A specially designed pillow may be used as treatment for young infants with developmental plagiocephaly ()
1. INTRODUCTION
The relationship between poverty and adverse health outcomes is indisputable [1-6]. This relationship reflects what Wagstaff [5] calls “causality in both directions” a “vicious cycle” of poverty, which generates ill health that keeps the poor in poverty and may lead to diseases, as well as high fertility, that can have a major impact on disposable income in families and become factors that can make the difference between being above or below the poverty line.
In all European countries the most disadvantaged groups have the poorest health outcomes and highest mortality. This is reflected in large differences in life expectancy between groups located at both ends of the social scale [7].
In Portugal, poverty has become an important issue in the political agenda and evidence shows its persistence in our society [8-11]. According to the latest available data [10], in Portugal poverty affects around 18% of the population. However, there is still too little research on the relationship between poverty and health in Portugal. Santana [12] refers to a strong relationship between high rates of mortality and morbidity and low educational levels, social class and income and states that the most disadvantaged social groups have weaknesses resulting from economic conditions, which also present additional barriers to health care access, mostly when the care needed is preventive or more specialized. That is the case for prenatal health care which is particularly important in the context of this research.
1.1. Fecundity
Over the last forty years fertility rates in Europe have declined to values below the replacement level (i.e. to a Total Fertility Rate below 2.1) with a great intraregional homogeneity of practices and representations. There are few couples who choose not to have children, with the largest concentration at around two children and a decline of those with a third child [13].
Portugal, after a delay of a decade, is following the European trend [14] with a total fertility rate aligned to the EU average since 1992 [15,16], ranging between 1.4 and 1.5. Existing surveys confirm the value placed on an ideal of family oriented to a “standard of 2 children” [14, 16]. The social context of families is central to understand the different patterns of fertility in Portugal [17, 18]. Poverty is a major element of such social context.
1.2. Access to and Utilization of Reproductive Health Care
There is evidence that the poor need more health care than the rich [19]. However, access to health care continues to follow an “inverse care law” [7,19,20]. Moreover, inequalities in access to essential health care are a key determinant of social inequalities in health. According to Whitehead and Dahlgren [7], although not the largest, this is a very important factor. The burden represented by the payment of health services is a growing cause of poverty, especially among vulnerable groups, and health sector has a special responsibility and opportunity to solve it effectively [21].
While there is some controversy about the role and effectiveness of prenatal health care [22], several authors [23-26] reinforce the importance of accessing appropriate prenatal care for all pregnant women.
The percentage of women without any surveillance is less than 0.5% in 10 European countries, but the percenttage of late access to prenatal care (e.g. after the first trimester of pregnancy) has been higher. Portugal is one of the countries in the study [26], with data pointing out to late access of the order of 18% to 29% (together with Greece, Hungary, Ireland and Scotland), and 40% of late access to care amongst Portuguese teenagers.
In Portugal there is still a relatively high proportion (always above 15%) of mothers with inadequate antenatal supervision—which is mainly a result of the large number of pregnant women with late onset of surveillance. And this high inadequacy in prenatal care was most frequent in women with higher obstetric risk (e.g. extreme age or high parity), low educational level and adolescents, which foreshadows the need for specific interventions among these populations [27,28].
Using a case-control study the main objectives of this study were to estimate the association between social status variables (degrees of poverty in women—very poor, poor and non-poor women) and variables of fecundity (number of children, representations, practices and control of fertility) and to compare the access to health care and utilization of reproductive health care in each gradient of poverty studied (very poor, poor and nonpoor women).
The first hypothesis under study was that a higher fecundity increases the risk of poverty for women, and the poverty of women increases the possibility of greater fecundity. The second hypothesis was that there are differences in access to health care and reproductive health care utilization patterns in each of the groups defined by the gradient of poverty considered in the study.
Therefore, this research aims to contribute to the advancement of knowledge about the relationship between poverty and variables related to fecundity, access and health care use.
2. POPULATION AND METHODS
2.1. Population
The study population consisted of fertile age women (15 - 49 years of age) living in the Municipality of Lisbon. An unmatched case-control study design was used, with two controls selected for each case [29]. In particular, this study compares cases (fertile age women considered very poor), with controls (fertile age women considered poor—controls 1; and fertile age women considered non-poor—controls 2), on the experience of motherhood/fecundity (parity, expectations, representations and practices) and the relationship with health services (patterns of access and of reproductive health care utilization).
Women were considered “very poor” (cases) if receiving RSI (Social Welfare Payment for Inclusion), “poor” (controls 1) if benefiting from some kind of support (namely, housing, access to health care and/or support to buy medication) of SCML (Santa Casa da Misericórdia of Lisbon—a very large Non-Governmental Organization who provides social support in the Lisbon Municipality, Portugal) but not receiving RSI at the time of the data collection and not having benefited from the RSI in the last two years; and “not poor” (controls 2) the users of the Municipality of Lisbon Health Centres, who were not receiving RSI and had not received any support from SCML in the last three years.
