Fixed Dose Combination of Magaldrate Plus Domperidone Is More Effective than Domperidone Alone in the Treatment of Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms: A Randomized Double-Blind Study ()
The current medical management of gastroesophageal reflux includes the prescription of antiacids, sodium alginate, prokinetics, H2-receptor antagonists or proton pump inhibitors, coupled with lifestyle advice [8,9]. Acid suppression is the main objective to treat gastroesophageal reflux, and proton pump inhibitors are the first-line therapy for their potency. However, 20% - 42% of patients treated with proton pump inhibitors fail to response symptomatically to these drugs [10,11]. In patients who failed proton pump inhibitors twice daily, medical treatment is focused in treat disordered gastroesophageal motility including reduced lower esophageal sphincter pressure, ineffective esophageal motility and delayed gastric emptying by using prokinetics [12,13].
Domperidone is a dopamine antagonist with antiemetic and gastroprokinetic properties. It promotes gastric emptying of several types of liquid and solid meals [14] without interfering with response of antiparkinsonism treatment [15]. Furthermore, domperidone provides relief of symptoms in patients with dyspepsia or gastroesophageal reflux in controlled clinical trials [16,17] such as regurgitation [18]. Additionally, domperidone shows controversial results to improve the efficacy of omeprazole in gastroesophageal reflux [19,20], and it fails to show any additional benefit combined with ranitidine [21].
Although prokinetics agents are usually used in combination with acid suppression agents such as antiacids, the evidence of a superior efficacy of domperidone plus antiacids combinations is scarce but consistent. In these studies, domperidone increases the efficacy of magnesium hydroxide and alumminium hydroxide [22] and reduces the amount of alginate required in gastroesophageal reflux [17,23]. However, there are not comparative studies between domperidone alone and domperidone plus magaldrate, an antiacid effective in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux [24].
For the reasons above described, the current study was focused to determine the efficacy and safety of chewable tablets of magaldrate plus domperidone in comparison with an equal formulation of domperidone alone, in patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Subjects
To determine whether magaldrate improved therapeutic profile of domperidone in patients with gastroesophageal reflux, one hundred volunteers (41 males and 59 females) were recruited to perform a double-blind, randomized and comparative clinical study. A comparison of the demographic data of the volunteers is shown in Table 1. All subjects included in the current study presented symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux disease according to Carlsson questionnaire [25] and were over 18 years old. In addition, the health status of patients was determined by medical history, clinical examination and suitable laboratory tests. If patients had alarm symptoms, a documented ulcer disease, gastric surgery, gastric cancer or severe concomitant medical conditions were excluded from the study. This study was carried out following the recommendations of the latest version of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki-Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects [26]. All participants read the protocol, which was approved by the Institutional Research and Ethics Committees of the Hospital General Culiacán, “Dr. Bernardo J. Gastélum (Sinaloa, Mexico) and Mexican Federal Commission for Protection against Health Risks (CAS/ OR/01/CMN/103300410B0480-0017/2011), and provided written informed consent for their participation in the study.
2.2. Study Design
After obtaining written informed consent, patients were randomly allocated to one of 2 groups to receive a chewable tablet to a fixed dose either of domperidone alone (10 mg) or magaldrate/domperidone combination (800 mg/10 mg) before each meal, and one more before
going to bed, during 30 days. All chewable tablets were provided by Productos Medix, S.A. de C.V. (Mexico City, Mexico). Each gastroesophageal reflux symptom was evaluated at 0, 15 and 30 days of pharmacological treatment by patients using a six-point Likert scale that had the words: absent (0), very mild (1), mild (2), moderate (3), severe (4) and very severe (5). The symptoms assessed were esophageal (pyrosis, regurgitation, dysphagia, hiccup, gastroparesis, sialorrhea, globus pharyngeus and nausea) and extraesophageal (chronic cough, hoarseness, asthmatiform syndrome, laryngitis, pharyngitis, halitosis and chest pain), and the severity of gastroesophageal reflux was measured adding the score obtained in each symptom.
Moreover, a quality of life questionnaire was applied to patients consulting symptoms frequency, eating disorders, sleep disturbances, job productivity and other medications required at 0, 15 and 30 days of treatment. Frequency was evaluated by a four-point Likert scale that had the words: never (0), sometimes (1), frequently (2) and always (3). The life quality questionnaire has a maximum of 15 points. At the end of the treatment, a global satisfaction scale of pharmacological treatment was filled out by the patients. In addition, adverse events reported by patients were also recorded.
