
1. Introduction
Southern corn leaf blight (SCLB) disease caused by the fungus Cochliobolus heterostrophus (anamorphs Bipolaris maydis, Helminthosporium maydis) constitutes a considerable threat to corn production worldwide [1] . No known genes confer complete immunity to this disease; instead, maize breeders rely on polygenic, quantitative resistance to SCLB [2] . Three races of C. heterostrophus known as O, T and C have been identified to date [3] [4] . Race O is considered to be the most common race in most areas and is controlled by nuclear genes. Race T, the cause of the 1970s epidemic in North America, is specific to maize containing Texas male-sterile cytoplasm (cms-T) and is controlled mainly by cytoplasmic factors. The most prominent difference between race O and T is that race O only attacks leaves while race T attacks leaves, stalks, leaf sheaths, ear husks, ears and cobs. Race C is a cms-C cytoplasm-specific race reported only in China [4] .
Virulence test methods are an important means to investigate phytopathogenic fungi and therefore the development of these methods is a continuous effort (see, for example, in Cryphonectria parasitica [5] ). To study and evaluate C. heterostrophus strains virulence, an accurate, sensitive, rapid, convenient and reproducible pathogenicity test is critical. The traditional test involves the inoculation of fungi on living maize plant leaves by spraying its spores [6] or mycelia fragments [7] . Alternatively, the leaves of the plants were dipped into homogenized mycelial suspension in order to obtain widespread lesions [8] . Other studies introduced a more precise method based on depositing mycelia fragments [9] or spores [10] drops on the leaves and qualitatively evaluating the symptoms severity. However, the preliminary droplets technique and especially the leaves spraying or dipping approaches are inaccurate and incapable of differentiating slight differences that are sometimes invisible to the naked eye.
Mutants in genes encoding conserved eukaryotic signal transducing proteins have been very helpful in efforts to understand the environmental mediated control of development and the sensory pathways that are needed to detect the host and establish invasive growth. Several such mutants have been constructed for the maize pathogen C. heterostrophus [6] [7] [9] [10] . In Ascomycetes, for which sufficient sequence information is available, there are three Ga-encoding genes, one Gb and one Gg gene [11] . Deletion of the MAP kinase gene chk1 [9] or the Gb gene cgb1 [7] has a huge effect on growth and development, and drastically reduces virulence under all conditions tested.
Cga1, a heterotrimeric G protein Ga subunit, is the C. heterostrophus ortholog of Magnaporthe grisea MAGB belonging to the fungal Gi class. Members of this class are often required for full virulence, while disruption of other Ga genes confers no major phenotype (for example, [12] [13] ). Mutants in C. heterostrophus cga1 produce conidia that germinate as abnormal, straight-growing germ tubes forming few appressoria [6] [10] . A Gα activated mutant, cga1Q204L, showed phenotypes resembling the null mutant in development, sporulation and hydrophobicity, indicating a possible role for cga1 as a stabilizer of these traits [14] . Nevertheless, the cga1 mutants can cause normal lesions on plants, unlike other filamentous fungal plant pathogens in which functional homologues of cga1 are required for full virulence [6] .
For cga1 strains, it was demonstrated that appressorium formation is not essential for virulence [6] . Indeed, inoculation with mycelium results in growth on the leaf surface followed by penetration into the leaf without noticeable appressorium formation: aggregates of mycelia sometimes localize to stomatal apertures, but apparently direct penetration of the epidermis is also possible [6] . Detailed examination indicated that under some host physiological conditions, cga1 disruption and deletion mutants are considerably less virulent [15] tes a possible role for cga1 in the regulation of hydrophobin secretion [10] . Determination of C. heterostrophus hydrophobins expression in cga1 mutants provided the molecular evidence for the role of cga1 in the suppression of hydrophobins expression [16] .
A large number of fungal genes encoding α subunits of heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins have been cloned in other fungi as well [12] [13] [17] . There is growing genetic evidence of the importance of these genes in pathogenicity [12] [13] [18] . Signaling through the cga1 G-protein pathway may be required for full fitness as a pathogen under some conditions but not others. For example, Liu and Dean (1997) showed that MAGB mutants have reduced virulence on young rice leaves but are fully pathogenic on older plants.