The sample size of 1513 was estimated based on the probability of exposure of cases and controls to previous pregnancy: the exposure in cases was considered to be 25% and in controls equals to 15% with a level of confidence of 95% and a power of 80%.
The 499 “cases” were selected according to a proportional stratified random sample (of women considered very poor) selected from the beneficiaries of RSI of SCML. The 507 “controls 1” were also selected according to a proportional stratified random sample of the remaining members of SCML receiving some kind of support. The 507 “controls 2” were submitted to a two phases selection process, first held with a simple random sampling of four health centres from the total of 48 in Lisbon and then all the women coming to these health centres, for the study period and who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were invited to participate.
2.2. Data Collection
Data were collected through a semi-structured questionnaire applied by trained interviewers. A total of 1054 women answered the questionnaire: 304 (60.9% response rate) cases (very poor), and 750 (73.9% response rate) controls [293 (57.8% response rate) belonging to the group of controls 1 (poor) and 457 (90.1%) from the group of controls 2 (non-poor)].
Interviews were conducted in two stages: first with cases and controls 1 at their homes from June to December 2007, later with controls 2 at selected Health Centers from March to April 2008.
In Figure 1 we present a schematic representation of the case-control study with the distribution of responses, according to the exposure factor: Motherhood/Fecundity (women with and without children, according to the study group).
Variables
1) Dependent Variable The dependent variable of this study is the social status according to a gradient of poverty: very poor women (“cases”), poor women (“controls 1”) and non-poor women (“controls 2”).
2) Independent Variables We adopted a set of eight independent variables related with fecundity [14: 1] parity ≥1; 2) total number of children. Representations of fecundity: 3) number of children that a woman thinks she would like to have; 4) ideal number of children. Practices of fecundity: 5) planning pregnancy of the last child; 6) pregnancy control of the last child (was she or her partner using a contraceptive when she became pregnant?); 7) current utilization
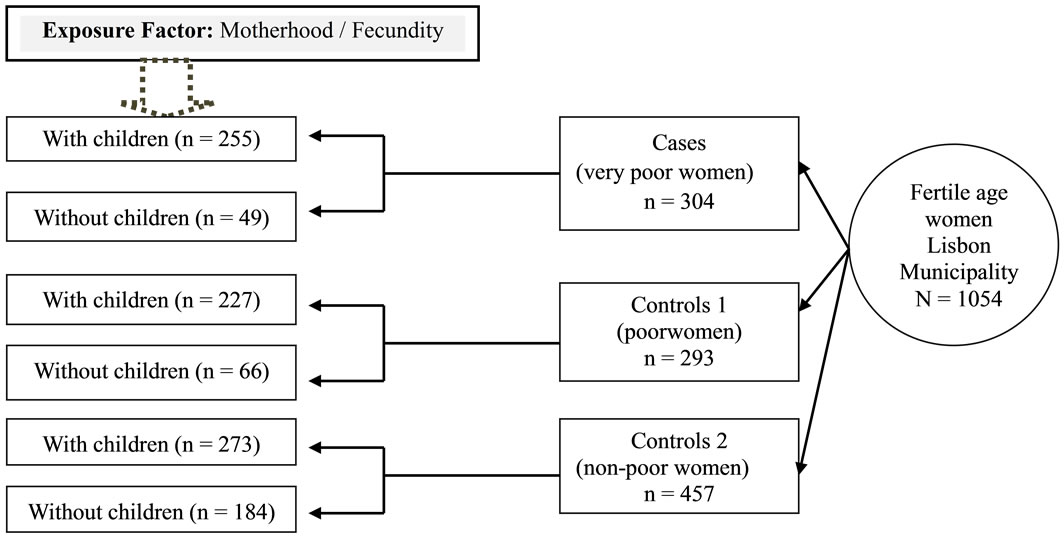
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the case-control study and distribution of responses.
of a contraceptive method; 8) abortions (pregnancy that ended in an abortion, legally induced abortion and/or dead fetus).
3) Potentially Confounding Variables In order to control for possible confounders data were collected on three potential types of confounding variables: socio-demographic variables: 1) age group, 2) ethnicity, 3) marital status, 4) educational level, 5) household income, 6) single motherhood; health care variables: utilization of reproductive health care, 7) preconception consultation of last child; 8) pregnancy surveillance—prenatal care for pregnancy of last child; 9) postpartum consultation after delivery of the last child; and access and utilization of health care variables: 10) time to get to hospital (in minutes), 11) time to get to health center (in minutes), 12) private health insurance, 13) financial incapacity to buy drugs for the woman and 14) financial incapacity to buy drugs for other person in the household.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 17.0. Initially, a descriptive analysis using absolute and relative frequencies for nominal and ordinal variables, secondly measures of location and dispersion for quantitative variables.
