Antibiotics/antibacterial drug use, their marketing and promotion during the post-antibiotic golden age and their role in emergence of bacterial resistance ()
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1. Antibiotics/Antibacterial Drugs and Their Sources
Antibiotics/antibacterial drugs are the most commonly used and abused antimicrobial agents in the management of bacterial infections globally. They have been used for more than 50 years to improve both human and animal health since and during the antibiotic golden age and post-antibiotic golden age [1]. The discovery of the antibiotics and antibacterial agents revolutionized the treatment of infectious bacterial diseases that used to kill millions of people during the pre-antibiotic golden age worldwide [2-4]. The major sources of antibiotics/ antibacterial agents include Streptomyces, Penicilliums, Actinomycetes and Bacilli (Table 1) [2,4-6].

Table 1. Sources of some common natural antibiotics [2,4-6].
1.2. The Antibiotics Golden Age and Their Discovery
The antibiotic golden age is the period when the entire antibiotics/antibacterial drug spectra were discovered and almost all the bacterial infections were treatable with these drugs. In this period bacterial infections and diseases were considered the diseases of the past (Box 1). The “golden age” of antimicrobial therapy began with the production of penicillin in 1941 to the discovery of nalidixic acid, the progenitor of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics in 1962 [4,7]. Currently, this period has been extended from 1940 to 1990s due to the discovery of newer antibiotics mainly synthetically [4,7]. During the period of two decades, almost all antibacterial spectra with different generations such as β-lactams, tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, aminoglycosides, macrolides, glycopeptides, streptogramines and quinolones with different mechanisms of action on bacteria were introduced in clinical practice [4,7]. And since the “Golden Age” many newer antibiotics/antibacterial agents have been produced either semi-synthetically or synthetically by chemical modifications of pre-existing antibiotics to produce different generations with improved efficacy and broad spectrum of activity (Figures 1 and 2) [4,7].
1.3. Post-Golden Antibiotic Age
Antibiotics are among the most important discoveries of medical science during the golden antibiotic age. During this period physicians could select almost any one of the many available antibiotics to treat the different types of bacterial infections in various patients including the critically sick individuals. However after this period, there


Figure 1. Golden age of antibiotic/antibacterial agent discovery (Adopted from cvm.msu.edu, 2011) [4].

Figure 2. Synthetic tailoring is widely used to create successive generations of antibiotic classes. Scaffolds are colored black; peripheral chemical modifications are colored red. The quinolone scaffold is synthetic, while the other scaffolds are natural products (Adopted from Fischbach & Walsh, 2009) [7].
have been few or no new antibiotics/antibacterial drugs that have been developed or introduced into clinical practice [3,8,9]. Therefore the “safe heaven” of the Golden Age of antibiotic use is over. The problem is further exacerbated by the lack of antibiotic innovations and the reduced investment by the pharmaceutical industry in developing newer drugs due to the fear that a lot of funds can be used in drug development but due to the increased irrational drug use, the resistance can develop before the cost of development of the new drug is recovered [3,8,9]. Also bacteria are developing resistance faster than the available drugs than pharmaceutical companies can develop new ones. Also the widespread irrational use of antibiotics in humans and animals has resulted in the selection of resistant bacterial population patterns that can spread rapidly globally. Also the antibiotic pressure applied to the environment or antibiotic pollution helps to select for bacteria with genes that provide antibiotic resistance by one of several mechanisms. Furthermore, these resistance mechanisms are highly mobile among and between bacterial species. The spread of antibiotic immunity among bacteria is an evolutionary phenomenon mediated by plasmids, transposons, and integrons that carry DNA encoding leading to the production of the attack enzymes, efflux pumps, and other protective devices thus threatening the public health achievements that was attained during the golden antibiotic age [3,4,8,9].
2. CLASSES OF ANTIBIOTICS AND THEIR SITES OF ACTION ON BACTERIA
The different antibiotics/antibacterial drugs have various targets on the bacteria including 1) cell wall and cell membranes, 2) ribosomes, 3) nucleic acids, 4) bacterial cellular metabolism and 5) bacterial cellular enzymes. There many different mechanisms by which these agents inhibits the multiplication and growth, and the destruction of bacteria. Among these include 1) Inhibition of cell wall synthesis such as beta lactams, 2) Disruption of cell-membrane function, 3) Inhibition of protein synthesis (both 50S and 30S) 4) Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis both the DNA synthesis and RNA synthesis and 5) action as antimetabolites (Figure 3) [6,10,11].
