1. INTRODUCTION
Breast cancer is the most common cause of malignancy among women and the second most frequent cause of cancer death after lung cancer worldwide. Incidence rates are high in developed countries accounting for 30% and 15% of cases respectively [1].
Breast ultrasound is an important investigative tool for the evaluation of breast lesions and is complementary to mammography [2-5]. Ultrasound is superior to mammography in the assessment of radio dense breasts, peripheral breast lesions and the evaluation of mammary cysts particularly in pre-menopausal patients and women receiving hormone replacement therapy [6].
The aim of this study was to find if Doppler ultrasound of the axillary and lateral thoracic arteries in breast cancer cases would differ from benign breast lesions and normal controls.
2. SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Two hundred patients were presented to Ain Shams university hospitals, with breast lumps in the period from January 2004 till January 2013. All patients accidentally discovered lumps or by self examination. All patients received an informed consent. A complete history was taken from all of them, including smoking, history of lactation, history of trauma, hormone replacement therapy (if post-menopausal), previous history of any gynecological lesions or malignancy and family history of breast cancer. General and local clinical examination, breast ultrasound, mammography and fine needle aspiration (FNA) or tru-cut biopsy were done for all cases. Lumpectomy or modified mastectomy was done for all cases and histopathological results were obtained. Machines used were either, GAIA (Medison, SA8800, Seoul, South Korea) or Voluson (730 Pro V, BT05, GE, USA).
Breast ultrasound included assessment of borders of the mass (regular/irregular), echogenicity (sonolucent/ heterogenous/hyperechoic), vascularity, and lump size in cm. Axillary scan included morphological and Doppler assessment of vascularity of axillary lymph nodes (if visible) and Doppler ultrasound for assessment of axillary artery resistance index (RI).
For detecting the lateral thoracic artery Doppler signal, patients were placed in the supine position with their arms flexed and hands under head. The ultrasound probe was positioned parallel to the edge of the pectoral muscle and moved in the lateral to medial direction and sliding down, till detecting the Doppler signal. If a persistent color Doppler signal indicative of the LTA was identified, the spectral (pulsed) Doppler gate was positioned, and spectral tracings of the arterial signals were recorded and analyzed.
Axillary artery was detected while patient was in supine position, hand under head and ultrasound probe positioned in the axilla in the same direction of arm. Fine needle biopsy or true-cut biopsy was done for all cases. Histopathological examination of all specimens was done.
Statistical analysis of all results was performed using the SPSS software version 15.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Continuous variables were presented as mean and 95% confidence interval (CI). The student’s t test and the χ2 test were used for comparing continuous and categorical variables, respectively.
3. RESULTS
Age ranged from 22 - 64 (43 ± 4.16) years and lump size ranged from 1 - 5.1 (2.93 ± 1.6). Medical history revealed that none of the patients was a smoker, on hormone replacement therapy or had previous history of gynecological malignancy. Three cases had a family history of breast cancer.
There were 81 malignant cases and 119 benign conditions. Ten cases had enlarged axillary lymph nodes and were depicted by ultrasound. Histopathological results of malignant cases and their sites are mentioned in Tables 1 and 2.
Analysis of data elicited by ultrasound was done and cases were divided into two groups benign and malignant. Statistically, lateral thoracic artery RI and axillary artery RI were used in absolute values, structural breaks were noted as present or absent, compressibility, present or absent, borders, regular (circular or oval) or irregular, echogenicity noted as sonolucent (jet black) or heterogeneous. The structural criteria by ultrasound describing benign lesions were sonolucent consistency, regular borders, and negative compression sign while the increased heterogeneity, irregular borders and structure breaks were more predictive for malignancy. Retracion sign was absent in all cases in this study.
There was a statistical significant difference between malignant and benign cases as regard borders, echogenicity, structural breaks, compression sign and lateral thoracic artery RI, while axillary artery RI revealed no statistical difference between benign and malignant groups (Table 3).
LTA RI ranged from 0.72 to 0.80 in benign group and ranged from 0.57 to 0.61 in malignant group (Figure 1).