The Chi-square test for homogeneity was used to compare the three populations of women with respect to some criterion of classification, in terms of proportions. In order to compare the three populations in terms of quantitative variables using parametric tests, the Levene test for homogeneity of variances and Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk tests for normality were performed to check the corresponding assumptions. When these assumptions underlying the ANOVA were not satisfied, the nonparametric alternative Kruskal-Wallis test [30] was applied. Multiple comparisons were performed when necessary. The odds ratio calculation of exposure to the variable “parity ≥ 1” was made according to Mantel-Haenszel [29: 213-216] to take into account the two controls per case.
We also used binary logistic regression models by Forward: LR (Likelihood Ratio) method [31] to assess the probability of being a case (very poor) rather than one of the controls. The results from binary logistic regression were the basis for the selection of variables used in the subsequent multinomial logistic regression [32]. The multinomial logistic regression models [31] were used to understand the relationship between a dependent variable with three categories [the three study groups: cases (very poor), controls 1 (poor) and controls 2 (not poor)] and a multitude of explanatory variables. In the multinomial regression the odds ratio is always relative to the reference class of the dependent variable, and in this study the reference class is “cases”—very poor.
Specifically, the probability of belonging to controls 1 and 2 was estimated from:
1) Fecundity variables: total number of children; already have had abortions; planning pregnancy of last child, control of pregnancy of last child.
2) Confounding socio-demographic variables: marital status; ethnicity; educational level of women; household income, and single motherhood.
3) Confounding access and health care utilization variables: postpartum consultation of last child; pre-conception consultation of last child; time needed to reach the Health Center; private health insurance; financial incapacity to buy drugs: woman and other person in the household; prenatal surveillance for pregnancy of last child.