To test the conditions under which the cga1 mutants differ the most from the wild type strain, we conducted a detailed, well controlled study of the virulence of C. heterostrophus cga1 mutants. The objective was to establish an assessing method that would enable us to define the virulence role of fungal signal transduction pathways. The developmental and physiological stages of the host leaf, the differences in susceptibility to the disease between the first, second and third seedlings leaves, the infection method and the incubation time could all be important factors in determining virulence differences.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
The strains used in this study are listed in Table 1.
2.2. Culture Conditions
Fungal strains were grown on complete medium (CM, [19] with or without 50 mg/ml hygromycin B for about 10 days at room temperature (24˚C - 26˚C) in continuous light from cool white and UVA-enriched fluorescent tubes (Philips, Eindhoven, the Netherlands). Conidia were collected by scraping the colony surface with a scalpel into sterile water containing 0.05% Tween 80. Spores were microscopically quantified by haemocytometer count. For inoculation with mycelia fragments, six culture agar disks, 6 mm in diameter, were cut from the margins of the colony and transferred to a 50 ml polycarbonate screw-capped test tube containing 20 ml liquid CM. The cultures were incubated diagonally in a rotary shaker at 230 rpm and at a temperature of 30˚C for 3-4 days. Mycelia were collected by centrifugation (10 min, 600 × g) and homogenized briefly (20 s, Polytron, Brinkmann Instruments, Westbury, NY). Fifty mg wet weight mycelia or 2 × 105 spores (unless otherwise indicated) per ml of 0.05% Tween 80 was used to infect the leaves.
2.3. Maize plant Growth Conditions
Sweet maize cultivar (Grand Jubilee), available at the Institute of Cereal Crops Improvement, Tel Aviv University, was used throughout. Plants were grown in a greenhouse with a 14 h photoperiod at 22˚C - 25˚C. Maize seedlings were 9 - 12 days old, unless otherwise indicated; within this day range, plants were used when the third leaf had emerged, remained partly rolled, and started to expand. Each repetition included leaves from one individual plant, i.e., the number of leaves is also the number of plants used for each experiment.
2.4. Virulence Assays
Seedlings were inoculated by depositing drops (5 ml 0.05% Tween 80) of the above mycelia fragments (250 mg wet weight/drop) or conidia (1000 conidia/drop, unless otherwise indicated) suspensions on the leaves. Usually, in young seedlings (9 - 12 days old), one drop was deposited on the upper third part of the first three detached or intact leaves. Alternatively, detached leaves from the older plants were long enough for a series of 2 - 4 drops to

Table 1. Strains used in this study.
be placed along the upper third part of the leaf. The plants, kept in a closed plastic bag with 100% humidity, or detached leaves in a closed Petri dish (with a wet Whatman no. 1 filter paper underneath), were then incubated in a growth chamber for 2 - 6 days at 30˚C under continuous white light.
2.5. Analysis of the Virulence Assay Results
The pathogenicity of the fungal strains was determined as percentages of the infected plants (plants that show any visible sign of disease) and by measuring the area of the necrotic patch (lesion area) caused by the pathogen. For quantitative analysis of the lesion area, leaves were scanned (300 dpi) and the lesion areas (calculated using Adobe Photoshop 6.0 and Tina 2.10 g software, Raytest, Straubenhardt, Germany) were used to evaluate the severity of the infection. Statistical analysis, conducted using Student’s t test, verified whether differences were statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05).
3. Results
3.1. G-protein and MAPK Mutants' Ability to Infect Maize Plants Leaves
We evaluated the ability of C. heterostrophus WT (C5), cga1 (G-protein Gα subunit deficiency strain), cgb1 (G-protein Gβ subunit deficiency strain) and chk1 (MAPK deficiency strain) (Table 1) to infect fully developed, detached leaves from maize plants of different ages, up to 81 days (time course in Figure 1). Infection was done on detached, mostly developed leaves in Petri dishes with wet filter paper by depositing 2 - 4 drops (5 ml of 0.05% Tween 80, the number of drops was according to leaf size) of spore suspension (WT and cga1 strains, 102 spores/drop) or mycelia fragments (cgb1 and chk1 strains, 250 mg wet weight per drop) on the upper third part of the leaf surface. Mycelial fragments, instead of spores, were used for the inoculation of cgb1 and chk1 mutants since they cannot produce spores efficiently [7] [9] .