A statistical significant difference regarding LTA RI between ipsilateral side and contra lateral side of breast lump in malignant group, while it was non significant in benign group (P < 0.001). Ipsilateral LTA RI was used in all the other statistical analysis. A highly significant difference was found between malignant and benign cases P < 0.001. ROC curve revealed a cut off value of 0.67
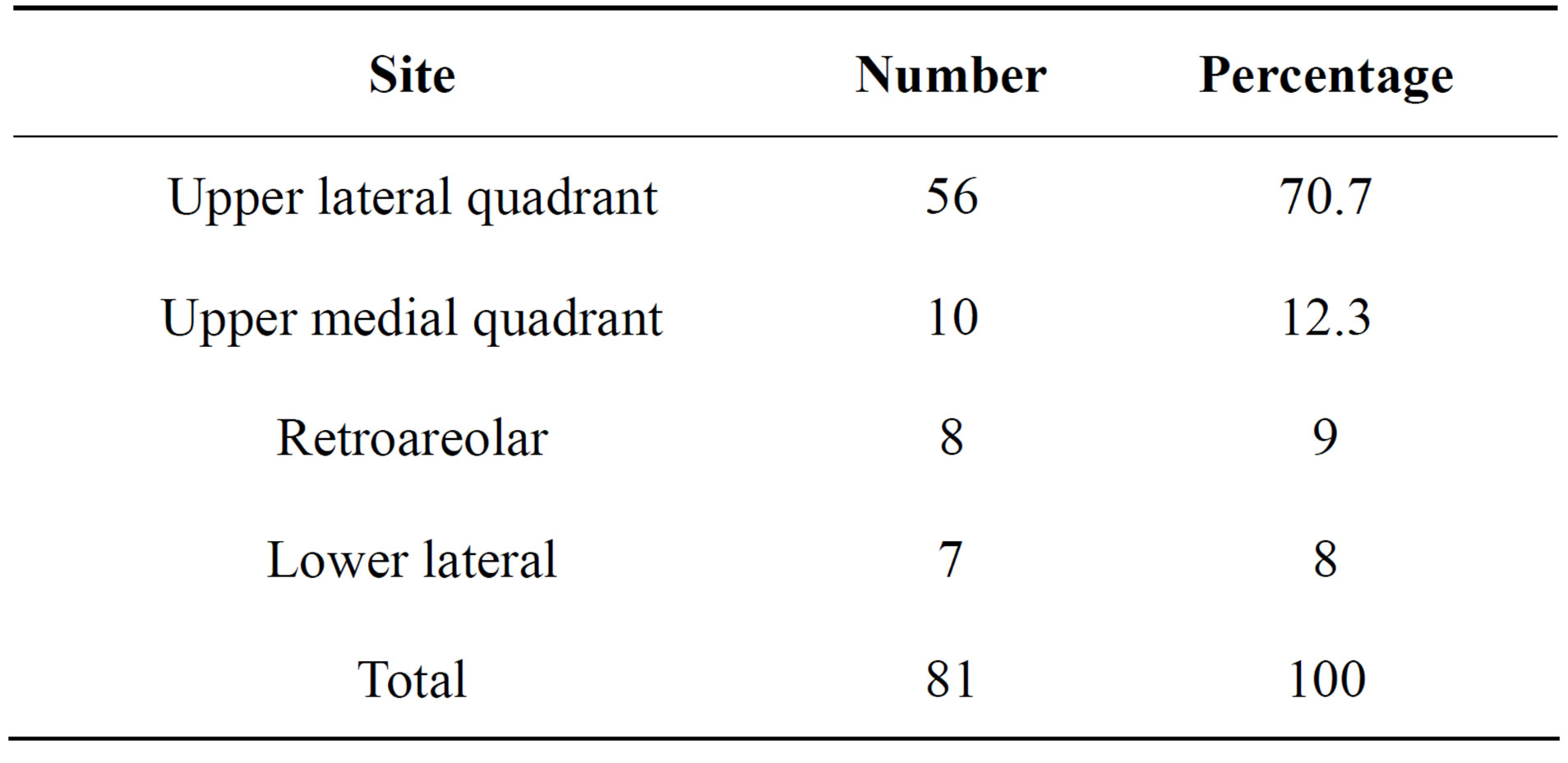
Table 1. Numbers and percentages of malignant cases according to location in breast.