3. RESULTS
Characteristics related with fecundity, socio-demographic and health care are summarized in Table 1. Some results regarding variables linked to representations of fecundity are presented in Table 2.
With respect to marital status there are significant differences among the three groups (p < 0.001) and marriage seems to increase with the reduction of poverty. Therefore, there are a greater number of single-mothers in the poorest group.
The proportion of ethnic minorities decreases with the reduction of poverty and the level of education increases with the reduction of poverty.
As expected very poor and poor women have lower income than non-poor women, with differences statistically significant (p < 0.001) between the groups. These differences persist when analyzing the household income, with very poor and poor women belonging to households with lower income as opposed to non-poor women.
Regarding fecundity variables, there are significant differences (p < 0.001), with the 73.7% of the very poor women who did not plan the pregnancy of the last child being higher than in the other two groups. The analysis of pregnancy control data shows that the very poor and poor groups presents similar results but non-poor women shows a different pattern (p < 0.001). Additionally, the distribution of pregnancies that ended in abortion and/or dead fetuses are similar for very poor and poor women, but differ from the non-poor group which have lower percentages (p < 0.001).
There are no significant differences between the study groups with regard to the current utilization of contraception.
For the health care variables, the very poor and poor women show lower percentages of utilization of preconception and postpartum consultations of the last child (p < 0.001).

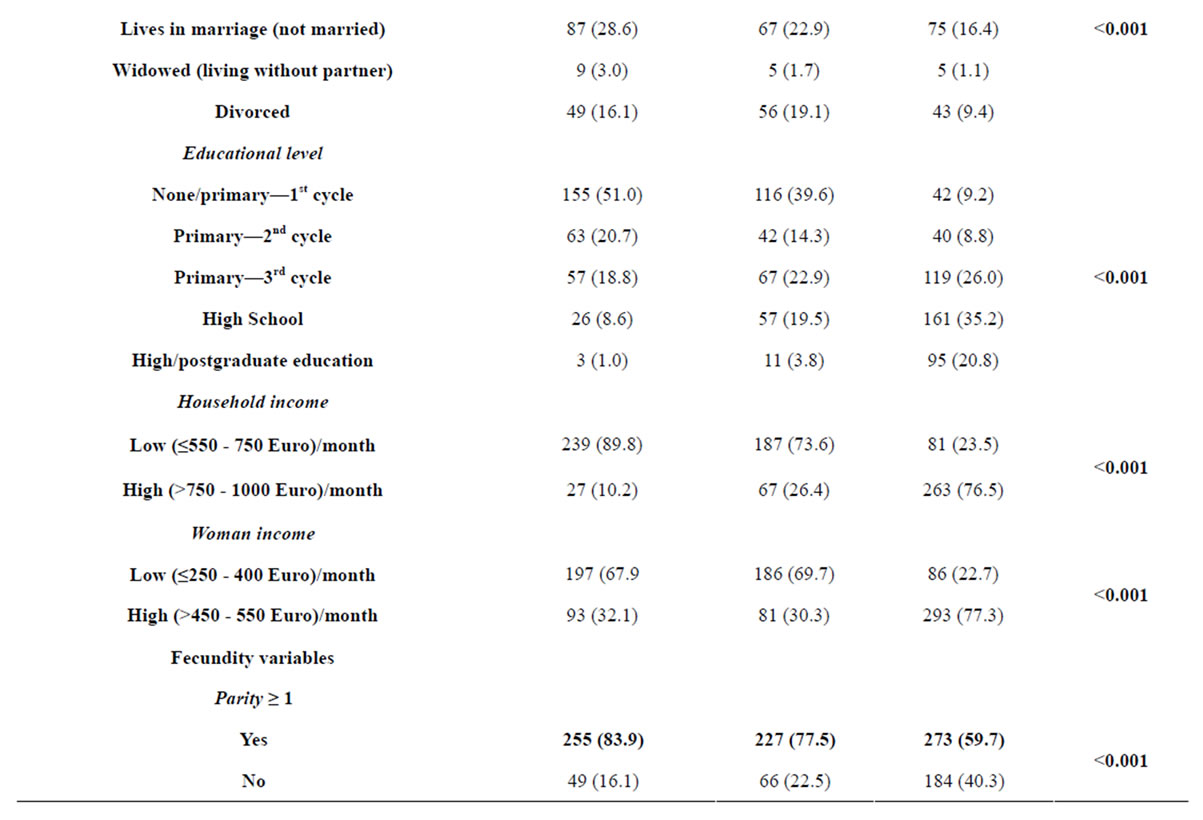
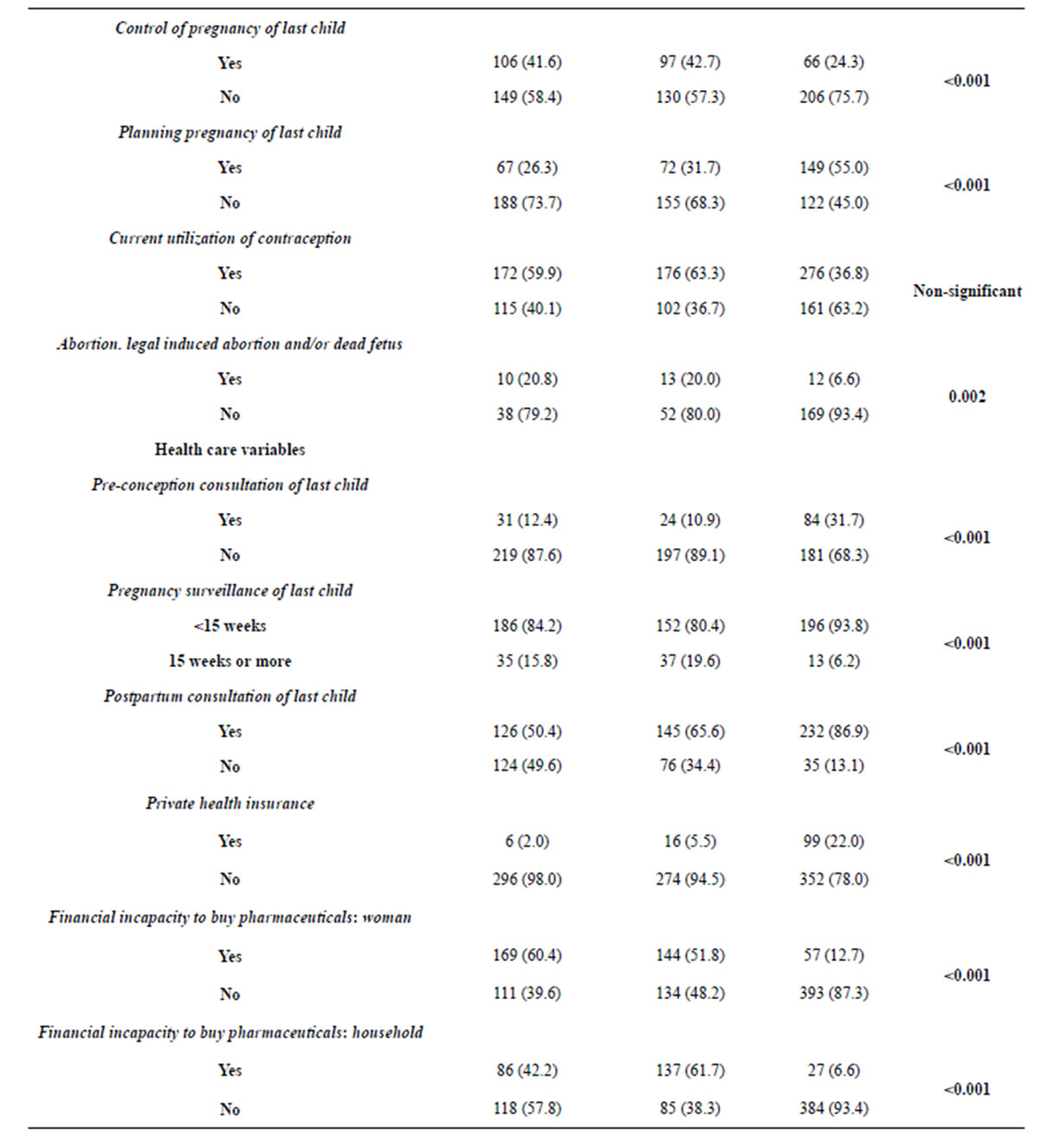
Table 1. Distribution of independent (fecundity) and confounding (socio-demographic and health care) variables.