The differences in the bacteria and mammalian cells especially the structural and metabolic differences enables the antibiotics/antibacterial agents to cause selective toxicity to the bacterial organisms without causing any damage to the host cells [6,11,12]. Currently there are a number of classes of antibiotics/antibacterial agents that are commonly used in clinical practice to treat bacterial infections (Table 2).
3. ANTIBIOTICS/ANTIBACTERIAL DRUG PROMOTION AND MARKETING
Pharmaceutical drug promotion and marketing is currently a common practice by pharmaceutical companies and their representatives globally (Box 1) [15-18]. Currently pharmaceutical companies spend a lot of money on promotion of pharmaceutical products especially the newer products [15-18]. In most cases, the drug marketing mainly targets health workers especially the prescribers and usually takes four (4) main forms including gifting, detailing such as providing drug samples, clinical trials and advertisements like direct-to-consumer advertising, promotional mailing and sponsoring educational, conferences and promotional meetings such as continuing medical education (CME) (Figure 4) [18,19].
The direct marketing such as the detailing usually involve face-to-face promotional activities towards the health workers and at times involve giving gifts such as textbooks [18-20]. The free medication (drug) samples are given to health workers and this increases the pre-

Figure 3. Classes of antibiotics/antibacterial agents and their modes of action on bacteria (Adopted from Labnotesweek4, 2013) [11].



Table 2. Classes of antibiotics/antibacterial drugs commonly used in management of bacterial infections [6,10,11,13,14].
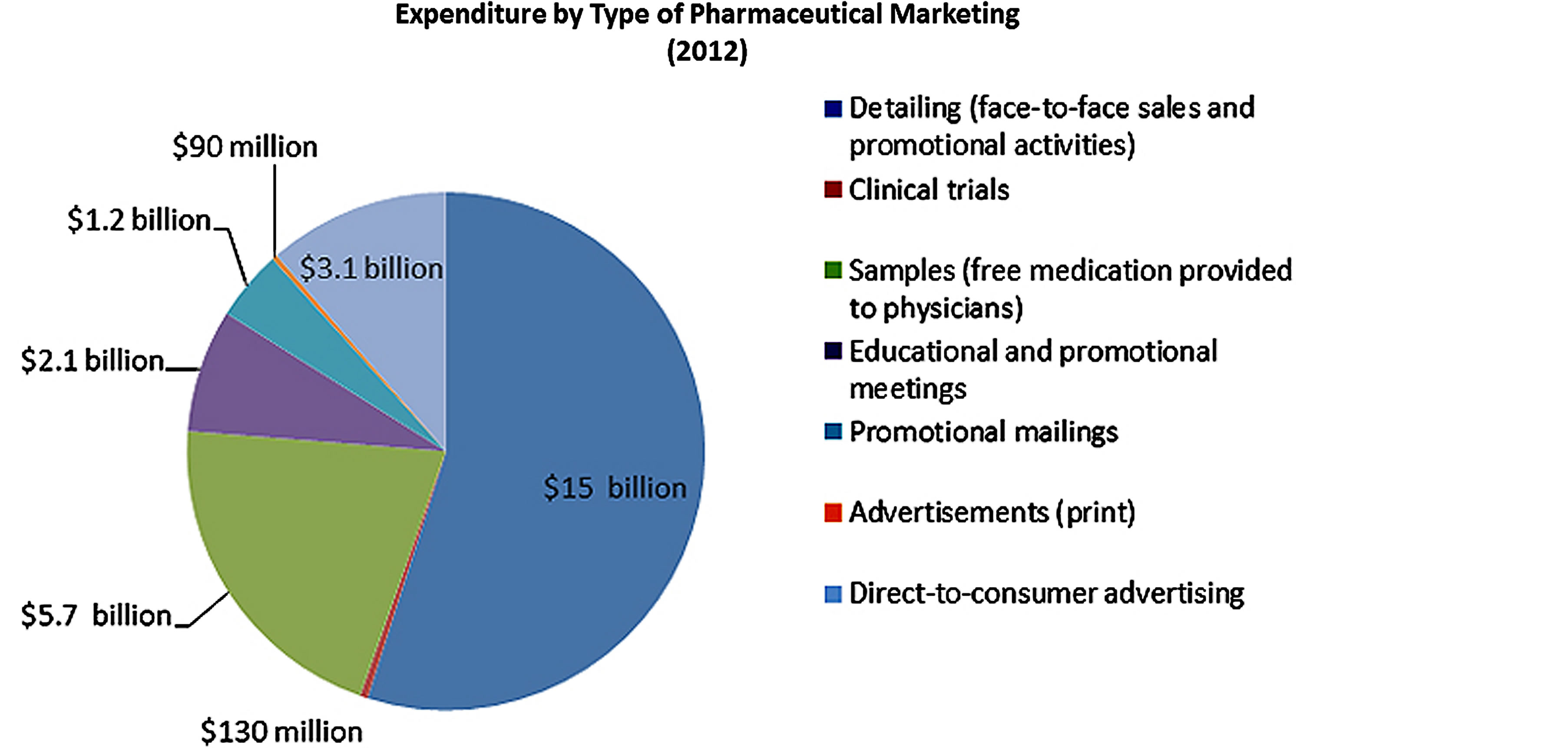
Figure 4. How does the pharmaceutical industry market its drugs and how much does it spend? Source: Cegedim Strategic Data, 2012 US Pharmaceutical Company Promotion Spending (2013). © 2013 The Pew Charitable Trusts [18].
scription of the promoted drugs and hence the exorbitant prescription costs as opposed to the less expensive generic alternative. For the CME, the pharmaceutical sales representatives commonly invite health workers especially the prescribers to discuss specific drugs on promotion on the paid pharmaceutical costs and most cases many pharmaceutical companies spend a lot money on this issue [18,21-24]. The direct-to-consumer advertising has been reported to motivate various patients to demand branded products promoted when the generic medications are available. While the indirect marketing involve CME, and its reported that pharmaceutical companies spend 32% ($752 of the $2.35 billion) of the total funding on CME especially in the USA [18-20]. Also often some funds are provided to patients advocates in forms of grants to recruit massive population with a specific illness especially those with chronic diseases and this in most cases benefit pharmaceutical companies that manufacture medications for their illnesses.
