simulation approach, and the results imply that the AIC dominates for the symmetric lag models (i.e. the AIC is more frequently used for selecting the lag-length for a model than the other criteria).
While surveying relevant literature, the traditional information criteria like the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) proposed by Rissanen [13] shows that the autocorrelation of the process might be characterized by large negative components. In addition, the Shibata [14] criterion (SIC) is also employed in this study, since SIC converges to BIC as selecting lower orders for moderate MA parameters while the sample size increases. As for the AR coefficients, the SIC selects a higher order for small samples, but converge to the BIC as the sample size increases. Thus, both criteria are concerned as lag-chosen criteria in this paper.
Hacker and Hatemi-J [7] show that Schwarz’s Bayesian Criterion (SBC) performs well in choosing the optimal lag order, but there are some situations where the SBC might have a relatively high possibility to pick the right lag with a higher lag order, and then outperform the SBC will be not as good as other lag-chosen criteria. Therefore, Hatemi-J [6] applies a Monte Carlo simulation experiment to investigate the performance of the HJC for choosing the optimal lag order in stable and unstable VAR models, and finds the performance of HJC is quite efficient in both models.
From the above literature, the chosen lag-length seems to be quite important in relevant empirical research, since it will influence the results of empirical studies. Thus, we investigate whether empirical results will be different among the six different lag-length criteria while choosing between the different lag-length according to these different criteria. Additionally, we also investigate whether the empirical results will be different if we employ different time zones to test the effect of money on output, and it will be a worthwhile topic to reinvestigate this issue, since money seems to play an important role in the area of financial economics.
2.2. The Relationship between Money and Output
Recently, Cheung and Fujii [15] examine the implications of conditional heteroskedasticity for testing the effect of money on output, and they find that the presence of ARCH effects could be attributed to uncertainties in monetary policy and output. In addition, their results highlight the possibility of the presence of conditional heteroskedasticity shown in their models. Hafer and Kutan [16] investigate the empirical relationships among money, interest rates, and output across several industrialized and developing countries. The results suggest that money often plays a significant role in explaining the fluctuations of real output. Across the different countries examined, money accounts for more of the variance in real output than normal interest rates in about half of these countries. Moreover, Moroney [17] develops a long-run approach to examine the quantity of money growth, real GDP growth, and inflation. The results show that money growth and GDP growth are nearly orthogonal, consistent with long-run monetary super neutrality. In Das’ [18] paper, he tries to explore the short-run relationships among money, price and output, exploits the characteristics of these variables by Vector Autoregressive and Moving Average models (VARMA models), and shows money has a significant effect on output in his empirical study. Berger and Osterholm [19] investigate whether money growth Granger-causes output growth in the United States. They find that the Granger-causal role of money appears to have vanished completely after the “great moderation”. Caraiani [20] examines the relationship between money and output using quarterly data from the US economy. He finds evidence of a weaker relationship within the Great Moderation as well as a stronger relationship during the Great Recession. Gefang [21] explores money-output causality within the context of a logistic smooth transition vector error correction model, and obtain strong support for nonlinear Granger causality from money to output. Haug and Dewald [22] study how fluctuations in money growth correlate with fluctuations in real output growth and inflation. They find that money growth does not lead or affect real output growth in the longer run.
All cited papers propose that money has a causal effect on output. However, we doubt if relationships can still go on by concerning different lag-length selection criteria used in VAR models. In this paper, the relationships between money and output are retested with more robustness concerns. In addition, we list six different criteria proposed by several scholars as shown in the relevant literature, but few papers cover these different lag-chosen criteria in their empirical studies. So, we wonder that their empirical findings might be based on special lag-chosen criteria. Thus, if all different criteria will produce similar empirical results, the empirical results will be more reliable by taking more robustness concerns into account.
2.3. Monetary Policy Transmission Mechanisms and Business Cycles
Some central banks in the world might adopt stable monetary policies such as the constant growth rate of money per month or per year; the money volatilities might not be high under such a circumstance. If the low money volatilities would not cause the fluctuation of output, it seems better to adopt stable monetary policies. On the contrary, adjusted money policies might be appropriate if the economy of a country should be stabilized by monetary policy instruments. Since money-output issues seem to be related to monetary policy, transmission mechanisms, and business cycles, we then address more literature for the above issues.
