Health related quality of life in paediatric chronic health conditions: A comparative study among children and adolescents in Jordan ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Living with the daily impact of a chronic illness constitutes a great challenge for children and their families. Chronic illnesses have an impact on a child’s life in a number of ways, including recurrent hospitalization with painful procedures, school absences and decreased socialization with peers [1]. With advances in medical care for childhood illnesses, health related quality of life (HRQoL) has become an increasingly important outcome of children’s treatment. If children survived their illness, they not only have longer lives to lead compared to adults, but they are less able to voice their concerns and therefore they are more vulnerable than adults [2]. Therefore, there has been increased focus internationally in the last few years on explicitly focusing on children’s views and concerns when evaluating the burden of diseases in patients [3].
Within the available definitions of quality of life, a consensus has emerged that health related qualities of life are seen as ways of capturing patients’ perspectives of their disease and treatment and their perceived value of health care services and disease outcomes [4]. Moreover, it has been argued that poor HRQoL is a better predictor of increased health care use and resource utilization, therefore, HRQoL can be implicit as an important parameter to help define health care needs and costs in the paediatric population. With this improvement in medical treatment and parental understanding of the ongoing healthcare needs related to their child’s chronic condition, assessment of HRQoL in children is imperative. Simply surviving a long term illness is not sufficient; the quality of survival for chronically ill children is a fundamental focus of comprehensive healthcare [5].
Until recently, a dramatic increase in the development and utilization of paediatric HRQoL measures was evident in paediatric population [4]. Although a number of studies have investigated the generic HRQoL in paediatric clinical trials and clinical practice [6], there have been no studies investigating HRQoL as an outcome measure for children in the Middle Eastern area. This is primarily because of a lack of practical and culturally adapted measures of quality of life for children and related to the fact that medical and nursing practices are often directed toward patients’ longevity than about patients’ quality of life [7].
A number of studies highlighted the need for culturally competent scholarship in the field of quality of life and the need for culturally appropriate measures for children [8,9]. Comparing the HRQoL scores between chronically ill children and healthy children is useful in understanding the relative clinical impact of different pediatric chronic health conditions on their HRQoL [10]. Central to the pursuit of this mean, it has become progressively more important to understand HRQoL domains from children’s own perspective in Jordan. Overall, this study was undertaken to determine the generic HRQoL in chronically ill children in Jordan and to compare HRQoL with their healthy peers.
2. METHODS
2.1. Sample and Settings
This was a cross sectional study where the Arabic version of the PedsQL™ 4.0 [11,12] was administered to two groups of children and adolescents aged between 8 and 16 years living in Jordan. The participants interviewed in this study were recruited from a number of hospitals and schools around Jordan.
2.2. Instrument
The PedsQL™ 4.0 Generic Core Scales [11] was used to measure HRQoL in both groups. This instrument has 23-items in 3-point Likert scale. The PedsQL™ 4.0 scales are designed to yield a total HRQoL score in two dimensions; the Physical Health Summary Score (the Physical Functioning Subscale) and the Psychosocial Health Summary Score (Emotional, Social, and School Functioning subscale). To obtain a total score, the items are reverse-scored and transformed to a 0 to 100 scale (0 _ 100, 1 _ 75, 2 _ 50, 3 _ 25, 4 _ 0). Scale scores are computed as the sum of the items divided by the number of items answered. The validity of the Arabic translated version of the PedsQL™ Generic Core Scales has been demonstrated through known group comparisons and has demonstrates good internal consistency for child _ 0.90 and parent _ 0.93) and construct validity in healthy children and children with chronic illnesses [12].
2.3. Procedure
The chronically ill children were approached as they were hospitalized at the paediatric ward, whereas the healthy controls were recruited from schools in the same geographical areas of the chronically ill children. Matching between groups was only possible for age, gender and place of residence. Before collecting the data, a written informed consent had been obtained from both the parent and the child. After information sheet was used to explain the study, children completed the Arabic PedsQL™ questionnaires in their classroom (for the healthy control) or at the paediatric clinics (for the patients group).
