A method to calculate the acetabular cup anteversion after total hip replacement based on 3D coordinate system ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Good acetabular cup anteversion and abduction were the basis of prosthesis stability, which was a key of a successful operation. Bad position of acetabular prosthesis easily leads to prosthesis loose which could lead to femoral head prosthesis prolapse [1-3]. Determining the Prosthesis location was very important in guiding postoperative rehabilitation and expecting long-term effect. Acetabular prosthesis included cement and non-cemented: the former was with a metal ring at the edge of the cup oval in hip anteroposterior X-ray films, the latter could only be seen a metal arc, elliptical arc, the middle part was blocked by the femoral head prosthesis. Due to the difficulty in measuring acetabular cup anteversion, Pettersson formula acetabular cup anteversion [4] and Riten Pradhan formula acetabular cup anteversion [5] were not corresponding to theory, so we determined a mathematical formula of theoretical acetabular anteversion by establishing a three-dimensional coordinate system. These were presented below.
2. METHOD
Establishing a three-dimensional coordinate system: O was the hip rotation center, X-axis was coronal axis, Yaxis was vertical axis, Z-axis was sagittal axis, Plane EDQP was the acetabular opening plane. The plane OHIF was cross-section through the hip joint rotation center, IF was projection of OI in the coronal plane, Plane OMJS was the vertical section of the acetabular opening plane through the hip rotation center, JS was projection OJ in the coronal plane, Rectangular plane HIKL vertical plane OMJS and plane OHL, KF was projection of OK in the coronal plane, Rectangular plane AGBC was vertical plane of acetabular opening through 1/5 point A of elliptical most diameter (supposing elliptical most diameter was R, acetabular radius was r), BC was projection of AB in the coronal plane. The plane OHL was the coronal plane through the hip joint rotation center.
Acetabular abduction δ was angle of acetabular opening and sagittal plane in the coronal plane. That was  1 in Figure 1, acetabular anteversion θ was angle of acetabular opening and sagittal plane in the cross-sectional plane. That was
1 in Figure 1, acetabular anteversion θ was angle of acetabular opening and sagittal plane in the cross-sectional plane. That was  OIH in Figure 1 [6], Pettersson formula [4] acetabular anteversion α was
OIH in Figure 1 [6], Pettersson formula [4] acetabular anteversion α was  OJM in Figure 1, Riten Pradhan formula [5] acetabular anteversion β was
OJM in Figure 1, Riten Pradhan formula [5] acetabular anteversion β was  ABG in Figure 1.
ABG in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Diagram of true acetabular cup anteversion and Pettersson formula acetabular cup anteversion and Riten Pradhan formula acetabular cup anteversion in a 3D system.
In Figure 1: Pettersson formula acetabular anteversion (α)  OJM = arcsin (2 OM/R) = arcsin (OM/r).
OJM = arcsin (2 OM/R) = arcsin (OM/r).
Riten Pradhan formula acetabular anteversion (β) 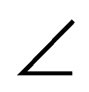 ABG = arcsin (AG/AB) = arcsin (5 AG/2R) = arcsin (1.25 AG/r).
ABG = arcsin (AG/AB) = arcsin (5 AG/2R) = arcsin (1.25 AG/r).
We can determine acetabular anteversion α = β.
Acetabular cup theoretical anteversion (θ)  1 = arctg
1 = arctg
(OH/HI)
 LK ∥ MJ
LK ∥ MJ
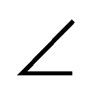
 LKO = α = β
LKO = α = β
 cosδ = OL/OH
cosδ = OL/OH
 OH = OL/cosδ
OH = OL/cosδ
 LK = HI
LK = HI
 θ =
θ = 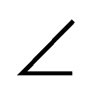 1 = arctg (OH/HI) = arctg [(OL/cosδ)/LK] = arctg [OL/(LK cosδ)] = arctg (tgβ/cosδ)
1 = arctg (OH/HI) = arctg [(OL/cosδ)/LK] = arctg [OL/(LK cosδ)] = arctg (tgβ/cosδ)
3. RESULT
The true acetabular cup anteversion and Pettersson formula anteversion and Riten Pradhan formula anteversion were quite different, the difference was increased with the acetabular cup abduction angle increasd. True acetabular cup anteversion θ = arctg (tgβ/cosδ).
4. DISCUSS
Good acetabular cup anteversion and abduction were the basis of prosthesis stability, which was a key of a successful operation. Bad position of acetabular prosthesis easily leads to prosthesis loose which could lead to femoral head prosthesis prolapse [1-3]. Determining the Prosthesis location was very important in guiding postoperative rehabilitation and expecting long-term effect. Acetabular prosthesis included cement and non-cemented: the former was with a metal ring at the edge of the cup oval in hip anteroposterior X-ray films, the latter could only be seen a metal arc, elliptical arc, the middle part was blocked by the femoral head prosthesis. Due to the difficulty in measuring acetabular cup anteversion, the fact that CT can not be used to measure acetabular cup anteversion, Pettersson formula [4] and Riten Pradhan formula [5] acetabular cup anteversion was not true. So the effect of acetabular abduction on anteversion was not taken into account and it was acetabular cup anteversion when the abduction was 0.
The results show: 1) Acetabular cup anteversion was impacted by the Acetabular cup abduction. There was a positive correlation between Acetabular cup anteversion and abduction. The anteversion was increased while the abduction was increased. Assumption for the Pettersson formula and Riten Pradhan formula acetabular cup anteversion was 20˚. When the abduction was 35˚, the real acetabular cup anteversion was 23.96˚. When the abduction was 45˚, the real acetabular cup anteversion was 27.24˚. When the abduction was 55˚, the true acetabular cup anteversion was 32.40˚; 2) When the abduction was 0, the true acetabular cup anteversion and Pettersson formula anteversion and Riten Pradhan formula anteversion were same; 3) When the acetabular abduction towards 90˚, the acetabular cup anteversion also tends to 90˚.
In short, the true acetabular cup anteversion and Pettersson formula anteversion and Riten Pradhan formula anteversion were quite different. The difference was increased with the acetabular cup abduction angle increased too. So intraoperation of total hip replacement placing acetabular cup needs to match abduction and anteversion, and taking the impact of acetabular abduction on acetabular anteversion into account, postoperation also needs to take the impact of acetabular abduction on acetabular anteversion into account in evaluating acetabular cup angle. The accuracy of Pettersson formula acetabular anteversion and Riten Pradhan formula acetabular anteversion had been confirmed. The formula was simple and accurate and worthy of clinical reference.