On the State of Stress in the Growth Plate under Physiologic Compressive Loading ()
1. Introduction
The growth plate, a cartilage plate separating the metaphysis from the epiphysis at each end of a long bone (Figure 1A), is responsible for the longitudinal growth of bone. It consists of chondrocytes embedded in an abundant extracellular matrix (ECM) [1]. The growth plate is composed of a cartilaginous component that has three histologically distinct zones: reserve or germinal, proliferative and hypertrophic [2] (Figure 1B). The longitudinal growth of bones is controlled by the rate of chondrocytic proliferation and the amount of chondrocytic enlargement (hypertrophy) in the growth direction [3]. From the epiphyseal side nutrients are provided by the epiphyseal blood vessels passing through the germinal zone and terminating at the proliferating layer and then progress through the growth plate via diffusion [4]. On the metaphyseal side vascular loops penetrate into the spaces of dying hypertrophic chondrocytes to provide nutrients for the osteoprogenitor cells producing bone on the primary spongiosa cartilage scaffolds.
The existence of chondrocytes in a soft collagen rich ECM nestled between calcified bones and subjected to significant mechanical loads render the growth plate to be a mechanobiological structure, which is highly sensitive

Figure 1. (A) Radiograph of a 1-inch coronal slice through the proximal tibial growth plate of a 5 month-old calf. Primary mamillary processes can be seen towards the left and right borders with the secondary mamillary processes just barely visible; (B) Histological zones of the proximal tibial growth plate of a 4 - 5 month-old calf.
to mechanical factors as well as biochemical signals. Broad laws have been proposed to govern bone modeling and remodeling, and longitudinal growth, such as Wolff’s law and Hueter-Volkmann law [5,6], respectively. Wolff’s law states that bone grows and remodels in response to the forces that are placed upon it. Hueter-Volkmann law states that increased pressure acting on the growth plate retards bone growth and conversely, reduced pressure or even tension accelerates it [3,5,6]. Frost proposed that for stresses not exceeding the physiological range, endochondral bone growth speeds up in the case of compression compared to tension, compression exceeding physiological range slows down or even inhibits growth [7]. It has further been proposed in engineering mechanics language similar to that used to describe failure theories, that hydrostatic pressure maintains cartilage while octahedral shear stress promotes its degradation and ossification [8,9].
Although discrepancies exist between these fundamental laws, it is clear that mechanical loading can modulate bone growth. This phenomenon has key implications in infant and juvenile pathological progressive musculoskeletal deformities, such as idiopathic scoliosis, bowlegs and others [10,11]. Meanwhile, although physiologic levels of compression are essential for bone development, excessive compressive loading may damage the physeal cells in the germinal and proliferative zones and lead to bone growth retardation or cessation causing such abnormalities such as late-onset tibia vara (Blount’s disease) [12]. Clinical treatment of these deformities is often directed at modifying the mechanical environment of the affected bone [1]. However, the compressive injury of the growth plate is clinically invisible and not easily diagnosed at the time of injury and the underlying mechanisms of this type of injury still remain unknown. Despite many studies, our quantitative and physiological understanding of how bone growth is regulated in response to mechanical loading is still limited [1]. Computational models of the growth plate under compression may yield insights into the micro-mechanical environment of the cells in the growth plate, which may help guide diagnoses and develop treatments in the future.
Several studies have reported the compressive mechanical properties of growth plate under different loading conditions using different animal models (Table 1). In this work, we analyzed the mechanical response of macroscopic bovine growth plate samples in uniaxial compression. The aim of this study was to use finite element (FE) analyses to obtain the inherent compressive mechanical properties of the growth plate assuming the cartilage tissue to be homogeneous and isotropic and linearly elastic and to explore the state of stress within this thin cartilage layer. We view this macroscopic model as a first in a series of steps needed to construct a more complete microscopic FE model of the growth plate structure including zonal and cellular details.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Previous Uniaxial Compression Experiments of Macroscopic Samples
Finite element models were developed to simulate uniaxial compression experiments that were previously conducted on bone-growth plate-bone samples prepared from three fresh-frozen 5-month-old calf proximal tibial growth plates [13]. The specimens were cut from four sites in each growth plate: antero-lateral and -medial and postero-lateral and -medial. All 7 × 7 × height mm block samples were prepared so as to maintain the minimum height without encroaching on the growth plate cartilage whilst keeping the orientation aligned with the tibial longitudinal axis. Samples were immersed in protease inhibitor solution and frozen until testing.