3. RESULTS
A total of 154 children approached in the chronically ill group, 149 (97%) agreed to participate. Two parents refused to participate related to time constraints while three other children diagnosed with cancer refused to talk or to be interviewed. Of the 162 questionnaires distributed to the healthy controls, none refused, giving a 100% response rate. Table 1 summarises the demographic variables of the 149 chronically ill children and 168 healthy controls.
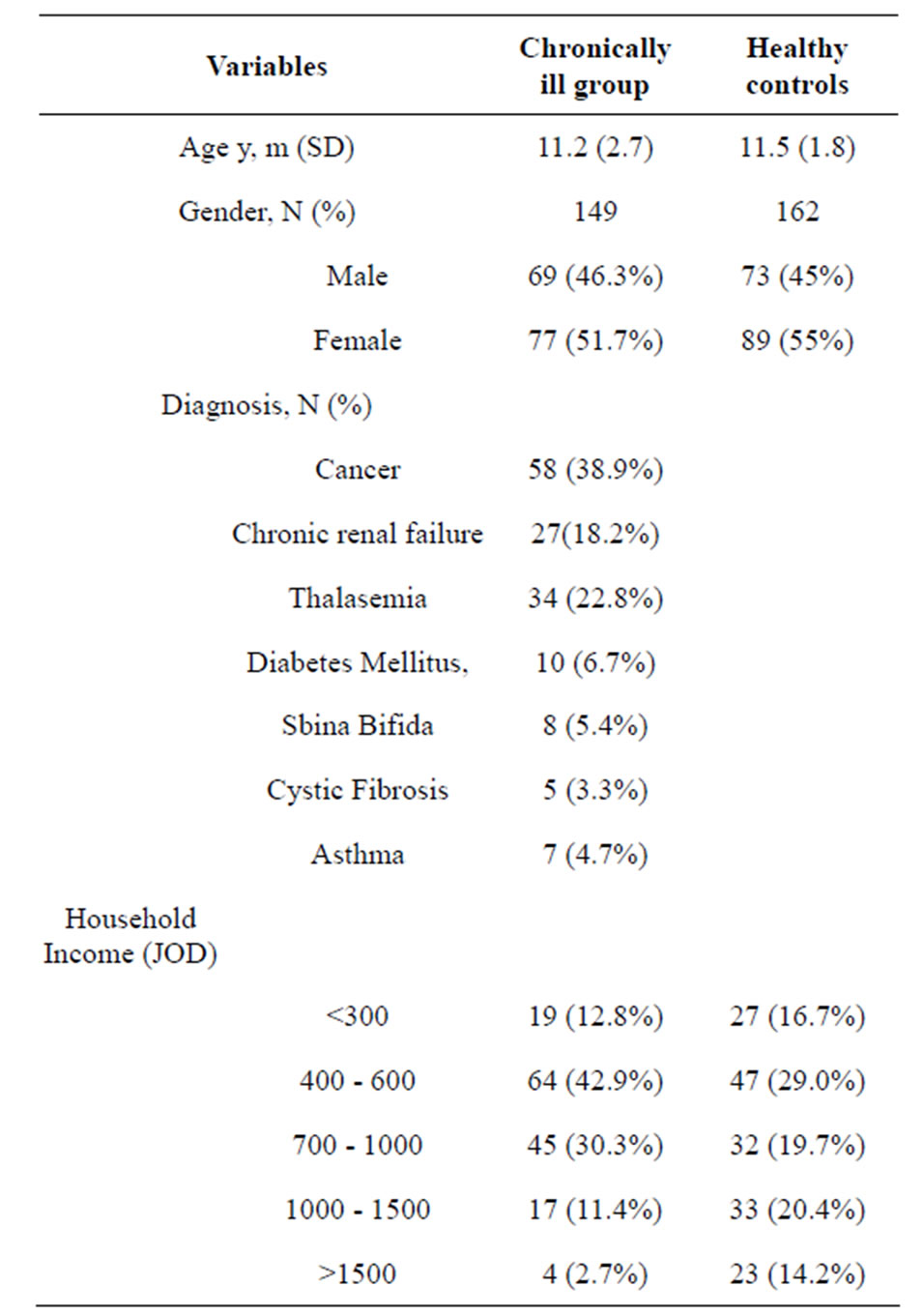
Table 1. Demographic characteristic of participants.
