A Study of Lateralized Cognitive Processes in Upper-Division Electrical Engineering Students’: Correlating Written Language Functions with Analytical Reasoning in Microelectronics ()
1. Introduction
Cognition is a partial foundation upon which psychomotor skills are manifested [1] -[4] . Cognition may either drive or suppress pending actions [3] . In doing so, cognition enables us to produce adaptable and complex movements referred to as psychomotor skills [5] .
One such psychomotor skill is writing. This current study however is not focused on the physiological mechanisms of how the brain and cognition produce or control writing; the focus is on the effects of cognition on writing as it relates to high-level problem-solving. Specifically, the study concentrates on identifying a relation between upper-division electrical engineering and computer engineering (EE/CpE) juniors’ analytical reasoning abilities and their descriptive writing ability. Descriptive writing is taken here to mean a students’ ability to identify key physical aspects of a mathematical model and to express—in words—a concise and well-balanced description that demonstrates a deep conceptual understanding of the devices, circuitry, and the mathematics that describe the operation of these devices. The initial question is: “is there an observable (clinical) relationship between these students’ adeptness in writing descriptions of microelectronic device and circuit phenomena and their analytical reasoning (problem solving) skills?” The latter is associated with the cognitive domain [6] ; the former is a psychomotor response [7] (the motor execution of articulation).
2. Conceptual Framework
Many cognitive models reported in the literature tend to define writing in terms of problem-solving [8] [9] . In this context, it follows that writing arises from an individual’s attempt to map language from their thoughts (cognitive domain) onto paper via the formation of written words (a psychomotor process). Summarizing this from a neurocognitive perspective, the former is primarily a phenomenon of the frontal lobes and the latter a phenomenon of the parietal and temporal lobes [4] (Figure 1).
Although these neuro-phenomena are controlled by different parts of the brain, education researchers often lump these into cognitive attributes that can be observed as behaviors, for instance, the classification of behaviors that make up Bloom’s taxonomy, which is also referred to as Bloom’s cognitive domain [10] .
Bloom’s cognitive domain informs us that there are six classifications of learning objectives or levels. Using written language to express one’s knowledge (Level 1); comprehension (Level 2); application (Level 3); analysis (Level 4); synthesis (Level 5); and evaluation of ideas or information (Level 6). Bloom’s taxonomy serves to emphasize one’s development of intellectual skills. For example, key words used or the identification of key concepts by “the writer” helps the writer to establish and encourage critical thinking skills [11] [12] . This suggests that a student who can map conceptual ideas from their working memory into writing may also demonstrate conceptual comprehension of the task at hand [13] [14] . In the context of this study, this might measure the ability of an EE/CpE student to map their conceptual ideas of physical semiconductor principles into words that demonstrate comprehension of these principles. What’s more, this can range from strategic considerations (such as the organization of physical ideas) to the implementation of motor plans [15] . For instance, choosing and writing key words to describe the physical abstractions within a mathematical model of a semiconductor device.
However, Bloom’s cognitive domain does not subcategorize for psychomotor skills, such as describing the

Figure 1. Those two portions of the human brain that are primarily responsible for higher-thought (cognitve domain) and writing (a psychomotor penomenon).
ability of a person to physically manipulate a pencil. These are processes that get described in the field of neurophysiology [16] . A question is therefore: “is there a method to observe one’s development of intellectual skills (cognitive domain) via psychomotor responses?” Simpson et al. [17] -[19] developed a “psychomotor taxonomy” in an effort to explain the behavior of a typical learner such as perception (the ability to respond to sensory cues to guide motor activity), responding to phenomena (via explaining and/or showing), and complex overt responses (i.e., where the learner displays mastery in explaining difficult concepts). Bereiter and Scardamalia [20] proposed that individuals who demonstrate skill in mapping thoughts into written language tend to “problematize” a writing task; adopting a strategy they called knowledge transforming. In contrast, a writer who is lower on Bloom’s cognitive domain (e.g., Level 1) will typically take a “knowledge-telling” approach, in which written content is generated through association, with one idea prompting the next.
Problem solving has been conceptualized in terms of information processing. Hayes [21] and Flower attempted to classify various activities that occur during writing and the relationships of these activities to: (1) the task environment; (2) the internal knowledge state of the individual. Hayes and Flower suggest that an individual’s long-term memory (an aspect of cognitive capacity) has various types of knowledge which not only account for an individual’s knowledge of a topic, but a stored plan for how they will demonstrate skill in mapping their thoughts into written, planned content. Hayes and Flower contend that writing involves complex problem solving, in which information is processed by a system of function-specific components in the brain [22] [23] .