As for the monetary policy, Isik and Acar [23] investigate the relationship between openness and the effectiveness of monetary policy on output by using annual data for the period of 1990-2000 for a panel of 42 countries. Their empirical results support the theoretical expectations that the more open the economy, the smaller the output effects of a given change in the money supply. Mojon [24] provides evidence about how US monetary policy contributes to the drop in the volatilities of US output fluctuations and to the decoupling of household investment from the business cycle. The results show that changes in the size of monetary policy shocks will affect both the correlation between output components and their volatility. Luporini [25] presents evidence on the channel of the monetary policy for the Brazilian economy of the 1990s. He analyzes the effects of an unexpected change in the baseline interest rate on output in a VAR system, and his empirical results show that a tightening in the monetary policy affects economic activity immediately, reducing the rate of growth of real GDP.
As for the transmission mechanisms, Boivin and Giannoni [26] determine whether the reduction in output and inflation variability has been associated with a change in the transmission of monetary policy, and conclude that the reduced effect of monetary policy shocks is mainly due to a more effective systematic behavior of monetary policy. Ireland [27] proposes that the monetary transmission mechanism describes how policy actions taken by the central bank induce changes in the short-term nominal interest rate or the nominal money stock in order to influence macroeconomic activity, since the central bank controls the monetary base, and is able to increase or decrease the money supply through open market operations, like buying or selling government bonds. ChihHsiang et al. [28] study the effects of money supply on real output and inflation in China between 1993 and 2008. The result reveals that real GDP growth in China responds to negative money supply shocks but not positive money supply shocks. Serletis and Rahman [29] investigate the effects of money growth uncertainty on real economic activity, and find evidence that money growth volatility has significant negative effects on output growth.
Concerning business cycles issues, Basistha [30] proposes that stabilization of business cycles is one of the primary goals of monetary policy. The US economy did not experience any recessions or significant inflationary regimes in 1992-2000. One of the potential explanations for this phenomenon is a better monetary policy adopted by the US government. However, Pedersen and Elmer [31] study the connection between the business cycle and economic growth by comparing dates of the business cycle turning point, and find that there might be a connection between the business cycle and economic growth.
Furthermore, Gawin and Kydland [32] find changes in the money supply have effects on the cyclical nature of nominal variables. Booth and Booth [33] also find that the presidential cycle has explanatory power beyond business conditions. Korenok and Radchenko [34] analyze the effect of a monetary policy shock on the business cycle and the extent to which a shift in a monetary policy affects the dynamics of the business cycle. The results reveal that monetary policy shocks have a small but significant impact on persistent and transitory parts of the cycle. From the above literature studies, we find that relevant research about monetary policy instruments, transmission mechanisms and business cycles are mentioned in previous studies.
In this paper, we also apply symmetric and asymmetric lags for the VAR and SUR models in order to distinguish if there exists any differences between the VAR and SUR models. Furthermore, we find that few articles employed by both real data and simulated data in empirical studies. In addition, some scholars like Fung and Kasumovich [35] study the effects of monetary shocks in VAR models for the G6 countries by using the real data. Others like Ozcicek and Mc Millin [4] use simulated data generated by Monte Carlo approach to study the performance of alternative lag-length chosen criteria for symmetric lag and asymmetric lag VAR models. Thus, our empirical study compare the empirical results for both symmetric lag models and asymmetric lag models with concerning different lag-length criteria by employing both actual data and simulated data.
Finally, we summarize what we are doing in this paper as follows: First of all, our empirical study concerns different lag-length selection criteria such as AIC, BIC, FPE, SBC, SIC and HJC. Second, we examine whether concerning asymmetric lag-length are different from concerning symmetric lag-length by employing the six mentioned lag-length chosen criteria. Third, the empirical results which employed simulated data are different from those that employed real data. Fourth, whether the empirical results employed short-term data are different from those employed long-term data.
3. Empirical Results
We obtain the monthly data of money (M2) and industrial production (IP) for Taiwan in the AREMOS database established by the Taiwan Economic Data Center for the period from January 1988 to December 2004. The M2 and industrial production are regarded as money variables and output variables respectively. The entire data period from January 1988 to December 2004 are tested. Meanwhile, two short-term data periods, January 1992 to December 2004 and January 1996 to December 2004, are tested in order to examine if different data periods will result in diverse empirical results.
3.1. Data and Unit Root Tests
Since several variables and lag-length selection criteria are mentioned many times in this paper, we, therefore assign abbreviations for these variables and criteria terms as shown below (Table 1 & Table 2).
Table 2 displays the statistics for M2, IP, MG and GIP, including the means, standard deviations, minimums, and maximums for the M2, IP, MG and GIP. In Table 1, the means for the MG and GIP are 0.0088 and 0.007, and the standard deviations for the MG and GIP are 0.0094 and 0.0933 respectively.
