The Mechanism of Interacting Stellar Winds beyond Red Giant Branch ()
1. Introduction
It is now widely accepted that Red Giant Branch (RGB) is the progenitors of the nebulae but the details of the transition from one type of objecting the other are not known [1,2]. The importance of mass loss is demonstrated by the fact that the remnant of the Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) stars, the Proto Planetary Nebulae (PPN) and white dwarfs have mass distributions peaked closely around (0.6 M☉) [3,4], while the main sequence masses of these objects must have been ≥1 M☉) [5,6].
It is significant that appreciable mass loss which occurs from red giant producing an extensive circumstellar envelope has become “visible” with the advent of IR and Microwaves techniques [7]. The importance of Red-Giant mass loss in the formation of PN is obviously dependent on the transition time from Red Giant to PN [5].
For stars with core masses between 0.6 and 1.2 M☉, Paczynski (1971) argued that the transition is relatively rapid, particularly for high mass stars. Renzini (1981) with Marigo (2002) and Kwok (2005) have also convincingly argued that this transition time cannot be longer than the expansion time of PN (~104 yr) otherwise the nebulae will not be ionized before it disperses into the interstellar medium [8,9]. Given the short transition time scale, the extensive circumstellar envelope created by steady mass loss during the AGB should not be neglected in the treatment of the formation process of PN, regardless of the ejection mechanism [1,8].
The interacting stellar winds model for the evolution stars has had considerable success in explaining various features for the planetary nebulae and white dwarf [10]. Stars can be divided into three main categories by mass-low, intermediate and high mass. The boundaries are determined by the minimum needed by a star to form its first degenerate core as shown in Table 1 [11].
• Low mass stars: develop degenerate He core while ascending the RGB. He ignition occurs explosively the helium flash. The increased core temperature causes the degeneracy to be lifted. The core expands, and He burning becomes stable. Eventually they develop degenerate C/O core before ending as white dwarf [2,10].
• Intermediate mass stars: burn He and then develop degenerate C/O cores.
• High mass stars: between 8 and 11 Msun (or M☉ (solar mass), stars undergo C fusion before developing

Table 1. The dependence of the mass on post main-sequence evolution.
O/Ne/Mg degenerate core [10,12].
In this paper, the ISW model was to take a step further and calculate the mass loss. Also, we shall attempt to demonstrate from calculations that there exists direct relation between Red Giant (RG) and Planetary Nebulae (PN) and to discuss a possible evolutionary scenario of the transition of RG into PN.
2. Basic Considerations of the Model and Calculations
The interacting stellar winds model (ISW) represents the basic model that is had considerable success in explaining various features in the formation and evolution stars from Red Giant to Planetary Nebulae stage [10,13].
In this model the hot central stars of PN emits a low density fast winds at a velocity in the range (1000 - 3000) km/s [14]. This fast winds catches up with slow wind resulting from the ejection of the progenitor Red Giant’s envelope moving at (≈ 10 km/s according to Socker model (1989)) and drive shock waves into it [15]. It also significant that Planetary Nebulae nuclei have stellar winds (through radiation pressure acting directly on the gas) with velocity one or two gas components must interact regardless of the details of the process leading from Red Giant to Planetary Nebulae [12].
In this paper the values of the velocities for slow and fast wind that will be adopted are (for slow wind V ~ 5 - 20 km/s, while for fast wind v ~ 1000). RV stars represents a very young Planetary Nebulae as it has been observed both in its RG phase and its emission line stage. Radio emission is found coming from the remnant of the Red Giant wind, that is ionized by the hot central star and optical observations indicate the presence of a gas shell expanding at (30 - 50 km/s) [2,16,17].