JOD is an acronym for Jordanian Dinar.
The mean age of the healthy controls was 11.5 years old and the age range was between 8 to 16 years old. The mean age of the chronically ill group was 11.2 years old and the age range was between 8 to 16 years old.
Approximately 38.9% of the chronically ill children had cancer, while 18.2% had chronic renal failure, 22.8% had thalassemia while other diagnostic categories (e.g., diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis, sbina bifida and asthma each represented <10% of all illnesses. Almost out 29.5 chronically ill children (42.9%) came from families with household income of less than 500 JOD. Of the 162 participants in healthy group, only 29% came from families with household income of less than 500JOD. The poverty line for Jordan is income <500 J0D per month. The mean length of time elapsed since diagnosis for children with chronic illnesses was 6.5 years (SD = 5 years).
The PedsQL™ scores ranged from 13.04 to 96.74 for the chronically ill group (m = 63.6; SD = 19.58) and for the healthy controls scores ranged from 31.52 to 100 (m = 78.4; SD = 14.8). Table 2 reported the mean scores and standard deviation of the PedsQL™ 4.0 subscales in both groups. The independent t-test demonstrates a main effect for sample, indicating that the healthy group has significantly better HRQoL than the chronically ill children (p < 0.001). This significant difference extended to all HRQoL domains except for the social functioning. The chronically ill children reported more problems with physical, emotional and school functioning compared to their healthy peers. The Psychosocial Health Summary (PCHS) is the average of the Emotional, Social and School Functioning and it was statistically significantly lower than those of the healthy control with p < 0.001.
Further analysis using a chi-square (x2) statistic was used to investigate whether distributions of categorical variables in the chronically ill children differ from one another. Significantly, better HRQoL scores were evidenced for children with cancer (p < 0.01) when compared to children in other diagnostic categories. Results showed that children diagnosed with cancer reported significantly better HRQoL on social domain and physical domain.
No significant relationships were found between child’s HRQoL and child age or time since onset or for marital status or child gender. Reported Means and Standard Deviations for the PedsQL™ 4.0 Generic Core Scales by Disease Cluster is reported n Table 3. There was a significant difference related to diagnostic category (p < 0.05).
4. DISCUSSION
Findings revealed that the mean scores and standard deviations on child HRQoL utilizing the PedsQL™ 4.0 Generic Core Scales from the child’s perspectives were low for chronically ill children. This is similar to the work done by other studies [10] which suggest that children with chronic health condition report progressively lower HRQoL compared to their healthy peers. Yet, the scores reported for the PedsQL™ subscales of chronically ill children in Jordan are low in comparison to scores reported in other studies. For example, Varni et al.’s study [10] reported mean of (73.25 - 77.50) with sd of (16.78 - 15.30) for children with cancer in the USA, and mean of (78.94 - 69.30) with sd of (14.24 - 14.24) for children with end stage renal failure. This is lower than scores reported for same illness categories in this study. A number of issues emerged while trying to compare the current work with previous literature, suggesting that it was not wise to group together children’s norms in this sample with previous norms published in previous HRQoL literature. This is mainly because the tool used in measuring HRQoL is different as well as the purpose of the study. In addition, the lack of a control group in some studies and the fact the study sample used here are heterogeneous in term of illness categories which make it difficult to compare.