We employ stationary tests to avoid the spurious results before the time series models are set up. Thus, we use unit roots test which test the stationary for the M2 and IP. In Table 3, the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) and the Augmented Phillips-Perron (APP) values for the level of the M2 and IP are not significant at the 5% level. Thus, differencing series are necessary, and we find the DF, ADF, PP, and APP tests for the log differencing M2 (MG) and log differencing IP (GIP) are all significant, implying that these series are stationary. Additionally, the meanings of log differencing variables for money and output have their economic meaning, since these two variables could be regarded as monetary policy and economic growth variables. Finally, we don’t find cointegration relationships between M2 and IP as shown in the cointegration tests9.
3.2. Granger Causality Results10
Because the presentation of the contents of empirical results for this paper are quite complicated, we therefore put all of the required information together in Table 4 to help readers understand the findings.
In addition, the meaning of equation one and equation two as shown as follows:
Equation One11: GIP = f (MGt−a, GIPt−b)H1: F value which a and b indicate the lag lengths chosen for the money variable and output variable12 for the GIP equation, and H1 is the hypothesis for the MG Granger-cause GIP. If the F value is significant, it means that the MG Granger-cause GIP.
Table 1. Abbreviations defined for criterion and variables.
Table 2. Statistics of M2, IP, MG and GIP.
Table 3. Unit root tests for M2 and IP.
| Panel A: Data Period (I): 1988.1-2004.12 |
| |
Variable |
Trend |
ADF(t) |
DF(t) |
APP(t) |
PP(t) |
| Level |
M2 |
No |
0.46 |
0.52 |
0.54 |
0.52 |
| Yes |
−2.01 |
|
−2.56 |
|
| IP |
No |
−0.34 |
−3.47 |
−2.42 |
−3.49 |
| Yes |
−2.53 |
|
−9.04* |
|
| Log Difference |
M2 |
No |
−5.60* |
−11.72* |
−11.92* |
−11.77* |
| Yes |
−8.22* |
|
−13.55* |
|
| IP |
No |
−8.87* |
−23.08* |
−30.84* |
−23.20* |
| Yes |
−8.85* |
|
−30.84* |
|
| Panel B: Data Period (II): 1992.1-2004.12 |
| |
Variable |
Trend |
ADF(t) |
DF(t) |
APP(t) |
PP(t) |
| Level |
M2 |
No |
−1.21 |
−0.70 |
−0.72 |
−0.70 |
| Yes |
−2.15 |
|
−2.40 |
|
| IP |
No |
−0.36 |
−3.79* |
−3.02 |
−3.79* |
| Yes |
−2.03 |
|
−7.53* |
|
| Log Difference |
M2 |
No |
−5.23* |
−10.23* |
−10.23* |
−10.23* |
| Yes |
−7.79* |
|
−26.23* |
|
| IP |
No |
−7.14* |
−20.55* |
−11.25* |
−20.55* |
| Yes |
−7.77* |
|
−26.11* |
|
| Panel C: Data Period (III): 1996.1-2004.12 |
| |
Variable |
Trend |
ADF(t) |
DF(t) |
APP(t) |
PP(t) |
| Level |
M2 |
No |
−0.41 |
−0.23 |
−0.22 |
−0.23 |
| Yes |
−2.00 |
|
−2.46 |
|
| IP |
No |
−0.47 |
−3.17 |
−2.48 |
−3.17 |
| Yes |
−2.13 |
|
−7.47* |
|
| Log Difference |
M2 |
No |
−5.70* |
−8.39* |
−8.23* |
−8.39* |
| Yes |
−5.86* |
|
−23.38* |
|
| IP |
No |
−6.63* |
−17.53* |
−8.23* |
−17.53* |
| Yes |
−6.60* |
|
−23.28* |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1) DF(t) means the value of Dickey-Fuller test, ADF(t) means the value of Augment Dickey-Fuller test, PP(t) means the value of Phillips-Perron test, and APP(t) means the value of Augmented Phillips-Perron test; 2) The lag-length of ADF and that of APP are chosen by the AIC criteria; 3) Star (*) means significant at 5% level.
Equation Two13: MG = f (MGt−c, GIPt−d)H2: F value in which c and d mean the lag lengths chosen for the money variable and output variable for the MG equation, and H2 is the hypothesis of whether the GIP Granger-cause MG. If the F value is significant, then it implies that the GIP Granger-cause MG.
3.2.1. Symmetric and Asymmetric Models by Employing Real Data
The symmetric lag models indicate the same lags chosen for each variable in each equation of the symmetric lag models, but the asymmetric lag models depict different lags chosen for each variable in each equation of the asymmetric lag models.
In this section, we employ the real data series for investigating the relationship between money and output. As shown in the table below, we put all of the information in Table 4 instead of putting information in several tables.
In the symmetric VAR models, the F values shown in Grange causality tests selected by the AIC and the SBC lag-length chosen criteria are significant in the both data periods from Jan. 1988 to Dec. 2004 and from Jan. 1992 to Dec. 2004, which means that there exists significant feedback effects between MG and GIP. In addition, in the data period from Jan. 1996 to Dec. 2004, the F values shown in the Grange causality tests selected by the AIC and the SBC lag-length chosen criteria are also significant in the first Granger causality tests, which show unidirectional significant effects from MG to GIP.
While separating the 2 by 2 VAR models into two OLS equations, each OLS equation could select the different lag-length for money and output by employing these lag-length chosen criteria. Similar to symmetric models, the feedback effects also exist between MG and GIP by using AIC, FPE, SBC and SIC lag-chosen criteria. It means that money affects output and output affects money in both data periods from Jan. 1988 to Dec. 2004 and from Jan. 1992 to Dec. 2004.
In the data period Jan. 1996 to Dec. 2004, the feedback effects exist between MG and GIP by using the AIC, FPE, SBC, SIC and HJC criteria, which also means that money affects output and output affects money.
3.2.2. Symmetric and Asymmetric Models by Employing Simulated Data
In this section, we simulate the money series by Monte Carlo methods14 and compare whether the simulated data will differ from the real data by employing three time zones data.
In the first Granger causality tests, the F tests are significant by employing AIC and SBC criteria in the data period (II). It indicates that money affects output and that the output affects money. However, it also reveals that money affects output only in the data period (III) (Table 5).
Similar to the symmetric models, the feedback effects also exist between MG and GIP by applying the AIC, SBC, SIC and HJC criteria (i.e. this means that MG affects GIP and GIP affects MG).