Bone/growth plate/bone specimens were first preloaded to 1 N and then compressed at 0.055 mm/min to a gripto-grip strain of 20% and held at this strain until 1400 sec had elapsed and complete stress relaxation had occurred (Figure 2). A schematic structure of sample geometry is shown in Figure 3A. The equilibrium modulus, which can be considered as the elastic modulus at 20% strain level, was calculated for each specimen by dividing the equilibrium stress by the grip-to-grip strain and reported previously [13]. The slopes of these twelve stress-strain curves, which reflect the extrinsic elastic moduli of these samples (EEX), were obtained by curve fitting a straight line to the data between 0 and 20% strain using Matlab (Natick, MA).
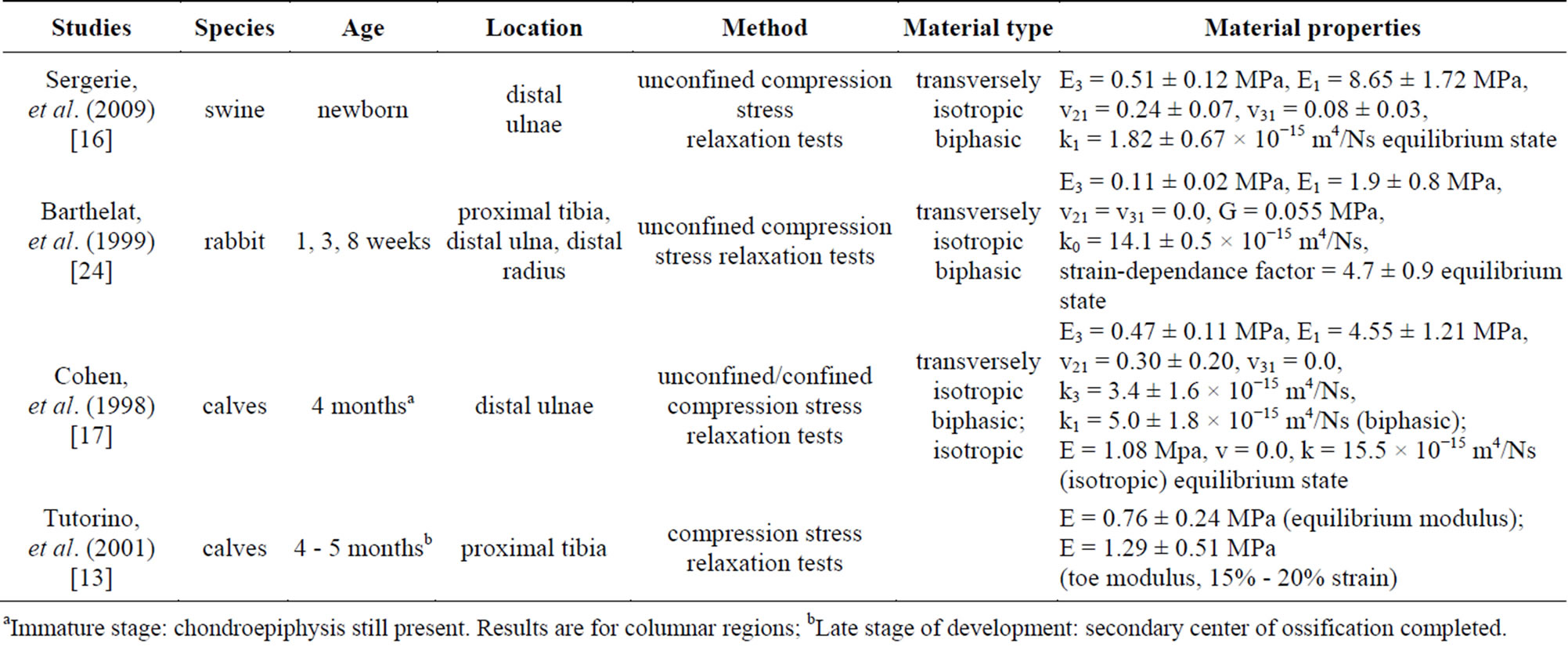
Table 1. Material properties of the growth plate obtained from various experimental modalities.
aImmature stage: chondroepiphysis still present. Results are for columnar regions; bLate stage of development: secondary center of ossification completed.