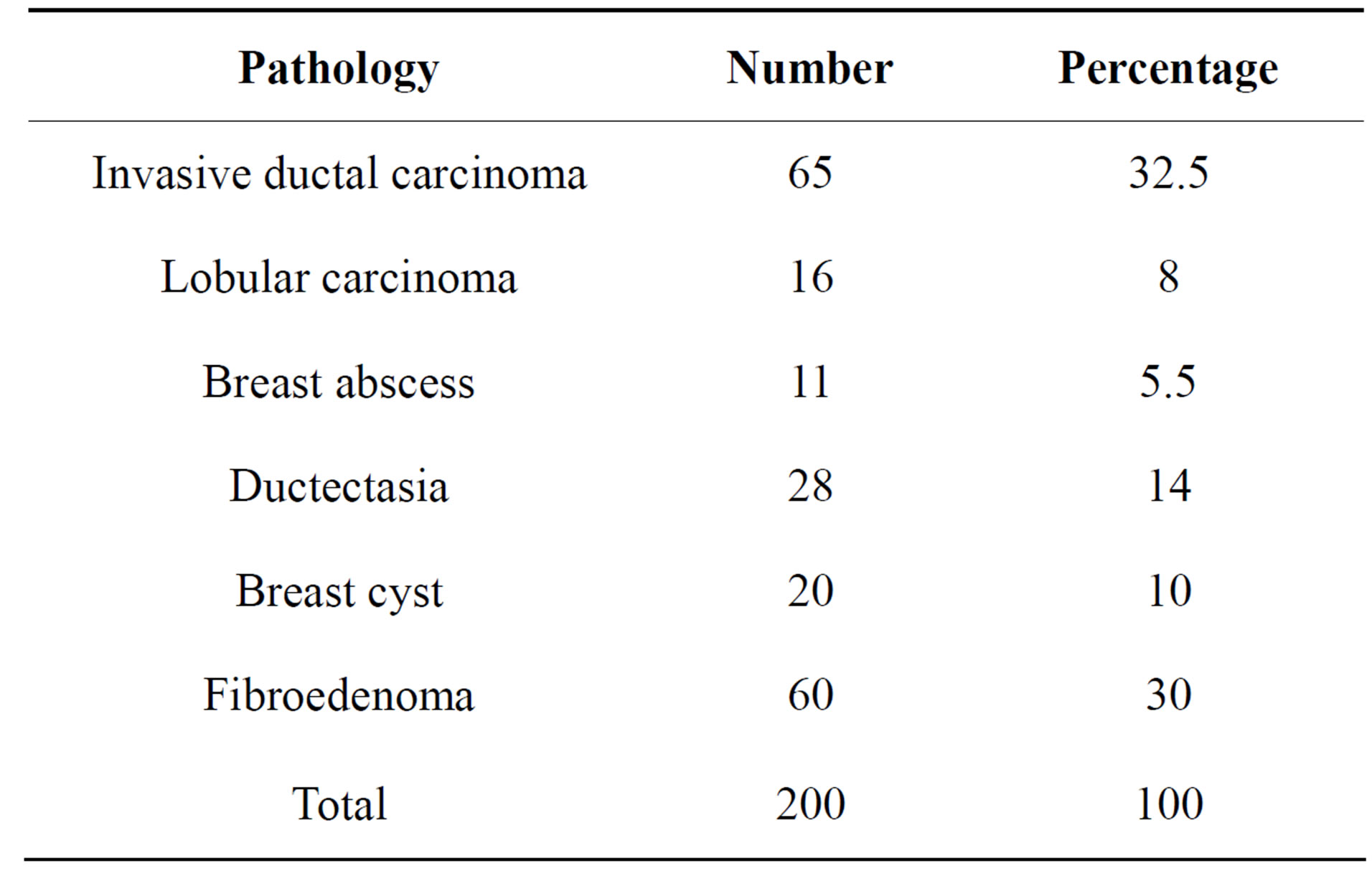
Table 2. Histopathological results of benign and malignant cases.