Table 4. Granger causality for symmetric and asymmetric models for real data.
1) Star (*) means significant at 5% level; 2) The criteria for BIC, SIC, and FPE are selected by equation by equation. The symmetric lag models will select the same lag length for each variable in each equation. Therefore, the empty spaces are due to the above reason.

Table 5. Granger causality for symmetric and asymmetric models for simulated data.
1) Star (*) means significant at 5% level; 2) The criteria for BIC, SIC, and FPE are selected by equation by equation. The symmetric lag models will select the same lag length for each variable in each equation. Therefore, the empty spaces are due to the above reason.
3.3. Comparison of the Real Data15 and Simulated Data
Based on the above empirical results, we try to compare the difference between the real data and the simulated data16. We then find that the empirical results are similar in employing either the real data or the simulated data, which are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6 shows the empirical results for symmetric models and asymmetric models by employing real data and simulated data in three time zones. The empirical results for asymmetric models show that feedback effects exist between money and output by applying six different lag-length chosen criteria, which seem to prove the monetary-business-cycle theory17 and the real-business-cycle theory18 in our empirical study. However, the results of the symmetric models are somewhat different from those of the asymmetric models by employing the simulated data. The results reveal unidirectional effects from money to output in the data period from Jan. 1996 to Dec. 2004. In addition, the empirical results show no significant relationship between money and output in the data period from Jan. 1988 to Dec. 2004 by applying the simulated data.
Since it doesn’t reveal some structure change for the data period, it implies that symmetric models which employed simulated data are not appropriate, i.e. asymmetric models would be more appropriate than symmetric models in this study.
4. Conclusions
This paper employs M2 and IP data from January 1988 to December 2004, and three time zones, January 1988