Continued
Regarding the pregnancy surveillance of the last child, the main differences occur between very poor and poor women as opposed to the group of non-poor women, presenting higher percentages of planned surveillance pregnancies (p < 0.001).
Non-poor women have higher percentages of private health insurance (p < 0.001). Very poor and poor women present similarities in the high percentages of financial incapacity unlike the non-poor women (p < 0.001).
The ideals of filiations outweigh the number of children that women actually have, and above all the number of children women think likely to have. Having children seems to increase the odds of being very poor by about 17% (OR = 1.17, p < 0.001, CI: 95% 1.08 - 1.26) com-
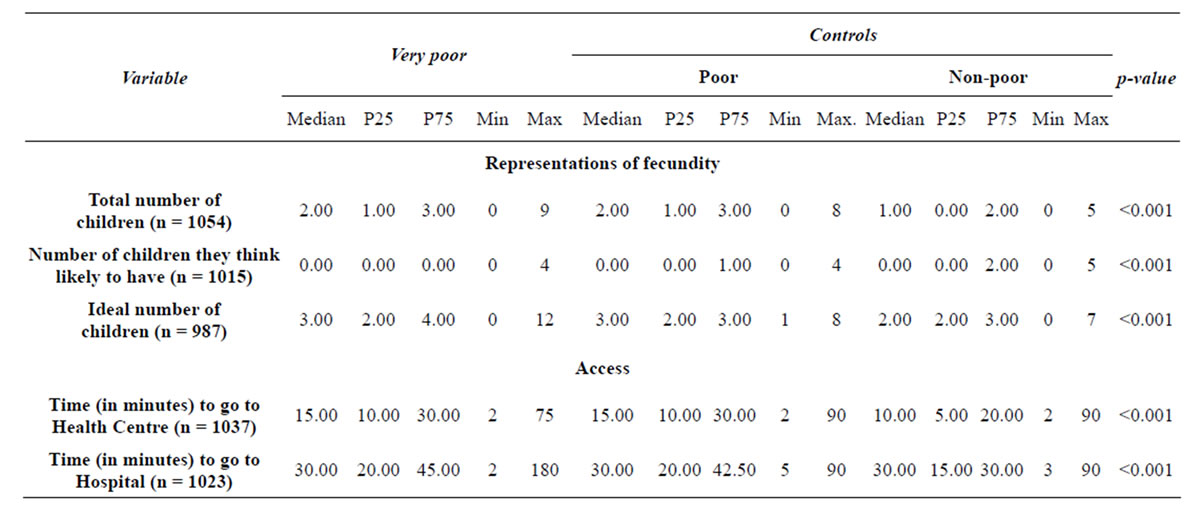
Table 2. Representations of fecundity.
pared with being poor and being non-poor.
Multinomial Regression
Several intermediate binary logistic regression models were performed in order to identify which variables would be included in the final multinomial regression models.
Considering the category “very poor” as the reference, we obtained a first final adjusted model that included selected variables of fecundity and socio-demographic variables. The second final adjusted model considered the same selected fecundity and socio-demographic variables of the first model, but added health care variables.
Both final adjusted models are statistically significant, the first one (G2 (28) = 415.668, p < 0.001) and the second one (G2 (26) = 358.931; p < 0.001). The estimates of odds ratios (and 95% CI) of the first final adjusted model are presented in Table 3 and the estimates of odds ratios (and 95% CI) of the second final adjusted model are shown in Table 4.
Table 3 indicates that the number of persons from household does not play a significant role in differentiating the “very poor” (reference class) from the “poor” (p = 0.703) women. However, that variable seems to play an important role in differentiating the “non-poor” from “very poor” women (OR = 0.549; p < 0.001). In other words, an extra person in a household decreases by 45% the odds of women becoming non-poor.