In a revised model Hayes [24] suggests that different aspects of working memory are inherent in the cognitive process of expressing written language. There is evidence of a correlation between an individual’s working memory capacity and their ability to perform analytical reasoning tasks [22] . Given the high levels of cognitive demand that skillful writing involves [25] , individuals who possess well-organized knowledge of a domain and concomitant interest in the subject areas have been shown to demonstrate competence in mapping their comprehension of subject matter into skilled, written language. Furthermore, studies suggest that skilled reasoning in mapping one’s comprehension of a topic into written language is associated with analytical reasoning [26] [27] .
What’s more, planning what knowledge to map into written language and the level of skill in the actual writing process has been found to depend upon one being able to recall relevant knowledge and manipulate it in working memory. For instance, Bereiter [20] and Scardamalia showed a correlation between writing quality and performance on tasks measuring working-memory capacity. Hambrick [28] reported that recall in a readingcomprehension task is facilitated both by high working-memory capacity and high levels of domain knowledge. Similar interactions appear to take place in planning and generating what words to write, where it has been argued that long-term knowledge activated by concepts in working memory functions (in effect) as long-term working memory, thus expanding the set of readily accessible concepts.
If a student is asked to present factual material via writing, some degree of natural conceptual organization is intrinsic to the material to be presented. For instance, to skillfully describe the physical operation of a MOSFET, one could argue that the natural approach would be for the student to begin organizing the written “presentation” in terms of the nand p-type layers and the electron-hole interactions in the presence of an electric field at the gate terminal. This suggests that students who experience difficulty inferring conceptual relationships when learning complex subject matter are likely also to have trouble inferring those relationships when asked to map their conceptualizations into structured, knowledgeable writing.
If this conceptual framework is applied to the study of upper-division EE/CpE students, then in summary, one might predict the following synopsis: Let’s say an EE/CpE junior demonstrates adeptness at mapping their comprehension of physical principles and the equations that govern these principles into written language. Let’s further say that this student demonstrates objective comprehension and validation of their ideas through written language. It is reasonable to predict that this student should likewise demonstrate effectiveness in executing analytical reasoning problem-solving tasks. Hence, the hypothesis underlying this study is now stated.
3. Hypothesis
Those EE/CpE juniors who demonstrate adeptness at mapping their comprehension of physical-based equations into written language that demonstrates objective comprehension and validation of their ideas should also demonstrate skill in executing analytical reasoning problem-solving tasks. Put another way, students that restrict their writing to “knowledge-telling” of physical relationships should be less adept at demonstrating objective comprehension of key physical principles or validation of their ideas via problem solving.
4. Design/Method
This study was conducted in two independent sections of Microelectronic Devices and Circuits during the fall semesters of 2012 and 2013 at a private university is NW Oregon. This course consists of three 50 minute weekly lectures and one 150 minute weekly lab. The students in this course are exclusively electrical or computer engineering majors (EE/CpE) at the junior level. The total sample for this study consisted of n = 25 students (22 males and 3 females).
The first step was to assess students’ adeptness at mapping their comprehension of physical-based equations into written language. The second step was to assess students’ quantitative and analytical problem-solving skills. This was accomplished over the course of three written examinations over the duration of each of the 2012 and 2013 fall semesters. Each exam was divided into two parts: (1) qualitatively describing Microelectronic Equations and Relations (a 20 - 30 minute closed-book and closed-note exam), immediately followed by; (2) quantitative analysis of microelectronic circuits (a 20 - 30 minute exam with a provided equation sheet).
Students were given a 30 minute review two days prior to each exam. They were informed of the exam expectations and that each exam would consist of two parts. They were provided with example problems. So for Part 1, they were shown an example microelectronics describing equation. The expectation was emphasized that they were not to do a literal translation symbol-by-symbol of the equation: that they were expected to demonstrate a conceptual understanding of the equations and the underlying physics. For instance, the following problem was presented on Exam #2: Consider the equation

a. (4) What microelectronic circuit model or device does this equation apply to?
b. (10) Describe what each of the variables are in this model and indicate their units:
c. (4) In your own words, explain what this equation means.
d. (4) Draw a circuit diagram of the physical situation where this equation would apply.
Label all circuit parameters.
Two-to-three writing problems like this were given on each of the exams. Each student’s response was scored as follows:
4 points: student demonstrates deep conceptual meaning of the underlying physics and model limitations.
3 points: student demonstrates some understanding of the underlying physics and/or the model limitations.
2 points: student provides a literal answer, where symbols are identified by correct physical quantities.
1 point: an incomplete or an incorrect answer 0 points: no answer.
