Hydrochemistry of Umm Er Radhuma Groundwater ()
ABSTRACT
Umm Er Radhuma Aquifer (UER) is the most important groundwater
aquifer in Saudi Arabia, extending over 1.6 M
·km
2 in the eastern part
of the Arabian Peninsula, forming the main aquifer throughout the Rub’ Al-Khali
(RAK). Groundwater salinity increased
from west to east, reaching more than 27,000 mg/L near the border with the United
Arab Emirates, where a Na+-Ca2+Clˉ-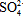 water type dominated. Gibbs diagrams indicated that the
dissolution/precipitation of carbonates and evaporation/precipitation of minerals,
especially anhydrite, gypsum, and halite account for the solutes and salinity in
groundwater. Most of the samples plot above the 1:1 line of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)
against
water type dominated. Gibbs diagrams indicated that the
dissolution/precipitation of carbonates and evaporation/precipitation of minerals,
especially anhydrite, gypsum, and halite account for the solutes and salinity in
groundwater. Most of the samples plot above the 1:1 line of (Ca2+ + Mg2+)
against 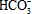 , indicating other sources of
Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the groundwater along with dolomite and calcium
carbonate minerals. Phreeqc model indicated that the main clay minerals are kaolinite
and gibbsite which had major effect on the cation exchange process as indicated
by the Chloro-Alkaline index (CAI), where most of groundwater samples had values
greater than zero which indicated the occurrence of reverse ion exchange between
the groundwater and its host aquifer. The water type Na+-Ca2+Clˉ-
, indicating other sources of
Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the groundwater along with dolomite and calcium
carbonate minerals. Phreeqc model indicated that the main clay minerals are kaolinite
and gibbsite which had major effect on the cation exchange process as indicated
by the Chloro-Alkaline index (CAI), where most of groundwater samples had values
greater than zero which indicated the occurrence of reverse ion exchange between
the groundwater and its host aquifer. The water type Na+-Ca2+Clˉ-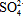 dominated in the eastern part of the aquifer as the anaerobic
conditions prevailed and the reduction of sulphate took place.
dominated in the eastern part of the aquifer as the anaerobic
conditions prevailed and the reduction of sulphate took place.
Share and Cite:
Gomaah, M. (2021) Hydrochemistry of Umm Er Radhuma Groundwater.
Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection,
9, 128-146. doi:
10.4236/gep.2021.94008.
Cited by
No relevant information.