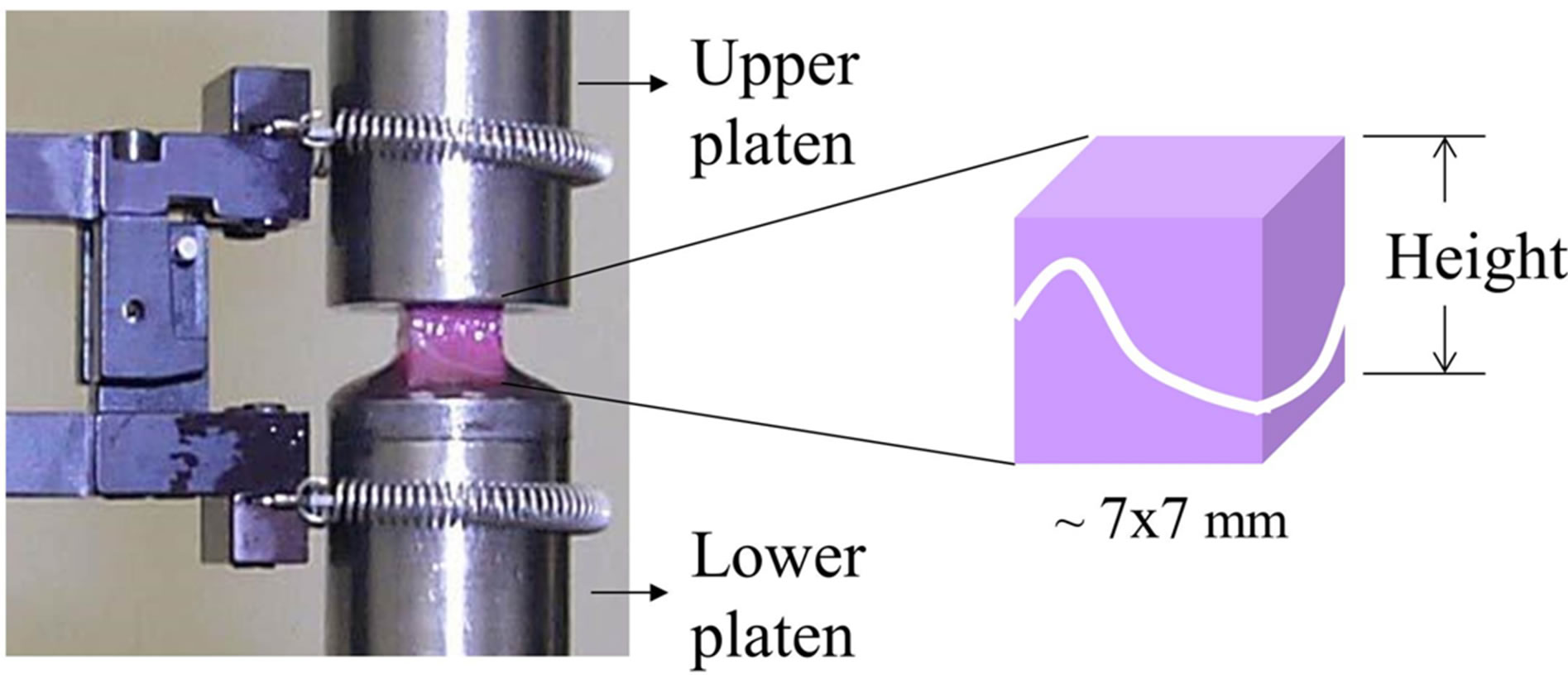
Figure 2. Testing set-up of previous compression experiments. Bone-growth plate-bone sample is held between the compression platens and the upper platen is lowered at a rate of 0.055 mm/min.

Figure 3. (A) Schematic of the experimental sample; (B) Typical finite element model. At least 6069 C3D8R type of elements were used. The XY, YZ and XZ planes are axes of symmetry.
2.2. Inverse Parametric Finite Element Analyses
Twelve FE models were built based on the actual dimensions of individual sample (Table 2) using ABAQUS (Providence, Rhode Island). The FE model shown in Figure 3B, 1/8 of an actual sample, shows the characterization of the bulk response of the growth plate from the uniaxial compression experiments. A homogeneous isotropic linear elastic material was used to model the growth plate cartilage. The Poisson’s ratio of the growth plate was chosen to be 0.45 in this study.

Table 2. Geometrical information of 12 specimens utilized in this study.
Based on material parameters used in previous studies, the elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio of trabecular bone was 100 MPa and 0.3, respectively [14]. Symmetric boundary conditions were implemented in the front, left and bottom surfaces of the model. Displacement control was applied incrementally on the top surface of the model until 20% strain level of the growth plate layer was reached. A mesh convergence study was also performed in order to determine an appropriate element size, especially for the growth plate region. Furthermore, in order to eliminate volumetric locking issues due to the near incompressibility of growth plate, 8 node solid elements with reduced integration formulation were used (C3D8R). Parametric studies were then conducted for each sample where the elastic modulus of the growth plate in the FE model was altered systematically in order to find the optimal fit between the FE simulated and experimental stress-strain curves.