The WT and cga1 strains are capable of producing normal conidia, so a spore suspension was used instead of mycelia fragment suspension. This could be done since the two suspensions had similar capability to infect maize intact leaves in both strains (Figure 2, P > 0.2). Infected leaves were incubated for three days. Wild type and the three signaling mutant were less virulent on leaves from mature plants than they were on younger plants (Figure 1). This reduction was more pronounced for cga1 and even more for cgb1 and chk1. Neither of the strains could infect leaves from 80-day-old plants. Interestingly, on leaves from 10-day-old seedlings, cga1 had a similar infection ability to that of wild type (P > 0.1). Wild type and cga1 caused significantly larger lesions (in diameter) on the upper part of the detached leaf than on the lower part (p < 0.05, data not shown).
A subsequent experiment was conducted in order to define the optimal measuring method to evaluate the vulnerable ability of the fungal strains. We estimated the percentages of the infected plants and measured the area of the necrotic patch caused by the pathogen. In both measuring methods, the wild type and the cga1 mutant could infect detached leaves more effectively than it could the leaves of intact plants (Figure 3, significant at p < 0.01). Nevertheless, the lesion area measuring method gave a better and more precise estimation of pathogen virulence ability (see also for comparison Figure 4). Therefore, this method was chosen for the subsequent experiments.
Interestingly, when we used 10-day-old detached leaves in Figure 1, the lesion area on detached first and second leaves caused by cga1 mutant was comparable to WT, while in the subsequent experiments (Figure 2 and Figure 3) the lesion area caused by cga1 was significantly (p < 0.02) smaller than WT. This difference may be explained by the use of one drop of inoculum (in Figure 2 and Figure 3) instead of two (Figure 1) to infect those relatively small leaves. It was previously shown that when 11-day-old seedlings were inoculated by a relatively massive amount of fungal spores, the symptoms caused by C4, C4cga1 and C5cga1 were nearly identical [6] [15] . Another interesting result was a noticeable difference between the susceptibility of the first and second leaves (Figures 2, Figure 3, significant at p < 0.003, found only for the WT strain). We further examined this difference in the subsequent experiments with intact leaves.
3.2. Adjustment of the Intact Leaves Virulence Assay Conditions
Intact leaves are better for modelling host-pathogen interactions in the field. Furthermore, in the intact leaves

Figure 1. Infection of detached leaves as a function of plant age. Most developed leaves from maize plants of different ages (10, 27, 64 and 81 days old) were inoculated by depositing 2 - 4 drops (5 ml of 0.05% Tween 80) of spore suspension (102 spores/drop) of Cochliobolus heterostrophus wild type (WT C5, ¢) or signal deficiency strain, cga1 (G-protein Gα subunit, p) along the upper third part of the leaf. For the non-sporulating signal deficiency strains, cgb1 (G-protein Gβ subunit, q) and chk1 (MAPK, ), 5 ml drops of 250 mg wet weight mycelia fragments per drop was used instead. Infected leaves were incubated in Petri dishes with wet filter paper for three days. Values represent an average lesion area (mm2) of 5 - 7 leaves of the same age ± standard error.
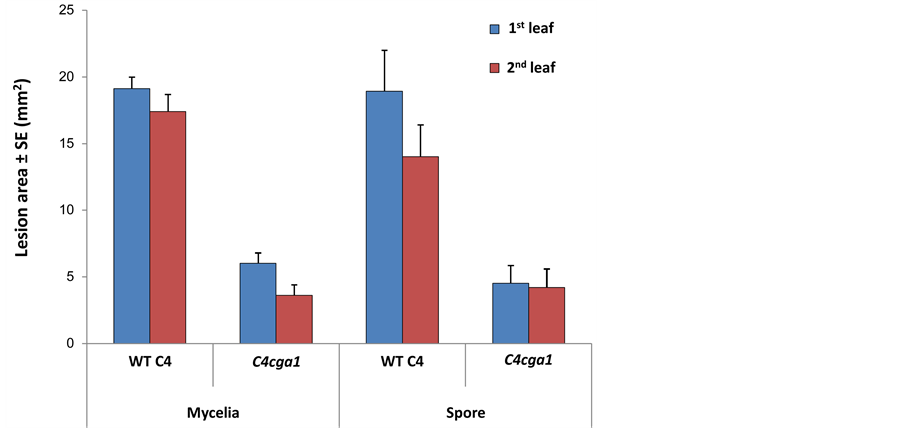
Figure 2. Mycelial inocula or conidial suspensions virulence assay for C4cga1 mutant in comparison to the wild type line (C4). Mycelial inocula or conidial suspensions of both strains were prepared as described in Figure 1. One drop (5 ml 0.05% Tween 80) was used to infect the upper third part of the first and second intact leaves obtained from 9 - 12 days old maize seedlings. Incubated time was three days. Values represent an average lesion area (mm2) of at least seven leaves ± standard error.
pathogenicity assay, the fungus has to deal with the host's defense mechanisms and develops in tissues that alter their structure and properties during plant growth and maturation. In addition, the balance of hormones in plant tissues subjected to changes during growth, and at least two of them, cytokinin and ethylene, were found previously [15] to influence the development of the pathogen.