The number density of the Red Giant wind can be expressed as [3]
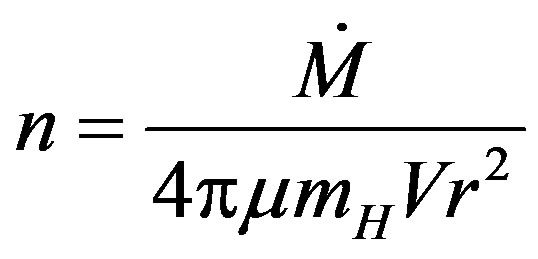 (1)
(1)
where : is the mass-loss rate in (M☉/yr) solar units
: is the mass-loss rate in (M☉/yr) solar units
µ: is the mean molecular weight mH: is the mass of a hydrogen atom V: is the expansion velocity of the slow wind (Red Giant and AGB phases) in (km/s) units r: is the distance from the central star in (km) units. At the interface between the two winds (slow winds and the central star winds) the mean free path of an atom (ι) from the central star wind in the Red Giant wind is then [3,18]
 (2)
(2)
For simplicity both the AGB and the superwind are assumed to be time independent. Schonberner (1991) and Schmidt & Koppen (1987) a have demonstrated that for too low AGB wind rates unrealistic high expansion velocities of the nebulae can be expected [14]. Therefore we adopted the values of AGB mass loss
 . For the superwind the mass loss
. For the superwind the mass loss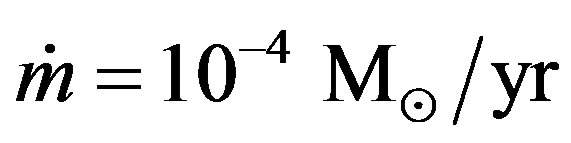 . These values are compared with the values that suggested by Schonberner (1991) [14,17]. We start our calculations at initial time to = 60 yr in comparing with the initial time that suggested by Schonberner (1991) (to = 50). The radial dependence of the wind density distribution given by [17,18]
. These values are compared with the values that suggested by Schonberner (1991) [14,17]. We start our calculations at initial time to = 60 yr in comparing with the initial time that suggested by Schonberner (1991) (to = 50). The radial dependence of the wind density distribution given by [17,18]
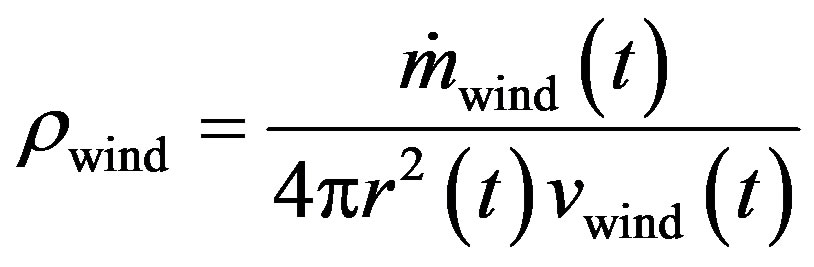 (3)
(3)
The wind speed is still rather low (~35 km/s) in comparing with value (~45 km/s) that is suggested by Schonberner (1991) [14,17] and the boundary between Central star of PN wind and superwind is at [8]
 (4)
(4)
where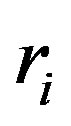 : is the inner radius at the initial time to,
: is the inner radius at the initial time to,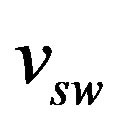 : is the superwind velocity.
: is the superwind velocity.
Figures 1 and 2 showed the radial mass density distribution of our initial model at to = 60 yr and Schonberner (1991) model at to = 50 yr. The gas is assumed to be initially neutral having temperatures of 100 K. The various density with the time is illustrated by the Figures 3 and 4. These figures showed that the maximum expansion velocity of about 35 km/s at t ≈ 3000 yrs, and therefore, the outer nebular rim is decelerated by accretion of the slow moving AGB wind gas. Note the density hump at the outer nebular rim due to this accretion at t < 500 yr before fast wind phase.
