1. Introduction
The problem statement has its focus on achieving an intelligent, predictive and responsive traffic model by improving the response time between road side infrastructure and routed vehicles on a least cost approach. The approach of balancing the network without prioritizing any set of vehicles frees the responsibility of roadside units to any specific vehicles, and instead, the units along with traffic lights in another version of the fully balanced algorithm significantly improve the network fairly for all road users so as to effectively achieve effectiveness in routing and re-routing in a timely manner. These improvements have a direct bearing on travel time for all road users on average. As a result, fuel consumption improves and green-house emissions reduce. An intelligent routing algorithm or set of algorithms are required to assist drivers so that the selfish nature of driving is mitigated with methodologies that result in benefits for all road users. Methods that benefit all road users would result in both drivers and passengers achieving travel satisfaction and reducing their frustrations. When a shortest route is known between an origin and a destination or a relative origin and destination (i.e. common points in the travel metrics that traffic moving to similar zones or passing through similar zones must transverse), all drivers would gravitate to that route causing the paradox scenario to become true. Traffic will load into this common perceived shortest path and would cause congestion referred to as the price of Anarchy. This situation is known as the Braess Paradox named after a German physicist, Braess who explored the paradox in 1968. From that time, it has been a well-known phenomenon that when drivers have knowledge of a shortest path, they will all elect that path and would increase the cost of travel. For example, when the 42nd street was closed in New York City, instead of the predicted gridlock traffic, flow improved because the road network became more balanced as opposed to the perceived shorter low weight link, which sooner than later became a high cost link due to the increase in traffic which works counter to the belief that traffic flow ought to improve due to its shortness. The Scientific American article [1] [2] highlights a recent example from Seoul, South Korea, in which the inverse/ converse occurred, that is, the removal of a road made users better off.
The proposed algorithms are aiming to increase the expectations of optimized consistent travel times that provide the following: 1) consistent travel times; 2) reducing passengers and drivers frustrations; 3) multiple shortest routes with time travel being as important as distance travelled; 4) re-routing dynamically on the shortest paths when traffic is re-assessed while travelling is taking place; 5) reduced Carbon Dioxide, Carbon Monoxide and Hydrocarbons; 6) reduced unnecessary re-routing.
2. Related Works
2.1. INRIX
A leading provider of highly accurate traffic services and real time traffic information base developed temporal accuracy for drivers to collect estimated travel times for multiple routes from which the drivers can reassess the routes and their requirements in order to elect the suitable routes.
The danger with this is that the drivers could all elect a common most attractive route to them thereby creating a Braess paradox. Partners for the INRIX project include Ford, TOMTOM, and Mapquest et al. [3] . [4] also discusses self-learning artificial intelligence approaches that learn the pattern of traffic to become predictive. Transportation databases as discussed in [5] can help to be online road side infrastructure to tap in, in organizing traffic and routing information to on-board devices on vehicles.
Waze [6] is a social GPS application for drivers to share traffic information, which recently helped to reduce the highly publicized Los Angeles’ so called Carmageddon when the world’s busiest road was closed for repairs on July 15th 2011. Garmins POI Loaders determine whether a file contains speed and proximately alert points based on Specific criteria [7] . POI refers to relative Points Out and Points in (POI), typically traffic lights will exhibit in out points, which is a separate cost from over sensitive routing algorithms, intelligently re-organizing and reconfiguration of the network under consideration.
