1. Introduction
The methods used to detect neutrons are commonly based on the emission of charged particles produced by the interaction of neutrons with He-3 or BF3 contained in the counters or detectors [1]. Another types of commonly used detectors are the BD, the Defender and the Defender XL which are Bubble Detector-Dosimeters. They are made of an elastic polymer gel in which minute droplets of superheated liquid are uniformly scattered. When these droplets are struck by neutrons, they evaporate and form small bubbles of gas that remain trapped in the elastic polymer [2]. The number of bubbles is in direct proportionality with the number and the energy of neutrons, in particular from the counted number of bubbles in these detectors and from their certified efficiency (Bubbles/mSv) one can obtain the dose equivalent of the neutrons that struck the detector. A further technique is based on CR39. The CR39 (PADC) are plastic detectors made of the polymer C12H18O7, whose density is 1.3 g·cm−3. They can detect both heavy charged particles and neutrons when the latter is converted into alpha particles by the nuclear reaction B-10 (n, α) Li-7 that takes place within a very thin homogeneous layer of B-10 that coats the surface of the CR39 [3]. These detectors have a very wide range of energy extending from tens of KeV
(40 KeV) up to some MeV (4 MeV). A further technique to measure neutrons is by activation of targets made of thin plates of ultra-pure Au, In, Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Al, Ti followed by the measurement of the gamma and beta activity of these plates. The detecting process described in this paper is based on a technique used by the authors in previous experiments in which polycarbonate plates (CR39) were surrounded by a layer of suitable thickness of granular boric acid H3BO3 [4]. In the present case, the polycarbonate plates were substituted for a normal photographic film made of an acetate substrate with a layer of silver halide spread on it. This film was surrounded by a layer of H3BO3 of suitable thickness as it was for the plates. In both cases, the grains of boric acid have the same dimension. Due to a patent pending on this technique we are not allowed to provide further details. This method is based on the same technique described above where neutrons are converted by the boric acid into lithium 7 and alpha particles by the reaction
 1 (1)
1 (1)
and the latter interact with a polycarbonate plate on which they produce peculiar tracks.
2. Description and Preparation of the Detectors
According to the reaction mentioned above, we developed a specific type of detector in which a usual black and white photographic film of 400 ISO made of a layer of silver halide was surrounded by a layer of boric acid. The choice to use a 400 ISO film was made in order to have a compromise between the brightness and the resolution of the image. The detector was made with few frames of photographic film, 24 × 36 mm, wound in order to form a cylinder by joining the two edges. The second step was to insert this cylindrical film inside a dark cylinder of Polyethylene and then fill this cylinder of boric acid as shown in Figure 1. All of the different tasks to set up the detector were made inside a dark room in complete obscurity, that is without turning on the inactinic light.
3. Experimental Measurements
We carried out measurements with three films of the same type described above for each test. (Table 1) In each measurement the three parts of the film were subjected to different conditions: the first part was kept in air and was not irradiated; the second part was kept in boric acid and it was not irradiated; the third part was immersed in boric acid and was put in front of the neutron flux. These experiments were carried out at the ENEA

Figure 1. The black cylinder contains a cylindrical layer of H3BO3 (the white granulate) which is in direct contact with the film (lucid external part of the white cylinder in this figure). More H3BO3 will be poured into the cylindrical remaining space and once that all the black cylinder is full of H3BO3, the cylindrical sheet of paper (visible in this figure), which only gives more rigidity to the film, is slipped away.