Table 6. The summary of evidence for all sample periods.
1)  money growth and output growth have feedback effects; 2)
money growth and output growth have feedback effects; 2)  money growth has unidirectional influence on output growth.
money growth has unidirectional influence on output growth.
to December 2004, January 1992 to December 2004 and January 1996 to December 2004, are investigated. The simulated data and real data are tested respectively in symmetric models and the asymmetric models by six different lag-chosen criteria are used to investigate whether the money will still affect the output.
In the empirical study, even though both symmetric models and asymmetric models employ six different laglength selection criteria, the empirical results still reveal that feedback effects exist between money and output by applying different lag-length chosen criteria. Therefore, these empirical results prove that the monetarybusiness-cycle theory and the real-business-cycle theory exist.
However, the results show somewhat different outcomes between the real data and the simulated data in symmetric models for the data period from Jan. 1988 to Dec. 2004, since the feedback effects exist between the money and output by using the real data, and no relationship exists between the money and output by using the simulated data. It might infer that the symmetric models employed simulated data that might not be appropriate, since the real data might be more reliable than the simulated data.
In addition, this paper has the following concerns which are different from the relevant literature. First, one of the concerns is that the Granger causality results are sensitive if the lag-length chosen criteria for testing Granger causality by employing different lag-length chosen criteria, such as AIC, BIC, FPE, SBC, SIC, and HJC are applied. Second, whether the empirical results used by asymmetric lag length models are different from those used by symmetric lag length models is examined. Third, whether the empirical results applied by simulated data might vary with those applied by real data is also covered in this study. Fourth, whether empirical results applied with the short-term data are different from those applied with the long-term data is also examined. Although the empirical results show little difference for the symmetric model in the data period from Jan. 1988 to Dec. 2004, most of empirical results show that money and output may have significant feedback effects. It implies that the policymakers need to cautiously stabilize monetary policies to avoid economic fluctuation in Taiwan.
Since empirical studies might be based on special models and special criteria, the empirical study might be necessary to have more robustness concerns in order to make the reader trustworthy. In this paper, we obtain more robustness results from Taiwan’s evidence, and hope that these robustness concerns can be achieved in other countries for future study. These concerns, when applying different lag-length chosen criteria, for the symmetric models and asymmetric models, by real data and stimulated data, investigated the empirical results by data from different time zones. These findings are important concerns for further empirical study.
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for giving precious suggestions.
NOTES
1One model chooses the same lag-length for different variables, and the other chooses the different lag length for different variables.
2AIC (Akaike’s Information Criterion), proposed by Akaike in 1973 and 1974 .