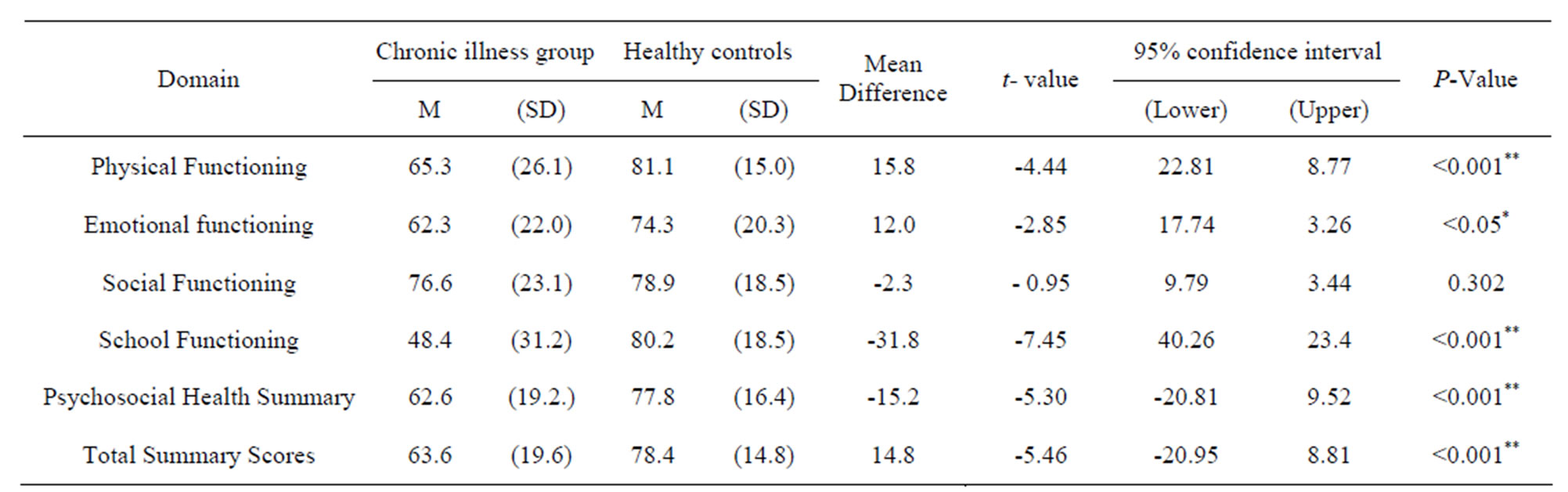
Table 2. Results of independent t-test for differences between chronically ill children and their healthy peers in quality of life measure.
*Significant at P < 0.05; **Significant at P < 0.001.
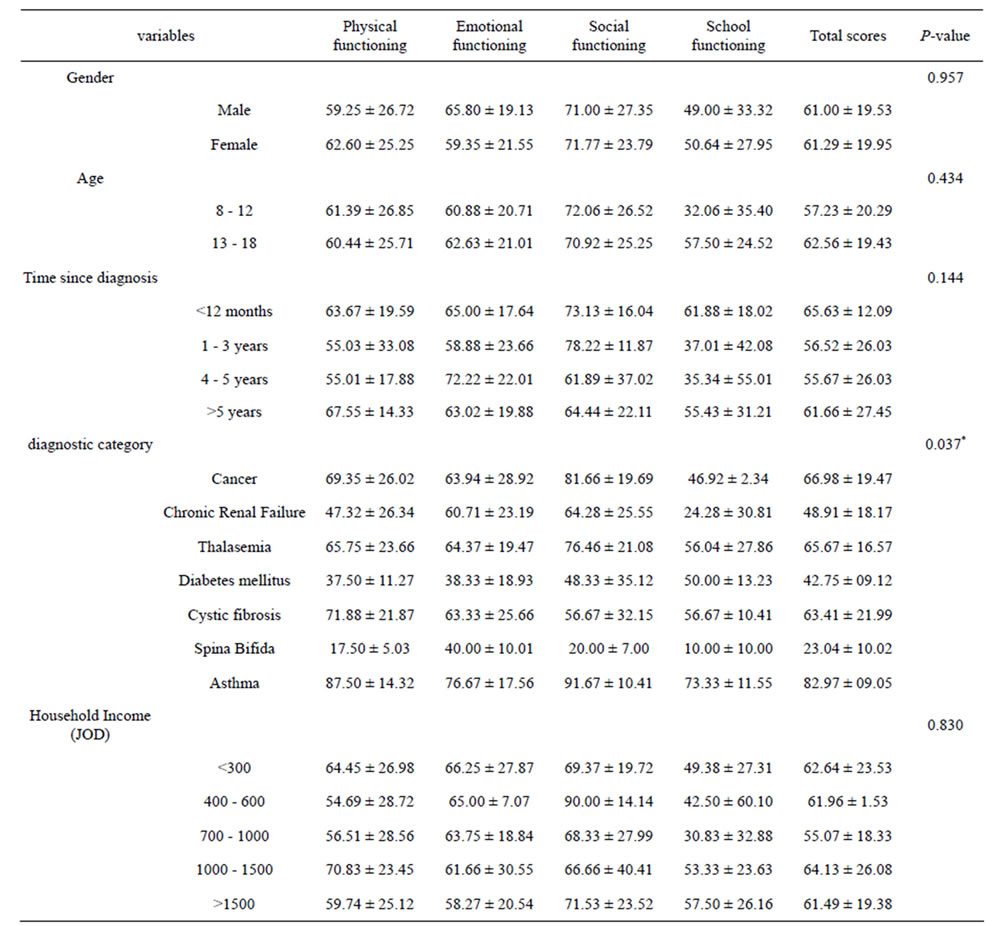
Table 3. Differences in HRQoL according to socio-demographics and clinical variables for the chronically ill children.
*Significant at P < 0.001.
In the present study, self-reported scores for chronically ill children were lower than their healthy peers on physical, emotional and school domains, with most differences reaching significance. Children with sbina bifida, chronic renal failure and diabetes mellitus self-reported the most impaired HRQoL, while patients with asthma self-reported the best HRQoL. The results demonstrate low self-reported HRQoL in the physical domain among these children which imply a significant presence of pain, aches and impaired physical activities in children living with long term illnesses in Jordan. However, in a social context, contrary to previous studies, the results showed that the chronically ill children did not report lower HRQoL than healthy controls. Actually, social functioning scores for the cancer group (81.66, SD = 19.69) were higher than their healthy peers suggesting that children living with cancer in Jordan did not perceive themselves socially isolated. Whether this is due to the cultural support system of the Jordanian community, the positive support of the extended family or other factors remains unclear. What is evident, however, is that this issue merits further researches.
The impaired self-reported HRQoL observed in this study, especially for school domains (48.4, SD = 31.2) could be explained by frequent school absences as a result of recurrent hospitalization, treatment-related complications and lack of any supporting programmes or education facilities provided for these children. The results of this study suggested that there were more potential benefits for establishing programmes for re-entry or reintegration of chronically ill children into schools of Jordan. The lowest self-reported HRQoL scores were among children with chronic failure (48.91, SD = 18.17) and children with sbina bifida (23.04, SD = 10.02). Results from previous studies [13] suggest that child’s returning to school after hospitalization may bring hope that the child could achieve a regular development again. Programmes for reintegration of chronically ill children into schools would likely provide opportunities for social, emotional and cognitive development [13,14]. Moreover, reintegration programmes can give these children a sense of normalization, a sense of control, as well as an increased self-esteem and lessened identification as patients [15].