Figure 1. Left lateral thoracic artery RI in a breast cancer case.
for prediction of malignancy among all cases. Adding LTA RI to the ultrasonographic morphological criteria improved the sensitivity for identifying cancers from 96.2% (B-mode) to 98% (B-mode and color Doppler) with a minimal reduction in specificity (92.5% to 90.7%) or accuracy (95.6% to 95.2%). Axillary artery RI ranged from 0.82 - 0.86 (84 ± 1.3) in benign group and between 0.81 and 0.85 (83 ± 1.07) in malignant group. No significant difference was found between malignant and benign groups. Lateral thoracic artery RI cut off value of 0.67 was predictive for malignancy in this study.
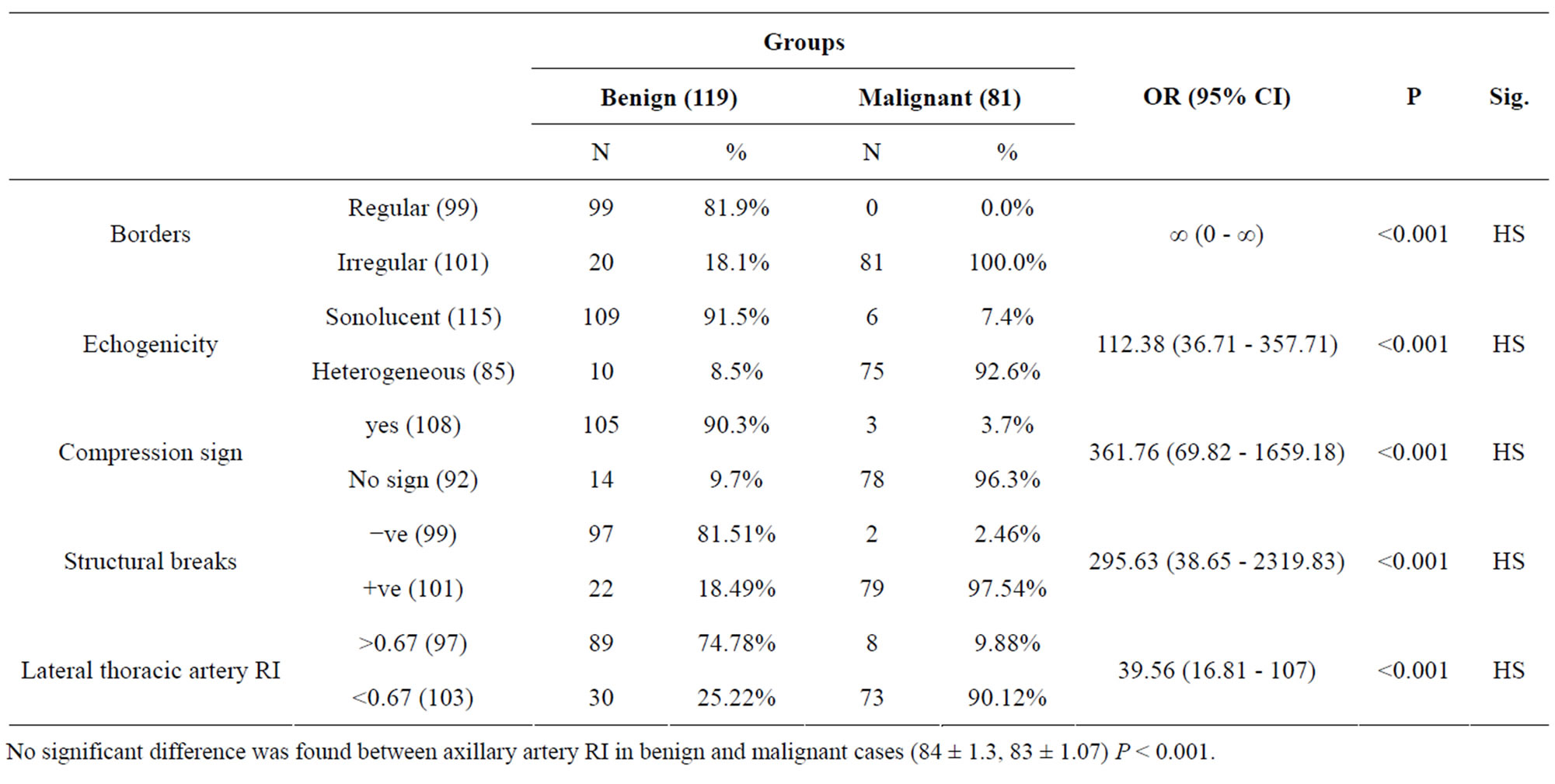
Table 3. Borders, echogenecity, compression sign, structural breaks and lateral thoracic artery RI comparison between benign and malignant cases.
