Comparison between different methods of estimation of vitamin D ()
1. INTRODUCTION
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that in 2010, there were 8.8 million (range, 8.5 - 9.2 million) incident cases of Tuberculosis (TB), 1.1 million (range 0.9 - 1.2 million) deaths from TB among HIV-negative people and an additional 0.35 million (range, 0.32 - 0.39 million) deaths from HIV-associated TB [1]. Tuberculosis (TB) is a deadly infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. At present drug regimes comprise four to five drugs administered in combination for 6 - 9 months. It was a common practice that patients stopped taking the drugs as soon as the symptoms ameliorated, and as a consequence, there was a rise in multidrugresistant TB cases, which were and are much more complicated to treat than those infected with a drugssusceptible strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis [2]. The primary goals of drugs development for tuberculosis are to shorten and simplify treatment of active TB, provide safer and more efficacious treatments for drug-resistant TB, eliminate drug-drug interactions for TB/HIV co-infections, and improve treatment for latent TB infections [3]. Successful development of new, safe and effecttive TB therapies faces a number of changes. Some are unique to TB drug discovery and development, many are with implications for other therapeutics indications. Natural products play a highly significant role in the drug discovery and development process [4]. This was particularly evident in the areas of cancer and infectious diseases, where over 60% and 75% of drugs currently usedrespectively, were derived from natural products or depended upon a natural product for their development [5]. Essential oils are homogeneous mixtures of organic chemical compounds from the same chemical family [6,7]; they are composed by terpenoids, especially monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes. Nevertheless, low molecular weight aliphatic compounds, acyclic esters or lactones may be present [8]. The essential oils chemical composition is affected by some factors as species and subspecies, geographical location, harvest time, the part of the plant used and the extraction methods used to obtain the essential oil [9]. Due to the difference in chemical compound groups in the essential oils, it is more likely that their antibacterial activity is not granted to a specific mechanism, but to different action of attack mechanisms in the cell with different targets [2]. It is known that these substances action is carried out mainly on the cell cytoplasmic membrane. The presence of a hydroxyl group is related to the enzymes inactivation. It is probable that this group cause losses of cell components, a change on fatty acids and phospholipids, and prevent the energy metabolism and the genetic material synthesis [10]. In this study, it was to evaluate the antimycobacterial activity of essential oils of cumin (Cuminum cyminum), Clove (Eugenia caryophyllata), Cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum), Laurel (Laurus nobilis) y anis (Pimpinella anisum) obtained by hydrodistillation process against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv sensitive to all five first-line antituberculosis drugs using the microplate alamar blue assay (MABA).
2. MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1. Plan Material
The vegetal materials used in this study anis (Pimpinella anisum), laurel (Laurus nobilis), cumin (Cuminum cyminum), clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) and cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) were provided by Comercial Cardona S.A. (Chihuahua, México).
2.2. Mycobacterium Species
The following M. tuberculosis strains were obtained from the Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición “Salvador Zubirán” in México, D.F.: M. Tuberculosis H37Rv sensitive to all five first-line antituberculosis drugs (streptomycin, isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol and pirazinamide), H37Rv (CH-8 and CH-15) isoniazid-resistant, H37Rv (CH-07 and CH-09) rifampicin-resistant, H37Rv (CH-03 and CH-06) streptomycin-resistant, H37Rv (CH-09 and CH-10) ethambutolresistant. All protocols used in this study were approved by the local ethics committee.
2.3. Extraction of Essential Oils
A modified Schilcher apparatus was utilized in hydroidstillation. The flow rate was 10 to 15 ml/min Cooling water was kept at 19˚C to prevent the higher molecular weight components from being stuck in the cooler. For cumin, clove and anis, 200 g of the spice was added to 4 L of water were introduced in a boiling flask; for cinnamon and laurel 400 g and 4 L of water were used. The system was heated to 100˚C during 5 h. The operating conditions depended on the vegetable material used, according to Hernandez-Ochoa et al. [11]. The essential oil was collected and diluted whit hexane in a volumetric flask; the obtained solutions were analyzed by GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry). The analysis of all essential oils was performed using a Gas Chromatographic System (Hewlett-Packard Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped whit a PE-5 column (60 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 mm film thickness) and a Mass Spectrometer Hewlett-Packard 5971 A as detector. The carrier gas was helium, at flow rate of 1 ml/min. For the GC-FID analysis, the temperature was increased from 70˚C to 180˚C at 1˚C/min. The injector and detector temperature were set at 180˚C.