The Momentum and Energy Interaction
The interaction can to be treated as momentum or energy conserving as the Kwok (2007) stated, the thermal pressure of high temperature zone may become an important factor in the dynamics of planetaries, if gas cooling at the interaction zone [18]. The interaction of the central planetary nebula wind with the nebular shell has only been treated in the momentum conserving case [17]. As it
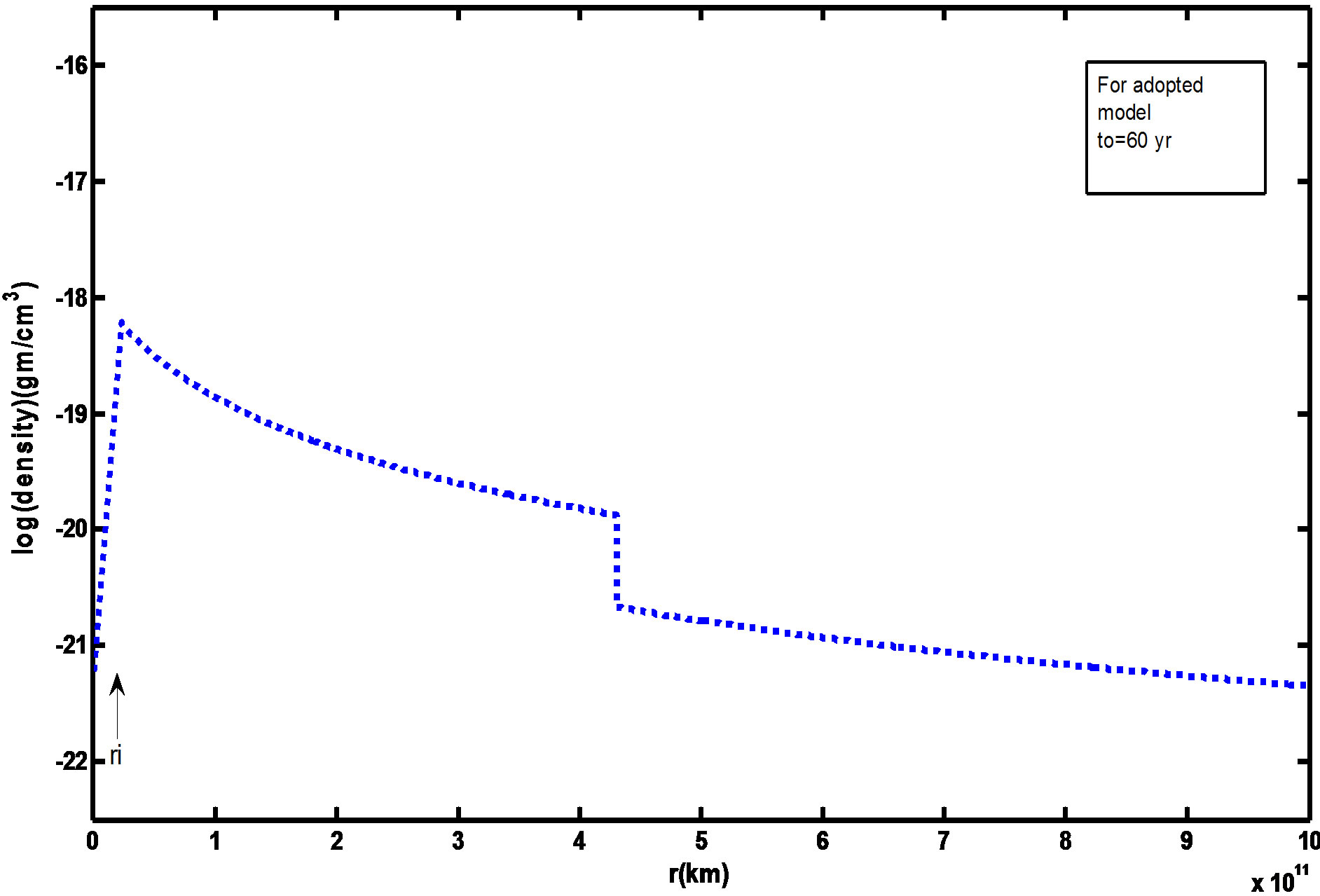
Figure 1. Radial mass density distribution of adopted initial time value (to = 60 yr).