A nominal stress was obtained by dividing the total reaction force, which is sum of the reaction forces at the base, by the initial cross-sectional area. Using this nominal stress, an intrinsic elastic modulus for the growth plate cartilage FE experiment (EIN) was calculated. The equilibrium modulus, which can be considered as the elastic modulus at 20% strain level, was calculated for each specimen by dividing the equilibrium stress by the grip-to-grip strain and reported previously [13]. The slopes of these twelve stress-strain curves, which reflect the extrinsic elastic moduli of these samples (EEX), were obtained by curve fitting a straight line to the data between 0 and 20% strain using Matlab (Natick, MA).
Based on these parametric studies, elastic modulus values for the growth plate cartilage (EIN) that provided the optimal fit between experimental and FE stress-strain curves were determined. The ratio of EIN and EEX was also calculated.
2.2.1. Simulation of Previous Uniaxial Compression Experiments of Macroscopic Samples
When the FE models were constructed, there was no detailed information regarding the internal geometry of these twelve samples. Therefore, the growth plate layer in the FE models was modeled to be flat. However, in order to investigate the impact of topography in the growth plate geometry in our calculated EIN, we constructed additional FE models with different geometrical structures of the growth plate layer, while maintaining all other dimensions and the underlying material properties the same. For comparison with the flat shaped model, we followed a previous study [15] and utilized “n” and “m” shaped growth plate layers (Figures 4A and B), which represent in a simplified manner the shape of secondary mammi-

Figure 4. Topography of the growth plate layer. (A) “n” shaped; (B) “m” shaped, representing the varied interdigitations observed in the test specimens. Photographs of specimens show the secondary mamillary processes after removal of the cartilage and marrow with a solution of bleach (C through E, epiphyseal bone on top).
lary processes found in these tested specimens from the cow (Figures 4C-E). The amplitudes of the modeled n and m shapes were twice the growth plate thickness values. We also computed the dependence of the difference between the EEX and EIN on the shape of growth plate.
2.2.2. Bilayered Growth Plate Model
In order to explore the influence of assuming homogeneity of Young’s modulus through the growth plate thickness on the EIN values derived from the twelve FE models, we constructed a FE model of one sample (#12) using a quarter model of the bone/growth plate/bone structure. The growth plate layer was assumed to be flat, but partitioned into two sections, consisting of the reserve zone and proliferative/hypertrophic zone. The proportion of the overall growth plate thickness or height occupied by the reserve zone (RZ%) was previously determined for each sample by averaging measurements on all four faces of each sample (Table 2). Since the reserve zone has been found to be nearly twice as stiff as the proliferative/hypertrophic zone in the loading direction [16,17], the elastic modulus of the reserve zone was constrained to be twice of the proliferative/hypertrophic zone, whilst the Poisson’s ratio kept the same as in previous models.
3. Results
3.1. Extrinsic Elastic Modulus of the Growth Plate Cartilage from Experiments
Twelve bovine growth plate samples were tested in quasi-static compression [13] and information pertaining to these samples is presented in Table 2. Results of the parametric study for one bovine growth plate sample are shown in Figure 5. The overall height of the compression samples averaged 5.95 ± 1.11 (SD) mm and the growth plate height (GPt) was 0.67 ± 0.09 (SD) mm on average. The average proportion of the reserve zone (RZ%) was 31.33% ± 10.00% (SD). The extrinsic elastic modulus for these samples is 1.11 ± 0.40 (STD) MPa.

Figure 5. Parametric finite element compression simulation of one sample.
3.2. Intrinsic Elastic Modulus of the Growth Plate Cartilage from Inverse FE Experiments
For each experimental sample, we constructed an individual FE model to obtain the underlying EIN. Table 3 shows the EEX and EIN for all twelve samples that underwent the inverse FE analyses. The resulting average EIN for the twelve bovine growth plate samples is 0.36 ± 0.15 MPa, which is about 30% of the EEX computed directly from the experiments. The extrinsic compressive elastic modulus, EEX, was between 2 and 4.4 times the value of the intrinsic modulus, EIN.