2.4. Test Inoculum Preparation
Each of the above strains was culture at 37˚C in Middlebrook 7H9 broth supplemented with 0.2% glycerol and 10% OADC (oleic acid albumin dextrose catalase, Difco) until logarithmic growth was achieved. Each culture was mixed with a sufficient volume of sterile supplemented Middlebrook 7H9 broth to reach a turbidity equivalent to that of McFarland’s nephelometer No. 1 standard. To obtain the test inoculum, this suspension was further diluted 1:20 with the same culture medium immediately before use.
2.5. Antimycobacterial Activity
The activity of all extract against the aforementioned M. tuberculosis strains was tested using the microplate Alamar blue assay (MABA) according to Camacho-Corona et al. [2]. Sterile distilled water (200 µL) was poured into the outer perimeter wells of the microplate. All other wells received 200 µL of supplemented Middlebrook 7H9 broth, then working extract solution 200 µL were poured into the first well of each row, from which twofold dilution series were made through the microplate column. The test inoculum (100 µL) was added to all testing wells, as well as to the drugs-free control wells. The final concentration of DMSO in wells was about 1% v/v. At the same time, 10:100 and 1:100 diluted controls were prepared from the bacterial suspension, representing the growth of 10% and 1% of the bacterial populations tested. The final concentrations tested of essential oils ranged from 0.78 µg/mL to 200 µg /mL. Each microplate was incubated for 5 days at 37˚C. After the incubation time, one control growth was developed with a mixture of 50 µL of alamar blue solution and 12 µL of sterile 10% Tween 80. The plates were incubated at 37˚C for 24 h. After this incubation time, if the well turned pink, all the wells received the mixture of Alamar blue and Tween solutions in the same way and were incubated for an additional 24 h. Wells with a well-defined pink color were score as positive for growth. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) was defined as the lowest concentration of sample that prevents a color change to pink. To analyze the effect of essential oils, a one-way ANOVA was used. Tukey was used for analysis of media, using a 0.95% confidence level. Statistical analysis was done using the computational software Minitab (version 14.0). All analysis was done by triplicate.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The anis, laurel, cumin, clove and cinnamon essential oils (EOs) were obtained by the hydrodistillation process. The results obtained by GC/MS from the essential oils of cumin showed that the cumynaldehyde was the major molecular compound (Table 1).
A number of minor compounds were identified including alcohol cuminic, α-Pinene, β-Pinene, β-Myrceneρ-Cymene, γ-Terpinene, p-menta-1,3-dien-7-al. Similar results were obtained by Iacobellis et al. [12] in the quantification of the main compounds in the hydrodistillation process of Cuminum cyminum. In the essential oil of clove (Eugenia caryophyllata), eugenol, caryophyllene and acetate of eugenile were identified as main compounds, representing about 99% of essential oil. The essential oil also contains small amounts of Humulene, Oxide de caryophyllene, methyl Salicylate and Chavicol. These results obtained showed similarity with those reported by Dzamic et al. [13]. Cinnamomun verum cinnamon bark oil contains as its major component cinnamaldehyde (65%); other major constituents identified were β-caryophyllene, β-pinene, carene, and geraniol. Rajeswara Rao et al. [14] obtained similar results. Eucalyptol is the main component in the essential oil of laurel, in minor proportion were identified iso-limonene, β- Myrcene, Ocymene, 4-allyl-1,6-herpadieno-4-ol, Sabynene hydrate. In the essential oil of anis, trans-anethol was the major molecular compound detected and in minor proportions limonene and germancrene. The anis, laurel, cumin, clove and cinnamon essential oils were evaluated for their activity against one drug-sensitive and drugresistant variants of M. tuberculosis H37Rv. The Table 2 showed the MIC of isoniazid (INH), rifampicin (RIF), streptomycin (STM) and ethambutol (ETB) for each of the strains used in this study.