2.2. Related Approaches to Resolve the Shortest Path Methods
There has been a shift in scientific circles to focus on the shortest travel time rather than the geographical shortest route as discussed by [8] in the examination of time based vectors for consistent travel time compared to distance based vectors. Discussions by [9] reveal approaches involving Genetic algorithms to project which route would yield the best travel time between a known origin or input origin “O” and a known destination “D” at a time “t”. [10] Also applies Genetic Algorithms with a discussion on parameters that include travel time along with distribution, journey distance and speed. Related to the discussion in [9] and [10] is another focusing on travel times using a Genetic algorithm method in [11] known as “random key”, which runs a form of random algorithm to route vehicles. The cost of Genetic Algorithms and the infancy in the research do not make them attainable in many environments. There is also an element of computational overheads about them. Reinforcement learning systems discussed by [12] do a lot to reduce computational overheads by applying a “minimal data” approach, yet allowing some learning and interpretation of the minimum relevant data for dynamic decision making. “Minimal data usage is also discussed and justified by [13] . [14] attempted an approach to reduce computational overheads but their efforts are not holistic as their proposed manipulation based on priority requires some increase in data being handled because vehicles have to poll priority weights hence an increase in data. Their efforts elsewhere to reduce computational overheads in EBkSP compared to RKSP are subdued as a result. The contributors in [14] build on the idea of multiple best routes (k paths) adapted from [15] . They describe three strategies for load balancing and routing. These strategies are 1) Dynamic Shortest Path (DSP); 2) Random balancing considering future Vehicle (RKSP); and 3) Entropy Balanced shortest Path (EBkSP) which balances the network at a relatively least cost.
The section below describes each the three strategies:
2.2.1. Dynamic Short Paths (DSP)
Dynamic shortest path is viewed as a traditional re-routing strategy that elects the shortest path for vehicles. It is the simpler one of the three and it computational cost is the lowest of them and can be described as O(E + Vlog(V)), where E is the number of road segments and V is the number of intersections it has been found not to be suited to switching high volumes of traffic load. Seems to work efficiently in manageable, highly predictable loads but fails when this threshold of predictability is surpassed as it is then viewed as simply being able to shift congestion from one segment to another that did not have it before so that there is no net benefit in such circumstances. Also the risk of a Braess Paradox situation we explained becomes increasingly high with this strategy.
2.2.2. Random K Shortest Paths (RKSP)
For each vehicle that is to be re-routed, a number of shortest paths (K) are computed i.e. K-shortest paths. The system assigns each selected vehicle to a selected path (one of the K paths) randomly. The objective is to overcome the limitation in the DSP which would switch congestion to another zone. Route balancing is achieved well by this strategy because congestion transfer is avoided. Naturally a higher price to pay for the computational complexity with the cost formulae being adjusted to O(KV(E + VLog(V))) [15] in “a procedure for computing the k shortest paths”, which increases linearly with K. With multiple K paths, concern is often on the variations on travel times between a similar origin O and a particular destination D increasing significantly. Improve versions of the Random K shortest paths have extra computation to ensure that the difference between the shortest travel time on a path Ks and the longest travel time on the model Ki is kept to a value of at most 20% difference.
2.2.3. Entropy Balanced K Shortest Paths (EBKSP)
This method is perceived the better of the three because in addition to possessing the advantages that “Random K Shorter Paths” has over the Dynamic shortest path, it overcomes the computational costs which random K shortest paths has so that information on re-routing etc. Information is pushed to vehicles long before congestion builds but computational time increase the latency involved in communicating.
2.3. Induction Loops (E1) and Detectors (E3)
In SUMO, an E1 is an Induction loop which gives feedback on lane, position on lane, aggregation time and on which vehicle to route. An E3 is a detector that measures congestion by calculating the amount of vehicles on halt, the speed, mean halt times, queue length, and the mean duration of halts within detectors. The E3 is a multi-entry, multi-exit detector [16] Using E1and E3 Induction loops (viii) Intelligent Traffic Lights again with built in E1 and E3 algorithms will assist in making the network intelligent and responsive and to become self-organizing depending on the suitability of the junction as too much of one technology can increase latency and reroute traffic unnecessarily which would be counter to the objective of this project.