Here, we used the intact leaves pathogenicity assay to determine the conditions under which the difference between cga1 and wild type is greatest. As previously mentioned, these two strains produce conidia so a spore suspension was used. The amount of spores (102 or 103 spores per 5 ml drop) used to infect the seedlings’ first three leaves was also a crucial parameter (Figure 5). High concentration of spores may blur the differences between the leaves since, when using 1000 spores/droplet, the pathogen causes a similar infection on the WT 2nd
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b) (c)
(c)
Figure 3. The infection pattern of cga1 and WT in detached and intact leaves. Maize seedlings, 9 - 12 days old, were inoculated by depositing one drop (5 ml 0.05% Tween 80 solution of 102 spores/drop) on the upper third part of the first two detached or intact leaves. The infected plants in a closed plastic bag with 100% humidity or detached leaves in a closed Petri dish (with a wet filter paper underneath) were incubated for four days. A. Values represent average lesion areas (mm2) of at least seven leaves ± standard error. B. Values represent infection (any visible injury) percentage calculated based on 10 - 14 leaves from the same age. C. The second leaves were photographed four days post infection. Dark areas indicate necrotic regions.
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 4. Infection time course for inoculation of intact leaves: effect of infection period on severity of lesions caused by wild type C4 and cga1. A. Conidial suspensions (103 spores/drop) were used to infect intact maize first seedling leaves at age of seven days; the seedlings were incubated for the indicated times at 25ºC. Values represent an average lesion size (mm2) of at least 10 leaves for each time point ± standard error. B. Values represent infection (any visible injury) percentage of the same plants.

Figure 5. Influence of spore concentration on WT and cga1 infection of different leaves. One drop of 5 ml containing 102 or 103 spores was deposited on the upper third part of the first three intact leaves (obtained from 9 - 12 days old maize seedlings). The plants were then incubated in a moist chamber for three days at 30oC in continuous white light. Values represent infection (any visible injury) percentage calculated based on 15 leaves from the same age.
and 3rd leaf, with slightly more severe symptoms on the 3rd leaves than on the 2nd leaves (Figure 5). When using 100 spores/droplet, the disease symptoms on the WT 3rd leaves were less than half as severe in comparison to those on the WT 2nd leaves (Figure 5). A 10-fold reduced inoculum load reduced the extent of the lesions (p < 0.05), but the differences between wild type and cga1 mutants remained in both spore concentrations (Figure 5, p < 0.05).
A clear difference in virulence between the first three intact leaves was observed when young seedlings (13-, 16- and 19-day-old maize seedlings) were inoculated (Figure 6). Both wild type and cga1 were more easily able to infect the first leaf than the second and third leaves (p < 0.05). Symptoms decreased with seedling age on the first leaf but increased slightly with seedling age on the second and third leaves (Figure 6). This apparently reflects some unique physiological property of the first leaf. With increased incubation time, the lesions caused by the mutant increased in size faster than those caused by wild type, resulting in almost no difference when assayed on the first seedling leaf six days after inoculation (Figure 4, significant between the two strains existing at the first two days, p < 0.0004, and on the second leaf at day 6, p < 0.02).
3.3. Virulence Assays for C. heterostrophus G-Protein Signaling Disrupted Strains
Up until now, we have primarily used spore suspension to inoculate the plants leaves. At this point, we intended to apply the conditions set determined in the above experiment and define the relative pathogenicity level of two additional signaling mutant strains, cgb1 and the double mutant cga1 cgb1 (G-protein Gα and Gβ subunit deficiency strain, Degani 2013a). These strains are incapable of producing conidia, so the mycelia fragment infection method was used instead. As described in Figure 2, the WT and cga1 strains spore suspension or mycelia fragments suspension could infect intact leaves equally well.