4.1. Limitations
Given the relatively low prevalence rate of most pediatric chronic conditions, we did not have a large sample size and we included heterogeneous sample for chronic conditions. In this perspective, three primary sample problems were evident: the inadequate sample size, the mixed illness composition in the chronic illness group, and the varied stages and severity of illness within each illness category. The small sample sizes of each diagnostic category within the chronic illness group may attenuate the statistical power to find significant differences. Subgroup differences across the entire chronic sample showed significant trends toward differences between children with cancer, children with chronic renal failure, children with thalassemia, and children with other chronic illness particularly on physical and social functioning domains. Consequently, further research is necessary to determine the extent these results generalized across all chronic illnesses. Results from this study indicate that there may be differences across diseases in average HRQoL scores; it is less clear, however, whether the physical, emotional, social functioning domains are the same or different across all chronic illnesses. A formal test for such difference was insignificant; however, the sample available in each illness subcategory was too small to measure the clinical impact of each illness on HRQoL. Carefully designed studies with larger homogeneous samples are necessary to study these differences in the future. Moreover, any future studies should relate children’s self-assessment to ratings done by nurses, parents, or friends who directly interact with them on a regular basis in order to further validate these findings. Besides the issues related to heterogeneity of sample in terms of diagnosis, it is important to point out another concern, specifically, regarding using of translated selfreported measures in children. Overall, the literature provided no satisfactory data of a multidimensional scale to assess HRQoL in children with chronic illnesses, as well as for the cultural differences, if any, between children from different cultures. It is significant to bear in mind the shortcoming of translated self-reported tools, especially in terms of the item ambiguity [7]. For example, can we assume that a child filling the PedsQL™ within the context of a lifelong illness would perceive the items in the same way as a healthy child? This may be the case for the items of the physical functioning. A child with cancer may perceive the item [it is hard for me to do sport activities or exercise] as relating to cancer treatment or to the time spent at hospital (e.g. it is hard for me to do sport activities or exercise since I am at hospital). A child from the general population may have no clear point in time or event with which to compare him/herself to some prior level (it is hard for me to do sport activities or exercise at school). All other items on the physical functioning have such “disseminate back references”. These items may systematically underestimate scores in the quality of life for the chronically ill group, because respondents do not have a clear point of reference for the response. Thus, the PedsQL™ scores obtained from healthy children may not be directly comparable to scores from children with chronic illnesses. Thus, there is a need for better measures to assess HRQoL domains in healthy children as well as those with chronic illness within the context of illness, treatment and cultural values. An ongoing development of any future research in Jordan should focus on children with chronic illnesses trying to understand their views and needs in order to improve their chances of leading a fulfilling life at present and in the future.
4.2. Conclusions
From this study, it is wise to conclude that the HRQoL of children with chronic illnesses in Jordan is indeed much lower than the quality of life of healthy controls regardless of age, gender, time since diagnosis and household income. We recommended that health care professionals in Jordan could better demonstrate the efficiency of nursing and medical intervention by adapting a contemporary view of holistic health. Although type of illness has emerged as a significant determent of child’s HRQoL, other demographics factors remain significant factors to children’s quality of life. The complex interplay among HRQoL variables and child’s demographics provides an important opportunity for collaboration among the health care sector and the education system. A holistic and individual approach to the education of these children requests reintegration programmes that are best facilitated by coordinated efforts between child’s home, school and hospital [13]. Findings not only imply that health care professionals must pay further efforts to enhance children’s quality of life in Jordan, but also raise the question of whether there are any governmental efforts directed toward this population. We can argue here that children’s quality of life in Jordan is greatly influenced by their medical condition, and then by improving the child’s health state, we can improve their quality of life. This can be achieved if health care professionals considered interventions that are aimed at reducing their symptoms and eventually improving their functional performance. Each HRQoL domain is important in children’s life and each health care professional has a significant role to play in improving the child’s outcomes.
5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are thankful for Dr James Varni and the Mapi Research Institute in France for their permission to use the Paediatric Quality of Life (PedsQL 4.0) for children in this study. We also extend our gratitude to Barbara Elliott and Dr Peter Draper from Hull University for their advice and support as well as for every child and parents participated in this study.