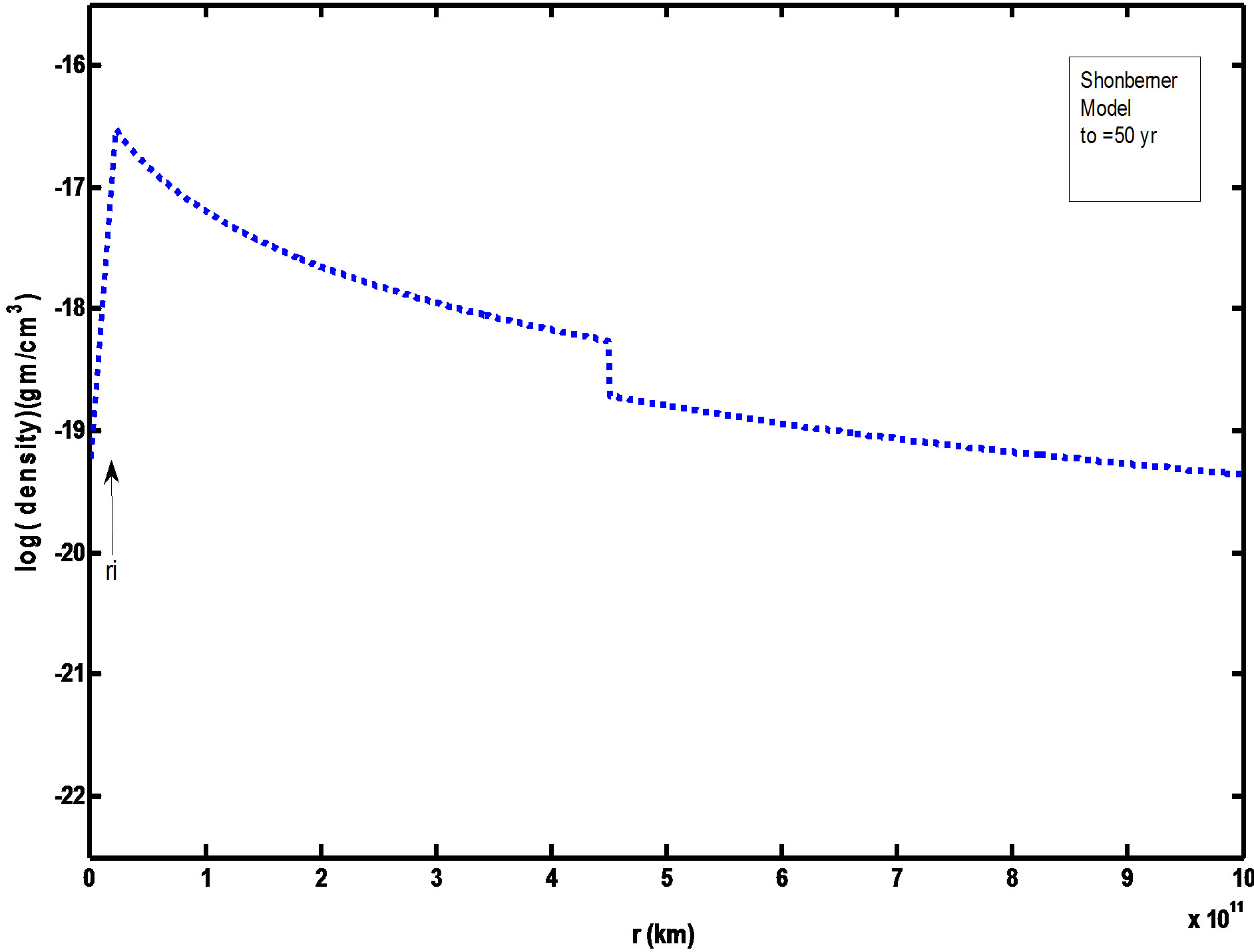
Figure 2. Radial mass density distribution of Schonberner model (1991) initial time value (to = 50 yr).

Figure 3. The relation between density and time at adopted initial time (to = 60 yr).