3.2.1. Different Growth Plate Topography
We also studied the impact of the topography of the secondary mammillary processes on the difference between EEX and EIN. As the results in Table 4 indicate, the shape of the growth plate does indeed influence the overall mechanical response of the bone/growth plate/bone sample under uniaxial compression and the material parameters. According to these results, the larger the ratio of GPt/height of the sample, the greater the impact of growth plate topography on the difference between EEX and EIN. Based on the results of the three idealized shapes, it shows that the “m” shaped growth plate layer can lead to a greater difference between EEX and EIN for the same sample compared to the “n” shaped one. For example,
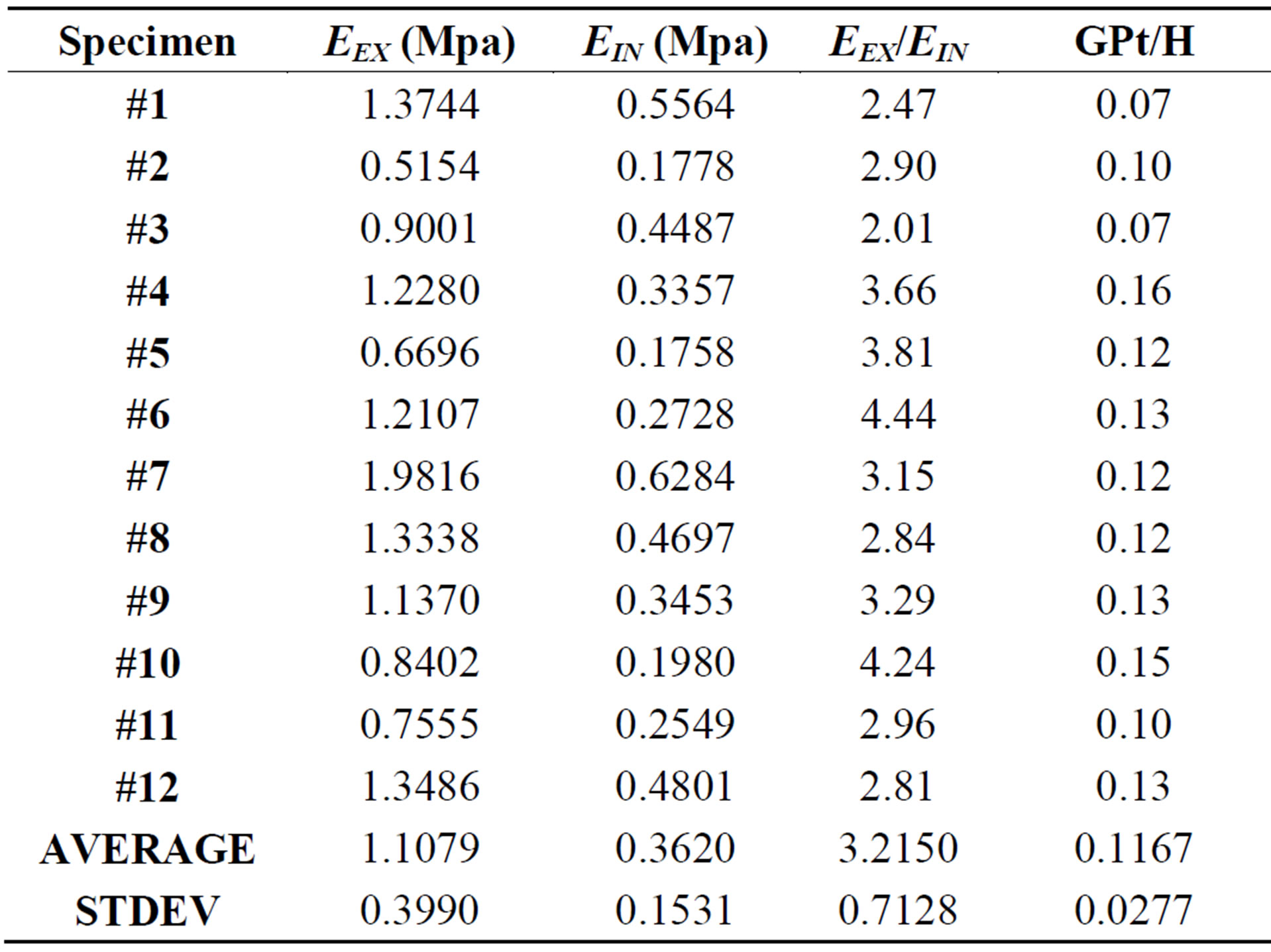
Table 3. Summarized results for twelve specimens.

Table 4. Influence of growth plate layer topography on the ratio (EEX/EIN).
the value for EIN for the “m” shaped growth plate can be 10.5% more than for a flat growth plate of the same height.
3.2.2. Bilayered Growth Plate Model
Recognizing that the growth plate is composed of microscopic features with significant differences between the histological zones, we aimed to refine our model by partitioning the growth plate into two zones. The reserve zone was 34% of the overall height of the growth plate and the elastic modulus, ERZ, was constrained to be twice that of the columnar and hypertrophic zones, modeled by a single layer, EP+H. Using this approach, compressive elastic moduli of the bovine reserve and proliferative/ hypertrophic zones were determined to be 0.74 MPa and 0.37 MPa, respectively.