The massive promotion and marketing of new drugs like antibiotics/antibacterial drugs has been reported to contribute to the increased prescribing of the medicines even when the safety profiles of the drug are fully known [18,21-24]. The newer drugs in most cases with trade names are very expensive and some times displace the older and generic drugs that are inexpensive and effective with proven therapeutic outcomes. Whereas the delivery of modern health care services currently involves the introduction of the personalized medicine in the patients care, this greatly requires the involvement of the pharmaceutical industries in the process of drug development and compounding. However, this influences the practice of medicine by the health workers through marketing and promotion [18,19,25].
However, also some prescribers consider promotion of newer drugs, to offer a better prescribing practices and promoting rational drug use. It is also viewed as the only source of information on the drugs and offers improved treatment cost-effectiveness. However, in the global health world, this is viewed otherwise [18,21-24]. In most cases, it is reported that drug promotions are associated with high risks like drug misinformation that is often biased. The selective use of information provided to prescribers and together with the increased global corruption greatly reduces the ability of the health workers to make a weighted decision based on the evidence available and this undermines the use of the effective, inexpensive generic drugs with possibly reduced toxicities [18,19,25]. The increased revenue generated by altered prescribing practices in response to drug promotion is considered by pharmaceutical companies as a direct return on investment and encourages further expenditure on drug promotion, reducing the proportion of the total company budget available for research and development [18,21-24]. In the long run, this has a negative impact on the size of the pipeline of new drugs to deal with the pressing medical problems, resulting in a reliance on drug promotion for revenue generation. Therefore the massive promotion of medicines like antibiotics/antibacterial drugs by the pharmaceutical drug companies and medical representatives increases the volume of the medicines in the healthcare facilities, communities and in the public and this greatly promotes the irrational drug use in both the medical and veterinary practice, food industries and in agriculture leading to the environmental antibiotic residues. The antibiotic drug residues thus continuously enter the environment contributing to antibiotic pollution and these destroy useful bacteria and promote the selection of resistant bacteria that can spread globally and hence contributing continuously to a global health problem.