Being a Roma woman reduces the odds of being poor, compared to very poor (OR = 0.128; p < 0.001) and reduces even more the odds of being non-poor (OR = 0.033; p = 0.016) compared to be very poor. Being a Caucasian woman reduces the odds of being poor, compared to very poor (OR = 0.520; p = 0.042), but does not have an explanatory value to differentiate between being very poor and non-poor (p = 0.404).
As expected, there is a statistically significant relationship between income and the dependent variable (p < 0.001). Belonging to a household with low income, in comparison to a higher one, reduces the odds of being poor (OR = 0.343; p < 0.001) comparatively to being very poor. A woman whose household income is low, in comparison to a higher income one, reduces the odds of being non-poor rather than being very poor (OR = 0.062; p < 0.001).
Low level of education is not a differentiating factor between the very poor and poor (p > 0.407 for all categories of educational level) but acts as a differentiator between the very poor and non-poor women for both 4 years of schooling (OR = 0.073; p < 0.001) and 6 years of schooling (OR = 0.151; p = 0.014) when compared with postgraduate university education. That is, the low educational level of women represents lower odds of being non-poor than being very poor, compared with having a higher education.
Marital status (p > 0.094 for all categories of marital status) is not a differentiating factor of the odds of being very poor or poor. However, in comparison to divorced women, a never married woman as a reduced odds of being non-poor (OR = 0.350; p = 0.017) and a married woman has an increased odds of being non-poor (OR = 3.561; p = 0.002), in contrast to very poor ones.
Planning the pregnancy of the last child differentiates the very poor and non-poor women (OR = 0.444; p = 0.005), but does not differentiate the very poor and poor groups (p = 0.258). That is, the planning of pregnancies is a characteristic more associated with non-poverty.
With regard to abortions, women who did not report this kind of practices, in comparison to those who did,
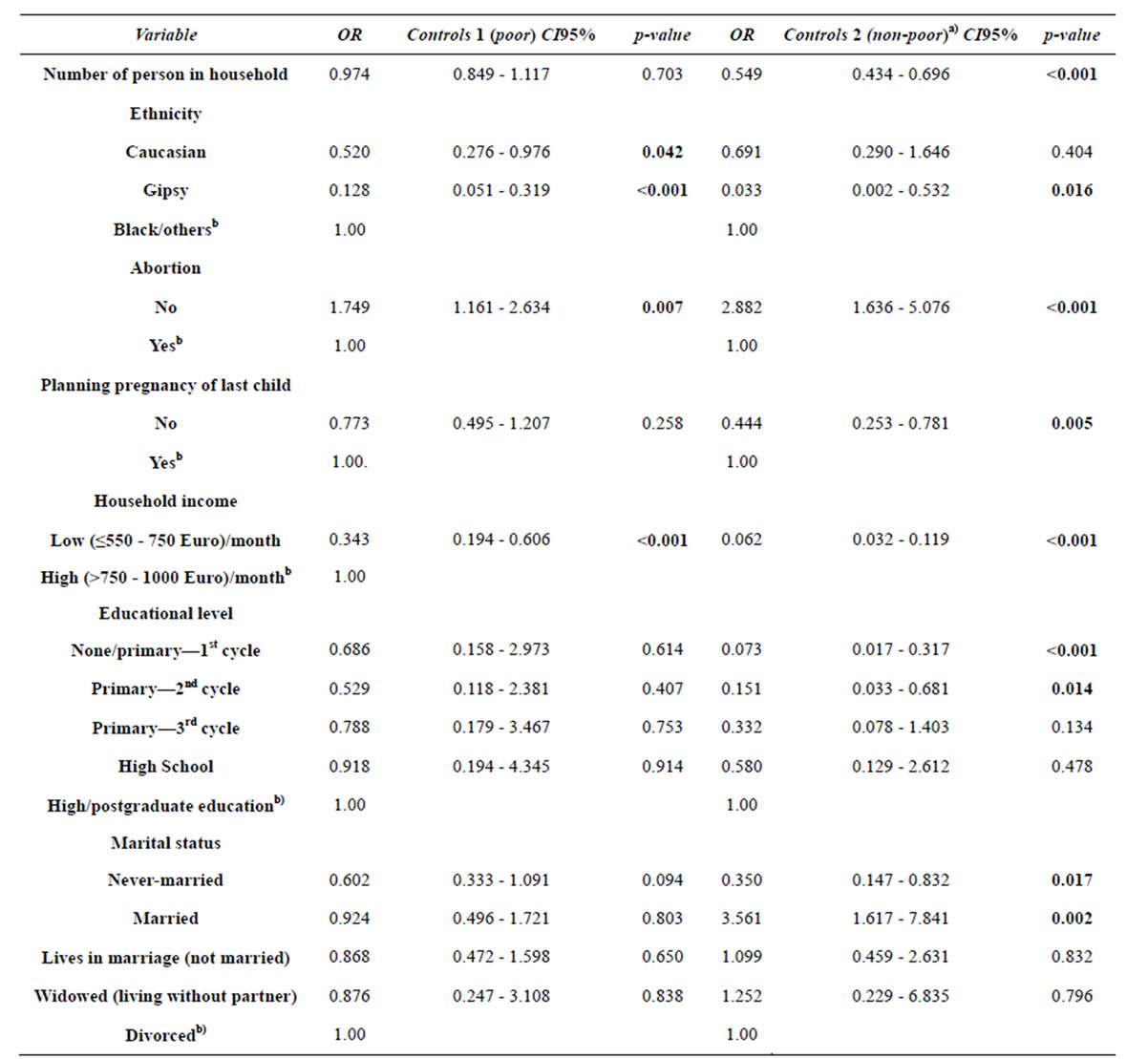
Table 3. First final adjusted model for the association between variables of fecundity and socio-demographic and women social statusa).