4. Discussion
In this study, we simulated compression tests on macroscopic bone/growth plate/bone samples to extract the intrinsic elastic modulus of bovine growth plate cartilage using parametric inverse FE analyses. The extrinsic elastic modulus was approximately 3 times greater than the estimated intrinsic growth plate cartilage elastic modulus. However, since we found a strong correlation between EIN/EEX and sample height: EIN/EEX = −0.071 + 0.067* height (R2 = 0.95, p < 0.0001) further discussion is warranted.
4.1. Triaxial Stress State during Growth Plate Compression
The intrinsic elastic modulus values we computed are in general lower than those previously reported [1,18]. Part of the reason for this discrepancy is that the triaxial state of stress present in a thin layer of soft material sandwiched between stiffer materials is usually not accounted for when the elastic modulus is calculated from uniaxial compression tests. This triaxial state of stress is known to exist in thin flat test samples that are constrained from lateral displacement at the surfaces perpendicular to the applied compression direction. Such conditions may be intentionally induced in order to examine a material’s behavior under hydrostatic stress, i.e. the pancake test [19]. Similarly, in the case of the growth plate of a long bone in which the original fully cartilaginous epiphysis (chondroepiphysis) has been transformed into bone just a thin layer of growth cartilage (1 - 2 mm) is left between the epiphyseal and metaphyseal bone on either side. This type of stress is also present in experiments where a thin layer of cartilage has been completely isolated from the bone and subjected to confined or unconfined compression unless friction at the platen surfaces can be significantly reduced. It is also reasonable to suggest that the compression of macroscopic test bone-growth plate-bone samples mimic the in vivo physiological state of stress in which the cartilage surface at the bone borders are partially constrained by the compatibility displacement conditions and are not free to expand.
4.2. Relevance to Bone Growth Theories
Hydrostatic stress state is thought to maintain cartilage and octahedral shear stress is thought to lead to calcification [8,9]. Therefore, we computed the hydrostatic and octahedral shear stress in the middle of the growth plate, i.e. halfway between the epiphyseal and metaphyseal borders (Figure 6). The absolute value of hydrostatic stress is an order of magnitude greater than the octahedral shear stress suggesting that the center of the growth plate is experiencing a near hydrostatic stress state. Both stresses exhibited dependence on the location from the free surfaces of the specimen, where their absolute magnitudes approached a similar value at the outer edge. For the center of the growth plate, where there was no outer edge effect, the hydrostatic stress and octahedral shear stress remained nearly constant (Figures 7 and 8). In order to compare the influence of different growth plate geometries, similar plots were then created for two other models with “n” and “m” shaped growth plate layers to show the stress distributions. As results show in Figure 8, they all followed a similar pattern with little or no difference in the hydrostatic or octahedral shear stress at the specimen center among these growth plates with differing geometry. Away from the center, the differences were at most about 20% for the hydrostatic and octahedral shear stress, relative to the flat growth plate geometry. Since the samples were cut from a large animal growth plate, they contain free surfaces, which are not present in the in situ state. Thus the variation in the state of stress from the center to the edge as determined for the tested specimens is not representative of what would be expected in situ or in vivo in a larger animal such as the cow, where

Figure 6. Hydrostatic and octahedral shear stresses in the middle of the growth plate (arrow indicates towards the outer edge).

Figure 7. Stress distribution of the center column of elements in the growth plate (arrow runs from epiphyseal to metaphyseal side).