3. System Model
The system builds on optimizing consistent travel times with a smart knowledge base for learning travel patterns and then balancing the load. The intelligence for this is built in the E1 and E3 Induction loops and detectors respectively. E3 detectors are built at intersection points and on the track of highways. Arguably, the logic is centralized at the induction loops or road side units’ traffic lights but communicating with drivers on board equipment. Key components are duarouter, a tool that computes shortest paths, dynamic user assignment, and optimal path routing as alternatives or extensions to simple shortest path used to re-route traffic based on calibrated parametres. Other tools include net converter, a tool for producing the map or network on which the simulation is to be evaluated and Traffic Control Intelligence (TraCI) built in traffic lights supporting roadside infrastructure and the rest of SUMO tools (Actually all this in the SUMO environment).
Whereas the “original” origin to destination is known to make the system more dynamic relative new origins are to be computed as the knowledge base learns of the new conditions and updates its current position as its new origin and re-computes the new route based on current conditions. Our models will not focus on distinguishing cars as “urgent” as in Entropy balanced K shortest paths (EBKSP) as this would cause a computational overhead. Whereas EBKSP is praised for reducing Computational overhead over Random K shortest paths (RKSP) by not moving congestion to another section, by pushing re-routing before vehicles pass the intersection and assigning an urgency weighted value on cars, so that most affected vehicles are given prioritized opportunity, it introduces its own additional constraint or extra requirement of ranking vehicles on a priority scale and using this as a paradigm for re-routing. This approach of prioritizing benefits some drivers at the expense of others. We propose a mutual benefit algorithm which spreads the benefits easily so that the earliest arrival time benefits the driver that started the earliest if their origin and destination were to be the same, and the network remained balanced with the remainder of the algorithms assigning edges (routes) to traffic.
The simulation is implemented using the modified example runner.py Python script (@version $Id: runner.py 14247 2013-07-01 11:56:51Z namdre $) originally, as demonstrated in the tutorial for traffic light control via the TraCI interface. We have modified generate_routefile() and run() functions.
4. Avoiding Unjustified Re-Routing
Re-routing would be better achieved if the start and the end of congestion are understood linearly so that false congestions do not cause unnecessary re-routing. We will define false congestion as corresponding to a “chain gun” of vehicles for about 1/2 km or even 1KM on say a 5 km link or any realistic threshold that may be set. In this example, it would imply that 4km of the stretch is free of congestion. If loops or road side units were located say less than 500 meters apart say 200 m into the “chain gun” and 700 m into the chain gun respectively, the induction loop would indicate a false alarm which would invoke re-routing. Equally 1 Kms length of slow vehicles probably due to a slow vehicle in front may result in false re-routing information being passed. Therefore alternative distributed and integrated feedback is required to produce realistic global view alerts which would be less costly and smarter. Without smarter approaches, the net effect would bring about introducing delay where there was little or none of it. So, careful design with rational distances is required in order to realize full benefits. Feedback as stated by [17] and [18] must be beneficial to transport intelligent planning. Contributors in [19] and [20] point out to improved traffic flows as solutions to congestion by involving route guidance agents.
Our model will take care of this by ensuring that congestion is declared only when it is longer than 10% of a link being considered. Only when the queue of jammed vehicles is longer than 10% of the linear distance being considered here referred to as the segment. In the scenario we have given above that should be more than 100 meter in a kilometer stretch for each it to be considered congestion, for 10km links 1km of the link having cars following each other on a bumper will warrant a congestion being delayed. Normally roads network are treated as directed, weighted graphs where roads would correspond to intersections, edges to roads segments and weights to estimated travel times. These are the normal parameters on which load balancing is attempted on a road network.
Greenfields model (14) states that the relationship between estimated road speed Vi and traffic density Ki is linear and Ki is the vehicle per meter on a road segment i, and Kjam and Vf are the traffic jam density and free flaw speed respectively on a road segment i and Ti and Li are the estimated travel times and length for the segment:
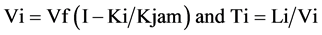
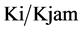 is the ratio between current-number-of-vehicles and the max-number-of-vehicles.
is the ratio between current-number-of-vehicles and the max-number-of-vehicles.