No significant difference was found between axillary artery RI in benign and malignant cases (84 ± 1.3, 83 ± 1.07) P < 0.001.
4. DISCUSSION
Breast examination is a part of gynecological examination; patients mostly present with mastalgia, breast lumps or nipple disharge including galactorrhea. The most important aspect in combating breast cancer is diagnosis at an early stage when the chance of curability with appropriate therapy is excellent [1].
Breast masses have become common in women. Such masses pose a potential threat to women especially in the era of increased cases of breast cancer worldwide. Breast carcinoma ranks first among the malignant tumors affecting females in many parts of the world with the rate of breast cancer being 1 in 8 in USA. There are currently more than 600,000 cancer deaths annually in Africa. By 2020, 70% of the 15 million new annual cancer cases will be in developing countries [7].
Diagnosis at an early stage depends on proper screening. The most accepted non invasive investigation used is mammography. However, mammography has its limitations, especially in echo dense breasts as in premenopausal and menopausal women on hormone replacement therapy [3,4].
Angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, plays a central role in both local tumor growth and distant metastasis in breast cancer. Consistency of the lump, the borders, visualization of axilla and axillary lymph nodes are depicted by ultrasound. Power Doppler ultrasound helps markedly in the detection of neo-angiogenesis and the assessment of increase in the blood flow in the main vessels by Doppler indices. Different Doppler modes with and without contrast agents and different examination techniques and ultrasound and Doppler criteria have been investigated in the literature [8- 17].
The current study focused on Doppler ultrasound role in differentiation of a breast cancer lump from a benign one by assessment of lump vascularity, lateral thoracic artery and axillary artery blood flow. Breast ultrasound is usually accepted by all women being a non invasive inexpensive office procedure, free of ionizing radiation exposure.
Ultrasound was proved to be significant in differentiating cystic from solid breast masses as well as detecting suspicious masses [7]. Criteria for prediction of malignancy by ultrasound included irregular borders, heterogeneous consistency, structural breaks, positive compression sign, axillary lymph nodes and Doppler ultrasound is added in the current study. In the current study, two hundred patients with breast lumps were investigated by breast ultrasound, mammography and fine needle aspiration or tru-cut biopsy. Malignant cases undergone lumpectomy or modified mastectomy. Doppler criteria for assessment of lumps and lateral thoracic artery Doppler were introduced by many authors [8,9].
The main arteries to the breast are the lateral thoracic artery and to a lesser extent the internal thoracic artery. In a prospective open diagnostic study of Obwegeser et al., ninety four women were involved in the study, comparing the intra individual differences of Doppler indices in the lateral thoracic (breast-feeding) artery of breasts affected by cancer with those unaffected by disease. Lateral thoracic arteries could be visualized in 88% of their study population. Significantly lower values for pulsatility and resistance indices and systolic/diastolic ratios were obtained in the lateral thoracic arteries of breasts affected by cancer as compared to the contra lateral breasts.