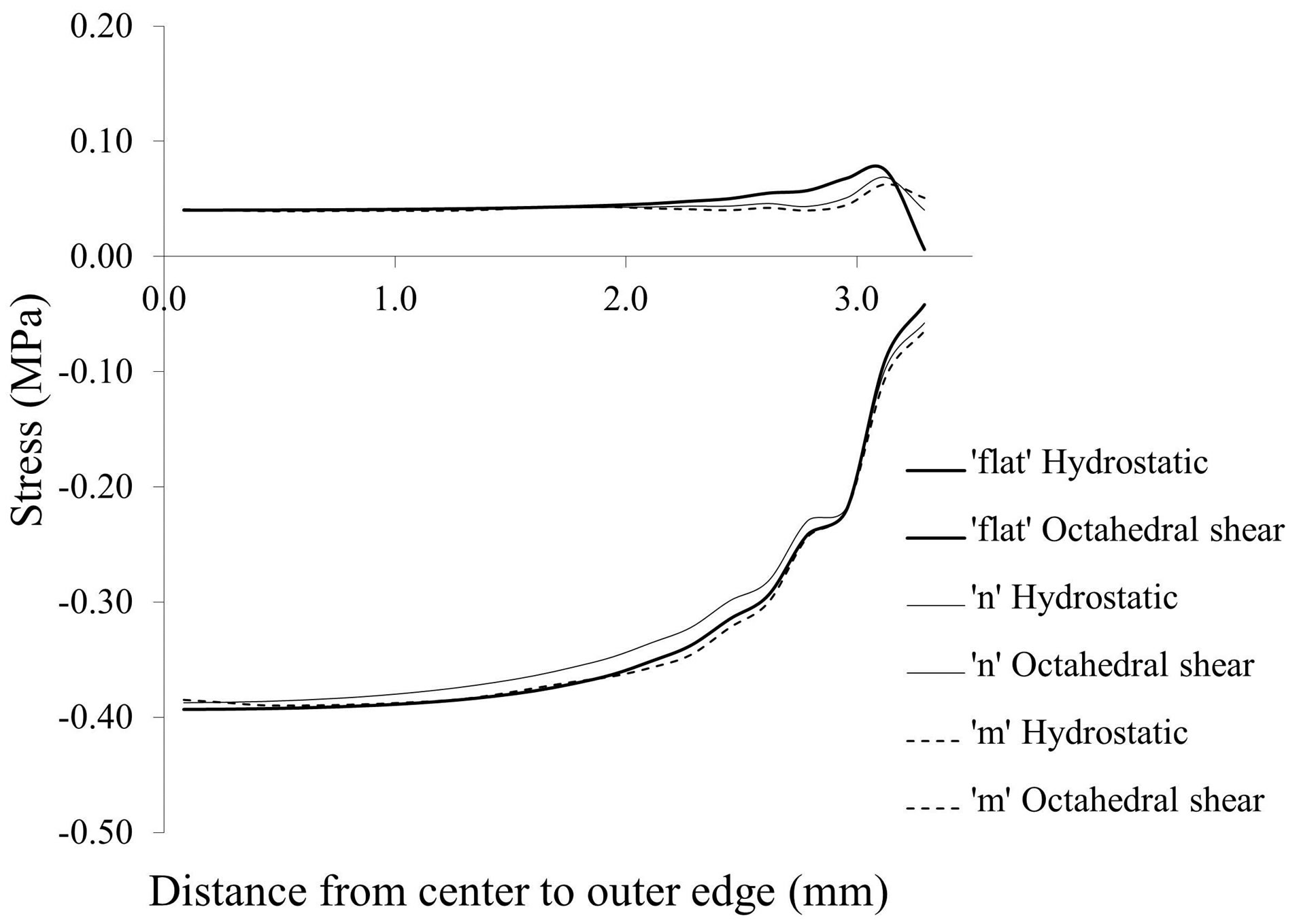
Figure 8. Influence of growth plate geometry on middle layer stresses in a different sample from that shown in Figure 6.
free surfaces only exist at the perichondrium.
On the other hand, it should be noted that there is a close correspondence between the specimen dimensions of these macroscopic growth plate samples, which were cut from the growth plate of a large mammal (cow), and the dimensions of the entire growth plate of a long bone in a small mammal such as a rat. Likewise the topography of the secondary mammillary processes in these specimens obtained from the cow corresponds to that of the primary mammillary processes in a small mammal such as rat. Thus the state of stress determined for the extracted cow samples may be representative of the state of stress in the entire growth plate of a small animal. This suggests then, if hydrostatic stress state maintains cartilage and octahedral shear stress causes cartilage degradation and accelerates ossification, that compression would promote bone formation near the external surfaces of the growth plate more so than at the center. Perhaps this explains the topography of the proximal tibial primary mammillary processes which, when viewed in a coronal slice, exhibit some convex curvatures at the medial and lateral borders (Figure 1A). This is similar in shape to what is seen in the rat proximal tibial growth plate in the frontal plane (coronal section) [20] and also similar to the m-shaped secondary mammillary process modeled in this study for macroscopic samples. The m-shaped primary mammillary processes found at the periphery of the growth plate in the rat and cow suggest that octahedral shear stress accelerates bone growth/formation and hydrostatic stress (near the center) retards growth by maintaining cartilage.