assumed by Kwok (1982) that all wind energy is converted to thermal pressure neglecting any radiative losses and change in the internal energy of the hot region. The momentum equation then becomes
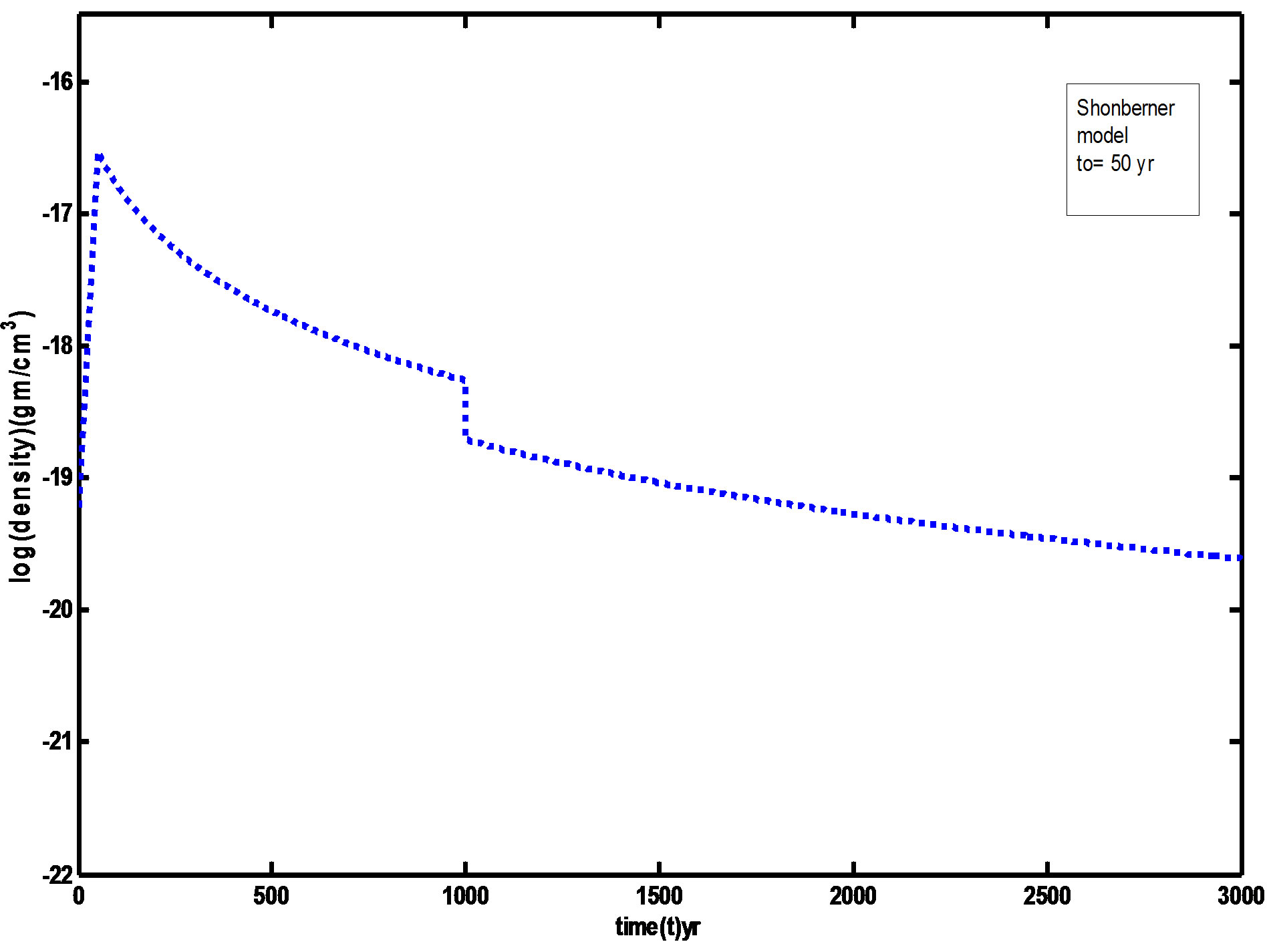
Figure 4. The relation between density and time at Schonberner initial time (to = 50 yr).
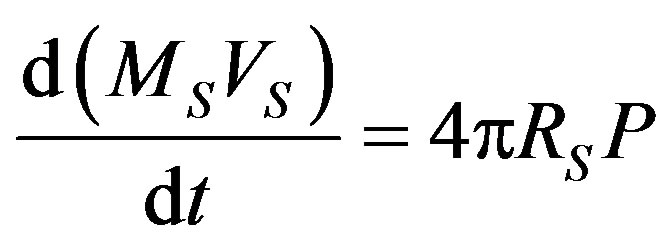 (5)
(5)
where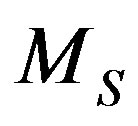 ,
, 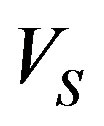 , and
, and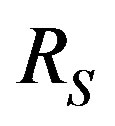 , respectively, the mass, velocity and radius of PN shell, and P the pressure is given by [5,8]:
, respectively, the mass, velocity and radius of PN shell, and P the pressure is given by [5,8]:
 (6)
(6)
Changes in the shell mass are given by [3]:
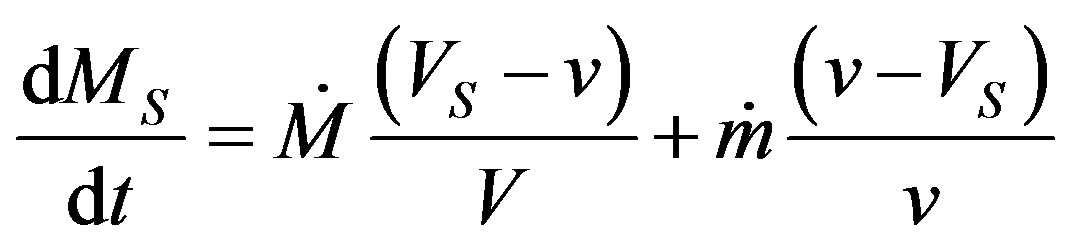 (7)
(7)
where  and
and  are the mass loss rate in M☉/yr (solar mass) unit, and Velocity of the red giant wind in (km/s) units, respectively.