5. Problem Formulation
The Challenge with the Entropy method discussed [14] has potential feedback overheads because when deriving Priority in ranking the vehicle the controlling roadside detectors incur overheads as all vehicles poll their data to this centralized system which must then assign priority values. In the Fully Balanced-Candidate Path algorithm (FBMkP) which we propose over EBkSP, we overcome the identified computational overhead in a different way from the way [12] and [13] approach it by balancing the network fairly for all vehicles without assigning priorities to certain vehicles as this may advantage those vehicles with higher priorities at the expense of others and equally having to store priority values communicated by every vehicle means keeping too much vehicle data. In our FBMkP, the road side units only read the Destination information as vehicles pass them and the E1s and E3s work together in a responsive fashion which evolves dynamically. The network as a whole is designed to fairly route vehicles across the network. The System also take care of unnecessary and costly re-routing.
Algorithm ideas (flow chart): Fully Balanced Multipath-candidate shortest Paths (FBMkP) algorithm (Pseudo Code).
Procedure main queuelength := obtainRoadSideUnitQueueLengths() congestedRoads := detectCongestion(queuelength) vehiclesDestinedCongestedRoad:=selectCongestionDestinedVehicles(congestedRoads) trips=updateTrips(vehiclesDestinedCongestedRoad) newTrips=findkShortestPaths(trips,vehiclesDestinedCongestedRoad) reroute(newTrips,vehiclesDestinedCongestedRoad) End Procedure procedure reroute for all vehicle in vehicleDestinedCongestedRoad do {origin,destination}=getVehicleOD(vehicle) update_paths=computeKPaths(newPaths,origin,destination) reroute(vehicle,update_path) end for end procedure In our simulation the Origin being in Kalombo Rd and Destination Kabulonga Rd in Lusaka, Zambia as represented by the trip file (
) in terms of Origin and Destination (O-D).
Duo-router, a SUMO tool, computes the k shortest paths between the origin and the destination.
(duarouter―trip-files trips.xml―net-file lusaka.net.xml―output-file result.rou.xml).
6. Model
In our model, we simulate 3 scenarios and compare the results;
1) Using the shortest path―Traffic flows from O-D using the shortest path. No rerouting is applied in this case.
2) Using congestion detection mechanism―Traffic flows from O-D but partial re-routing occurs but is restricted in terms being done once. The shortest path gets congested at some points, traffic is rerouted to the next possible/alternative shortest path 3) Using intelligence built in traffic lights on scenario 2 such that the Induction loop for feedback known as E3s continually perform re-routing for every congestion hence giving us a fully balanced re-routing algorithm. Traffic flows are rerouted and TLS is controlled by allowing the route which is more likely to have less traffic to have priority.
In the first Scenario, it’s assumed that drivers will always choose to use the shortest path and in this case, the shortest path is O-D via Great East road computed by duarouter as shown in the appendix map to this document. Congestion will build up because every driver will default to the route which they think is the shortest. We run the Simulation for 3000 steps. Results obtain as below Example of the Traffic Control loops at Makishi road and Great East road junctions in Lusaka showing roadside infrastructure and vehicles.
E1 and E3 detectors have been used to detect flows on the network. In our Simulation, E3 detectors, will measure congestion by calculating the amount of vehicles on halt. A threshold is set that assumes congestion being true. If congestion is greater than threshold, congestion is set to true and rerouting is triggered by using E1 detectors to determine which vehicles to reroute. In this way congestion is controlled by rerouting traffic to alternative routes as in partially Balanced and Fully Balanced models. Better CO and CO2 outputs are presented by the Fully Balanced re-routing method as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 respectively. In the Fully Balanced Re-routing method, we have set up more iterations and re-Routing intelligence and this method shows more gain in fuel efficiency as shown in Figure 3. Partial re-routing shows partial improvements indicating every degree of multiple shortest paths has improvements over a single shortest path method through the network. To ensure that traffic is balanced over the network, all points where traffic is likely to build up such as near traffic lights and junctions, have detectors placed there to measure congestion and in this way, traffic is rerouted to the alternative shortest path as computed by Duarouter. Feedback onto the traffic lights is provided by both the E1 and E3 systems to make the traffic lights more responsive in a network relay with the loops and detectors here seen as Road side Infrastructure. This results in an FBMkP algorithm integrated with traffic light control Intelligence (TraCI) to create TLC or simply Traffic Light Intelligence.