4. ANTIBIOTIC USE IN POST-ANTIBIOTIC GOLDEN AGE
The antibiotics/antibacterial (AB) drug use during the antibiotic golden age greatly improved the health of humans and animals globally and in 1960’s, most of the bacterial diseases were considered as the diseases of the past but when bacterial resistance was noticed, the thinking changed and currently bacterial resistance is of great public health concern globally. AB have long been used to treat bacterial infections in both humans and animals, in tissue cultures, growth promoters by farmers though however in some countries especially in the developed world, the use of antibiotics as growth promoters has been discouraged in favor of other alternatives that do not promote bacterial resistance. They are also used as food preservatives in the food industries and in commercial ethanol production in breweries. And because of their wide use globally, the high AB demand during the postantibiotic golden age has lead to an increase in massive production of these drugs. It is estimated that about 100,000 tons of antibiotics are produced globally [2-4,6]. This has also contributed to easiness of AB accessibility to even the non-healthcare providers such as the patients, consumers and the communities. The poor regulation and corruption especially in developing countries have contributed to irrational drugs use coupled with the increased pharmaceutical marketing and promotion of these drugs. Self-medication with the antibiotics/antibacterial drugs is a global problem that has also greatly contributed to the emergence of drug resistance to bacterial infections which were treatable by the same drugs [26]. It is a common problem and it’s exacerbated by the increased marketing and promotion of these drugs directly to the consumers. Also the global increased access to internet has made many people able to access information on health care issues, various types of medicines such as antibiotics/antibacterial drugs by both health professionals and non-professionals and this has worsened the irrational AB use. And as a result, in some cases the antibiotics/antibacterial drugs are used in nonbacterial infections and diseases such as viral infections like flu and most especially the acute respiratory viral infections. The global increase in irrational antibiotics in humans and animals have resulted in increasing selection of antibiotic resistant bacterial organisms that also has resulted in reduced pharmaceutical companies investing in production of newer and effective drugs [27]. According to the Center for Disease Control and prevention(CDC), approximately 70 percent of the bacterial infections, the humans get in hospitals, are resistant to at least one antibiotic [28,29]. And currently, antibiotics resistance has outpaced the production of new antibiotic/antibacterial drugs required for the treatment of the life threatening bacterial diseases in both humans and animals [28,29].
Environmental Antibiotics/Antibacterial Drug Pollution and Selection of Resistant Bacteria
Global antibiotic production and sales, total more than 50 million pounds annually of which 25 million pounds are prescribed for human use and the rest used on agriculture, veterinary practice, food industries and commercial ethanol production [29-31]. The dispensing of antibiotics in medical health care facilities like hospitals with poor disposable facilities contributes to the antibiotic/antibacterial medical waste that is discharged in the environment leading to selection of resistant bacteria in the environment. The drug residues are discharged in sewage or landfill daily by humans and others from animals and food industries where they eventually enter the environment causing environmental pollution and hence affect the environmental bacterial organisms as well as promoting the growth of resistant bacterial organisms some of which are pathogenic to humans and animals. Many resistant bacterial infections to various antibiotics/ antibacterial drugs have been documented in nature and in some human pathogens. Also the discharge of antibiotic/antibacterial drugs by the pharmaceutical plants and from the various healthcare facilities like hospitals and industries in waste water and various water bodies have been associated with an increase in the selection and the prevalence of singleand multiple-antibiotic resistance in indicator organisms. The antibiotics and antibacterial agents are added to the environment at a rate of over a million pounds per week by several routes including the non-metabolized antibiotics in excreta like feces and urine from both human and animal bodies into the sewerage or waste water treatment plants (Figures 5 and 6) [29,32,33]. However, many of these antibiotics especially the natural substances are rapidly degraded in the environment while the synthetic antibiotics like quinolones undergo varying degrees of biodegradation and photodegradation [33-37]. In the environment, some of the microbiotas are destroyed by the antibiotic/antibacterial drug residues thus affecting the microenvironment as well as selection of resistant bacterial organisms (Figure 5).