Here are sample writings of student responses (Part c.) that were scored using this scale:
4 points: This equation models the current that flows through a non-ideal forward-biased pn-junction diode from an outside source. The current i is dependent on the saturation (or drift) current IS which is a natural consequence of thermally-generated minority carries that flow from the nto the p-side of the device junction. The current i becomes exponentially large when the voltage v applied to the diode exceeds barrier voltage of the junction. Current I is dependent on the thermal voltage VT and the ideality factor n, but any variations in these values have little effect on i once the barrier voltage is exceeded.
3 points: This equation tells us that the current flowing in a forward-biased diode is dependent on the saturation current IS, the thermal voltage VT, the factor n, and the forward-bias voltage that we apply to the diode. The higher the voltage the higher the current i.
2 points: This equation tells us that the diode current i is equal to saturation current IS multiplied by the exponent of the voltage v divided by n times the thermal voltage minus 1. If i » IS we can ignore the 1.
1 point: The diode current i depends on many thermal and material property factors such as the saturation current IS and the thermal voltage VT and the ideality factor n.
5. Results and Analysis
A fundamental question to address is: “is there a meaningful correlation between the students’ conceptual writing scores and their performance on the analytical portion of each exam?” Statistically speaking: “is there a spatial pattern among those students who demonstrate adeptness at mapping their comprehension of microelectronic equations into writing and their microelectronic analytical problem solving skills?”
The conceptual written-description score totals from the combined 2012 and 2013 populations were taken as the independent variable; the analytical problem solving score totals were taken as the dependent variable. The first step was to confirm the regression assumption of normality (Figure 2). This plot was done on the residuals and not on the response variables. The justification is that the latter would result in a pseudo-normal probability plot. A pseudo-normal plot would not reflect a correct representation of the population’s exam scores. Hence, the initial focus was on the residuals to see if they came from a normal curve. Deviations of the dependent observations (student scores on the analytical portion) from the fitted function are the residuals.
The more linear the distribution of the residuals (i.e., the more a linear function can be fitted to the data) the more faith that the residuals come from a normal curve. As evident in Figure 2 the model’s residuals are wellbehaved and are not heteroscedastic. Also, the normal scores are Z-scores. The Z-scores permit the conversion of the independent data sets into scores that can be compared to each other. This analysis method removes arbitrary aspects that may be present in the population and is a widely-accepted statistical tool to check the regression assumption of normality [29] . The conclusion is that the residuals come from a normal distribution.
On the basis of normality a correlation test was done. The rationale: to test for a relationship between the written and analytical exam scores. For the purposes of this study, the goal was merely to show that a relation between these two variables exists, not that the action of achieving a score on the written exam caused a particular score on the analytical portion.
Regression analysis supports that the two exam score variables occur together (Figure 3). Again, the purpose is to provide evidence that the variables are significantly related—not to suggest causality. Arguments made for
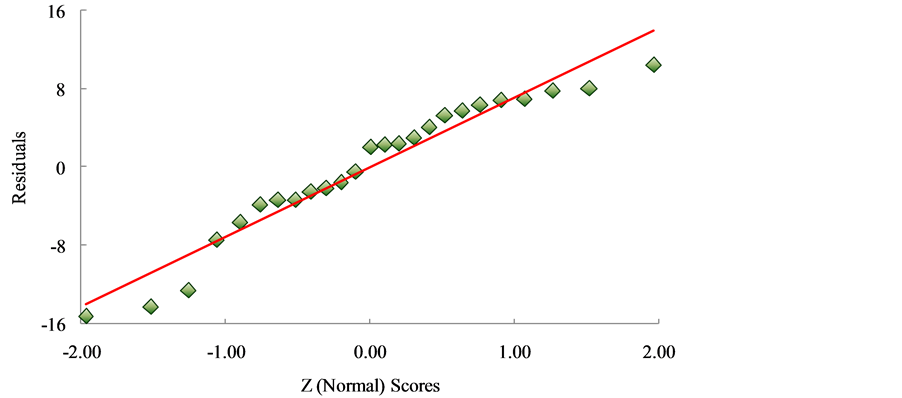
Figure 2. Normal probability plot representing the combined total scores for Microelectronics Exams I, II and III (2012 and 2013 EE/CpE student population). The normality assumption for the sample population tested is supported.

Figure 3. Regression analysis of the combined scores for Microelectronics Exams I, II and III (2012 and 2013 EE/CpE student population).
the Pearson’s correlation coefficient of r2 = 0.5854 being a statistically significant indicator of correlation are discussed as follows.
First, directionality is not an issue. Student’s performance on the analytical portion of the exam was measured after they took the written portion of the exam. Thus, the latter could not have possibly caused the former.