Table 1. Main general characteristics of the available neutron sources.
Casaccia Research Centre, with three types of neutron sources: Am241-Be source; horizontal channel in the thermal column of the nuclear reactor TRIGA; radial channel 2 of the nuclear reactor TAPIRO.
The irradiation time was 1 hour (3600 s) and the dose rate of neutrons was 100 μSv/h for all of the irradiated film. The dose rate had been previously ascertained by an He-3 dosimeter which was placed in the same position where the boric acid detectors will have been placed. In Figure 2 we report the characterization of the Am-241 - Be source as to the fluence of its neutrons and its neutron spectrums. The characterization was carried out by the neutron spectrometer MicroSpec-2 [5] Neutron Probe [6] (Bubble Technology Industry) which comprises two detectors (He-3 and liquid scintillator NE213) for two neutron energy intervals. In Figures 3 and 4 we report the fluence and the spectrum, which were measured by the same spectrometer, of the neutrons from the reactors TRIGA and TAPIRO. In all the three measurements, the films with H3BO3, after development, presented visible and clear traces which, conversely, were present neither on the control film screened by H3BO3, nor on the control film in air that were not irradiated. By comparing this experience with a previous one in which we irradiated, in similar conditions, CR39 plates with neutrons in front of the radial channel 2 of the reactor TAPIRO, we find out a very peculiar similarity between the traces obtained on the CR39 screened by boric acid and those obtained on the silver halide of the film screened by boric acid. This detecting technique produces different images for different neutron sources, but for the same neutron source, the images are the same independently of the type of detector used (CR39 or film with silver halide). At the end of the


Figure 2. Fluence and neutron spectrum of the Am-241 - Be source: 100 μSv/h. Duration of the measurement: 1 hour. Counts per second: 400 cps. Measuring instrument: Neutron Spectrum MicroSpec-2 Neutron Probe (Bubble Technology Industry).


Figure 3. Fluence and neutron spectrum of the source TRIGA: thermal column horizontal channel. Dose Rate: 100 μSv/h. Duration of the Measurement: 1 hour. Counts per second: 1000 cps. Measuring instrument: Neutron Spectrum MicroSpec-2 Neutron Probe (Bubble Technology Industry).

Figure 4. Fluence and neutron spectrum of the source TAPIRO: radial channel 2. Dose Rate: 100 μSv/h. Duration of the Measurement: 1 hour. Counts per second: 30 cps. Measuring instrument: Neutron Spectrum MicroSpec-2 Neutron Probe (Bubble Technology Industry).
irradiations, the boric acid that had played the role of converting material (it converted neutron into alpha particles) for the irradiated detectors or of a simple screen for the non irradiated ones, was analysed by mass spectrometry. This analysis was conducted in order to look for possible traces of the neutron-into-alpha converting reactions (see 1). In these reactions, the isotope of Boron with higher capture cross section for thermal and slightly epithermal neutrons is B-10. When it captures a neutron, it splits yielding an alpha particle and a nucleus of Lithium-7. Thus, by mass spectrometry we searched both for a possible change in the natural occurring ratio of Boron-11 and Boron-10, expecting a slight decrease of the lighter isotope and a corresponding increase of Lithium-7.
4. Results
In Figures 5-7 we report respectively the film screened by boric acid and irradiated by the neutrons from the Am-241 - Be source, from the nuclear reactor TRIGA and from the nuclear reactor TAPIRO. Other films, either in air (not screened) or screened by boric acid but not irradiated, were our experimental zero and, after development they turned out to be uniformly dark and did not present any macroscopical tracks. In Figure 8, there is the visual comparison between two images: the tracks on the CR39 and those on the acetate film with silver halide. These images were obtained by the same source (reactor