It is reported that about 46.4% of the bacteria from the sewerage plants, hospitals and pharmaceutical plants are resistant to multiple antibiotics [29-31]. The water bodies like the rivers, ponds, lakes, seas, oceans and other water channels get contaminated with antibiotic resistant bacteria from contaminated antibiotic urban effluents and agricultural water runoff [29-31]. The antibiotics/antibacterial drugs enter the environment in a complex vicious cycle. The bacterial organisms in the environment get exposed to sub-therapeutic antibiotic concentrations from excessive overuse of antibiotics and hence promoting the development of antibacterial resistant mechanisms that spreads in many organisms in the environment. This then can spread globally thus threatening the lives of both humans and animals [38-40]. They can also affect the microbiota in the ecosystem leading to the disruption of the various environmental cycling of the organic matter and the resistance is also transferred to animals and to human pathogens. They also cause alterations of the bacterial flora both in sediments and in the water column [41].
5. MASSIVE IRRATIONAL ANTIBIOTICS/ANTIBACTERIAL DRUGS USE AND THEIR ROLE IN EMERGENCE OF ANTIBACTERIAL RESISTANCE IN POST-ANTIBIOTIC GOLDEN AGE
The increased irrational antibiotic/antibacterial drug use worldwide in medical and veterinary practice, communities, farmers, agriculture especially in tissue culture, food preservative in food industries, ethanol production in breweries, self-medication and increased pharmaceutical marketing and promotion has led to post-antibiotic golden age antibacterial resistance which is a global problem the world is facing today. This has lead to serious
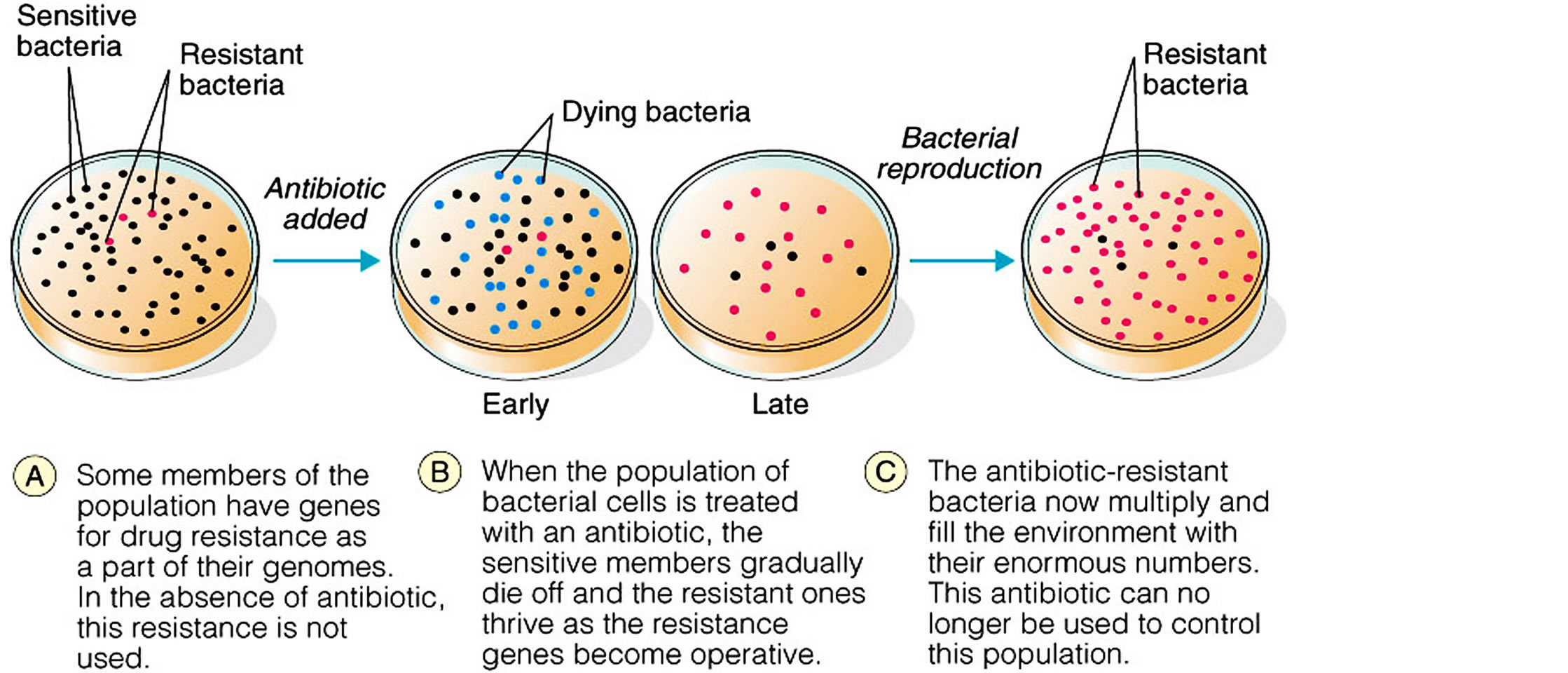
Figure 5. Selection of microbial resistance.

Figure 6. Epidemiology of Antimicrobial Resistance in the environment (Adopted and modified from Linton (1977) by Rebecca Irwin, Health Canada (Prescott, 2000) and IFT with permission) [42].
environmental antibiotic/antibacterial drug pollution leading to destruction of useful bacteria and selection of resistant bacterial organisms. The antibiotic resistant bacterial organisms are selected from the several populations of bacteria in the environment mainly by horizontal gene transfer mechanisms, development of resistance mechanisms that then spread to both humans and animals globally causing severe bacterial diseases that contribute to high morbidity and mortality (Figures 7, 8 and Table 3).