are the mass loss rate in M☉/yr (solar mass) unit, and Velocity of the red giant wind in (km/s) units, respectively. 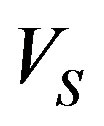 can be calculated from Equation (3) of Kwok (1982) paper [3,17]. This equation can be solved analytically and solutions are plotted in Figures 5 and 6 for
can be calculated from Equation (3) of Kwok (1982) paper [3,17]. This equation can be solved analytically and solutions are plotted in Figures 5 and 6 for  ~ 10−9 to 10−6 (M☉/yr) and V = 5, 10 and 20 as it adopted by Kwok [17,18], Expansions velocity of the shell
~ 10−9 to 10−6 (M☉/yr) and V = 5, 10 and 20 as it adopted by Kwok [17,18], Expansions velocity of the shell 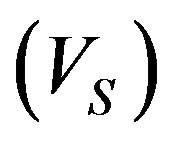 lies between two curves, also these figures demonstrated that the expansion velocities can be obtained under a wide range of combinations of
lies between two curves, also these figures demonstrated that the expansion velocities can be obtained under a wide range of combinations of  and V. The velocity of the fast wind that which adopted in this paper is (v = 1000 km/s), in comparing with the value that adopted by Kwok (1982) which is (v = 2000 km/s).
and V. The velocity of the fast wind that which adopted in this paper is (v = 1000 km/s), in comparing with the value that adopted by Kwok (1982) which is (v = 2000 km/s).
3. Discussion and Conclusions
The results of the stellar evolution calculations beyond Red Giant Branch through to the end of the AGB phase with mass loss have been presented. The mass loss rates used are based on empirical determinations for the slow wind and fast wind interaction. The mass loss rates produced by superwind are similar to those required for Planetary Nebulae production, and the occurrence of
Figure 5. Expansion velocity of the shell nebula as a function of mass loss rate (Adopted value of the fast wind velocity = 1000 km/s). Each pair of curves corresponds to the— energy and momentum conserving cases respectively.