Figure 5. Neutron Detection from the Am-241 - Be source. Silver halide black and white film: sensitivity: 400 ISO; granular H3BO3.
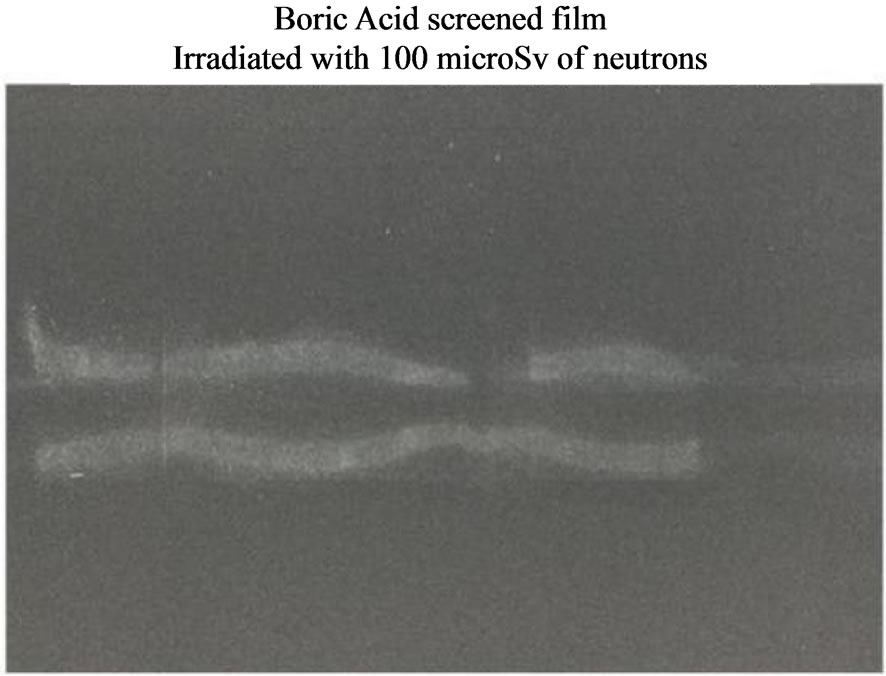
Figure 6. Neutron Detection from the reactor TRIGA: thermal column horizontal channel. Silver halide black and white film: sensitivity: 400 ISO; granular H3BO3.

Figure 7. Neutron Detection from the reactor TAPIRO: radial channel 2. Silver halide black and white film: sensitivity: 400 ISO; granular H3BO3.


Figure 8. Comparison between two neutron images obtained on two different imaging substrates screened by the same filter by neutrons of the reactor TAPIRO from radial channel 1 and radial channel 2. The two images have the same morphology.
TAPIRO) and with the same thickness of boric acid surrounding the CR39 and the acetate film. For both of the substrates, we reckon that alpha particles are directly responsible for the images which were produced on the two different substrates (polycarbonate for the CR39 and silver halide for the film). Let’s spend some words about the differences and the possible analogies between the two images. On the CR39 the image is made up of many bright spots, each spot corresponding to the hit of an alpha particle. As to the film, conversely, the image looks smooth and not made of spots. This difference between the two images is due to the completely different substrates and the way alpha particles interact with them. For the polycarbonate, the hit of an alpha particle produce a more localised damage in the molecular chains, while for the film, the hit involves a much wider area of silver halide and adjacent hits overlap. However, the overlap of tracks may happen also on the CR39, as is clearly visible for the elongated bright track, when many hits of alpha particles concentrate in a small area. Moreover, also on the film it is possible to have separated spots, as long as the density of hits of alpha particles per unit surface is small, as it is intuitively visible on the border of images where the brightness fades away (however, the possibility of distinguishing single spots depends strongly on the ISO of the film which determines its granularity once developed). The image on the film is made of two parts: a thin one which looks like an arc of a circle with a brighter section; a bulkier one, made of a thick bright mark and a thinner one close to each other. The image on the CR39, conversely has only one thick bright mark and some other single track scattered on the rest of the surface. The primary reason for the difference in shape and position of the thick tracks on the two substrates lies with their different superficial extensions (10 × 10 mm for the CR39 and 24 × 36 mm for the photographic frame) and the extension of the circular aperture of the neutron channel (radius of 20 mm). Both the CR39 plate and the photographic frame were centred in front of the circular aperture of the neutron channel, but while the CR39 covered only the central part of the channel, the frame covered a wider surface that extended up to the border of the channel. Hence, the places where neutrons arrived (there is no uniform neutron flux in the channel) and converted into alpha particles produced an image, are different. However, as to the mechanism that generates the images on the photographic film, we would like to report a second sound hypothesis, other than the direct interaction between silver halide and alpha particles, which was put forward by and anonymous reviewer of the paper and communicated to us by the journal editor. The damages generated by alpha particles on the polycarbonate of the CR39 are very subtle and only the etching process makes them visible as circular tracks. Conversely, as it was pointed out in the case of the film, there are no individual tracks visible. This suggests that the response of the film to individual alpha particles is sufficiently subtle that the result is completely invisible. However, one would expect granular boric acid to respond to alphas very much like a scintillator. In this case a single energetic alpha will make a very large number (perhaps 10s of thousands or more) of photons, sourced over a distance on the order of the range in the granules (many microns). Since the boric acid granules are distributed over a moderate distance above the film surface, most of the alphas will be produced millimeters away from the film. In this case, the light signal associated with a single alpha should be a relatively large (mm) spot of low exposure. Many alphas striking close together will lead to quite a few photons in the same general area, producing a soft image very much like what appears in the data. Hence, one may also think that the new detector is basically a scintillator detector with pretty good spatial resolution on the film. One way to test this hypothesis would be to expose the film using an alpha source directly, and see what the response is.
With regards to the analyses by mass spectrometer, we found out a fairly significant variation of the ratio between B-11 and B-10 in the detectors irradiated by neutrons. In particular, we found out the two following ratios between Boron-11 and Boron-10 for the non-irradiated Boron and for the irradiated one, respectively2.