Several mechanisms have evolved in bacteria which confer them with antibiotic resistance and they include inactivation, rapid physical removal of the drug from the cell, or modifying the target site (Box 1) [43-49]. Antibiotic resistance arises in two ways by inherent trait or naturally resistant organisms and through acquired means where there is mutation in DNA or acquisition of resistance from other sources of DNA [43-49]. The intrinsic or inherent or natural resistance is due to lack of target sites or molecules for the antibiotic to bind and lack of transport system for an antibiotic into the organisms [43-49]. The acquired resistance arises by either modifying the existing genetic material or the acquisition of new genetic material from another source [43-49]. And once resistant genes have developed, they are transferred directly to all the bacterial progeny during DNA replication in the process of vertical gene transfer or vertical evolution. In this way, the wild type (non mutants) bacteria are killed and the resistant mutant survives and grows. The horizontal gene transfer is another mechanism beyond spontaneous mutation that is responsible for the acquisition of antibiotic resistance. Lateral or horizontal gene transfer (HGT) is a process in which the genetic material contained in small packets of DNA can be transferred between individual bacteria of the same species or even between different species [43-49]. The spread of antibiotic immunity among bacteria is an evolutionary phenomenon mediated by plasmids, transposons, and integrons that carry DNA that encodes attack enzyme, efflux pumps, and other protective devices (Table 3) [43-49]. Spontaneous mutations that are selected, favors spread of antimicrobial resistance that are stably inherited by daughter cells following cell division and such genes can escape from the chromosome into plasmids, transposons, or integrons that may occur as mobile genetic elements which can be disseminated into similar or dissimilar species through the process of conjugation, transduction and transformation (Figure 7), and in these processes the resistant genes are shared among bacteria and they can stay long in the environment [13,50-52].
Bacterial organisms can acquire resistance through different mechanisms such as [13,50-52]: 1) Conjugation where bacteria can fuse and exchange plasmids and some
times chromosome fragments. The plasmids have a broad host range and are able to cross genus lines during the gene transfer. 2) Transfection or transduction is where viruses can infect bacteria and fungi, passing along genes from one infected organism to the next (phage). These genes sometimes encode resistance factors. The use of antibiotic growth promoters in animal husbandry may increase the amount of free phage in the gastrointestinal tract that may contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance. 3) Transformation is where a bacterium lyses in its environment such that some of the actively-growing bacteria in that vicinity can pick up its DNA leading to antibiotic resistance that can spread in the bacterial population due to plasmids such as R plasmids that are more easily used by the recipient bacterium than chromosomal material (Table 3 and Figures 7, 8) [29,30].