Second, it is important to dispense with the existence of a possible third-variable. This would imply the exam scores may be statistically related if there was an unaccounted for variable affecting both sets of exam scores (even in the absence of causality). Thus, to add to the defense of the acceptability of r2 the question should be asked: “is it possible that a third-variable may have caused the EE/CpE students to score well (or poorly) on both exam portions?” If such a variable exists it may not necessarily be related to one or both exam scores; it is sufficient that the existence of such a variable produces an incidental (spurious) correlation between the scores.
For instance, it can be speculated that the third variable is a students’ intelligence quotient (IQ). IQ measures an individual’s spatial, mathematical, language and memory abilities [30] . For IQ to be a third variable it would have to cause students to score well (or poorly) on both portions of the exam; either case would produce a statistical relationship between conceptual written explanations and one’s analytical problem solving ability. Although it seems reasonable to speculate that IQ may influence one’s ability to think analytically and to skillfully communicate their comprehension of difficult concepts, it seems unlikely that IQ would have a consistent effect on one’s ability to articulate—via writing—difficult physical and engineering concepts.
Other unaccounted for variables may exists. But just knowing that the written and analytical exam scores are related is interesting, regardless of whether a third-variable exists or not. Rather than continuing to speculate a spurious correlation due to a possible third variable, an additional statistical measure was deemed as a safeguard —the determination of Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, r [31] —a nonparametric measure of statistical dependence between two variables. It assesses how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function. When each of the variables is a perfect monotone function of the other, than r = +1 or –1. Spearman’s rank analysis is warranted since both variables are quantitative and the sample size is relatively small (n = 25). Spearman’s rank for the population tested is r = 0.75 which implies a strong measure of monotonicity between the exam score variables.
6. Conclusions and Discussion
This study focused on determining the existence of a correlation between upper-division EE/CpE students’ analytical reasoning abilities and their descriptive writing skills. Descriptive writing was taken to mean a student’s ability to identify key physical aspects of a mathematical model and to express—in words—a concise and wellbalanced description that demonstrates a deep conceptual understanding of the model.
Two behavioral components were examined: 1) each student’s ability to map their understanding of microelectronics device and circuit models into written language; 2) each student’s analytical problem-solving skills of microelectronics device and circuit analysis problems. The initial question asked was: “is there an observable (clinical) relationship between these students’ adeptness in writing descriptions of microelectronic device and circuit models and their analytical problem solving skills?” The former is the psychomotor response; the latter is associated with the cognitive domain (refer to Figure 1).
There is convincing evidence that those students who objectively wrote-out knowledgeable and conceptuallysound descriptions of semiconductor device and circuit equation models were likewise skillful at solving analytical microelectronics problems. Furthermore, the few students within this population that demonstrated a profound conceptual understanding of microelectronics concepts and provided written validation of their ideas likewise earned the highest-end scores on the analytical portion of their exams.
Regression analysis and a test of monotonicity support a significant correlation between this populations’ physical understanding of concepts via writing and solving problems. This seems intuitive—students who perform better on solving analytical-based problems should have more comprehension of the material. The results of the analysis are not meant to imply that the independent variable (writing scores) caused the outcome of the dependent variable (the analytical problem solving scores). It just means there is a statistically significant relationship between the two, thus providing substantial support to the hypothesis (p. 4).
The intellectual merit of this study is that it provides an observable and clinical relationship between EE/CpE junior’s adeptness in writing descriptions of microelectronic device and circuit phenomena (students’ psychomotor response) and their analytical reasoning (a window into the cognitive domain). Although the former and the latter are lateralized cognitive processes, the research methods carried out in this study enables the engineering educator to research a clinical view into: 1) EE/CpE students’ learning behaviors; 2) the level at which EE/CpE juniors are in Bloom’s cognitive domain.
The broader impact is this work bridges cognitive science and engineering education in such a way to advance understanding of: 1) the limitations of high-level, analytical problem solving in the absence of students’ written evaluation of underlying concepts; 2) Bloom’s cognitive domain in the context of a small and unique group of undergraduate students; 3) how to observe engineering students’ development of intellectual skills (cognitive domain) through psychomotor responses (writing)—both considered lateralized neurocognitive processes.
7. Subsequent Research
The subsequent research ambitions of the author are to continue to apply this research technique to subsequent groups of upper-division engineering students, not just EE/CpE juniors per sé, but to seniors too and aerospace and mechanical engineering upper-division students as well. With a larger collection of such data across wider population types, perhaps a more thorough understanding into students’ lateralized cognitive processes will be realizable. Particularly, the types of cognitive mechanisms that predict how these students store plans for how they’ll demonstrate skill in mapping their knowledge of complex subject matter into written language that demonstrates a deep conceptual meaning of the content.