2.3. Data Analysis
Data were grouped by treatment. Potential differences of demographic data between groups were assessed by Student t-test or χ2 tests. Statistical analysis of the timecourse obtained from gastroesophageal reflux symptoms or life quality was performed by Kruskall-Wallis followed by the Dunn’s test. The score of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms or life quality was obtained adding the points of each item. Patient perception of global assessment of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms relief was evaluated by χ2 test. Differences were considered statistically significant when P ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
Demographic data on the patients are shown in Table 1. Domperidone alone and magaldrate/domperidone mixture groups were equilibrated regarding treatment, sex, age, weight, height and Carlsson scale values, and there were no violations to the protocol that may have interfered with the study variables. There were 59 female and 41 male and the mean ± standard deviation age was 36.8 ± 9.6 years with a range of 18 to 58 years. The predominant esophageal symptoms in patients were pyrosis in 100%, regurgitation in 93%, nausea in 67% and dysphagia in 42%, the rest of esophageal symptoms had a percentage below 40%. On the other hand, the main extraesophageal symptoms were chest pain with 43%, halitosis with 37% and pharyngitis with 33%, other extraesophageal reflux symptoms were present at less than 20% of patients.
3.2. Efficacy and Safety of Domperidone Alone against Magaldrate Plus Domperidone Combination
Baseline mean total reflux symptoms scores were 15.25 ± 1.90 for domperidone alone and 15.75 ± 1.57 for the mixture of magaldrate plus domperidone. Both treatments produced a gradual reduction of total reflux symptoms values in a dependent manner of time, but only the time course of the group treated with magaldrate plus domperidone showed a diminution significantly different (P ≤ 0.05 by Kruskall-Wallis, followed by the Dunn’s test) than its respective control group. In addition, magaldrate/domperidone group had a significantly superior efficacy to domperidone group at 15 and 30 days (Figure 1).
When the symptoms were sub-classified according with the symptom origin in esophageal and extraesophageal symptoms. The results of esophageal symptoms for the domperidone alone and magaldrate/domperidone groups were quite similar to those previously described in the analysis of total reflux symptoms. Again, domperidone group showed a tendency to decrease the symptoms, but it was not enough to reach a statistically

Figure 1. Time course of total gastroesophageal reflux symptoms obtained during thirty days in patients that received either domperidone alone or magaldrate/domperidone combination. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *Significantly different from respective control group at time 0 and #significnatly different from domperidone group at the same time (P ≤ 0.05), as was determined by KruskallWallis followed by the Dunn’s test.
difference, whereas the group of magaldrate/domperidone reduced in a significant manner (P ≤ 0.05) the esophageal symptoms at 15 and 30 days and was more effective than domperidone group at 15 days (Figure 2(a)). On the other hand, domperidone group did not show any tendency to improve the extraesophageal symptoms, but magaldrate/domperidone group significantly (P ≤ 0.05) decreased the extraesophageal symptoms more than 50% at 15 and 30 days (Figure 2(b)).
After symptom by symptom analysis, it was revealed that the tendencies showed by domperidone group in the previous results was due to that domperidone reduced significantly (P ≤ 0.05) the regurgitation symptom at 15
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 2. Time course of esophageal (a) and extraesophageal (b) reflux symptoms obtained during thirty days in patients that received either domperidone alone or magaldrate/domperidone combination. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *Significantly different from respective control group at time 0 and #significnatly different from domperidone group at the same time (P ≤ 0.05), as was determined by Kruskall-Wallis followed by the Dunn’s test.
and 30 days (31.6% ± 10.4% and 44.4% ± 10.4%, respectively), as well as, nausea at 30 days (45.6% ± 14.8%), whereas, magaldrate/domperidone group improved mainly and in a significant manner (P ≤ 0.05) pyrosis (71.9% ± 7.3% and 81.3% ± 6.6%), regurgitation (56.7% ± 9.8% and 58.5% ± 6.5%) and nausea (55.8% ± 12.8% and 68.0% ± 14.1%) within esophageal symptoms, and laryngitis (86.3% ± 9.1% and 100%) and pharyngitis (75.0% ± 12.6% and 80.9% ± 13.2%) as extraesophageal symptoms at 15 and 30 days, respectively.
Respect to life quality questionnaire, domperidone group showed only a tendency to increase the life quality of patients (Figure 3); however, it was able to decrease statistically (P ≤ 0.05) eating disorders (49.7% ± 12.7%) at 30 days. On the contrary, magaldrate/domperidone group improved significantly (P ≤ 0.05) the life quality of patients respect to its own control and respect to domperidone group in both times of evaluation (Figure 3). Consequently, this group reduced in a significant manner (P ≤ 0.05) the symptoms frequency (51.9% ± 4.6% and 51.7% ± 6.3%), eating (45.8% ± 11.4% and 33.3% ± 11.4%) and sleep disturbances (35.3% ± 16.7% and 79.8% ± 7.4%) and requirement of other medications (75.0% ± 11.9% and 42.6% ± 17.4%); likewise, it also increased job productivity (53.8% ± 15.3% and 91.2% ± 6.1%) at 15 and 30 days.