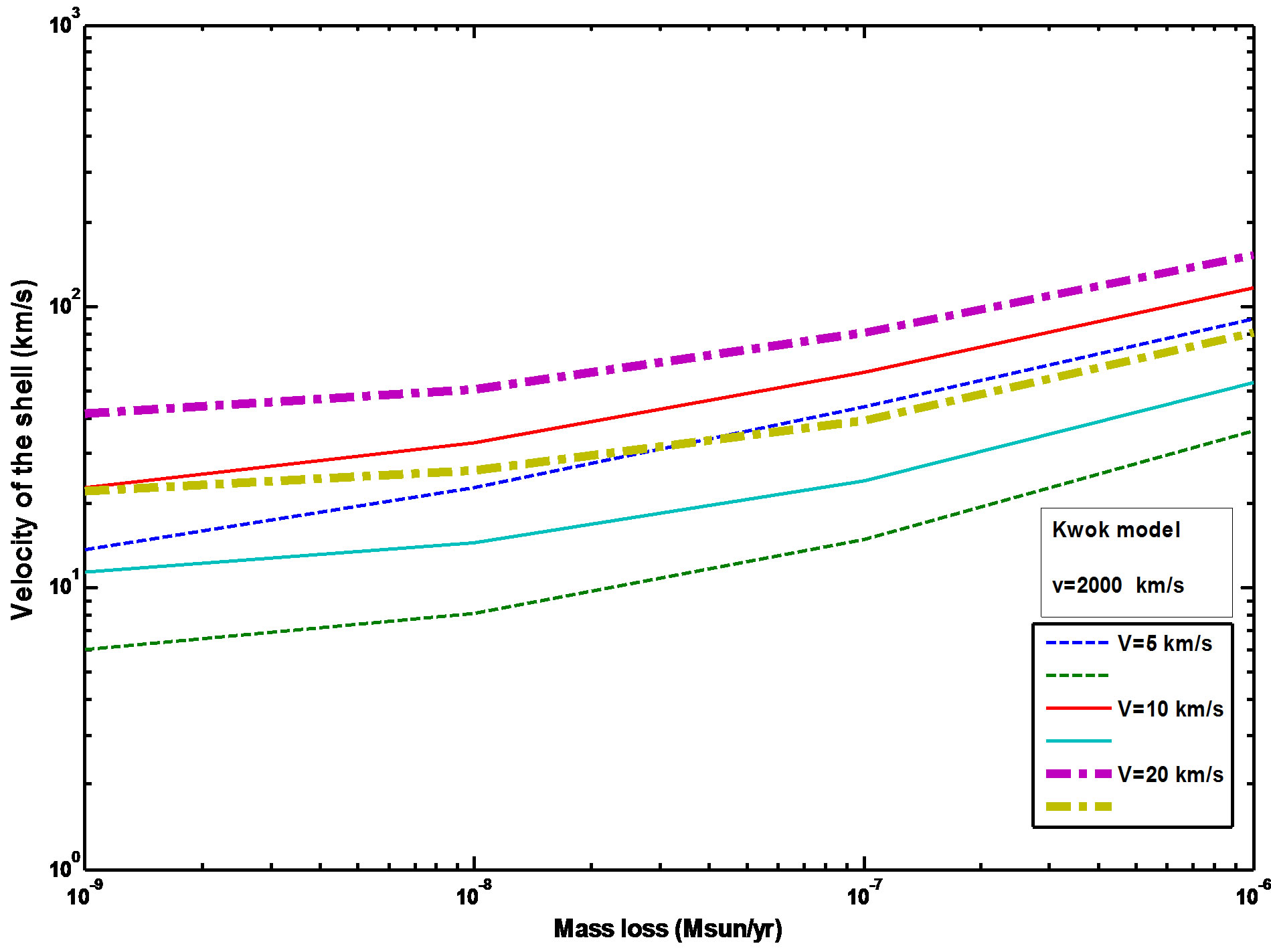
Figure 6. Expansion velocity of the shell nebula as a function of mass loss rate (Kwok’s value of the fast wind velocity = 2000 km/s). Each pair of curves corresponds to the—energy and momentum conserving cases respectively.
multiple superwind phases can account for the existence of Asymptotic Giant Branch stars with hollow shells and multiple shell of Planetary Nebulae. However the following conclusions must be considered:
1) At the outer boundary, which is the nebula’s outer rim to resolve the shock between nebular shell and AGB wind properly, the AGB wind is assumed to develop a stationary flow given by Equation (3).
2) The outer nebular rim is decelerated by accretion of slow moving AGB wind gas. The density humps at the outer nebula rim due to this accretion at t ≤ 1000 yr.
3) The radial density gradient within the nebular shell becomes even more negative.
4) The velocity increases towards the outer edge up to 50 km/s. This rapid flow causes dilution of the nebula which grows in volume while the density is diminished especially in the outer. So that the density decreases towards the outer rim as shown in Figures 1 to 4 in comparison with Schonberner (1991) calculations.
5) The results showed that for the momentum and energy conserving cases, the expansion velocities are increasing as a result of increasing strengths of the central star wind or the result of a change from momentum to energy conserving.
6) The results indicates that the maximum velocity is about ~35.5 km/s at t ~ 3000 yrs, while the expansion velocity for Kwok model is about ~25 km/s, which is due to the differences in mass loss value calculations during early AGB phase.
4. Acknowledgements
It is pleasure to thank Dr. S. K. H in Hong Kong University, China, for his many critical comments on earlier drafts of his manuscript, and for Dr. B. T. Chiad in Baghdad University, whose comments have also led to improvements of the paper.
NOTES