They concluded that the intraindividual difference in Doppler indices in women with breast cancer may be a useful test for the diagnosis of breast lesions. In the current study, lateral thoracic artery RI of a cut off value of 0.67 was predictive for malignancy which agrees with another previous study with smaller numbers which had a cut off value for prediction of breast cancer by LTA RI of 0.6 [10]. Lymph nodes were found in ten cases with no increased vascularity detected by Doppler ultrasound. It should be noted that microvessels would not be detected by Doppler ultrasound and that may explain the low perfusion of malignant lumps and lymph nodes in this study. None of the cases in this study had retraction sign. Ultrasonographic retraction sign is usually found in an advanced cancer reaching to the skin and associated with peau d’orange clinical sign which is a very late sign of cancer. None of the cases of this study reached this stage and that explain absence of this sign in all cases of this study.
In a study of Svensson et al., they aimed to evaluate the use of vascular morphology, around and within the B-mode region of abnormality, for improving the diagnostic accuracy of two of the most common solid breast pathologies [15].
In their study, the B-mode and Doppler images of 117 breast cancers and 366 fibroadenomas and lesions with a fibroadenoma-like appearance were reviewed retrospectively and the morphology of the vascular pattern was evaluated. The ratio of external to internal color Doppler, the external vascular pattern and the connecting vessels to internal vessels were assessed and differentiated into benign and malignant vascular patterns. These patterns were correlated with the histological diagnosis [15].
The Vascularity was demonstrated in their study in 95% of cancers and in 46% of benign lesions with a trend to increasing vascularity in cancers. This provided poor specificity for excluding cancer in fibroadenomas. Variations in vascular pattern were recorded. The observed benign vascular patterns were either avascularity or vascularity in the periphery and peripheral marginal vessels connecting with internal vascularity. The observed malignant vascular patterns were radially aligned external vessels with internal vessels being more numerous than external vessels which connected to radial vessels.
They concluded that the presence of vascularity within a lesion, by itself, is no longer a good predictor of malignancy because of the increase in Doppler sensitivity associated with improvements in ultrasound technology [15].
Their results agree with the results of the current study in which the local vascularity was not found markedly in cases of breast cancer. Color Doppler ultrasound vascular pattern morphology improves the accuracy and sensitivity of B-mode image diagnosis, breast cancers and fibroadenomas with a minimal loss of specificity. Any breast lesion with radial rather than marginal connecting vessels should be regarded with suspicion [15].
Color Doppler imaging may help in differentiating between malignant and benign solid breast masses, but it doesn’t show high predictive values, so its role is only complementary to the high-sensitive B-mode evaluation raising or confirming the doubts upon suspicious lesions [16]. In a study of Yang et al. to document differences in color Doppler flow and gray-scale ultrasonographic features between benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes in women with primary breast cancer in 135 women with primary breast cancer. They concluded that color Doppler flow and gray-scale US features applicable to the identification of disease in palpable axillary nodes in patients with breast cancer are not applicable to nonpalpable nodes [15]. In the current study, blood flow of the feeding arteries of breast was detected by ultrasound as a trial to add another additional predictive ultrasonographic sign for prediction of breast cancer. The larger trunk of axillary artery-than lateral thoracic artery and lateral thoracic artery being the main breast blood supplier especially the lateral compartment, can explain the significant statistical difference in LTA Doppler in this study while axillary artery Doppler was not significant.
Breast Doppler ultrasound as a non invasive procedure widely accepted by all women worldwide and available in many gynecologic clinics, can be an additional investigation for breast lumps. Assessment of larger numbers by Doppler ultrasound and follow up of many high risk cases prior to the appearance of lumps may lead us to reach a LTA RI cut off value for prediction of breast cancer prior to its clinical appearance.
5. CONCLUSION
Lateral thoracic artery Doppler can be added to the ultrasound criteria for prediction of malignancy in breast cancer with a cut off value of 0.67.
NOTES