a)The reference class of dependent variable is “cases” (very poor). b)Reference category in the variable.
have higher odds of being poor rather than very poor ones (OR = 1.749; p = 0.007). There are even greater odds of belonging to the non-poor group than to the very poor group (OR = 2.882; p < 0.001). This model shows that as the condition of poverty decreases, the association with unsafe abortions and/or occurrence of stillborn fetus increases.
The second model presented in Table 4 confirms the association between several socio-demographic variables and women social status, already identified in the previous model: household size; household income; ethnicity; educational level and marital status.
We would like to emphasize that from all access and utilization of health care variables, only “financial incapacity to buy pharmaceuticals for woman” remains in the final adjusted model. However, these variable is not a differentiating factor between the “very poor” and “poor” (p = 0.230). The women that did not report financial incapacity to buy pharmaceuticals for themselves have higher odds of being non-poor than being very poor (OR = 5.053; p < 0.001).
4. DISCUSSION
This study does confirm the association between our
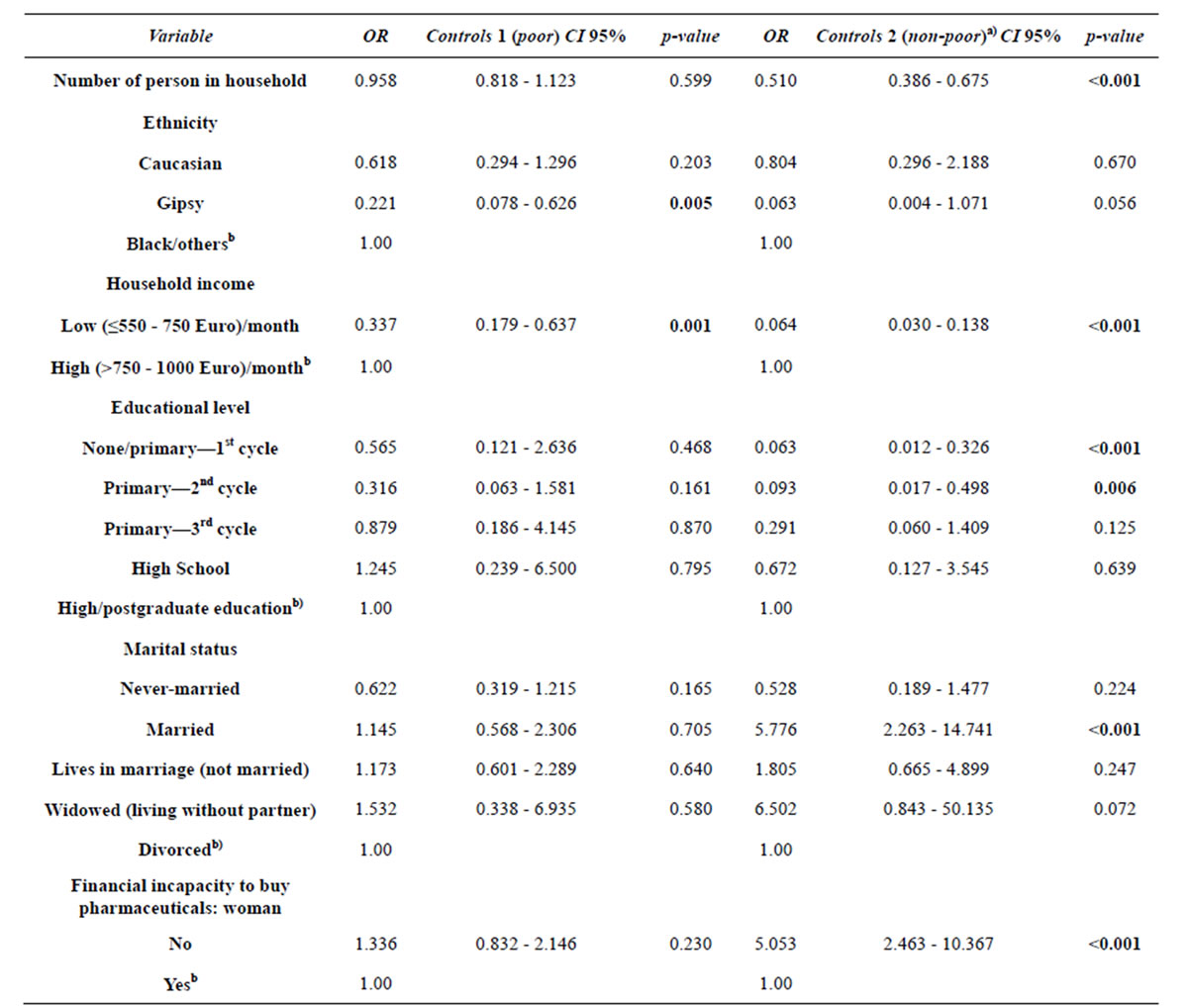
Table 4. Second final adjusted model for the association between variables of fecundity, socio-demographic and health care assess and utilization, and women social statusa).
a)The reference class of dependent variable is “cases” (very poor). b)Reference category in the variable.
definition of poverty and variables of fecundity, clarifying a complex relationship between a social classification of poverty and a number of “variables”.
Bivariate analysis seemed to support the hypothesis under study. As for other studies poverty seemed to be associated with:
Mothers living alone and working women with low income [11,33,34];
Ethnicity, e.g. Roma women are poorer, according to a well-described situation of that ethnic minority, which is particularly exposed to higher rates of poverty [35];
Marital status of women, with benefits showed for married women. In fact, the decline in marriage is a well-known and well-documented phenomenon with major consequences for poverty, inequality and the use of welfare programs [36,37];
Educational level of women, which is inversely associated with poverty, i.e., the lower the educational level, the greater the poverty condition [8-11,33,34];
Differences based on socioeconomic status for entry in parenting, which is related with how the planning of children and willingness of couples to have, or have not, children occurs at the time that the pregnancy happens [14,38];
Most women did not think to become pregnant when they had the last child, described in Portugal [14] and internationally [38], where at least one child after the first one was not planned;
Patterns of utilization of pre-conception and postpartum consultations of the last child, with the very poor and poor women presenting lower rates of utilization [26-28];