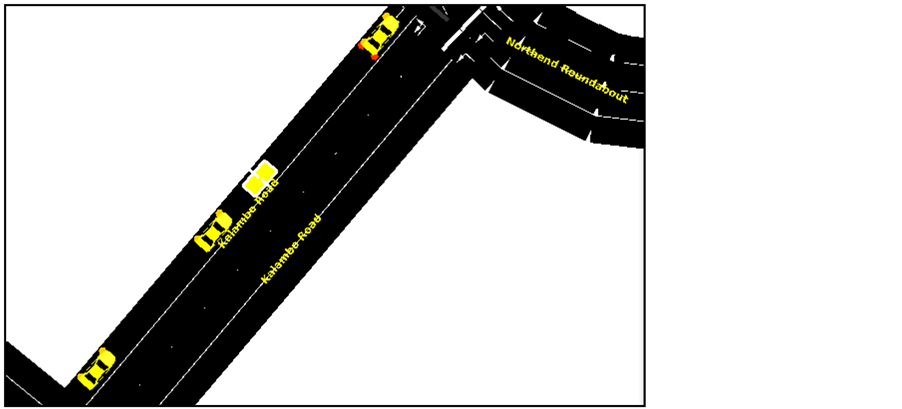
Figure 1. Showing vehicles in the simulation.
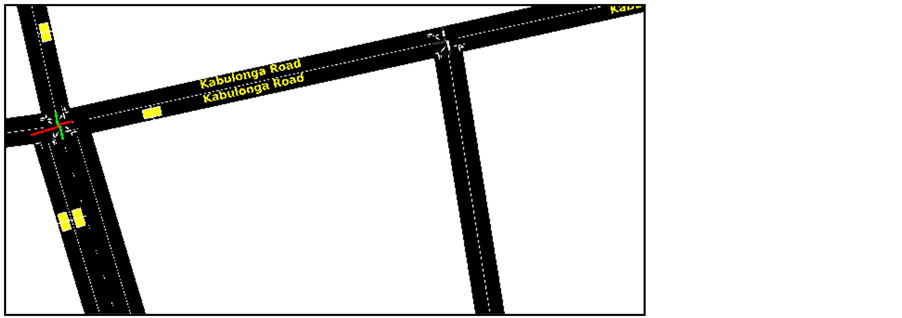
Figure 2. Showing roadside intelligence at an intersection.
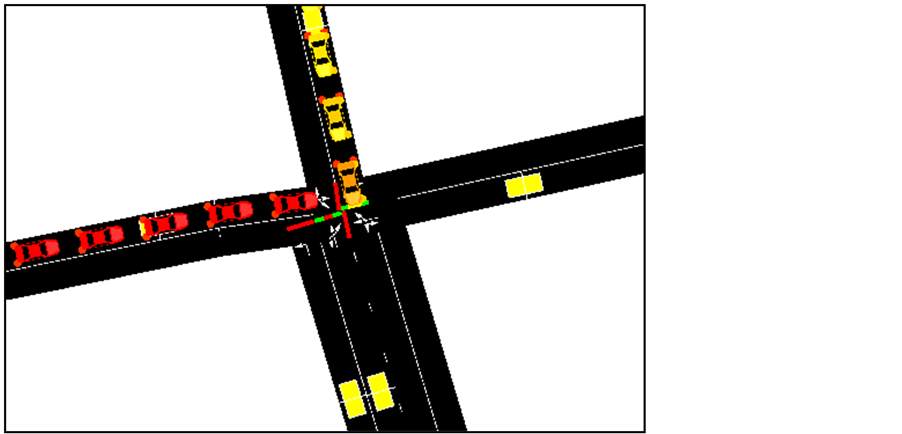
Figure 3. Showing vehicles, roadside units and traffic intelligence as interactive objects.