Finally, we used the well-defined method developed here to evaluate all our G-protein signaling deficiency mutant strains in order to evaluate their role in determining the pathogenic behavior of C. heterostrophus (Figure 7). The virulence assays condition set involved placing 5 µl drop of 50 mg wet weight mycelia per ml of 0.05% Tween 80 suspension on the upper third part of each of the first three intact leaves, incubation for four days in a wet chamber and measuring the lesion area. This experiment enabled us to classify the mutants in order of decreasing virulence: WT > cga1 > cgb1 > cga1 cgb1 (Figure 7, significant difference from the WT, p < 0.05 for the first leaf of cga1, the two first leaves of C4cga1, and for all three leaves of cgb1 and the double mutant, cga1 cgb1). As can be clearly seen, symptoms production is virtually abolished on the double, cga1 cgb1 mutant leaves. A deeper examination of the results revealed an interesting difference in the pathogenic behavior of the mutant strains (Figure 7). When infected with single mutant cgb1, the 1st and 3rd leaves displayed comparable resistance, which is greater than the 2nd leaf. This observation was similar to the scenario of infection with cga1 cgb1 double mutant. In contrast, the two cga1 mutant strains generated different results: the 1st and 2nd leaves became equally resistant to cga1 mutant infection while the 3rd leaf was the most susceptible one.
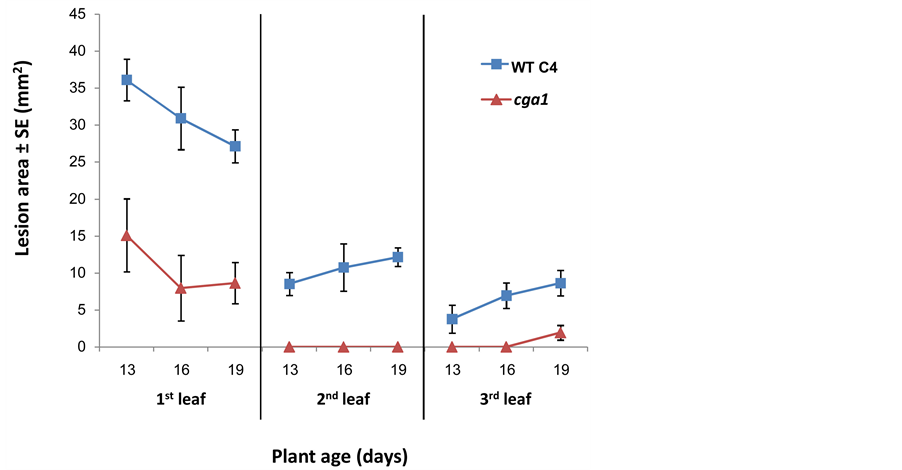
Figure 6. The effect of seedling age on infection severity. Wild type and cga1 spore suspensions (103 spores/drop) were used to infect intact leaves of 13-, 16- and 19-day-old maize seedlings. (¢), wild type; (p), cga1. Incubated time was four days. Values represent average lesion areas (mm2) of at least nine leaves of the same age ± standard error.

Figure 7. Virulence assays for the WT and G-protein signaling disrupted mutant strains. The first three intact leaves were inoculated by depositing drops (5 ml 0.05% Tween 80) of mycelial suspension (250 mg wet weight/drop) on the upper third part of each leaf. Incubated time was four days. Values represent an average lesion size (mm2) of 18 leaves ± standard error.
4. Discussion
Mutants in the Gα subunit gene cga1 cause lesions on the host leaf despite the abnormal development of germ tubes and decreased ability to form the small appressoria characteristic of this species [6] [15] . Following spray inoculation and incubation for 6 - 7 days, symptoms caused by wild type and mutant were very similar. Here, we develop an in vitro pathogenicity assay that is based on conditions under which the wild type has a clear advantage over the mutant. The largest difference is especially noticeable on intact, young (9 - 12 days) leaves. On detached leaves (Figure 3) or on the first seedling leaf when scored six days after inoculation (Figure 4), the cga1 mutants cause symptoms that are almost as severe as those caused by the wild type isolate. The simplest explanation for these differences is that the advantage conferred by an active cga1 pathway is most evident under the conditions that are the most difficult for the pathogen.