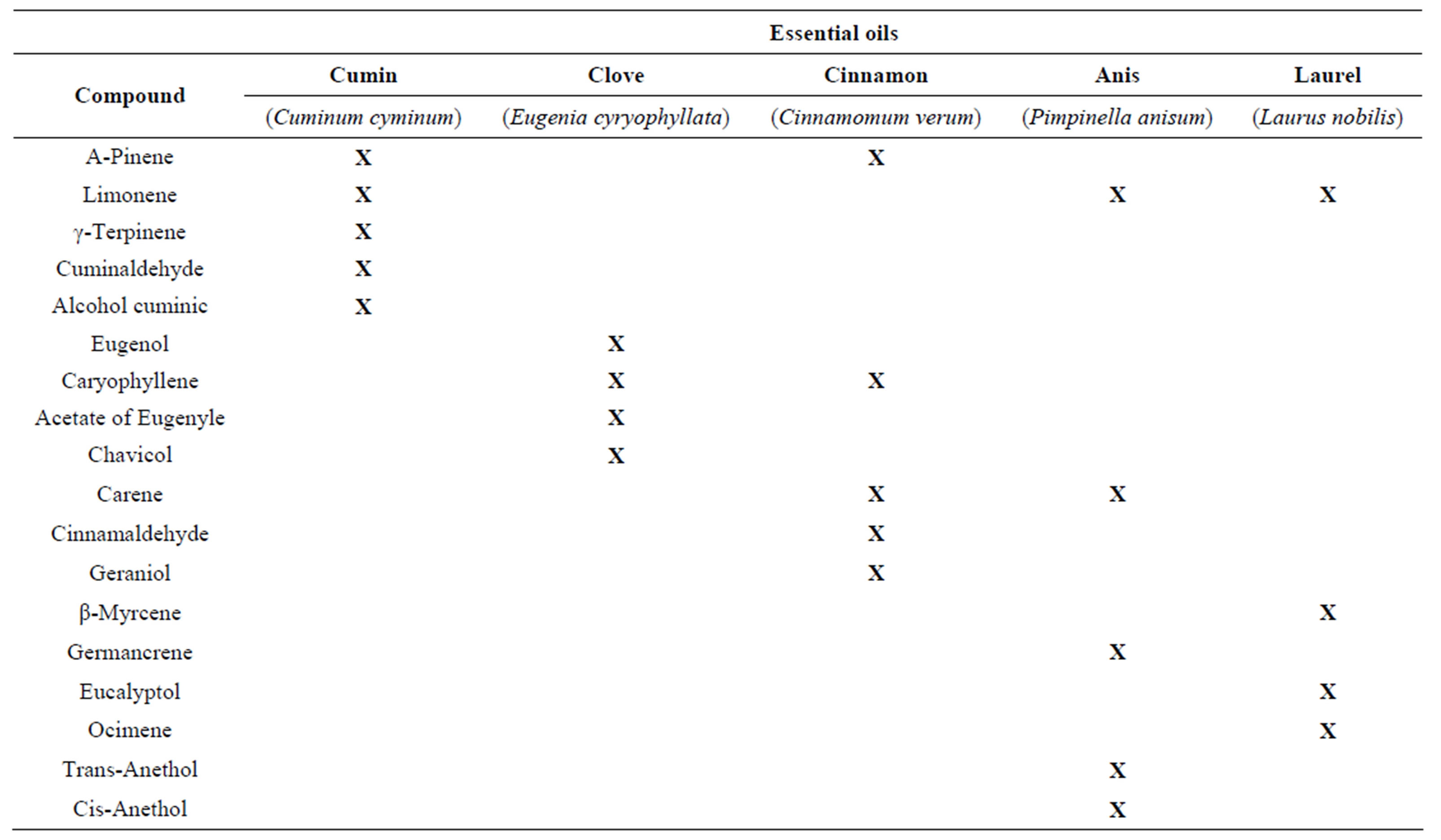
Table 1. The major molecular compounds identified in the essential oils of cumin, clove, cinnamon, anis and laurel using gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS).