7. Discussions on the Figures Below
In all of the graphs in this paper used, the order of the bars is blue, red, green and purple (this colour, purple is included only where the experiments have included the modified fully balanced algorithm integrated with traffic light control feedback TLC), This is also the order in which the bars are arranged from left to right in Figure 1 to Figure 7 with the exception of Figure 8 where the graph lines vary with time and Figure 9 where they are discussed from bottom to top in the same order. In Figure 5 to Figure 10, an extra examination of an attempt to balance the networks by centring the load balance using traffic light control approach is shown in purple at the very end of the first three strategies is indicated. Included is an additional strategy, the traffic light control (TLC) strategy with balanced re-routing in it and this is shown in purple Bars. What we have been able to demonstrate is motivated by many research groups and requirements in [21] for example, which is a clear testimony of how eager governments are in mitigating green-house effects and costs resulting from longer travel times and fuel costs, health and safety issues, which are directly proportional to vehicular network volumes and average vehicle time spent on the networks. The philosophy detailed in the handbook on emissions factors in road transport [22] , sets out an agenda on the need to quantify emissions on urban transport for better planning for healthy cities. This paper translates its findings along that paradigm as shown in some the figures below relating to emissions.
Some figures also show what we are calling the “Traffic Light Control FBMkP or simply TLC”, which is a variation of the Fully Balanced Multiple-Candidates shortest Paths incorporating Traffic Control Intelligence

Figure 4. Effect of intelligent re-routing on CO2 emissions.

Figure 5. Effect of intelligent re-routing on Carbon Monoxide emissions.

Figure 6. Effect of intelligent re-routing on fuel consumption.
Figure 7. Effect of intelligent re-routing on HCs.
(TraCI). TLC is part of our work in progress on achieving a distributed control system between road side infrastructure and traffic light intelligence on improving traffic lights and as such TLC is a proposed component of FBMkP our main algorithm. Our graphs do show that main FBMkP and TLC are yielding best results on a number of measures such as these below.
Figure 8. Showing vehicle state in the simulation period.
Figure 9. Showing that fully balanced re-routing has the least travel time.
1) Figure 1 shows us the point on Kalambo road where the simulation begins or where the vehicles are generated from, The SUMO id for this point is “166752211#6”.
2) Figure 2 simply shows a typical intersection on Kabulonga road in Lusaka with the road side units for intelligent support.
3) Figure 3 shows vehicles at a traffic light intersection. The lighter coloured vehicles are ready to go as their side is currently on “green”. The darker or red cars are in that colour to indicate the state of antsy as they wait for the signal to go.
4) Figure 4 shows us a comparison of results for CO2 emissions for the routing strategies namely FBMkP (FBR), shortest path only (SP) and Partial Re-routing (PR). The shortest path emits the highest CO2 and the FBMkP, the least proving that a balanced multiple routing strategy is best for reducing CO1, CO2, CO and HC are Hand Book of Emissions Factors (HBEFAs) attributes 5) Figure 5 is a Prototype of the Figure 4 experiments but in it, is carbon monoxide is evaluated against four strategies that now include a variant of FBMkP known as Traffic Light-control system FBMkP (TLC). TLC performs best in reducing CO. TLC is fully balanced but with extra intelligence on traffic lights to vary the length of “green” or “red” signs on the basis of vehicle queue length.
6) Figure 6 has the same four routing strategies as in 5. The focus is on emitted hydro carbons per mg. FBMkP and FBMkP-TLS (TLS) perform the best. http://www.tdm-beijing.org/files/news/Emission%20Quantification%20Workshop/Schmied_INFRAS_-_Development_of_Emission_Factors_in_Europe.pdf
7) Figure 7 is discussed in the context of emitted, running and completed vehicles on the road. What we see is that given a sizeable sample of distance, more FBMkP and TLC vehicles completed in a predetermined time. This is an indication of higher predictability on the part of the balanced approaches FBMkP and FBMkP-TLS (TLS) over the others8) Figure 8 shows us the total travel times between the origin and destination in the experiments. TLS and FBMkP (FBR) obtain the least travel time. As TLS performs slightly better than FBMkP, the factor of traffic light intelligence is also assessed in this way.