The global profile of pain relief perception favored to the group treated with the combination. A significant greater number of patients under treatment with magaldrate plus domperidone had a good perception of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms relief (n = 14) in

Figure 3. Time course of quality life reported during thirty days by patients that received either domperidone alone or magaldrate/domperidone combination. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *Significantly different from respective control group at time 0 and #significnatly different from domperidone group at the same time (P ≤ 0.05), as was determined by Kruskall-Wallis followed by the Dunn’s test.
comparison with patients treated with domperidone alone (n = 6) (Table 2).
Both treatments were well tolerated, since only six patients were withdrawn from the study, four for lack of efficacy and two for adverse events. A subject in the domperidone alone group was withdrawn for emesis and three for lack of efficacy, whereas that in the magaldrate/domperidone group was withdrawn a subject for mastalgia and galactorrhea and one more for lack of efficacy. Other adverse events reported by patients were mild, including two events of headache and one of diarrhea in the domperidone group, and two of dizziness, one of allergic rhinitis and one of constipation in the combination group.
4. Discussion
Domperidone is a peripheral dopamine D2-receptor antagonist, commonly used to treat regurgitation and vomiting due it increases motility and gastric emptying and decreases postprandial reflux time. However, the evidence of its efficacy in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms continues being scarce and questioned, mainly in infants and children [27].
In this study, oral administration of chewable tablets of 10 mg domperidone four times each day during 30 days, reduced in a significant manner regurgitation and nausea esophageal symptoms, as well as, eating disorders. Notwithstanding, it only showed a tendency of improvement in the global gastroesophageal reflux symptoms or the total life quality score. Our data agree with a previous study performed in 23 patients over 8 weeks demonstrated that domperidone is superior to placebo in reducing regurgitation, but had not effect on the incidence of heartburn or on healing of the esophageal mucosa [18]. Similarly, Clara found in thirty-two children aged 2.5 months to ten years with chronic regurgitation and vomiting diagnosed clinically that 0.6 mg/Kg domperidone three times a day improved symptoms in a good or excellent manner in 93% of the patients compared with 33% of the controls [28]. In the same way, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial performed in fortyseven children with excessive regurgitation and vomiting associated to gastroesophageal reflux showed that 0.5 mg/kg domperidone abolished completely vomiting in 75% of patients, compared with 43% in the metoclopramide group and 7% in the placebo group after 2 weeks of treatment [29]. On the contrary, Carrocio et al. reported that 0.3 mg/Kg domperidone was no significant different to placebo, after eight weeks of treatment, in the degree of improvement of pH metric variables of pediatric patients with severe gastroesophageal reflux [22]. Summarizing, domperidone seems to improve regurgitation and vomiting of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, but fails in reduce other symptoms or modify pH values. For this reason, it is probable that domperidone mainly exerts its activity regulating disordered gastroesophageal motility [12,13,17].