One aspect might be the availability of nutrients. This hypothesis was also suggested as an explanation for the influence of culture conditions on saprophytic growth of G-protein mutants of Cryphonectria parasitica [20] . Detaching the leaf accelerates senescence and increases degradation of macromolecules [21] . If the mutant is deficient in secreted enzymes, as reported for Botrytis [12] , a detached leaf is likely to be a more accessible nutrient source [22] . Consistent with this explanation, in saprophytic cultures, wild type and cga1 show no major difference in growth rate (same culture diameter on complete medium plates). Indeed, in saprophytic culture, the G-protein α subunit mutant strains had WT levels of cellulase, pectinase and protease degradation activities, but it grew significantly slower on minimal medium containing maltose [23] . This weakened ability implies an essential role of the G-α subunit signaling in some poor nutritional environments. The first leaf may be acting as a source of carbon for the second and third leaves, which would act as a sink as they develop. This interpretation is supported by the observation of decreased infection of the first leaf and increased infection of the second and third leaves during early development of the seedlings (Figure 6). The first leaf may therefore be a favored nutritional surface for the growing fungus. Similarly, very young seedling leaves may be a less accessible source of nutrients, e.g., sugars might not be as available since the photosynthetic rate has not yet peaked. Thus, easily available nutrients may minimize the difference between wild type and mutant.
Nutrient availability is probably not the only factor responsible for the difference in virulence between wild type and mutant. The deficiency in appressorium formation may also slow penetration of the mutant into the leaf. The loss of difference between wild type and mutant with increased incubation time (Figure 4) is consistent with this second hypothesis. Indeed, the delay in infection by the MAPK mutant, chk1 (Figure 1), and the double cga1 cgb1 mutant (Figure 7), which completely lack appressoria, is much more extreme and full wild type virulence has never been observed [8] [9] . Nevertheless, when chk1 penetrates the leaf, some necrosis does occur (Figure 1). The expression of two cellulase genes reaches wild type levels after a further delay that apparently results from both the slowed penetration and the direct modulation of cellulase gene expression by chk1 [8] [23] .
Senescence may enhance fungal infection, providing a third factor relevant to the difference between wild type and mutant. In Arabidopsis plants, detachment-associated physiological and molecular state changes of the leaf, such as initiation of salicylic acidand ethylene-dependent senescence and inactivation of defense pathways seems to contribute to the colonization of the plant by Colletotrichum spp. [24] . In this work the cga1 strain was less effective than wild type in infecting leaves detached from maize plants 27 days old or older. On leaves detached from seedlings younger than 10 days, cga1 had virulence similar to wild type. On intact leaves, however, cga1 was always less virulent than wild type. Stresses, e.g., nitrogen limitation and dryness, promote leaf senescence [25] . The cga1 mutant was less virulent towards benzyladenine (BA, a commercial cytokinin)- treated detached leaves, which senesce more slowly, supporting the hypothesis that senescing leaves are more susceptible to attack by cga1 [15] .
A fourth explanation for the difference between wild type and mutant might be the ability of the mutant to respond to plant surface signals, which play a major role in fungal infection [26] . Topographical features of the plant surface and chemicals on the surface can trigger germination of fungal conidia and the differentiation of germ tubes into appressoria [27] [28] . Despite their importance, the nature of the plant signals that trigger such programmed differentiation is poorly understood.
Thus, nutrient accessibility, developmental and senescence stage of the host leaf, appressorium formation and surface sensing may all be important for determining the best method to study pathogenic variations in the fungal strains. The phenotypic variation that we have described here implies that the roles of fungal signal transduction genes must be defined in the context of the physiological state of the host. It is well known that host plants are more susceptible to fungal infection at some time in their growth cycle [29] . Fungal signal transduction pathways are therefore likely to be important in the timing of plant susceptibility to fungal disease.
The intact leaves droplets assay offers many advantages over other C. heterostrophus virulence tests. Within only four days of inoculation with the fungi, an accurate estimation of virulence can be made. The results are clear, consistent and correlate well with results from other virulence-test methods using the same fungal mutant strains published previously [6] [7] [9] [10] . Additionally, it is economical, saves time and can be used to identify any possible genetic variability among C. heterostrophus strains, even slight changes that are barely observed by the naked eye. The same approach, with some adjustments, could be used to evaluate pathogenic variations in other foliar fungal diseases.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Dr. Benjamin A. Horwitz (Technion—Israel Institute of Technology, Israel) for his guidance and helpful advice and Dr. Sophie Lev for her many helpful suggestions.