Elastic moduli determined for each of the two sections of the growth plate from the bilayer FE model are comparable in magnitude to those previously reported [16,17]. However, direct comparison with other studies is difficult due to the use of different animal species [16], anatomic regions, stage of development [17], test methodology and material property assumptions [17]. One study [17] conducted confined and unconfined compression of 2 mm thick cartilage discs prepared from 5-month-old calf distal ulnar growth plates by cutting the cartilage at the metaphyseal border. Since the epiphyseal side in this location consisted of a chondroepiphysis the other end could be trimmed to leave a disk consisting only of cartilage [17]. Although it is not clear whether this could be done without damaging the hypertrophic layer, given the undulations of the mammillary processes, this would not at all be possible to do in a growth plate that is fully developed and consists of bone on both sides of the growth plate, unless the thickness of the cartilage is sufficient and the mammilary processes are small. Interestingly, in the case of the rat, a careful microCT study has shown that the normal time course of growth plate closure by bone bridging in the proximal tibial in the rat occurs first around the periphery and then progresses toward the center [20]. This sequence may also be related to the nature of the stress distribution at the time of growth plate closure when the cartilage cells reach apoptosis. Perhaps octahedral shear stress accelerates the formation bone bridges while hydrostatic stress preserves cartilage.
4.3. Limitations and Underlying Assumptions
We recognize that there are limitations to our approach. In our model, we only considered the condition of slowly ramped compressive loading along an axis perpendicular to the main plate direction and ignored fluid related contributions to the stress. In addition, we analyzed experimental data in which a 20% grip-grip strain level was slowly applied and maintained until the nominal stress reached equilibrium. This allowed us to consider the bovine growth plate as a linearly elastic material, although we are aware of the various nonlinear material models that have been considered [8,14]. There are various types of material models which have been used for the growth plate when it comes to FE modeling, such as nonlinear biphasic models [21], linear biphasic poroelastic models [22], transversely isotropic biphasic models [17]. Compared to these, a linear elastic model is still very attractive and sufficient enough to be used to describe the basic mechanical behavior of the growth plate under uniaxial compression [8,14], at least to relatively lower strain levels and slowly applied compression. Another important parameter in our modeling is the Poisson’s ratio of the growth plate, which prior studies report anywhere from ≤0.1 [1] to slightly less than 0.5 [23]. In this study, 0.45 was used based on the assumption of nearly incompressible mechanical response of the growth plate due to the high cellular content.
A major limitation to our study was the lack of full geometrical information of the samples. The topography of the growth plate cartilage can be very different from one specimen to another (Figures 4C-E). Due to lack of information regarding the internal topography of the growth plate cartilage layer, the models did not fully take into account of the undulations of the cartilage layer. The models assumed the growth plate layer to be flat and perpendicular to the force and height of the specimen. We found a strong linear dependence of EIN/EEX on height (R2 = 0.95, p < 0.0001). The explanation for this is that the model assumed the growth plate to be flat and perpendicular to the force and height of the specimen.
Two simplified mildly undulating shapes of the growth plate layer were modeled to compare with the flat shape. However, the actual mamillary undulations in the samples were more severe than the modeled shapes and encompassed the entire specimen height and slopes changes can be aggressive. The more sloped it is (i.e. higher specimen) the more shear the growth plate cartilage is exposed to. However, the models used to estimate the intrinsic modulus consisted of a growth plate, which is primarily exposed to compression. Therefore, the intrinsic modulus extracted from this model for these specimens is more likely that of the modulus in combination of shear and compression, which explains the dependence of EIN/ EEX on specimen height. Therefore, the unique topography of the growth plate layer in each sample should be taken into account while using data from such experiments.
Secondly, the zone of calcified cartilage/primary spongiosa, which lies between growth plate and metaphyseal bone, is a region of likely increased compliance compared to the more mature secondary spongiosa and this was not taken into account in the models. Since this zone has a thickness comparable to that of the growth plate cartilage, including this in the model may alter the calculated intrinsic modulus of the less mineralized proliferative and hypertrophic zones and reserve zones. One could argue that the zone of provisional calcification or primary spongiosa should be considered as part of the growth plate proper, though most biomechanical studies to date have not considered this.
5. Conclusions and Summary
In summary, we report the state of stress in the growth plate cartilage of block-shaped samples containing bone and growth-plate with 7 × 7 mm cross sections, excised from the proximal tibias of 5 month old calves. We utilized FE analysis to model the sample structure and to estimate the intrinsic elastic modulus of the growth plate cartilage by simulating and matching the uniaxial compression tests. The stress state in the growth plate was triaxial, nonuniform across the cross section, and predominantly hydrostatic over most of the central region but became an equal mixture of octahedral shear stress and hydrostatic stress near the external surface of the bone samples.
Limitations of the current model include the relatively flat approximation of the mamillary processes in the model compared to the more extreme undulations of the experimental specimens and the exclusion of the zone of provisional calcification. The latter may function as a mechanical buffer zone between the resilient growth plate cartilage and the comparatively stiffer secondary spongiosa. We believe that further improvement of these models will lead us to a better understanding of how macroscopic loads are experienced by chondrocytes at the microscopic level.
NOTES