On the other hand, the mixture of 10 mg domperidone/800 mg magaldrate produced a better therapeutic profile to significantly increase the quality of life and to reduce the intensity of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms respect to domperidone group. In line with these results, a previous randomized double blind clinical trial showed the existence of an additive effect between domperidone and omeprazole, since the combination was superior in efficacy respect to monotherapy with omeprazole in sixty dyspeptic patients with heartburn and/or regurgitation that received the treatments for 2 weeks [19]. Although, other studies point out that domperidone is not able to improve the efficacy of omeprazole [20] or ranitidine [21] in the treatment of esophageal reflux. Independently to the above described studies, domperidone and antiacid combinations seem to give results more consistent and they are according with the current study. So, a doubleblind randomized study showed that domperidone plus magnesium hydroxide and aluminium hydroxide was superior to domperidone plus alginate, domperidone alone or placebo in the control of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in 80 children treated for 8 weeks [22]. Moreover, in a 4-week study in 22 patients with reflux esophagitis was demonstrated that domperidone reduced the amount of alginate-antiacid required when compared
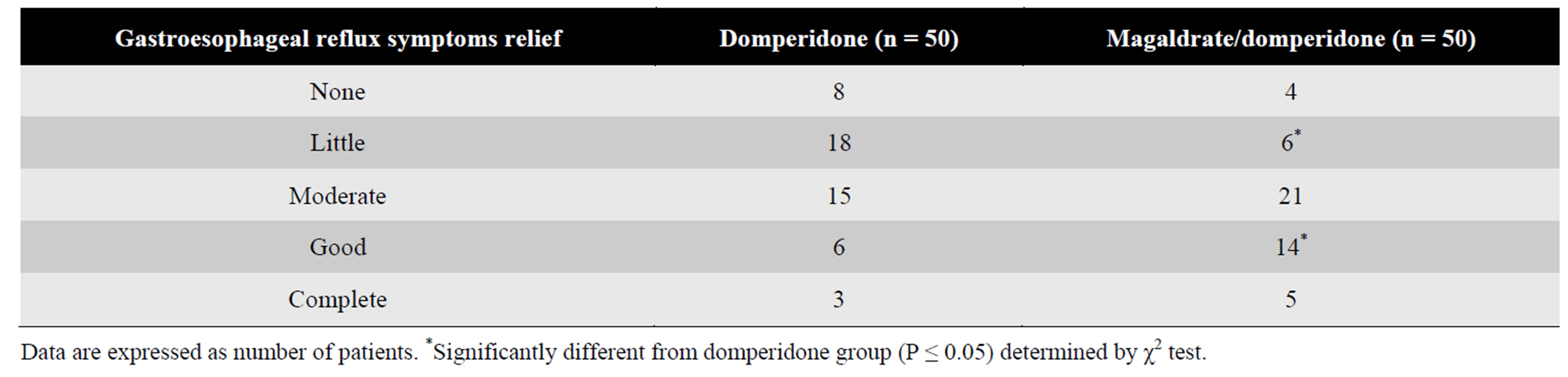
Table 2. Patient’s perception about gastroesophageal reflux symptoms relief at the end of treatment.
with placebo [17,23]. Results suggest that the combination of domperidone/magaldrate is better in gastroesophageal reflux symptoms relief than domperidone alone. It is fair to say that, although the literature suggests that domperidone may improve the efficacy of antiacids drugs to treat gastroesophageal reflux, the prescription of these combinations should be given carefully in patients with cardiovascular disorders and children, since recent evidence points out that domperidone prolongs QTc interval increasing the risk of sudden cardiac death [30,31].
The better therapeutic profile of domperidone/magaldrate combination therapy versus domperidone alone to increase life quality and reduce the intensity of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms could be related to the addition of the different action mechanisms of the drugs. In the case of domperidone, there is evidence that this drug increases the amplitude of esophageal motor function, enhances antral-duodenal contractions and coordinates peristalsis across the pylorus with the subsequent acceleration of gastric emptying [32], due it has a high affinity for gastrointestinal tissue and high concentrations of the drug are found in the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine [33]. Its prokinetic activity is mainly attributed to stimulation of gastrointestinal transit through antagonism of D2-dopamine receptors localized on post-synaptic cholinergic neurons [34]. In addition, domperidone exerts its antiemetic activity inhibiting the chemoreceptor trigger zone, which is on the blood side of the blood-brain barrier in the fourth ventricle [17]. On the other hand, the magaldrate efficacy in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux could be mainly attributed to its ability to rise rapidly and consistently the intragastric pH [22,35]. However, other studies have reported that magaldrate is also able to inactivate pepsin and binding to bile acids and lysolecithin, aggressors in case of gastroesophageal reflux [35,36]. Furthermore, magaldrate activates other gastroprotective mechanisms, such as, increment in gastric mucus secretion [37], stimulation of endogenous prostaglandin E2 [38] and protection of gastric mucosa of lipid peroxidation [39].
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, the data suggest that the combination of magaldrate/domperidone produces a greater efficacy in the reduction of esophageal and extraesophageal reflux symptoms, as well as a better life quality and relief perception than domperidone alone, in patients with gastroesophageal reflux symptoms. Data indicate that the combination of magaldrate/domperidone could be a better option than domperidone alone in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux symptoms, mainly in refractory patients to pump proton inhibitors without cardiovascular disorders. Notwithstanding, the main limitation of the current study is its sample size, so larger double-blind clinical trials are needed to confirm this possibility. Furthermore, this study was performed to determine the superior efficacy of magaldrate plus domperidone combination over domperidone, but it does not give evidence of action mechanism involved in the interaction. For this reason, it is lacking a pharmacodynamic clinic study to explain this issue.
Aknowledgements
Authors kindly akcnowlegde Productos Medix, S.A. de C.V., Mexico City, Mexico for the formulations provided for this study. This work is part of the M.Sc. thesis of Shendel Nyx Rodriguez-Sanchez.
NOTES