9) Figure 9 gives us yet another indication of how the fully balanced algorithms FBMkP and TLC result in the least time on the network between origin and destination. The focus is much on getting the least time and not the least kilometres travelled between the same origin and destination.
10) Figure 10 discusses queuing times and queuing lengths for each of the four strategies as collected from the simulation.
11) Figure S1 in the appendix shows a section of Lusaka, Zambia which is the city used for our simulations in this paper with the shortest path shown in red between the origin and the destination.
The ultimate solution is what we have coined as the “Fully balanced multiple shortest paths” (FBMkP) for short. The FBMkP, unlike the entropy balanced method that assigns priority values to cars, will be fully balanced for all cars giving them an equal opportunity instead of assigning urgency on specific vehicles as this would increase computational overheads. In FBMkP, we have built the intelligence in the induction loops E3s and E1s. Since routes are fewer than cars, the computational overhead is lower when the responsibility is held by road side infrastructure. Instead of all the cars polling their urgency or weighted indices, each car only polls its destination once and loops relay its next edge after every intersection.
8. Conclusions
From what has been observed and recorded in the experiments, there is a relationship between travel time and emissions. The higher the latency, the greater the carbon footprint. As this is in a multi-valued objective set up, Pareto optimization reveals that a balance between speed and carbon footprint has to be obtained and that speed and time should also be in a balance as too much of any of the two has the potential to increase the carbon footprint for example, where vehicles are in a gridlock shortest path or a state of the braess paradox, more carbon will be emitted and time of travel will be higher, equally high speeds indicate more carbon per kilometre travelled than moderate speeds. The efficiency of the FBMkP algorithm and TLC (a variant of FBMkP) is set up over two main issues namely its simplicity in balancing for all road users rather than for prioritizing some, hence it does not transfer overheads to other segments and secondly in its integration of feedback between vehicles and road side units at several intersections. The systems should also have the intelligence to check the weight of the routes that we are selecting, so that the results are dynamic per time of day and this would mean a certain selection set would not always yield the better results over other paths for the same O-D matrix. See details detailing some results achieved so far. Further assessment of factors in a multi-valued environment using Pareto optimisation and will be investigated using Lusaka, London and New York to build a research result that could be useful to London transport and other stakeholders. The slight increase in fuel consumption in FBMkP-TLC as shown in Figure 6 can be attributed to increased speeds in free flow due to the proper balance of TLC which may see an increase in speed due to increased space per vehicle in the network.
Appendix
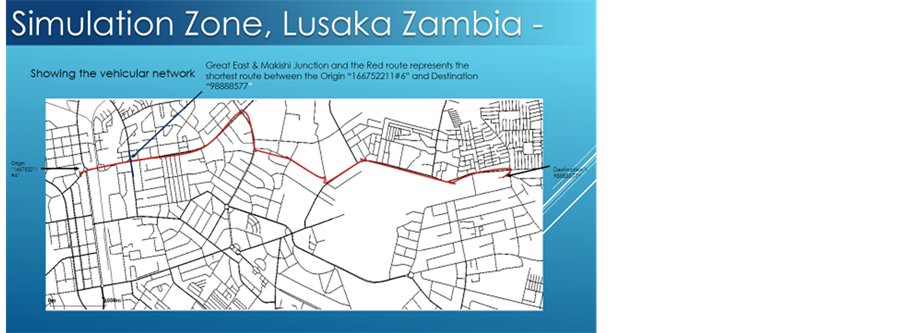
Figure S1. A section of Lusaka, Zambia which is the city used for our simulations in this paper with the shortest path shown in red between the origin and the destination.