The acquired resistance genes cause the bacterium to express the various resistance mechanisms as a way to avoid the antibiotics exposed to them. The various mechanisms of acquired resistance expressed by bacterial include [13,14,47,52,54,55]: 1) the presence of an enzyme that inactivates the antimicrobial agent or enzymatic alteration of the antibiotic 2) metabolic bypass of the targeted pathway or the presence of an alternative pathway for the enzyme that is inhibited by the antimicrobial agent 3) a mutation in the antimicrobial agent’s target, which reduces the binding of the antimicrobial agent or drug sequestering by protein binding 4) posttranscriptional or post-translational modification of the antimicrobial agent’s target, which reduces binding of the antimicrobial agent or modification of targets 5) reduced uptake of the antimicrobial agent 6) active efflux of the antimicrobial agent or active pumping of drugs out of the cell 7) overproduction of the target of the antimicrobial agent (Figure 8 and Table 4).

Figure 8. Mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in bacteria and the various antibiotic resistance strategies (Adopted from Kenneth Todar, 2011; Sara Wilcox, 2013, Encyclopædia-Britannica, 2013) [14,52,54,55].

Table 3. Characteristics of different elements involved in resistance gene spread [13,50-52].


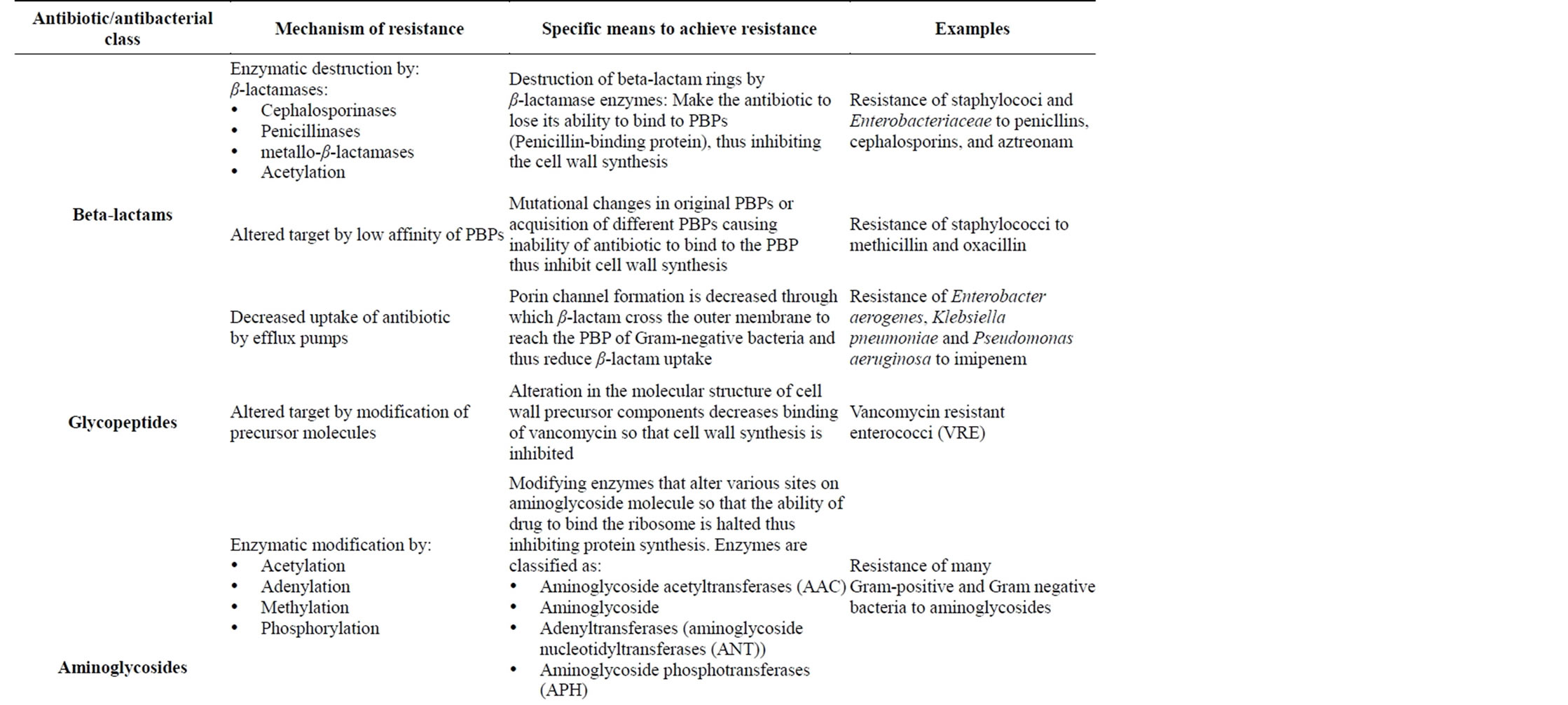
Table 4. Mechanisms of resistance against different antibiotic/antibacterial drugs [44,45,47,48].