Despite this piece of evidence, nothing is possible to say about the presence of Lithium since, even with a significant variation of B-10, the corresponding variation of Lithium-7 was below the minimum value that could be discerned by the mass spectrometer3.
5. Conclusion
We developed a new and cheap technique which is capable to detect neutron emission and we verified its accountability by testing it with different sources. These tests produced different images for different sources possessing the same dose rate (Figures 5-7). Besides, the same neutron source produces similar images on different substrates (Figure 8), screened by the same thickness of boric acid, independently of the revealing substrate (polycarbonate and silver halide). A further proof of the accountability of this technique is available in Figure 6 where the picture shows the shape of the neutron collimating horizontal slit at the end of the thermal column channel.
6. Aknowledgements
We want to thank for their kind, precious and active collaboration the following people: Giovanni Silvestri owner of the Hobby Photo Laboratories, based in Sulmona (Italy) for the preparation of the film and its development; Massimo Sepielli managing director of the UTFISST ENEA; the team of the nuclear reactor TRIGA of the ENEA Casaccia Research Centre, Daniele Baiano (BAS IONIRP ENEA), Monica Lammardo (UTFISSTREANUC ENEA) reactor operator, Emilio Santoro (UTFISST-REANUC ENEA) director of the reactor TRIGA; the team of the nuclear reactor TAPIRO of the ENEA Casaccia Research Centre Barbara Bianchi (UTFISSTREANUC ENEA), Orlando Fiorani (UTFISST-REANUC ENEA) and Alfonso Santagata (UTFISST-REANUC ENEA). As to the analyses of Boron isotopical composition and the Lithium research by different techniques, we want to thank for their kind, subtle and proficient help, Samuele Agostini researcher of the Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources of the National Research Council of Italy (Pisa) and Filippo Ridolfi researcher of the Department of Geological Sciences of the Carlo Bo University of Urbino.
NOTES
1The available energy is devided between the alpha particle and the Lithium atom. When the latter is left in a non-excited state (about the 6% of the time) the available energy is 2.792 MeV while when the Lithium atom is left in an excited state (about the 94% of the time) the available energy is 2.31 MeV.
2The technique used to find out the following ratios between B-11 and B-10 is the Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry (TIMS) carried out by the TIMS Laboratory at the Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources of the National Research Council of Italy. This laboratory has a deep and proficient know how of the analytical techniques for the isotopical study of Boron dedicated to its isotopical geochemistry [7,8].
3The analyses to find out the concentration of Lithium were carried out by the standard procedure called Ultratrace-3 at Actlabs which are 17025 ISO accredited laboratories [9].