where T is number of usable observations  is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
3BIC (Bayesian Information Criterion), proposed by Rissanen in 1978.

where T is the number of usable observations,  is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
4FPE (Final Prediction Error) criterion, proposed by Akaike in 1969 and 1970 .

where T is the sample size, n is the lag-length being tested, SSR is the sum of squared residuals, and N denotes the maximum lag-length over which the search is carried out.
5SBC (Schwarz’s Bayesian Criterion), proposed by Schwarz in 1978 .

where T is the number of usable observations,  is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
6SIC (Shibata Criterion), proposed by Shibata in 1981.

where T is the number of usable observations,  is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
7HJC, proposed by Hacker and Hatemi-J in 2008.

where T is the sample size,  is the maximum likelihood estimate of the variance-covariance matrix Ω when the lag order used in estimation is j, and n is number of variables.
is the maximum likelihood estimate of the variance-covariance matrix Ω when the lag order used in estimation is j, and n is number of variables.

8Hannan-Quinn Criterion (1978) : 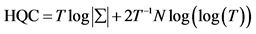
where T is the number of usable observations,  is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.
is the determinant of the variance/covariance matrix of the residuals and N is the total number of parameters estimated in all equations.

9ADF of residual series are not significant due to insignificant statistics, p = 0.12, which is greater than 0.05.
10Actually, the policy will have lag effects as mentioned in Money and Banking, such as fiscal policy lags and monetary policy lags. Thus, the lead-lag relationships are important concerns in this paper. In addition, the contemporary issue may dwell on in this paper by the nonlinear or multivariate specification. However, we choose six lag chosen criteria, symmetric and asymmetric chosen lags in our models due to policy lag concerns. Thus, the issues of contemporary effects might not be the main concerns in this paper. Additionally, the statistics of contemporary effects are insignificant after running the econometrics models.
11If a = 3, and b = 2 in equation one, then the regression could be shown as below:
GIPt = β0 + β1MGt−1 + β2MGt−2 + β3MGt−3 + β4GIPt−1 + β5GIPt−2 + εt
12We apply both the original data and the seasonally adjusted data, and the empirical results are similar.

13If c = 2, and d = 3 in equation two, then the regression could be shown as below:
MGt = γ0 + γ1MGt−1 + γ2MGt−2 + γ3GIPt−1 + γ4GIPt−2 + γ5GIPt−3 + εt

14We conduct the simulation process by the Monte Carlo method and describe the process as follows. First, we use the behavior of historical data for the simulation base. Second, we apply the Monte Carlo method to simulate the data used in this paper. Finally, we use the simulated data to make further inferences, such as the estimation of the VAR model.

15As shown in the Chow tests and figures in the context of this paper. There is a marginal significant structural break between the period from January 1996 to December 2004 and the period from January 1988 to December 1995 for the level of data, i.e. M2 and IP. Actually, the concerns of this paper are the growth of money (monetary policy) and the growth of output (economic growth), and the Chow tests are insignificant. Therefore, while we run the empirical results by extending the short period data (8 years) to long period data (16 years) for robustness, the empirical results are almost the same.
16The sub-sample could be chosen by threshold methods, and we find the break cut-off point for time series data. Since the empirical results are similar to what we found in Table 4 and Table 5, we just mentioned them here in order to save space.
17Monetary-business-cycle theory: explains that changes in the growth of the money supply causes changes in output growth (i.e., money causes output).
18Real-business-cycle theory: assign a causal role to real economic activity in affecting money supply (i.e., changes in output growth cause changes in growth of the money).