Table 2. MIC values (µg/mL) of essential oils against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant variants of M. tuberculosis H37Rv.
The result from the screening showed that the reference strain H37Rv was susceptible to all drugs supplied, while other strains showed resistance to one or more different drugs. It was observed that strains CH-08 and CH- 15 are resistant to isoniazid, strains CH-07 and CH-09 resistant to rifampicin, strains CH-09 and CH-10 to Ethambutol and all strains except H37Rv strains were resistant to streptomycin, the first drug to be used as antituberculosis therapy [15]. The next step of the screening was to evaluate the essentials oils against four drugsresistant variants of H37Rv strain. The results obtained are shown in Table 2, it can be observed that of the five essential oils tested, cumin and cinnamon were active against the sensitive strains M. tuberculosis H37Rv, the two extracts were active with a MIC value of 12.5 mg/ml. the essential oil of clove was active to 25 mg/ml and essentials oils of anis and laurel were less active with MIC value of 100 mg/ml. The five essentials oils were effective against the Isoniazid-resistant variant of H37Rv with MIC values in the range 12.5 - 100 mg/ml, the most potent being the cumin and cinnamon (MIC = 12.5). Similar results were obtained against rifampicin-resistant variant of H37Rv with MIC values in the range 12.5 - 100 mg/ml, the most active in this case were essential oils of cumin and cloves. Iacobelis et al. [12] attribute the cumin EO antimicrobial activity to a high level of cumynaldehyde and to other minority compounds that may contribute to the antimicrobial activity, such as β-pinene, limonene and α-pinene. The antimicrobial activity shown by the clove EO may be attributed to the presence of Eugenol, since this phenol compound is linked to damage to the bacterial cell envelope [16]. Other minority compounds also possess antimicrobial properties, such as caryophyllene [17]. Thus, Dorman and Deans [18] state that the oils’ antimicrobial activity is related to the composition of the plant’s volatile oils, the structural configuration of the oils’ constituent compounds and their functional groups and potential synergistic interactions among the compounds. The essential oils of anis and laurel were active against the sensitive strains M. tuberculosis H37Rv, Isoniazid-resistant variant of H37Rv and rifampicin-resistant variant of H37Rv with MIC value the 100 mg/ml. Clove, cumin, and cinnamon essential oils were active against all strains utilized in this study, with MIC values in the range 6.25 mg/ml - 25 mg/ml. These data suggest that these plants could be an important source of compounds whit antimycobacterial activity against multidrugs-resistant M. tuberculosis. Furthermore, as described above, it was observed that drugsresistant variants of H37Rv were more susceptible to the active extract that the sensitive variant, a point that supports the proposal of simultaneous screening of extract against pan-susceptive as well as drug resistant reference strains (like the mono-resistant variant of H37Rv). Based on these findings it can be proposed that active plants contain more than one antituberculosis compound and their activity is not related to that of streptomycin, isoniazid, rifampicin or ethambutol. Plants material remains—as an important source to combat serious diseases in the world. Investigations of the active molecular compounds contained in essential oils are being carried out in our group to find novel for the development of new anti TB drug resistant agent.
4. CONCLUSION
The chemical analysis of essential oils indicated that the major compounds for cumin, clove, cinnamon, anis and laurel are cumynaldehyde, eugenol, cinnamaldehyde, trans-anethol and eucalyptol respectively. The essential oils of Clove, cumin, and cinnamon were active against all strains utilized in this study, with MIC values in the range 6.25 mg/ml to 25 mg/ml. The results of present studies support the use of this plant in ethnomedicine as an alternative remedy for symptoms of tuberculosis and this plant may be a potential candidate for further phytochemical and pharmacological studies for obtaining compound effective against M. tuberculosis.
NOTES