Economic access and especially the results related to the incapacity to access certain health care and/or payment of medication, especially for women, corroborates the results from studies that have shown that the burden of payment for health services constitutes a cause of poverty [21].
According to the above associations extreme poverty, of the type that allows access to special social inclusion subsidies in Portugal, seems associated with: ethnicity [35]; household characteristics, such as size, with each extra person in a household increasing the chance of being poor [10] and income [10,33,34]; personal characteristics, namely the association between low levels of education and higher odds of being poor [10,33,39]; and marital status, with marriage appearing as a protective factor of poverty [36,37]. Our first multivariate model also confirms the association between poverty and patterns and representations of fecundity in respect to pregnancy planning, unsafe abortion and marital status.
But it should also be noted that none of the fecundity variables remained in the second final adjusted multinomial logistic regression model as an explanatory factor for the women’s social status. That is, when we add financial access and utilization of health care variables, fecundity variables lose explanatory power suggesting that, despite their importance, their association with poverty is probably related to reduced access to care because of diminished financial capacity. Thus, the incapacity to afford the cost of health care appears as a central aspect of access to health care in a deprivation context [7]. Our study indicates the existence of significant differences between social groups regarding capacity to afford the cost of pharmaceuticals (a proxy for reduced financial access to health care), first for themselves and others in the household and lastly for their children [40,41].
The results of this case-control study thus confirm the usefulness of comparative health system research strategies to highlight existing social inequalities [19,42,43].
5. CONCLUSIONS
The fact that women live in poverty is associated with a number of factors, such as ethnicity, single motherhood, low household income, low educational level of women and marital status.
The association of poverty with not planning the pregnancy of the last child on one hand and large household size on the other hand points to a vicious circle that sustains poverty and leads to extreme poverty.
Limited financial access to health care seems to mediate the association between women’s poverty and low coverage of family planning as well as the lack of access to safe termination of pregnancy, pointing to the need to formulate health policies that ease the financial barriers to care.
6. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Research Grants from the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia—POCI 2010, Fundo Social Europeu. There are no conflicts of interests.