6. POST-ANTIBIOTIC GOLDEN AGE EFFECTS AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES TO THE GLOBAL PUBLIC HEALTH
Currently global health is being threatened by the increased emerging bacterial resistance to the commonest bacterial infections against antibiotic/antibacterial drugs that used to be effective during the antibiotic golden age as a result of increased irrational drug use as well as the rise in the marketing and promotion of these drugs. These have promoted the emergence of resistant bacterial such as multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) and extremely drug resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA or golden staph), Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci (VRE) and many other common bacterial infections [28,56,57]. The emergence of bacterial resistance during the post-antibiotic golden age has affected the global health by [28, 56-58]: 1) reduction in the quality of the drugs thus leading to increased morbidity and mortality; 2) wastage of resources to non-essential drugs that are expensive [59]; 3) rampant increase in adverse drug reactions especially those on the second-line or third-line drug therapies; 4) increased treatment failure rate leading to prolonged hospitalization and higher cost; 5) There is increased death due to resistant bacterial diseases and it has been reported that more than 25,000 people in Europe die annually due to resistant bacterial infections [27]; 6) The treatment of resistant bacterial infections drains scarce resources especially in the poor developing nations of the world; 7) Various people in the communities may tend to believe that there is “a pill for every illness” hence increasing the demand for the drugs; 8) The prolonged use of antibiotics especially the broad spectrum antibiotics destroys body normal flora and hence individuals become susceptible to opportunistic infections [40,60,61]. And in animals like humans, there are many other consequences including the following [38,62-66], 1) Poor health, growth and production of the animals. 2) Increased emergence of resistant zoonotic bacterial diseases. 3) Increased economic loss to countries that rely on animal production. 4) There are increased levels of malnutrition due to lack of nutrients from animals foods especially in poor developing nations [67].
7. CONCLUSION
The antibiotic/antibacterial drugs significantly improved the health of both humans and animals and they revolutionized the control and treatment of bacterial diseases for more than 50 years during the antibiotic golden age. However the trend changed during the post-antibiotic golden age when the emergence of antibiotic resistance threatened the global health as a result of increased irrational AB use due to their increased marketing and promotion by the pharmaceutical industry to the various healthcare facilities and communities thus making these medicines easily accessibe. Also it leads to the displacement of the low cost efficacious generics and favors the very expensive proprietary drugs. The lack or poor regulation of the use of these drugs coupled with increased levels of corruption by various government authorities especially in the developing countries has led to massive irrational use of these drugs. The massive use of antibiotic/antibacterial drug in the medical, veterinary practice, food industries, agriculture and commercial ethanol production and increased production of these drugs globally has also contributed to the environmental antibiotic pollution leading to destruction of useful bacteria and favoring the selection of resistant bacteria thus affecting the global health. Therefore there is an urgent need of the collective effort among all the stakeholders including the pharmaceutical industry, the general pubic to be sensitized on the rational drug use and its consequences especially the resistant bacteria that is threatening the global health.